FPT Software AI Center
Zero-shot Text-to-Speech (TTS) aims to synthesize high-quality speech that mimics the voice of an unseen speaker using only a short reference sample, requiring not only speaker adaptation but also accurate modeling of prosodic attributes. Recent approaches based on language models, diffusion, and flow matching have shown promising results in zero-shot TTS, but still suffer from slow inference and repetition artifacts. Discrete codec representations have been widely adopted for speech synthesis, and recent works have begun to explore diffusion models in purely discrete settings, suggesting the potential of discrete generative modeling for speech synthesis. However, existing flow-matching methods typically embed these discrete tokens into a continuous space and apply continuous flow matching, which may not fully leverage the advantages of discrete representations. To address these challenges, we introduce DiFlow-TTS, which, to the best of our knowledge, is the first model to explore purely Discrete Flow Matching for speech synthesis. DiFlow-TTS explicitly models factorized speech attributes within a compact and unified architecture. It leverages in-context learning by conditioning on textual content, along with prosodic and acoustic attributes extracted from a reference speech, enabling effective attribute cloning in a zero-shot setting. In addition, the model employs a factorized flow prediction mechanism with distinct heads for prosody and acoustic details, allowing it to learn aspect-specific distributions. Experimental results demonstrate that DiFlow-TTS achieves promising performance in several key metrics, including naturalness, prosody, preservation of speaker style, and energy control. It also maintains a compact model size and achieves low-latency inference, generating speech up to 25.8 times faster than the latest existing baselines.
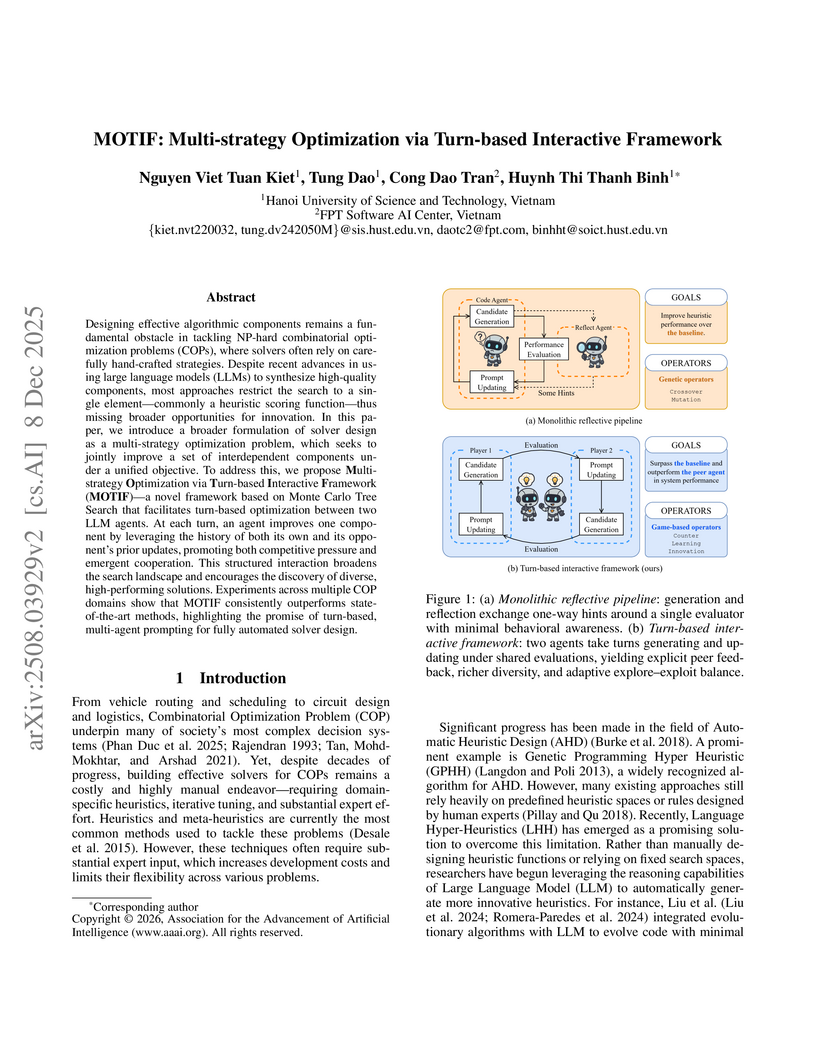
Designing effective algorithmic components remains a fundamental obstacle in tackling NP-hard combinatorial optimization problems (COPs), where solvers often rely on carefully hand-crafted strategies. Despite recent advances in using large language models (LLMs) to synthesize high-quality components, most approaches restrict the search to a single element - commonly a heuristic scoring function - thus missing broader opportunities for innovation. In this paper, we introduce a broader formulation of solver design as a multi-strategy optimization problem, which seeks to jointly improve a set of interdependent components under a unified objective. To address this, we propose Multi-strategy Optimization via Turn-based Interactive Framework (MOTIF) - a novel framework based on Monte Carlo Tree Search that facilitates turn-based optimization between two LLM agents. At each turn, an agent improves one component by leveraging the history of both its own and its opponent's prior updates, promoting both competitive pressure and emergent cooperation. This structured interaction broadens the search landscape and encourages the discovery of diverse, high-performing solutions. Experiments across multiple COP domains show that MOTIF consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods, highlighting the promise of turn-based, multi-agent prompting for fully automated solver design.
Researchers developed REPOEXEC, a Python benchmark that assesses CodeLLMs' repository-level code generation by evaluating both functional correctness and their ability to leverage existing dependencies with a new metric, Dependency Invocation Rate (DIR). Experiments highlight performance variations across context types and model architectures, demonstrating enhancements from multi-round debugging and instruction tuning.
The HYPERAGENT research introduces a generalist multi-agent system designed to tackle various software engineering tasks by emulating human developer workflows. It achieves a 33.00% success rate on SWE-bench-Verified, a 53.33% Pass@5 on RepoExec for context retrieval, and 22.9% correct fixes across 835 bugs on Defects4J, showcasing competitive performance against specialized systems.
Multi-objective combinatorial optimization problems (MOCOP) frequently arise in practical applications that require the simultaneous optimization of conflicting objectives. Although traditional evolutionary algorithms can be effective, they typically depend on domain knowledge and repeated parameter tuning, limiting flexibility when applied to unseen MOCOP instances. Recently, integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into evolutionary computation has opened new avenues for automatic heuristic generation, using their advanced language understanding and code synthesis capabilities. Nevertheless, most existing approaches predominantly focus on single-objective tasks, often neglecting key considerations such as runtime efficiency and heuristic diversity in multi-objective settings. To bridge this gap, we introduce Multi-heuristics for MOCOP via Pareto-Grid-guided Evolution of LLMs (MPaGE), a novel enhancement of the Simple Evolutionary Multiobjective Optimization (SEMO) framework that leverages LLMs and Pareto Front Grid (PFG) technique. By partitioning the objective space into grids and retaining top-performing candidates to guide heuristic generation, MPaGE utilizes LLMs to prioritize heuristics with semantically distinct logical structures during variation, thus promoting diversity and mitigating redundancy within the population. Through extensive evaluations, MPaGE demonstrates superior performance over existing LLM-based frameworks, and achieves competitive results to traditional Multi-objective evolutionary algorithms (MOEAs), with significantly faster runtime. Our code is available at: this https URL.
Inspired by how humans reason over discrete objects and their relationships, we explore whether compact object-centric and object-relation representations can form a foundation for multitask robotic manipulation. Most existing robotic multitask models rely on dense embeddings that entangle both object and background cues, raising concerns about both efficiency and interpretability. In contrast, we study object-relation-centric representations as a pathway to more structured, efficient, and explainable visuomotor control. Our contributions are two-fold. First, we introduce LIBERO+, a fine-grained benchmark dataset designed to enable and evaluate object-relation reasoning in robotic manipulation. Unlike prior datasets, LIBERO+ provides object-centric annotations that enrich demonstrations with box- and mask-level labels as well as instance-level temporal tracking, supporting compact and interpretable visuomotor representations. Second, we propose SlotVLA, a slot-attention-based framework that captures both objects and their relations for action decoding. It uses a slot-based visual tokenizer to maintain consistent temporal object representations, a relation-centric decoder to produce task-relevant embeddings, and an LLM-driven module that translates these embeddings into executable actions. Experiments on LIBERO+ demonstrate that object-centric slot and object-relation slot representations drastically reduce the number of required visual tokens, while providing competitive generalization. Together, LIBERO+ and SlotVLA provide a compact, interpretable, and effective foundation for advancing object-relation-centric robotic manipulation.
20 Apr 2025
The SWE-Synth framework generates high-quality, verifiable, and process-aware synthetic bug-fix datasets, directly addressing the data scarcity for Large Language Models in Automated Program Repair. Models trained on the full SWE-Synth dataset achieved a 15.3% resolve rate on SWE-Bench Lite, demonstrating that this scalable synthetic data can enable open-source LLMs to achieve competitive performance comparable to models trained on manually curated data.
The paper introduces RepoHYPER, a framework that enhances repository-level code completion by constructing a Repo-level Semantic Graph (RSG) to capture program-semantic relationships. It employs Search-then-Expand strategies with a GNN-based link predictor for intelligent context retrieval, leading to improved Exact Match and CodeBLEU scores on the RepoBench benchmark compared to similarity-based methods.
Large Language Models (LLMs) achieve strong results on code tasks, but how they derive program meaning remains unclear. We argue that code communicates through two channels: structural semantics, which define formal behavior, and human-interpretable naming, which conveys intent. Removing the naming channel severely degrades intent-level tasks such as summarization, where models regress to line-by-line descriptions. Surprisingly, we also observe consistent reductions on execution tasks that should depend only on structure, revealing that current benchmarks reward memorization of naming patterns rather than genuine semantic reasoning. To disentangle these effects, we introduce a suite of semantics-preserving obfuscations and show that they expose identifier leakage across both summarization and execution. Building on these insights, we release ClassEval-Obf, an obfuscation-enhanced benchmark that systematically suppresses naming cues while preserving behavior. Our results demonstrate that ClassEval-Obf reduces inflated performance gaps, weakens memorization shortcuts, and provides a more reliable basis for assessing LLMs' code understanding and generalization.
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is an essential and effective tool for diagnosing heart diseases. However, its effectiveness can be compromised by noise or unavailability of one or more leads of the standard 12-lead recordings, resulting in diagnostic errors or uncertainty. To address these challenges, we propose TolerantECG, a foundation model for ECG signals that is robust to noise and capable of functioning with arbitrary subsets of the standard 12-lead ECG. TolerantECG training combines contrastive and self-supervised learning frameworks to jointly learn ECG signal representations alongside their corresponding knowledge-retrieval-based text report descriptions and corrupted or lead-missing signals. Comprehensive benchmarking results demonstrate that TolerantECG consistently ranks as the best or second-best performer across various ECG signal conditions and class levels in the PTB-XL dataset, and achieves the highest performance on the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database.
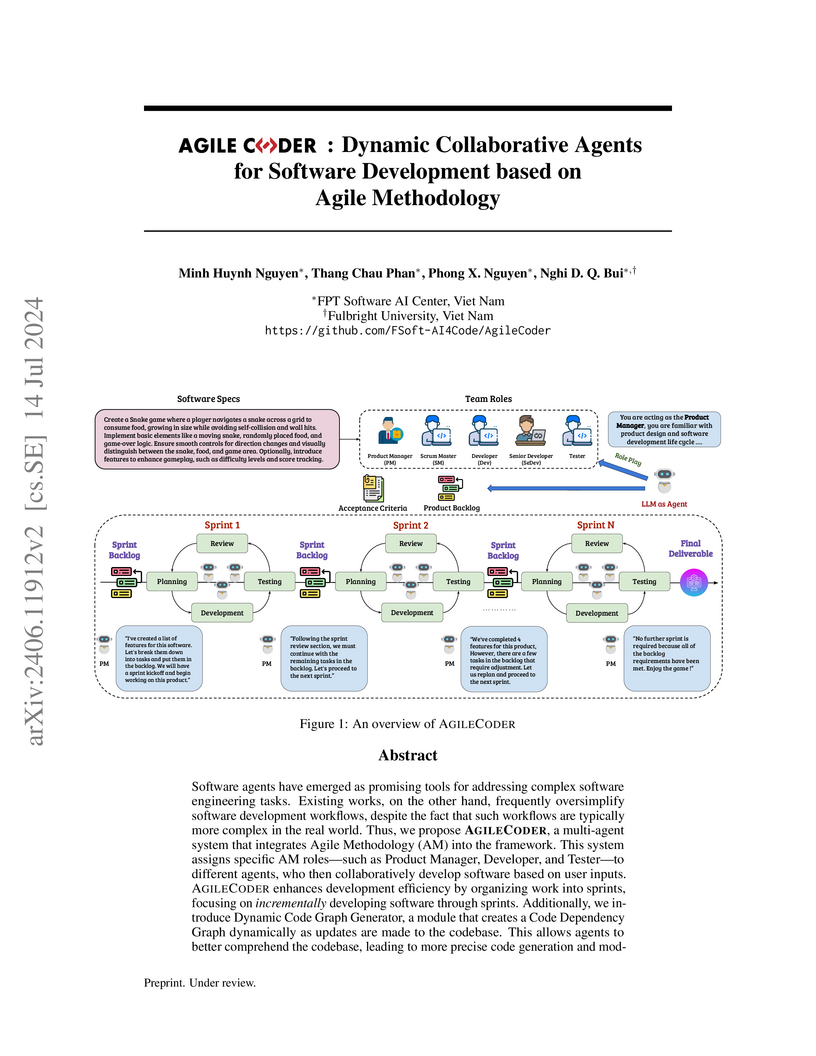
Software agents have emerged as promising tools for addressing complex
software engineering tasks. Existing works, on the other hand, frequently
oversimplify software development workflows, despite the fact that such
workflows are typically more complex in the real world. Thus, we propose
AgileCoder, a multi agent system that integrates Agile Methodology (AM) into
the framework. This system assigns specific AM roles - such as Product Manager,
Developer, and Tester to different agents, who then collaboratively develop
software based on user inputs. AgileCoder enhances development efficiency by
organizing work into sprints, focusing on incrementally developing software
through sprints. Additionally, we introduce Dynamic Code Graph Generator, a
module that creates a Code Dependency Graph dynamically as updates are made to
the codebase. This allows agents to better comprehend the codebase, leading to
more precise code generation and modifications throughout the software
development process. AgileCoder surpasses existing benchmarks, like ChatDev and
MetaGPT, establishing a new standard and showcasing the capabilities of multi
agent systems in advanced software engineering environments.
19 Jul 2025
Language-driven grasp detection has the potential to revolutionize human-robot interaction by allowing robots to understand and execute grasping tasks based on natural language commands. However, existing approaches face two key challenges. First, they often struggle to interpret complex text instructions or operate ineffectively in densely cluttered environments. Second, most methods require a training or finetuning step to adapt to new domains, limiting their generation in real-world applications. In this paper, we introduce GraspMAS, a new multi-agent system framework for language-driven grasp detection. GraspMAS is designed to reason through ambiguities and improve decision-making in real-world scenarios. Our framework consists of three specialized agents: Planner, responsible for strategizing complex queries; Coder, which generates and executes source code; and Observer, which evaluates the outcomes and provides feedback. Intensive experiments on two large-scale datasets demonstrate that our GraspMAS significantly outperforms existing baselines. Additionally, robot experiments conducted in both simulation and real-world settings further validate the effectiveness of our approach. Our project page is available at this https URL
Estimating human dance motion is a challenging task with various industrial applications. Recently, many efforts have focused on predicting human dance motion using either egocentric video or music as input. However, the task of jointly estimating human motion from both egocentric video and music remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we aim to develop a new method that predicts human dance motion from both egocentric video and music. In practice, the egocentric view often obscures much of the body, making accurate full-pose estimation challenging. Additionally, incorporating music requires the generated head and body movements to align well with both visual and musical inputs. We first introduce EgoAIST++, a new large-scale dataset that combines both egocentric views and music with more than 36 hours of dancing motion. Drawing on the success of diffusion models and Mamba on modeling sequences, we develop an EgoMusic Motion Network with a core Skeleton Mamba that explicitly captures the skeleton structure of the human body. We illustrate that our approach is theoretically supportive. Intensive experiments show that our method clearly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches and generalizes effectively to real-world data.
ConxGNN, a Graph Neural Network framework, improves emotion recognition in conversations by modeling multi-scale temporal context and multivariate relationships across textual, visual, and acoustic modalities. The model achieves 68.52% accuracy and 68.64% weighted-F1 on IEMOCAP, and 66.28% accuracy and 65.69% weighted-F1 on MELD, surpassing previous state-of-the-art methods.
Video Scene Graph Generation (VidSGG) aims to represent dynamic visual content by detecting objects and modeling their temporal interactions as structured graphs. Prior studies typically target either coarse-grained box-level or fine-grained panoptic pixel-level VidSGG, often requiring task-specific architectures and multi-stage training pipelines. In this paper, we present UNO (UNified Object-centric VidSGG), a single-stage, unified framework that jointly addresses both tasks within an end-to-end architecture. UNO is designed to minimize task-specific modifications and maximize parameter sharing, enabling generalization across different levels of visual granularity. The core of UNO is an extended slot attention mechanism that decomposes visual features into object and relation slots. To ensure robust temporal modeling, we introduce object temporal consistency learning, which enforces consistent object representations across frames without relying on explicit tracking modules. Additionally, a dynamic triplet prediction module links relation slots to corresponding object pairs, capturing evolving interactions over time. We evaluate UNO on standard box-level and pixel-level VidSGG benchmarks. Results demonstrate that UNO not only achieves competitive performance across both tasks but also offers improved efficiency through a unified, object-centric design.
Grasp detection is a persistent and intricate challenge with various industrial applications. Recently, many methods and datasets have been proposed to tackle the grasp detection problem. However, most of them do not consider using natural language as a condition to detect the grasp poses. In this paper, we introduce Grasp-Anything++, a new language-driven grasp detection dataset featuring 1M samples, over 3M objects, and upwards of 10M grasping instructions. We utilize foundation models to create a large-scale scene corpus with corresponding images and grasp prompts. We approach the language-driven grasp detection task as a conditional generation problem. Drawing on the success of diffusion models in generative tasks and given that language plays a vital role in this task, we propose a new language-driven grasp detection method based on diffusion models. Our key contribution is the contrastive training objective, which explicitly contributes to the denoising process to detect the grasp pose given the language instructions. We illustrate that our approach is theoretically supportive. The intensive experiments show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches and allows real-world robotic grasping. Finally, we demonstrate our large-scale dataset enables zero-short grasp detection and is a challenging benchmark for future work. Project website: this https URL
09 Apr 2025
Recent advances in Code Large Language Models (CodeLLMs) have primarily
focused on open-ended code generation, often overlooking the crucial aspect of
code understanding and reasoning. To bridge this gap, we introduce CodeMMLU, a
comprehensive multiple-choice benchmark designed to evaluate the depth of
software and code comprehension in LLMs. CodeMMLU includes nearly 20,000
questions spanning diverse domains, including code analysis, defect detection,
and software engineering principles across multiple programming languages.
Unlike traditional benchmarks that emphasize code generation, CodeMMLU assesses
a model's ability to reason about programs across a wide-range of tasks such as
code repair, execution reasoning, and fill-in-the-blank challenges. Our
extensive evaluation reveals that even state-of-the-art models struggle with
CodeMMLU, highlighting significant gaps in comprehension beyond generation. By
emphasizing the essential connection between code understanding and effective
AI-assisted development, CodeMMLU provides a critical resource for advancing
more reliable and capable coding assistants.
To overcome computational challenges of Optimal Transport (OT), several
variants of Sliced Wasserstein (SW) has been developed in the literature. These
approaches exploit the closed-form expression of the univariate OT by
projecting measures onto (one-dimensional) lines. However, projecting measures
onto low-dimensional spaces can lead to a loss of topological information.
Tree-Sliced Wasserstein distance on Systems of Lines (TSW-SL) has emerged as a
promising alternative that replaces these lines with a more advanced structure
called tree systems. The tree structures enhance the ability to capture
topological information of the metric while preserving computational
efficiency. However, at the core of TSW-SL, the splitting maps, which serve as
the mechanism for pushing forward measures onto tree systems, focus solely on
the position of the measure supports while disregarding the projecting domains.
Moreover, the specific splitting map used in TSW-SL leads to a metric that is
not invariant under Euclidean transformations, a typically expected property
for OT on Euclidean space. In this work, we propose a novel class of splitting
maps that generalizes the existing one studied in TSW-SL enabling the use of
all positional information from input measures, resulting in a novel
Distance-based Tree-Sliced Wasserstein (Db-TSW) distance. In addition, we
introduce a simple tree sampling process better suited for Db-TSW, leading to
an efficient GPU-friendly implementation for tree systems, similar to the
original SW. We also provide a comprehensive theoretical analysis of proposed
class of splitting maps to verify the injectivity of the corresponding Radon
Transform, and demonstrate that Db-TSW is an Euclidean invariant metric. We
empirically show that Db-TSW significantly improves accuracy compared to recent
SW variants while maintaining low computational cost via a wide range of
experiments.
6-DoF grasp detection has been a fundamental and challenging problem in robotic vision. While previous works have focused on ensuring grasp stability, they often do not consider human intention conveyed through natural language, hindering effective collaboration between robots and users in complex 3D environments. In this paper, we present a new approach for language-driven 6-DoF grasp detection in cluttered point clouds. We first introduce Grasp-Anything-6D, a large-scale dataset for the language-driven 6-DoF grasp detection task with 1M point cloud scenes and more than 200M language-associated 3D grasp poses. We further introduce a novel diffusion model that incorporates a new negative prompt guidance learning strategy. The proposed negative prompt strategy directs the detection process toward the desired object while steering away from unwanted ones given the language input. Our method enables an end-to-end framework where humans can command the robot to grasp desired objects in a cluttered scene using natural language. Intensive experimental results show the effectiveness of our method in both benchmarking experiments and real-world scenarios, surpassing other baselines. In addition, we demonstrate the practicality of our approach in real-world robotic applications. Our project is available at this https URL.
Multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR) in the medical domain serves
as a foundational task for various downstream applications such as speech
translation, spoken language understanding, and voice-activated assistants.
This technology improves patient care by enabling efficient communication
across language barriers, alleviating specialized workforce shortages, and
facilitating improved diagnosis and treatment, particularly during pandemics.
In this work, we introduce MultiMed, the first multilingual medical ASR
dataset, along with the first collection of small-to-large end-to-end medical
ASR models, spanning five languages: Vietnamese, English, German, French, and
Mandarin Chinese. To our best knowledge, MultiMed stands as the world's largest
medical ASR dataset across all major benchmarks: total duration, number of
recording conditions, number of accents, and number of speaking roles.
Furthermore, we present the first multilinguality study for medical ASR, which
includes reproducible empirical baselines, a monolinguality-multilinguality
analysis, Attention Encoder Decoder (AED) vs Hybrid comparative study and a
linguistic analysis. We present practical ASR end-to-end training schemes
optimized for a fixed number of trainable parameters that are common in
industry settings. All code, data, and models are available online:
this https URL
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.