Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen)
Researchers from Tsinghua University, Southern University of Science and Technology, and Harbin Institute of Technology introduce FedLuck, an Asynchronous Federated Learning (AFL) framework that jointly and adaptively optimizes local updating frequency and gradient compression rates. This approach, grounded in a derived convergence factor, achieved up to 55% faster training times and 56% less communication consumption on average across various tasks compared to existing baselines.
F₁, a Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model, integrates explicit visual foresight into its decision-making process, moving beyond purely reactive control. This approach yields enhanced robustness in dynamic environments and improved generalization across a range of real-world and simulated robotic manipulation tasks.
01 Sep 2025
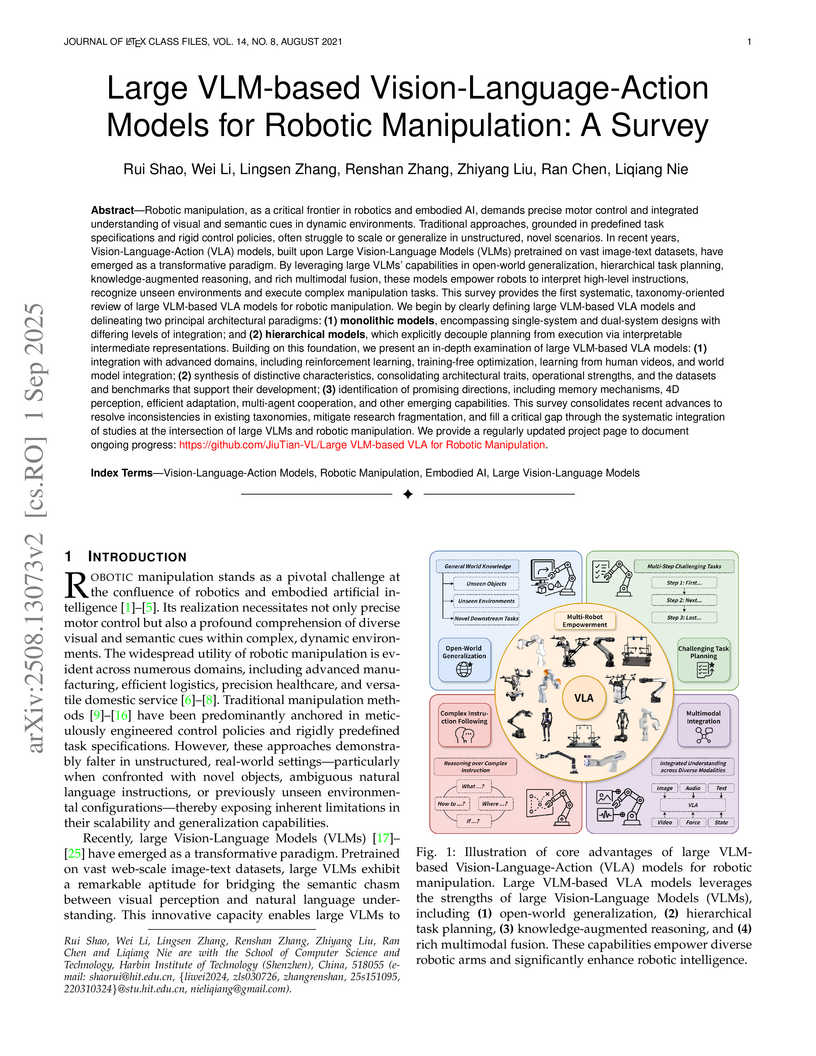
The survey presents the first systematic, taxonomy-oriented review of large Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models for robotic manipulation, consolidating diverse research and proposing a coherent framework. It identifies key architectural paradigms, integration strategies, and distinctive characteristics while outlining critical future research directions.
South China University of Technology Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences University of Science and Technology of ChinaShanghai AI LabShenzhen UniversityHarbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen)Shanghai University of Electric Power
University of Science and Technology of ChinaShanghai AI LabShenzhen UniversityHarbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen)Shanghai University of Electric Power Southern University of Science and TechnologyShenzhen MSU-BIT UniversityShenzhen University of Advanced TechnologyShenzhen Key Laboratory for High Performance Data Mining, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Southern University of Science and TechnologyShenzhen MSU-BIT UniversityShenzhen University of Advanced TechnologyShenzhen Key Laboratory for High Performance Data Mining, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences University of Science and Technology of ChinaShanghai AI LabShenzhen UniversityHarbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen)Shanghai University of Electric Power
University of Science and Technology of ChinaShanghai AI LabShenzhen UniversityHarbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen)Shanghai University of Electric Power Southern University of Science and TechnologyShenzhen MSU-BIT UniversityShenzhen University of Advanced TechnologyShenzhen Key Laboratory for High Performance Data Mining, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Southern University of Science and TechnologyShenzhen MSU-BIT UniversityShenzhen University of Advanced TechnologyShenzhen Key Laboratory for High Performance Data Mining, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of SciencesResearchers from a consortium of Chinese institutions systematically surveyed 283 Large Language Model benchmarks, categorizing them into a three-tiered taxonomy. The work identifies critical issues like data contamination and cultural bias, while proposing a design paradigm for more robust and fair future evaluations.
06 Jul 2025
Researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen, surveyed Large Multimodal Reasoning Models (LMRMs), tracing their evolution through four stages from perception-driven modularity to language-centric reasoning. The survey highlights current limitations of state-of-the-art models in omni-modal and agentic benchmarks, and proposes Native Large Multimodal Reasoning Models (N-LMRMs) as a future paradigm for inherently multimodal and integrated AI systems.
Concerto, a joint 2D-3D self-supervised learning framework developed by researchers from The University of Hong Kong, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, and Harbin Institute of Technology, synergistically combines intra-modal 3D self-distillation and cross-modal 2D-3D joint embedding prediction. This approach learns unified spatial representations, achieving 80.7% mIoU for 3D semantic segmentation on ScanNet and demonstrating robust data efficiency.
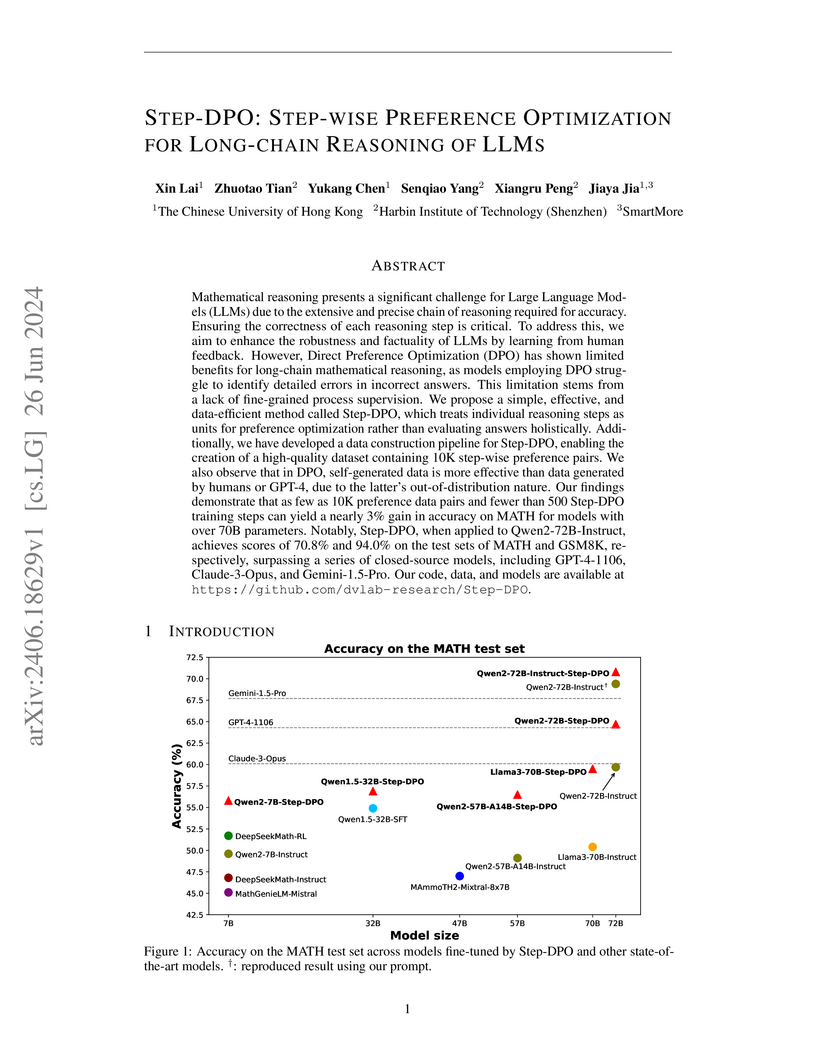
Researchers at The Chinese University of Hong Kong and Harbin Institute of Technology developed Step-DPO, a method that adapts Direct Preference Optimization for fine-grained, step-wise supervision in long-chain mathematical reasoning. This approach enabled open-source models like Qwen2-72B-Instruct to achieve 70.8% accuracy on MATH and 94.0% on GSM8K, outperforming several state-of-the-art closed-source models including GPT-4-1106 and Claude-3-Opus.
R2ec introduces a unified large recommender model that intrinsically integrates reasoning and recommendation capabilities within a single architecture, optimizing performance and interpretability without relying on human-annotated reasoning data. The model consistently surpasses existing baselines in recommendation quality across multiple datasets while maintaining competitive inference efficiency.
KDRL (Knowledge Distillation and Reinforcement Learning) introduces a unified post-training framework that integrates knowledge distillation and reinforcement learning to enhance reasoning capabilities in LLMs, achieving notable performance improvements and increased efficiency on mathematical reasoning benchmarks. This framework addresses the limitations of applying these methods separately by jointly optimizing both objectives.
Researchers from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University and collaborators developed a framework that enables parallel test-time scaling for latent reasoning models, addressing the challenges of generating and evaluating diverse reasoning paths in continuous latent spaces. This approach enhances the performance of models like COCONUT, CODI, and CoLaR on arithmetic reasoning tasks by effectively leveraging additional inference compute.
01 Oct 2025
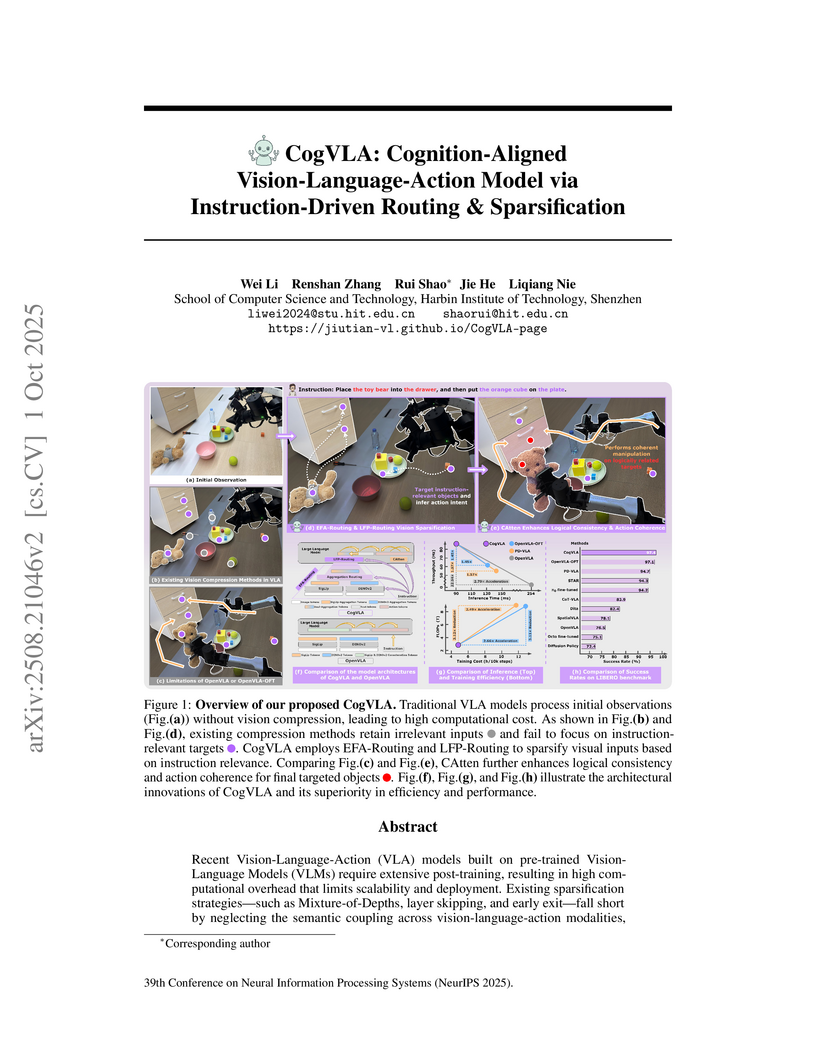
CogVLA, developed by researchers at Harbin Institute of Technology, introduces a cognition-aligned, instruction-driven framework for Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models. It achieves a 97.4% average success rate on the LIBERO benchmark and 70.0% on real-world ALOHA tasks, while also reducing inference time by 2.79x and FLOPs by 3.12x compared to leading baselines.
Researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology, Tsinghua University, Peng Cheng Laboratory, and HKUST introduce HLFormer, a hyperbolic learning framework for Partially Relevant Video Retrieval (PRVR). This model achieves state-of-the-art results on ActivityNet Captions, Charades-STA, and TVR benchmarks by effectively modeling video's semantic hierarchy and enforcing partial relevance through a novel hyperbolic loss.
19 Oct 2025
Repo2Run introduces an LLM-based agent capable of automating the creation of executable test environments for code repositories, achieving an 86.0% success rate in building environments and running tests on a new 420-repository benchmark. This system synthesizes reproducible Dockerfiles, providing foundational infrastructure for training more capable software engineering LLMs.
A new framework, Video-of-Thought (VoT), mimics human cognition by breaking down complex video reasoning into five structured steps, from perception to cognitive interpretation. The MotionEpic model, which implements VoT with Spatio-Temporal Scene Graph integration, demonstrates superior performance over existing video MLLMs on complex video question-answering tasks and competitive grounding capabilities.
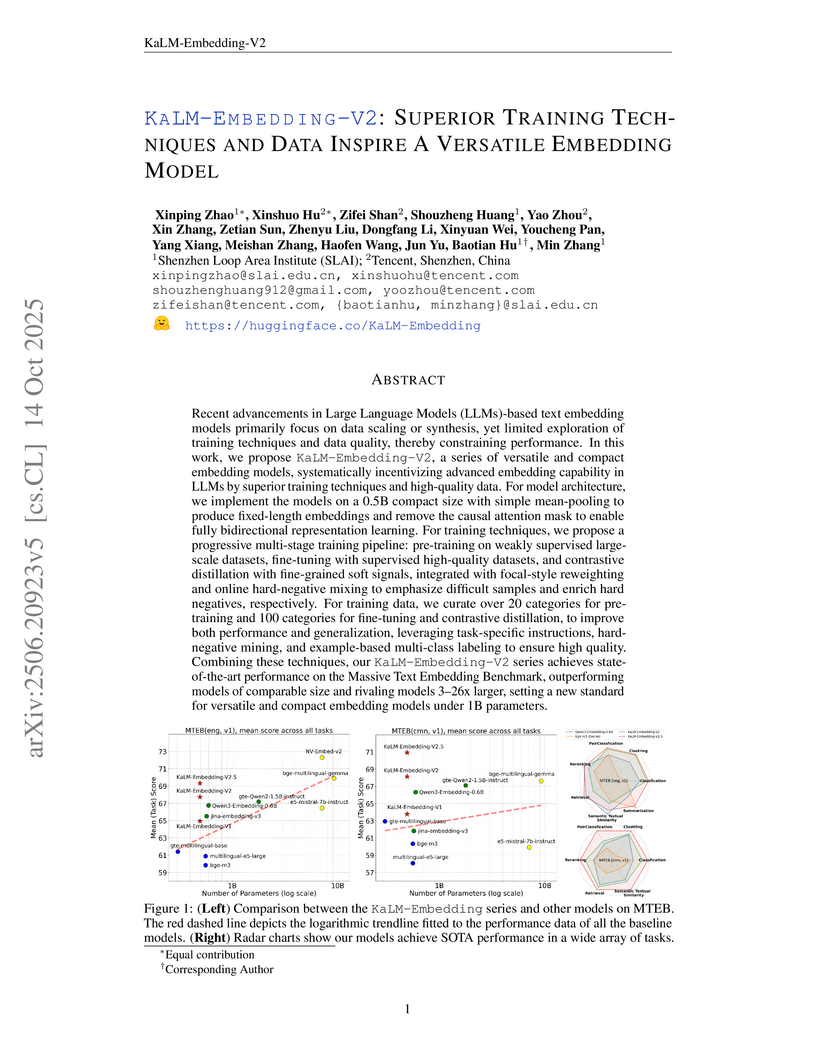
The KaLM-Embedding-V2 series introduces compact (0.5B parameter) and versatile text embedding models that achieve state-of-the-art performance on MTEB benchmarks for their size. Developed by SLAI and Tencent, these models utilize superior training techniques and meticulously curated data, offering a fully open-sourced solution for improved RAG and diverse NLP applications.
Video Individual Counting (VIC) has received increasing attention for its importance in intelligent video surveillance. Existing works are limited in two aspects, i.e., dataset and method. Previous datasets are captured with fixed or rarely moving cameras with relatively sparse individuals, restricting evaluation for a highly varying view and time in crowded scenes. Existing methods rely on localization followed by association or classification, which struggle under dense and dynamic conditions due to inaccurate localization of small targets. To address these issues, we introduce the MovingDroneCrowd Dataset, featuring videos captured by fast-moving drones in crowded scenes under diverse illuminations, shooting heights and angles. We further propose a Shared Density map-guided Network (SDNet) using a Depth-wise Cross-Frame Attention (DCFA) module to directly estimate shared density maps between consecutive frames, from which the inflow and outflow density maps are derived by subtracting the shared density maps from the global density maps. The inflow density maps across frames are summed up to obtain the number of unique pedestrians in a video. Experiments on our datasets and publicly available ones show the superiority of our method over the state of the arts in highly dynamic and complex crowded scenes. Our dataset and codes have been released publicly.
This survey provides a comprehensive overview of LLM-based social simulation, categorizing existing work into Individual, Scenario, and Society simulations based on their scale and precision requirements. It details the architectures, construction methods, objectives, and evaluation approaches for each category, highlighting research trends and future directions in the field.
Researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen, and Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab developed SemanticVLA, a framework for robotic manipulation that addresses perceptual redundancy and superficial instruction-vision alignment. It achieved a 97.7% success rate on the LIBERO benchmark, reducing training cost by 3.0x and inference latency by 2.7x compared to OpenVLA, while demonstrating robust performance in real-world tasks.
AutoSurvey presents a multi-phase, agent-based framework that automates the creation of comprehensive literature surveys, achieving a substantial speed increase (up to 73.59 surveys per hour for 64k tokens) while maintaining citation and content quality metrics comparable to human-authored benchmarks.
A framework called CoRe-MMRAG improves multimodal retrieval-augmented generation by reconciling conflicts between a model's internal knowledge and external data, as well as inconsistencies between visual and textual information. The system achieves 3.5 percentage points higher accuracy on InfoSeek and 2.9 percentage points on Enc-VQA compared to leading baselines in knowledge-based Visual Question Answering.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.