IISER Kolkata
Researchers from IIT Kanpur, IISER Kolkata, and Symbiosis Law School developed NyayaAnumana, the largest Indian legal dataset comprising over 800,000 labeled cases, and INLegalLlama, a specialized large language model. This model achieves approximately 90% accuracy in binary legal judgment prediction and provides comprehensible explanations for its decisions, enhancing transparency and trust in AI-assisted legal processes.
Critical coupling has emerged as a prominent area of research in recent years. However, most theoretical models are based on scalar theories (and occasionally coupled mode theories), which inadequately account for the polarization states of the incident light. To bridge this gap, we revisit the concept of critical coupling in planar multilayer structures using a full vectorial theory, where conventional plane wave illumination is replaced by well-defined vector beams with and without orbital angular momentum (OAM). Our investigation explores the possibility of complete absorption of monochromatic beams without and with intrinsic OAM (such as Gaussian and Laguerre-Gaussian (LG)), incident on the multilayer structure at normal or oblique incidence. A two-component metal-dielectric composite film is chosen as the absorbing layer in the system. Our results demonstrate a significant reduction in the intensities of the reflected and transmitted beams at normal incidence, with reduced efficiency for oblique incidence due to the lack of spatial overlap of multiply reflected components. Interestingly, we also observe super-scattering from the same structures when conditions for constructive interference of the various reflected components are satisfied. This work highlights the need to incorporate the vector nature of beams by retaining the complete polarization information of off-axis spatial harmonics in future studies.
The DeepRetro framework combines large language models (LLMs) with traditional computer-aided synthesis planning tools in an iterative, validated loop. It successfully discovers chemically plausible and sometimes novel multi-step retrosynthetic pathways for complex organic molecules, including those not previously reported in literature, leveraging human-in-the-loop guidance.
QuickSilver is a framework that accelerates Large Language Model inference by dynamically adapting computation at runtime using four synergistic mechanisms: Dynamic Token Halting, KV Cache Skipping, Contextual Token Fusion, and Adaptive Matryoshka Quantization. This approach achieves up to 60% FLOPs reduction and 49% speedup with negligible accuracy degradation, reducing the computational and environmental costs of LLMs.
Bipolar Magnetic Regions (BMRs) that appear on the solar photosphere are surface manifestations of the solar internal magnetic field. With modern observations and continuous data streams, the study of BMRs has moved from manual sunspot catalogs to automated detection and tracking methods. In this work, we present an additional module to the existing BMR tracking algorithm, AutoTAB, that focuses on identifying emerging signatures of BMRs. Specifically, for regions newly detected on the solar disk, this module backtracks the BMRs to their point of emergence. From a total of about 12000 BMRs identified by AutoTAB, we successfully backtracked 3080 cases. Within this backtracked sample, we find two distinct populations. One group shows the expected behaviour of emerging regions, in which the magnetic flux increases significantly during the emerging phase. The other group consists of BMRs whose flux, however, does not exhibit substantial growth during their evolution. We classify these as non-emerging BMRs and examine their statistical properties separately. Our analysis shows that these non-emerging BMRs do not display any preferred tilt angle distribution nor show systematic latitudinal tilt dependence, in contrast to the trends typically associated with emerging BMRs. This indicates that including such regions in statistical studies of BMR properties can distort or mask the underlying physical characteristics. We therefore emphasise the importance of excluding the non-emerging population from the whole dataset when analysing the statistical behaviour of BMRs.
Quantization is an essential technique for making neural networks more efficient, yet our theoretical understanding of it remains limited. Previous works demonstrated that extremely low-precision networks, such as binary networks, can be constructed by pruning large, randomly-initialized networks, and showed that the ratio between the size of the original and the pruned networks is at most polylogarithmic.
The specific pruning method they employed inspired a line of theoretical work known as the Strong Lottery Ticket Hypothesis (SLTH), which leverages insights from the Random Subset Sum Problem. However, these results primarily address the continuous setting and cannot be applied to extend SLTH results to the quantized setting.
In this work, we build on foundational results by Borgs et al. on the Number Partitioning Problem to derive new theoretical results for the Random Subset Sum Problem in a quantized setting.
Using these results, we then extend the SLTH framework to finite-precision networks. While prior work on SLTH showed that pruning allows approximation of a certain class of neural networks, we demonstrate that, in the quantized setting, the analogous class of target discrete neural networks can be represented exactly, and we prove optimal bounds on the necessary overparameterization of the initial network as a function of the precision of the target network.
Researchers from this study created SELF-PERCEPT, a psychologically-informed prompting framework, and MultiManip, a new dataset of reality TV dialogues, to improve Large Language Models' ability to detect subtle manipulation in multi-person conversations. The framework consistently achieved higher accuracy and F1 scores across multiple LLMs compared to existing prompting strategies.
In the landscape of Fact-based Judgment Prediction and Explanation (FJPE),
reliance on factual data is essential for developing robust and realistic
AI-driven decision-making tools. This paper introduces TathyaNyaya, the largest
annotated dataset for FJPE tailored to the Indian legal context, encompassing
judgments from the Supreme Court of India and various High Courts. Derived from
the Hindi terms "Tathya" (fact) and "Nyaya" (justice), the TathyaNyaya dataset
is uniquely designed to focus on factual statements rather than complete legal
texts, reflecting real-world judicial processes where factual data drives
outcomes. Complementing this dataset, we present FactLegalLlama, an
instruction-tuned variant of the LLaMa-3-8B Large Language Model (LLM),
optimized for generating high-quality explanations in FJPE tasks. Finetuned on
the factual data in TathyaNyaya, FactLegalLlama integrates predictive accuracy
with coherent, contextually relevant explanations, addressing the critical need
for transparency and interpretability in AI-assisted legal systems. Our
methodology combines transformers for binary judgment prediction with
FactLegalLlama for explanation generation, creating a robust framework for
advancing FJPE in the Indian legal domain. TathyaNyaya not only surpasses
existing datasets in scale and diversity but also establishes a benchmark for
building explainable AI systems in legal analysis. The findings underscore the
importance of factual precision and domain-specific tuning in enhancing
predictive performance and interpretability, positioning TathyaNyaya and
FactLegalLlama as foundational resources for AI-assisted legal decision-making.
Automating legal document drafting can significantly enhance efficiency,
reduce manual effort, and streamline legal workflows. While prior research has
explored tasks such as judgment prediction and case summarization, the
structured generation of private legal documents in the Indian legal domain
remains largely unaddressed. To bridge this gap, we introduce VidhikDastaavej,
a novel, anonymized dataset of private legal documents, and develop NyayaShilp,
a fine-tuned legal document generation model specifically adapted to Indian
legal texts. We propose a Model-Agnostic Wrapper (MAW), a two-step framework
that first generates structured section titles and then iteratively produces
content while leveraging retrieval-based mechanisms to ensure coherence and
factual accuracy. We benchmark multiple open-source LLMs, including
instruction-tuned and domain-adapted versions, alongside proprietary models for
comparison. Our findings indicate that while direct fine-tuning on small
datasets does not always yield improvements, our structured wrapper
significantly enhances coherence, factual adherence, and overall document
quality while mitigating hallucinations. To ensure real-world applicability, we
developed a Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Document Generation System, an interactive
user interface that enables users to specify document types, refine section
details, and generate structured legal drafts. This tool allows legal
professionals and researchers to generate, validate, and refine AI-generated
legal documents efficiently. Extensive evaluations, including expert
assessments, confirm that our framework achieves high reliability in structured
legal drafting. This research establishes a scalable and adaptable foundation
for AI-assisted legal drafting in India, offering an effective approach to
structured legal document generation.
In this paper, we address the task of semantic segmentation of legal
documents through rhetorical role classification, with a focus on Indian legal
judgments. We introduce LegalSeg, the largest annotated dataset for this task,
comprising over 7,000 documents and 1.4 million sentences, labeled with 7
rhetorical roles. To benchmark performance, we evaluate multiple
state-of-the-art models, including Hierarchical BiLSTM-CRF,
TransformerOverInLegalBERT (ToInLegalBERT), Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), and
Role-Aware Transformers, alongside an exploratory RhetoricLLaMA, an
instruction-tuned large language model. Our results demonstrate that models
incorporating broader context, structural relationships, and sequential
sentence information outperform those relying solely on sentence-level
features. Additionally, we conducted experiments using surrounding context and
predicted or actual labels of neighboring sentences to assess their impact on
classification accuracy. Despite these advancements, challenges persist in
distinguishing between closely related roles and addressing class imbalance.
Our work underscores the potential of advanced techniques for improving legal
document understanding and sets a strong foundation for future research in
legal NLP.
Significant developments in techniques such as encoder-decoder models have enabled us to represent information comprising multiple modalities. This information can further enhance many downstream tasks in the field of information retrieval and natural language processing; however, improvements in multi-modal techniques and their performance evaluation require large-scale multi-modal data which offers sufficient diversity. Multi-lingual modeling for a variety of tasks like multi-modal summarization, text generation, and translation leverages information derived from high-quality multi-lingual annotated data. In this work, we present the current largest multi-lingual multi-modal summarization dataset (M3LS), and it consists of over a million instances of document-image pairs along with a professionally annotated multi-modal summary for each pair. It is derived from news articles published by British Broadcasting Corporation(BBC) over a decade and spans 20 languages, targeting diversity across five language roots, it is also the largest summarization dataset for 13 languages and consists of cross-lingual summarization data for 2 languages. We formally define the multi-lingual multi-modal summarization task utilizing our dataset and report baseline scores from various state-of-the-art summarization techniques in a multi-lingual setting. We also compare it with many similar datasets to analyze the uniqueness and difficulty of M3LS.
30 Apr 2020
Long and consistent sunspot area records are important for understanding the
long-term solar activity and variability. Multiple observatories around the
globe have regularly recorded sunspot areas, but such individual records only
cover restricted periods of time. Furthermore, there are also systematic
differences between them, so that these records need to be cross-calibrated
before they can be reliably used for further studies. We produce a
cross-calibrated and homogeneous record of total daily sunspot areas, both
projected and corrected, covering the period between 1874 and 2019. A catalogue
of calibrated individual group areas is also generated for the same period. We
have compared the data from nine archives: Royal Greenwich Observatory (RGO),
Kislovodsk, Pulkovo, Debrecen, Kodaikanal, Solar Optical Observing Network
(SOON), Rome, Catania, and Yunnan Observatories, covering the period between
1874 and 2019. Mutual comparisons of the individual records have been employed
to produce homogeneous and inter-calibrated records of daily projected and
corrected areas. As in earlier studies, the basis of the composite is formed by
the data from RGO. After 1976, the only datasets used are those from
Kislovodsk, Pulkovo and Debrecen observatories. This choice was made based on
the temporal coverage and the quality of the data. In contrast to the SOON data
used in previous area composites for the post-RGO period, the properties of the
data from Kislovodsk and Pulkovo are very similar to those from the RGO series.
They also directly overlap the RGO data in time, which makes their
cross-calibration with RGO much more reliable. We have also computed and
provide the daily Photometric Sunspot Index (PSI) widely used, e.g., in
empirical reconstructions of solar irradiance.
In this work we have investigated various properties of a spinning gyroscope in the context of Horndeski theories. In particular, we have focused on two specific situations --- (a) when the gyroscope follows a geodesic trajectory and (b) when it is endowed with an acceleration. In both these cases, besides developing the basic formalism, we have also applied the same to understand the motion of a spinning gyroscope in various static and spherically symmetric spacetimes pertaining to Horndeski theories. Starting with the Schwarzschild de-Sitter spacetime as a warm up exercise, we have presented our results for two charged Galileon black holes as well as for a black hole in scalar coupled Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet gravity. In all these cases we have shown that the spinning gyroscope can be used to distinguish black holes from naked singularities. Moreover, using the numerical estimation of the geodetic precession from the Gravity Probe B experiment, we have constrained the gauge/scalar charge of the black holes in these Horndeski theories. Implications are also discussed.
The rapid proliferation of Large Language Models (LLMs) has significantly contributed to the development of equitable AI systems capable of factual question-answering (QA). However, no known study tests the LLMs' robustness when presented with obfuscated versions of questions. To systematically evaluate these limitations, we propose a novel technique, ObfusQAte and, leveraging the same, introduce ObfusQA, a comprehensive, first of its kind, framework with multi-tiered obfuscation levels designed to examine LLM capabilities across three distinct dimensions: (i) Named-Entity Indirection, (ii) Distractor Indirection, and (iii) Contextual Overload. By capturing these fine-grained distinctions in language, ObfusQA provides a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LLM robustness and adaptability. Our study observes that LLMs exhibit a tendency to fail or generate hallucinated responses when confronted with these increasingly nuanced variations. To foster research in this direction, we make ObfusQAte publicly available.
11 Nov 2023
In this paper we compute the celestial operator product expansion between two outgoing positive helicity gravitons in the self dual gravity. It has been shown that the self dual gravity is a w1+∞-invariant theory whose scattering amplitudes are one loop exact with all positive helicity gravitons. Celestial w1+∞ symmetry is generated by an infinite tower of (conformally soft) gravitons which are holomorphic conserved currents. We find that at any given order only a \textit{finite} number of w1+∞ descendants contribute to the OPE. This is somewhat surprising because the spectrum of conformal dimensions in celestial CFT is not bounded from below. However, this is consistent with our earlier analysis based on the representation theory of w1+∞. The phenomenon of truncation suggests that in some (unknown) formulation the spectrum of conformal dimensions in the dual two dimensional theory can be bounded from below.
18 Oct 2025
Electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) is well known as a quantum optical phenomenon that permits a normally opaque medium to become transparent due to the quantum interference between transition pathways. This work addresses multi-soliton dynamics in an EIT system modeled by the integrable Maxwell-Bloch (MB) equations for a three-level Λ-type atomic configuration. By employing a generalized gauge transformation, we systematically construct explicit N-soliton solutions from the corresponding Lax pair. Explicit forms of one-, two-, three-, and four-soliton solutions are derived and analyzed. The resulting pulse structures reveal various nonlinear phenomena, such as temporal asymmetry, energy trapping, and soliton interactions. They also highlight coherent propagation, elastic collisions, and partial storage of pulses, which have potential implications for the design of quantum memory, slow light and photonic data transport in EIT media. In addition, the conservation of fundamental physical quantities, such as the excitation norm and Hamiltonian, is used to provide direct evidence of the integrability and stability of the constructed soliton solutions.
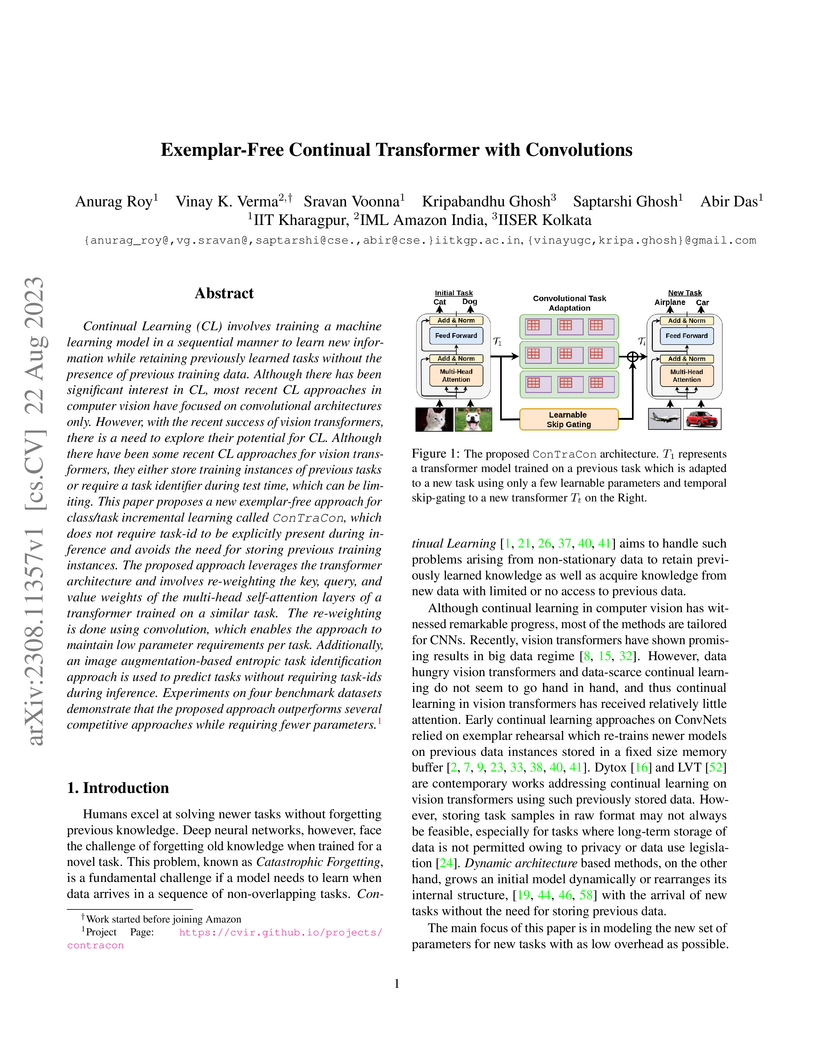
Continual Learning (CL) involves training a machine learning model in a
sequential manner to learn new information while retaining previously learned
tasks without the presence of previous training data. Although there has been
significant interest in CL, most recent CL approaches in computer vision have
focused on convolutional architectures only. However, with the recent success
of vision transformers, there is a need to explore their potential for CL.
Although there have been some recent CL approaches for vision transformers,
they either store training instances of previous tasks or require a task
identifier during test time, which can be limiting. This paper proposes a new
exemplar-free approach for class/task incremental learning called ConTraCon,
which does not require task-id to be explicitly present during inference and
avoids the need for storing previous training instances. The proposed approach
leverages the transformer architecture and involves re-weighting the key,
query, and value weights of the multi-head self-attention layers of a
transformer trained on a similar task. The re-weighting is done using
convolution, which enables the approach to maintain low parameter requirements
per task. Additionally, an image augmentation-based entropic task
identification approach is used to predict tasks without requiring task-ids
during inference. Experiments on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that the
proposed approach outperforms several competitive approaches while requiring
fewer parameters.
Automatic summarization of legal case judgements has traditionally been
attempted by using extractive summarization methods. However, in recent years,
abstractive summarization models are gaining popularity since they can generate
more natural and coherent summaries. Legal domain-specific pre-trained
abstractive summarization models are now available. Moreover, general-domain
pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, are known to
generate high-quality text and have the capacity for text summarization. Hence
it is natural to ask if these models are ready for off-the-shelf application to
automatically generate abstractive summaries for case judgements. To explore
this question, we apply several state-of-the-art domain-specific abstractive
summarization models and general-domain LLMs on Indian court case judgements,
and check the quality of the generated summaries. In addition to standard
metrics for summary quality, we check for inconsistencies and hallucinations in
the summaries. We see that abstractive summarization models generally achieve
slightly higher scores than extractive models in terms of standard summary
evaluation metrics such as ROUGE and BLEU. However, we often find inconsistent
or hallucinated information in the generated abstractive summaries. Overall,
our investigation indicates that the pre-trained abstractive summarization
models and LLMs are not yet ready for fully automatic deployment for case
judgement summarization; rather a human-in-the-loop approach including manual
checks for inconsistencies is more suitable at present.
In the era of precision cosmology, the cosmological constant Λ gives
quite an accurate description of the evolution of the Universe, but it is still
plagued with the fine-tuning problem and the cosmic coincidence problem. In
this work, we investigate the perturbations in a scalar field model that drives
the recent acceleration in a similar fashion that the cosmological constant
does and has the dark energy (DE) density comparable to the dark matter (DM)
energy density at the recent epoch starting from arbitrary initial conditions.
The perturbations show that this model, though it keeps the virtues of a
ΛCDM model, has a distinctive qualitative feature, particularly it
reduces the amplitude of the matter power spectrum on a scale of $8 h^{-1}\,
\mbox{Mpc},\sigma_{8}$ at the present epoch.
Feedback from active galactic nuclei (AGN) plays a critical role in shaping
the matter distribution on scales comparable to and larger than individual
galaxies. Upcoming surveys such as Euclid and LSST aim to precisely
quantify the matter distribution on cosmological scales, making a detailed
understanding of AGN feedback effects essential. Hydrodynamical simulations
provide an informative framework for studying these effects, in particular by
allowing us to vary the parameters that determine the strength of these
feedback processes and, consequently, to predict their corresponding impact on
the large-scale matter distribution. We use the EAGLE simulations to explore
how changes in subgrid viscosity and AGN heating temperature affect the matter
distribution, quantified via 2- and 3-point correlation functions, as well as
higher order cumulants of the matter distribution. We find that varying
viscosity has a small impact (≈10%) on scales larger than 1h−1
Mpc, while changes to the AGN heating temperature lead to substantial
differences, with up to 70% variation in gas clustering on small scales
(≲1h−1 Mpc). By examining the suppression of the power spectrum
as a function of time, we identify the redshift range z=1.5−1 as a key
epoch where AGN feedback begins to dominate in these simulations. The 3-point
function provides complementary insight to the more familiar 2-point
statistics, and shows more pronounced variations between models on the scale of
individual haloes. On the other hand, we find that effects on even larger
scales are largely comparable.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.