Dartmouth College
Dartmouth CollegeResearchers developed a three-stage pipeline to assess how well foundation models transfer to precision medicine applications involving physiological signals, utilizing BioGears for synthetic data generation and evaluating embedding quality. Initial application to the Moirai model demonstrated limitations in zero-shot transfer, including the introduction of spurious correlations, poor signal reconstruction, and distorted temporal dynamics in physiological embeddings.
Researchers from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Dartmouth College, Max Planck Institute, Google DeepMind, and others developed Prophet, a training-free adaptive decoding paradigm for Diffusion Language Models (DLMs) that leverages early answer convergence. The method achieves up to 3.4 times faster inference by dynamically committing to answers when model confidence is high, often improving output quality compared to full-step decoding.
The paper introduces "Trajectory Fields" as a novel 4D video representation, mapping each pixel's continuous 3D path over time. The "Trace Anything" neural network predicts these fields in a single pass, achieving state-of-the-art performance in dynamic scene understanding and dense 3D tracking while being orders of magnitude faster than prior methods.
22 Sep 2025
Recent advances have shown that scaling test-time computation enables large language models (LLMs) to solve increasingly complex problems across diverse domains. One effective paradigm for test-time scaling (TTS) involves LLM generators producing multiple solution candidates, with LLM verifiers assessing the correctness of these candidates without reference answers. In this paper, we study generative verifiers, which perform verification by generating chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning followed by a binary verdict. We systematically analyze verification dynamics across three dimensions - problem difficulty, generator capability, and verifier generation capability - with empirical studies on 12 benchmarks across mathematical reasoning, knowledge, and natural language reasoning tasks using 14 open-source models (2B to 72B parameter range) and GPT-4o. Our experiments reveal three key findings about verification effectiveness: (1) Easy problems allow verifiers to more reliably certify correct responses; (2) Weak generators produce errors that are easier to detect than strong generators; (3) Verification ability is generally correlated with the verifier's own problem-solving capability, but this relationship varies with problem difficulty. These findings reveal opportunities to optimize basic verification strategies in TTS applications. First, given the same verifier, some weak generators can nearly match stronger ones in post-verification TTS performance (e.g., the Gemma2-9B to Gemma2-27B performance gap shrinks by 75.5%). Second, we identify cases where strong verifiers offer limited advantage over weak ones, as both fail to provide meaningful verification gains, suggesting that verifier scaling alone cannot overcome fundamental verification challenges.
TimeSformer introduces a convolution-free video understanding architecture that leverages self-attention mechanisms to achieve state-of-the-art action recognition performance on multiple benchmarks with significantly improved training and inference efficiency.
11 Oct 2025
Dartmouth College researchers developed MA-RAG, a training-free multi-agent framework that uses collaborative Chain-of-Thought reasoning to improve Retrieval-Augmented Generation for complex information-seeking tasks. The system achieves state-of-the-art performance, with a Llama3-70B version scoring 59.5 EM on NQ and 52.1 EM on HotpotQA, while demonstrating strong generalization to medical and web search benchmarks.
This survey from Dartmouth College, Adobe Research, and other institutions offers a comprehensive overview of personalized Large Language Models, proposing a unified framework that bridges personalized text generation and downstream applications. It introduces multi-dimensional taxonomies for usage, granularity, techniques, evaluation, and datasets, providing a structured understanding of the field.
LegalBench: A Collaboratively Built Benchmark for Measuring Legal
Reasoning in Large Language Models
LegalBench: A Collaboratively Built Benchmark for Measuring Legal
Reasoning in Large Language Models
 University of Toronto
University of Toronto University of Southern California
University of Southern California University of Chicago
University of Chicago Stanford University
Stanford University University of Virginia
University of Virginia Dartmouth CollegeHarvard Law SchoolTélécom Paris, Institut Polytechnique de ParisGeorgetown University Law CenterHarvard Kennedy SchoolStanford Law SchoolSouth Texas College of Law HoustonGolden Gate University School of LawMaxime ToolsCasetextOsgoode Hall Law School, York UniversityLuddy School of Informatics - Indiana University BloomingtonStanford Center for Legal Informatics - CodeXLawBetaSt. Thomas University Benjamin L. Crump College of Law
Dartmouth CollegeHarvard Law SchoolTélécom Paris, Institut Polytechnique de ParisGeorgetown University Law CenterHarvard Kennedy SchoolStanford Law SchoolSouth Texas College of Law HoustonGolden Gate University School of LawMaxime ToolsCasetextOsgoode Hall Law School, York UniversityLuddy School of Informatics - Indiana University BloomingtonStanford Center for Legal Informatics - CodeXLawBetaSt. Thomas University Benjamin L. Crump College of LawLEGALBENCH provides a comprehensive, collaboratively-built benchmark designed to assess Large Language Models' (LLMs) capabilities in legal reasoning. It incorporates input from legal professionals and categorizes 162 tasks by the IRAC framework, demonstrating that GPT-4 generally leads performance, though no single model excels across all legal reasoning aspects.
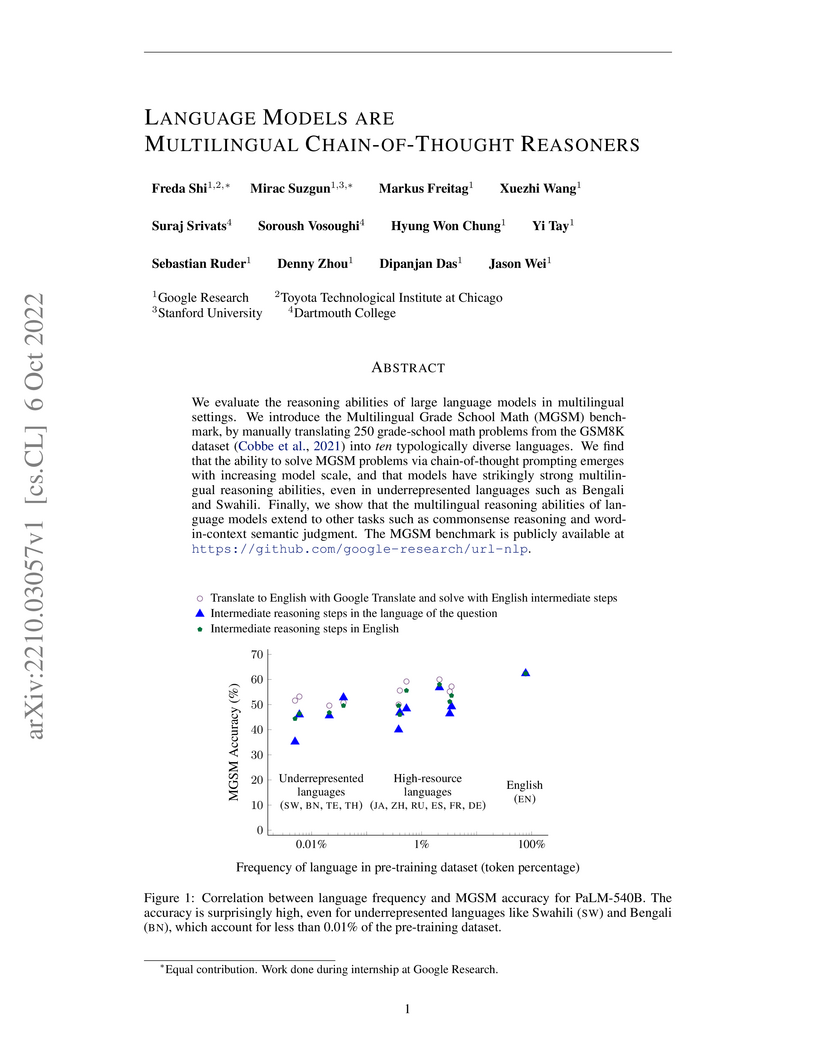
Large language models, particularly PaLM-540B, demonstrate the ability to perform complex, multi-step reasoning across diverse languages, including those less represented in pre-training data, when prompted with Chain-of-Thought. The research shows that English Chain-of-Thought can effectively elicit these reasoning capabilities in multilingual contexts, achieving an average solve rate of 55% on a new multilingual arithmetic reasoning benchmark.
 Northeastern University
Northeastern University Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University Meta
Meta University of Maryland, College Park
University of Maryland, College Park University of California, San Diego
University of California, San Diego Arizona State University
Arizona State University University of ArizonaUniversity of Massachusetts Amherst
University of ArizonaUniversity of Massachusetts Amherst Dartmouth CollegeUniversity of OregonState University of New York at Buffalo
Dartmouth CollegeUniversity of OregonState University of New York at Buffalo AdobeIntel AI Research
AdobeIntel AI ResearchA survey by researchers from the University of Oregon, Carnegie Mellon University, Adobe Research, and Meta AI provides the first dedicated examination of Small Language Models (SLMs). The work introduces a structured taxonomy and outlines key techniques, applications, and challenges in balancing model performance with practical deployment considerations.
Researchers from Dartmouth College and the Allen Institute for AI developed Genesys, an LLM-driven system that automates the discovery of novel language model architectures by simulating the scientific research process. The system successfully proposed and verified over 1,000 unique designs, with top-performing discoveries demonstrating competitive performance against human-designed state-of-the-art models like GPT2 and Mamba2 on multiple benchmarks.
This survey paper by Junda Wu and colleagues systematically categorizes and examines visual prompting techniques for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). It outlines how visual cues, such as bounding boxes and pixel-level masks, enhance MLLMs' abilities in visual grounding, object referring, and compositional reasoning by providing direct control over model attention.
Recent advancements in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have focused on integrating multiple modalities, yet their ability to simultaneously process and reason across different inputs remains underexplored. We introduce OmniBench, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate models' ability to recognize, interpret, and reason across visual, acoustic, and textual inputs simultaneously. We define language models capable of such tri-modal processing as omni-language models (OLMs). OmniBench features high-quality human annotations that require integrated understanding across all modalities. Our evaluation reveals that: i) open-source OLMs show significant limitations in instruction-following and reasoning in tri-modal contexts; and ii) most baseline models perform poorly (around 50% accuracy) even with textual alternatives to image/audio inputs. To address these limitations, we develop OmniInstruct, an 96K-sample instruction tuning dataset for training OLMs. We advocate for developing more robust tri-modal integration techniques and training strategies to enhance OLM performance. Codes and data could be found at our repo (this https URL).
University of California Berkeley, Oxford University, and Dartmouth researchers develop LIFT (Low-rank Informed Sparse Fine-Tuning), which identifies "Principal Weights" by performing rank-r approximation on weight matrices via SVD and selecting the largest magnitude parameters from the low-rank representation for sparse fine-tuning, achieving superior performance over Full FT on reasoning tasks (2.02% higher on GPQA Diamond with Qwen-2.5, 1.14-1.60% higher on MATH-10K with LLaMA models) while reducing optimizer memory overhead from 27GB to 1.3GB for LLaMA-2-7B through dynamic mask updates that store optimizer states only for selected sparse parameters, with empirical validation showing that perturbing LIFT-identified weights drastically degrades performance while random parameter perturbation has minimal impact.
Researchers from leading institutions and industrial labs provided the first comprehensive survey on LLM-based Active Learning, introducing a unifying taxonomy that organizes current techniques by their data querying and annotation strategies. The work highlights LLMs' expanded roles from traditional data selection to data generation and cost-effective annotation, while also identifying critical open challenges for future research.
Researchers from Shanghai AI Laboratory and collaborators introduce DevEval, a comprehensive framework to evaluate large language models (LLMs) across the full software development lifecycle. Their case study reveals that current LLMs, including GPT-4-Turbo, struggle significantly with repository-level implementation tasks, achieving less than a 10% pass rate, while demonstrating the critical role of execution-feedback for performance improvement.
We introduce VLM-Lens, a toolkit designed to enable systematic benchmarking, analysis, and interpretation of vision-language models (VLMs) by supporting the extraction of intermediate outputs from any layer during the forward pass of open-source VLMs. VLM-Lens provides a unified, YAML-configurable interface that abstracts away model-specific complexities and supports user-friendly operation across diverse VLMs. It currently supports 16 state-of-the-art base VLMs and their over 30 variants, and is extensible to accommodate new models without changing the core logic.
The toolkit integrates easily with various interpretability and analysis methods. We demonstrate its usage with two simple analytical experiments, revealing systematic differences in the hidden representations of VLMs across layers and target concepts. VLM-Lens is released as an open-sourced project to accelerate community efforts in understanding and improving VLMs.
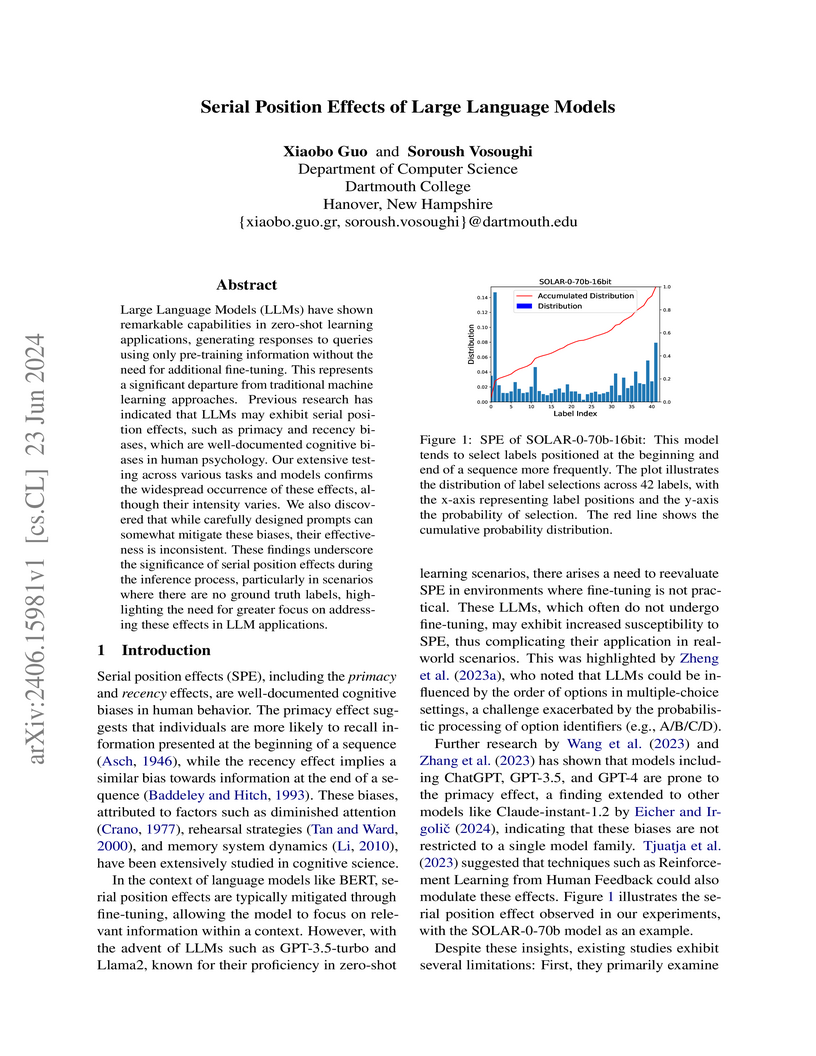
Researchers at Dartmouth College systematically investigated serial position effects (SPE) in large language models, demonstrating their widespread occurrence across both encoder-decoder and decoder-only architectures, with a predominant primacy effect in classification and a recency effect in summarization tasks. The study found that while basic prompt engineering was inconsistent, Chain-of-Thought reasoning offered a more reliable method for mitigating these biases.
AlphaPruning introduces a novel layer-wise pruning method for Large Language Models that leverages Heavy-Tailed Self-Regularization theory to allocate sparsity based on the spectral properties of weight matrices. This approach successfully prunes LLaMA-7B to 80% sparsity while maintaining perplexity, achieving a 3.06x speedup on CPUs and an average 4.6% gain on zero-shot tasks compared to uniform pruning baselines.
Recent work has documented striking heterogeneity in the performance of
state-of-the-art vision language models (VLMs), including both multimodal
language models and text-to-image models. These models are able to describe and
generate a diverse array of complex, naturalistic images, yet they exhibit
surprising failures on basic multi-object reasoning tasks -- such as counting,
localization, and simple forms of visual analogy -- that humans perform with
near perfect accuracy. To better understand this puzzling pattern of successes
and failures, we turn to theoretical accounts of the binding problem in
cognitive science and neuroscience, a fundamental problem that arises when a
shared set of representational resources must be used to represent distinct
entities (e.g., to represent multiple objects in an image), necessitating the
use of serial processing to avoid interference. We find that many of the
puzzling failures of state-of-the-art VLMs can be explained as arising due to
the binding problem, and that these failure modes are strikingly similar to the
limitations exhibited by rapid, feedforward processing in the human brain.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.