Guizhou University
CAMS is a compositional zero-shot learning framework from Guizhou University and Shanghai Jiao Tong University that enhances CLIP-based models by employing Gated Cross-Attention for fine-grained feature extraction and Multi-Space Disentanglement for semantic separation. The framework achieved state-of-the-art AUC scores on three benchmarks, including a 2.1% improvement on C-GQA, while also demonstrating superior computational efficiency.
SplitFlux introduces a framework for disentangling image content and style from a single image using the Flux model, employing Rank-Constrained Adaptation (RCA) and Visual-Gated LoRA (VGRA). This method achieves improved content identity preservation and flexible recontextualization in generated images, outperforming existing approaches.
With the intensification of global climate change, accurate prediction of air quality indicators, especially PM2.5 concentration, has become increasingly important in fields such as environmental protection, public health, and urban management. To address this, we propose an air quality PM2.5 index prediction model based on a hybrid CNN-LSTM architecture. The model effectively combines Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for local spatial feature extraction and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks for modeling temporal dependencies in time series data. Using a multivariate dataset collected from an industrial area in Beijing between 2010 and 2015 -- which includes hourly records of PM2.5 concentration, temperature, dew point, pressure, wind direction, wind speed, and precipitation -- the model predicts the average PM2.5 concentration over 6-hour intervals. Experimental results show that the model achieves a root mean square error (RMSE) of 5.236, outperforming traditional time series models in both accuracy and generalization. This demonstrates its strong potential in real-world applications such as air pollution early warning systems. However, due to the complexity of multivariate inputs, the model demands high computational resources, and its ability to handle diverse atmospheric factors still requires optimization. Future work will focus on enhancing scalability and expanding support for more complex multivariate weather prediction tasks.
The Z2 gauging of ZN symmetry can enforce certain elements of the fermion Yukawa couplings to vanish. We have performed a systematical study of texture zero patterns of lepton mass matrices in the minimal seesaw model, and we present all the possible patterns of the charged lepton Yukawa coupling YE, neutrino Yukawa coupling Yν, right-handed neutrino mass matrix MR and the light neutrino mass matrix Mν which can be derived from the Z2 gauging of ZN symmetry. The realization of the textures with the maximum number of zeros and the second maximum number of zeros from non-invertible symmetry is studied, and the phenomenological implications in neutrino oscillation are discussed.
The rapid spread of multimodal misinformation on social media calls for more effective and robust detection methods. Recent advances leveraging multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown the potential in addressing this challenge. However, it remains unclear exactly where the bottleneck of existing approaches lies (evidence retrieval v.s. reasoning), hindering the further advances in this field. On the dataset side, existing benchmarks either contain outdated events, leading to evaluation bias due to discrepancies with contemporary social media scenarios as MLLMs can simply memorize these events, or artificially synthetic, failing to reflect real-world misinformation patterns. Additionally, it lacks comprehensive analyses of MLLM-based model design strategies. To address these issues, we introduce XFacta, a contemporary, real-world dataset that is better suited for evaluating MLLM-based detectors. We systematically evaluate various MLLM-based misinformation detection strategies, assessing models across different architectures and scales, as well as benchmarking against existing detection methods. Building on these analyses, we further enable a semi-automatic detection-in-the-loop framework that continuously updates XFacta with new content to maintain its contemporary relevance. Our analysis provides valuable insights and practices for advancing the field of multimodal misinformation detection. The code and data have been released.
06 Aug 2025
Researchers at Guizhou University developed the Predictive Pruning Framework (PPF), an automated system for adaptively compressing Large Language Models (LLMs) via structured pruning. PPF utilizes a reinforcement learning agent guided by a fast, CNN-based performance predictor to generate optimal layer-wise pruning policies, achieving substantial perplexity reductions and improved zero-shot accuracy while enabling dynamic pruning capabilities.
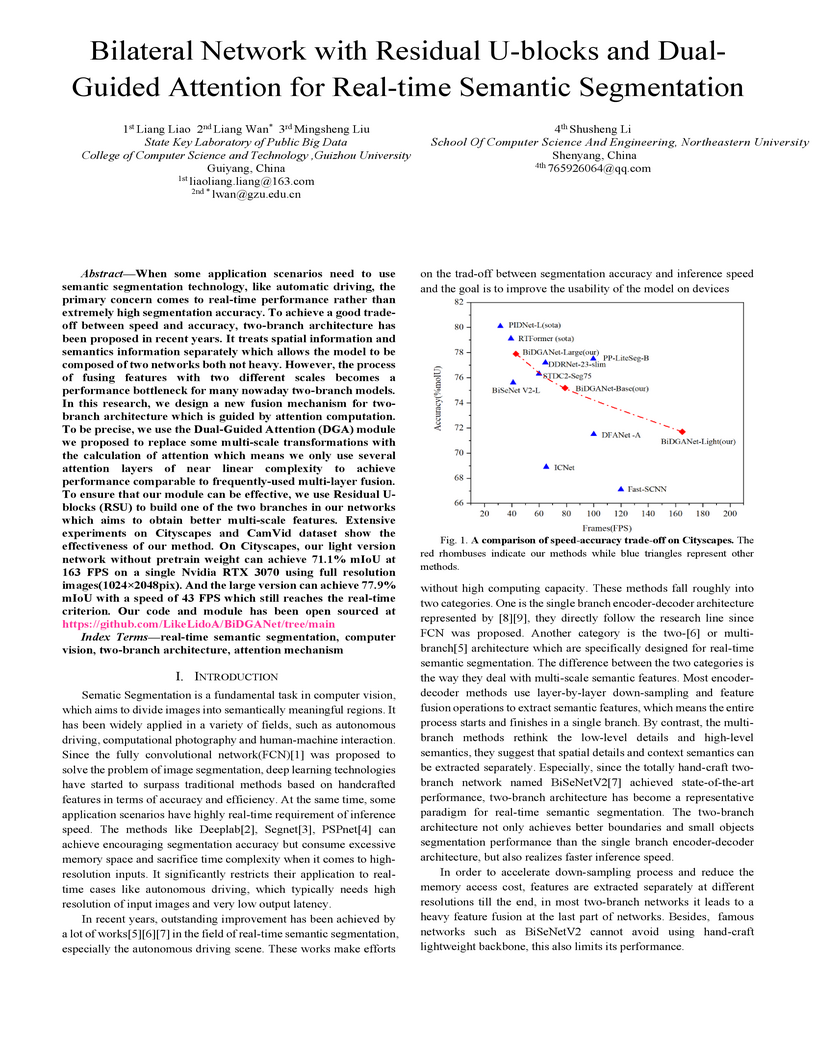
When some application scenarios need to use semantic segmentation technology, like automatic driving, the primary concern comes to real-time performance rather than extremely high segmentation accuracy. To achieve a good trade-off between speed and accuracy, two-branch architecture has been proposed in recent years. It treats spatial information and semantics information separately which allows the model to be composed of two networks both not heavy. However, the process of fusing features with two different scales becomes a performance bottleneck for many nowaday two-branch models. In this research, we design a new fusion mechanism for two-branch architecture which is guided by attention computation. To be precise, we use the Dual-Guided Attention (DGA) module we proposed to replace some multi-scale transformations with the calculation of attention which means we only use several attention layers of near linear complexity to achieve performance comparable to frequently-used multi-layer fusion. To ensure that our module can be effective, we use Residual U-blocks (RSU) to build one of the two branches in our networks which aims to obtain better multi-scale features. Extensive experiments on Cityscapes and CamVid dataset show the effectiveness of our method.
In sophisticated existing Text-to-SQL methods exhibit errors in various proportions, including schema-linking errors (incorrect columns, tables, or extra columns), join errors, nested errors, and group-by errors. Consequently, there is a critical need to filter out unnecessary tables and columns, directing the language models attention to relevant tables and columns with schema-linking, to reduce errors during SQL generation. Previous approaches have involved sorting tables and columns based on their relevance to the question, selecting the top-ranked ones for sorting, or directly identifying the necessary tables and columns for SQL generation. However, these methods face challenges such as lengthy model training times, high consumption of expensive GPT-4 tokens in few-shot prompts, or suboptimal performance in schema linking. Therefore, we propose an inventive schema linking method in two steps: Firstly, generate an initial SQL query by utilizing the complete database schema. Subsequently, extract tables and columns from the initial SQL query to create a concise schema. Using CodeLlama-34B, when comparing the schemas obtained by mainstream methods with ours for SQL generation, our schema performs optimally. Leveraging GPT4, our SQL generation method achieved results that are comparable to mainstream Text-to-SQL methods on the Spider dataset.
Inspired by the principle of self-regulating cooperation in collective institutions, we propose the Group Relative Policy Optimization with Global Cooperation Constraint (GRPO-GCC) framework. This work is the first to introduce GRPO into spatial public goods games, establishing a new deep reinforcement learning baseline for structured populations. GRPO-GCC integrates group relative policy optimization with a global cooperation constraint that strengthens incentives at intermediate cooperation levels while weakening them at extremes. This mechanism aligns local decision making with sustainable collective outcomes and prevents collapse into either universal defection or unconditional cooperation. The framework advances beyond existing approaches by combining group-normalized advantage estimation, a reference-anchored KL penalty, and a global incentive term that dynamically adjusts cooperative payoffs. As a result, it achieves accelerated cooperation onset, stabilized policy adaptation, and long-term sustainability. GRPO-GCC demonstrates how a simple yet global signal can reshape incentives toward resilient cooperation, and provides a new paradigm for multi-agent reinforcement learning in socio-technical systems.
Automated Program Repair (APR) is a task to automatically generate patches
for the buggy code. However, most research focuses on generating correct
patches while ignoring the consistency between the fixed code and the original
buggy code. How to conduct adaptive bug fixing and generate patches with
minimal modifications have seldom been investigated. To bridge this gap, we
first introduce a novel task, namely AdaPR (Adaptive Program Repair). We then
propose a two-stage approach AdaPatcher (Adaptive Patch Generator) to enhance
program repair while maintaining the consistency. In the first stage, we
utilize a Bug Locator with self-debug learning to accurately pinpoint bug
locations. In the second stage, we train a Program Modifier to ensure
consistency between the post-modified fixed code and the pre-modified buggy
code. The Program Modifier is enhanced with a location-aware repair learning
strategy to generate patches based on identified buggy lines, a hybrid training
strategy for selective reference and an adaptive preference learning to
prioritize fewer changes. The experimental results show that our approach
outperforms a set of baselines by a large margin, validating the effectiveness
of our two-stage framework for the newly proposed AdaPR task.
08 Oct 2025
We present the first systematic search for "changing-look" ("CL") behavior in the broad He ii {\lambda}4686 emission line in quasars, utilizing repeated spectroscopy from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS). The He ii line, originating from high-ionization gas and powered by extreme ultraviolet photons, serves as a sensitive tracer of changes in the ionizing continuum. After applying strict spectral selection criteria and visual inspection to a parent sample of over 9,000 quasars with multi-epoch spectra, we identify a sample of 34 He ii "changing-look" quasars that show a significant appearance or disappearance of the broad He ii {\lambda}4686 line. Compared with previously known H\{beta} "CL" quasars, the He ii "CL" sample exhibits similarly strong continuum variability and broad-line flux changes, yet shows a preference for higher Eddington ratios and lower host-galaxy contamination. These results highlight the value of He ii line in studying the central variable engines of AGNs and uncovering a more complete census of extreme quasar variability. A comparison with H\{beta} "CL" further underscores the profound selection biases inherent in "changing-look" studies, especially those associated with line strength, host-galaxy contamination, and spectral signal-to-noise ratio.
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Carnegie Mellon UniversityBudker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RASGyeongsang National UniversityGuangxi Normal UniversityCentral China Normal UniversityGuizhou UniversityGuangxi UniversityFujian Normal UniversityHenan Normal UniversityHangzhou Normal UniversityG.I. Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RASHelmholtz-Institut Mainz, GSI Helmholtzzentrum f
u
r Schwerionenforschung GmbHInstitut f
u
r Kernphysik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universit
u
t MainzGSI Helmholtzzentrum f
u
r Schwerionenforschung GmbH
Carnegie Mellon UniversityBudker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RASGyeongsang National UniversityGuangxi Normal UniversityCentral China Normal UniversityGuizhou UniversityGuangxi UniversityFujian Normal UniversityHenan Normal UniversityHangzhou Normal UniversityG.I. Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RASHelmholtz-Institut Mainz, GSI Helmholtzzentrum f
u
r Schwerionenforschung GmbHInstitut f
u
r Kernphysik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universit
u
t MainzGSI Helmholtzzentrum f
u
r Schwerionenforschung GmbHWe report a direct search for a new gauge boson, X, with a mass of 17 MeV/c2, which could explain the anomalous excess of e+e− pairs observed in the 8Be nuclear transitions. The search is conducted in the charmonium decay χcJ→XJ/ψ (J=0,1,2) via the radiative transition ψ(3686)→γχcJ using (2712.4±14.3)×106 ψ(3686) events collected with the BESIII detector at the BEPCII collider. No significant signal is observed, and the new upper limit on the coupling strength of charm quark and the new gauge boson, ϵc, at 17 MeV/c2 is set to be |\epsilon_c|<1.2\times 10^{-2} at 90% confidence level. We also report new constraints on the mixing strength ϵ between the Standard Model photon and dark photon γ′ in the mass range from 5 MeV/c2 to 300 MeV/c2. The upper limits at 90% confidence level vary within (2.5−17.5)×10−3 depending on the γ′ mass.
Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA) is the task aimed at predicting the sentiment polarity of aspect words within sentences. Recently, incorporating graph neural networks (GNNs) to capture additional syntactic structure information in the dependency tree derived from syntactic dependency parsing has been proven to be an effective paradigm for boosting ABSA. Despite GNNs enhancing model capability by fusing more types of information, most works only utilize a single topology view of the dependency tree or simply conflate different perspectives of information without distinction, which limits the model performance. To address these challenges, in this paper, we propose a new multi-view attention syntactic enhanced graph convolutional network (MASGCN) that weighs different syntactic information of views using attention mechanisms. Specifically, we first construct distance mask matrices from the dependency tree to obtain multiple subgraph views for GNNs. To aggregate features from different views, we propose a multi-view attention mechanism to calculate the attention weights of views. Furthermore, to incorporate more syntactic information, we fuse the dependency type information matrix into the adjacency matrices and present a structural entropy loss to learn the dependency type adjacency matrix. Comprehensive experiments on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms state-of-the-art methods. The codes and datasets are available at this https URL.
14 Jun 2022
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University Tel Aviv University
Tel Aviv University University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Nanjing University
Nanjing University Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University Boston University
Boston University University of Maryland
University of Maryland Huazhong University of Science and Technology
Huazhong University of Science and Technology Australian National UniversityUniversity of GenevaYunnan UniversityGuizhou UniversityMax Planck Institute for Solar System ResearchTsung-Dao Lee Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityBeijingXi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of SciencesPurple Mountain Observatories, Chinese Academy of SciencesMax-Planck-Institute f
ür Astronomie
Australian National UniversityUniversity of GenevaYunnan UniversityGuizhou UniversityMax Planck Institute for Solar System ResearchTsung-Dao Lee Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityBeijingXi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of SciencesPurple Mountain Observatories, Chinese Academy of SciencesMax-Planck-Institute f
ür AstronomieWe propose to develop a wide-field and ultra-high-precision photometric
survey mission, temporarily named "Earth 2.0 (ET)". This mission is designed to
measure, for the first time, the occurrence rate and the orbital distributions
of Earth-sized planets. ET consists of seven 30cm telescopes, to be launched to
the Earth-Sun's L2 point. Six of these are transit telescopes with a field of
view of 500 square degrees. Staring in the direction that encompasses the
original Kepler field for four continuous years, this monitoring will return
tens of thousands of transiting planets, including the elusive Earth twins
orbiting solar-type stars. The seventh telescope is a 30cm microlensing
telescope that will monitor an area of 4 square degrees toward the galactic
bulge. This, combined with simultaneous ground-based KMTNet observations, will
measure masses for hundreds of long-period and free-floating planets. Together,
the transit and the microlensing telescopes will revolutionize our
understandings of terrestrial planets across a large swath of orbital distances
and free space. In addition, the survey data will also facilitate studies in
the fields of asteroseismology, Galactic archeology, time-domain sciences, and
black holes in binaries.
29 Sep 2025
Investigating the bubbles generated by the interaction between asymptotic giant branch stellar outflows and the interstellar medium (ISM) is pivotal for elucidating the mechanism by which evolved low- to intermediate-mass stars enrich the ISM with heavy elements. Using archival datasets from the Galactic Plane Pulsar Snapshot survey and the Galactic Arecibo L-Band Array \ion{H}{1} survey, we have identified 14 bubbles within interstellar atomic hydrogen (\ion{H}{1}) maps, each showing evidence of potential association with planetary nebulae (PNe).We pursue two primary objectives centered on the identified ISM bubbles and their association with PNe. First, leveraging the calibrated distance measurements of PNe from Gaia Data Release 3, we utilize these ISM bubbles as observational tracers to investigate and constrain the Galactic rotation curve. Second, we note that distance determinations for some PNe remain unreliable, partly because their central stars are obscured by extended nebular envelopes or are misidentified. Therefore, we develop a novel methodological framework to derive kinematic distances for PNe by leveraging the velocities of their associated ISM bubbles and constraints from the Galactic rotation curve.
MoCha-V2 presents a new learning paradigm for stereo matching, utilizing a 'white-box' Motif Correlation Graph to identify and reconstruct geometric structures from feature channels. It achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on Scene Flow with 0.39 px EPE and ranks first on Middlebury 2014 with 11.4% Bad 1.0 error, demonstrating superior detail matching and robust zero-shot generalization to real-world data.
Dynamic reconfiguration is crucial for nanoplasmonic structures to achieve
diversified functions and optimize performances; however, the dynamic
reconfiguration of spatial arrangements remains a formidable technological
challenge. Here, we showcase in-situ dynamic spatial reconfiguration of
plasmonic nanowire devices and circuits on dry solid substrates, by harnessing
a photothermal-shock tweezers platform. Owing to its versatility, nanoscale
precision, real-time operation, and large external output force, the multimodal
platform enables dexterous fine-tuning of positions, overlap lengths, and
coupling distances and orientations of discrete components in situ. Spatial
position-dependent optical properties that have not been reported before or are
challenging to achieve through traditional micro/nanomanipulation are easily
tuned and observed, such as the intensity evolution of axial photon-plasmon
coupling from near field to far field, and the resonant mode evolution of
photonic cavity-plasmonic cavity coupling from weak to strong. We also employ
the nanorobotic probe-based operation mode to optimize the side-mode
suppression ratios of single-mode lasers and the intensity splitting ratios of
3-dB couplers. Our results are general and applicable to materials of almost
any size, structure, and material type, as well as other narrow or curved
micro/nano-waveguide surfaces, which opens new avenues for reconfigurable
nanoplasmonic structures with dynamically tunable spatial features.
15 Oct 2025
This paper introduces a novel approach to approximating continuous functions over high-dimensional hypercubes by integrating matrix CUR decomposition with hyperinterpolation techniques. Traditional Fourier-based hyperinterpolation methods suffer from the curse of dimensionality, as the number of coefficients grows exponentially with the dimension. To address this challenge, we propose two efficient strategies for constructing low-rank matrix CUR decompositions of the coefficient matrix, significantly reducing computational complexity while preserving accuracy.
The first method employs structured index selection to form a compressed representation of the tensor, while the second utilizes adaptive sampling to further optimize storage and computation. Theoretical error bounds are derived for both approaches, ensuring rigorous control over approximation quality. Additionally, practical algorithms -- including randomized and adaptive decomposition techniques -- are developed to efficiently compute the CUR decomposition. Numerical experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods in drastically reducing the number of required coefficients without compromising precision.
Our results bridge matrix/tensor decomposition and function approximation, offering a scalable solution for high-dimensional problems. This work advances the field of numerical analysis by providing a computationally efficient framework for hyperinterpolation, with potential applications in scientific computing, machine learning, and data-driven modeling.
01 Jun 2024
Using a large sample of fast radio bursts (FRBs) from the first CHIME/FRB catalog, we apply the Lynden-Bell's c− method to study their energy function and formation rate evolutions with redshift. It is found with the non-parametric Kendell's τ statistics that the FRB energy strongly evolves with the cosmological redshift as E(z)∝(1+z)5.23. After removing the redshift dependence, the local energy distribution can be described by a broken power-law form of Ψ(E0)∝E0−0.38 for the low-energy segment and Ψ(E0)∝E0−2.01 for the high-energy segment with a dividing line of ∼2.1×1040erg. Interestingly, we find that the formation rate of CHIME FRBs also evolves with redshift as ρ(z)∝(1+z)−4.73±0.08. The local formation rate ρ(0) of the CHIME FRBs is constrained to be about 1.25×104Gpc−3yr−1 that is comparable with some previous estimations. In addition, we notice the formation rate not only exceeds the star formation rate at the lower redshifts but also always declines with the increase of redshift, which does not match the star formation history at all. Consequently, we suggest that most FRBs could originate from the older stellar populations.
The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the medical domain has
stressed a compelling need for standard datasets to evaluate their
question-answering (QA) performance. Although there have been several benchmark
datasets for medical QA, they either cover common knowledge across different
departments or are specific to another department rather than pediatrics.
Moreover, some of them are limited to objective questions and do not measure
the generation capacity of LLMs. Therefore, they cannot comprehensively assess
the QA ability of LLMs in pediatrics. To fill this gap, we construct
PediaBench, the first Chinese pediatric dataset for LLM evaluation.
Specifically, it contains 4,117 objective questions and 1,632 subjective
questions spanning 12 pediatric disease groups. It adopts an integrated scoring
criterion based on different difficulty levels to thoroughly assess the
proficiency of an LLM in instruction following, knowledge understanding,
clinical case analysis, etc. Finally, we validate the effectiveness of
PediaBench with extensive experiments on 20 open-source and commercial LLMs.
Through an in-depth analysis of experimental results, we offer insights into
the ability of LLMs to answer pediatric questions in the Chinese context,
highlighting their limitations for further improvements. Our code and data are
published at this https URL
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.