SmartMore
QuickLLaMA (Query-aware Inference for LLMs) introduces a training-free inference acceleration method that allows Large Language Models to efficiently process and accurately reason over arbitrarily long contexts, extending capabilities to up to 1 million tokens. The approach significantly improves performance on long-context benchmarks, outperforming prior state-of-the-art methods like InfLLM by over 7% on LLaMA3 while maintaining linear scaling of time and memory.
A new model, LISA, introduces "reasoning segmentation," enabling multimodal large language models to generate precise segmentation masks from complex, implicit natural language queries. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on a new benchmark, outperforming baselines by over 15 gIoU points in zero-shot settings while maintaining strong performance on standard referring segmentation tasks.
Researchers from the Chinese University of Hong Kong and SmartMore developed VisionReasoner, a unified framework for visual perception that integrates a large vision-language model with reinforcement learning. This system handles diverse tasks including detection, segmentation, and counting through a shared reasoning process, demonstrating improved performance across these benchmarks and generating interpretable thought traces without explicit reasoning training.
ARPO (Agentic Replay Policy Optimization) introduces a comprehensive reinforcement learning framework to train GUI agents by addressing challenges like sparse rewards and high data generation costs. The method achieves a 62.50% success rate on in-domain OSWorld benchmark tasks, demonstrating improved performance over baseline supervised and standard policy optimization approaches.
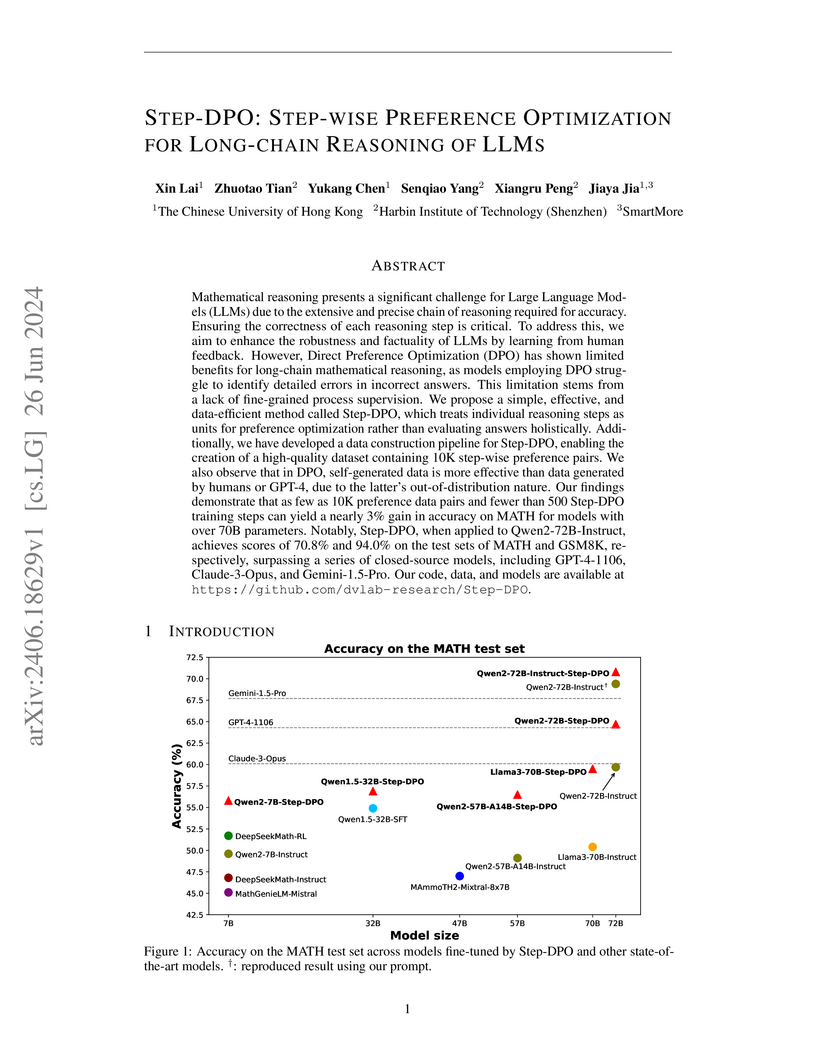
Researchers at The Chinese University of Hong Kong and Harbin Institute of Technology developed Step-DPO, a method that adapts Direct Preference Optimization for fine-grained, step-wise supervision in long-chain mathematical reasoning. This approach enabled open-source models like Qwen2-72B-Instruct to achieve 70.8% accuracy on MATH and 94.0% on GSM8K, outperforming several state-of-the-art closed-source models including GPT-4-1106 and Claude-3-Opus.
LISA++ improves upon the prior LISA model by enabling reasoning instance segmentation and more natural conversational integration of segmentation results. It achieves this by curating instruction-tuning data using GPT-4V, demonstrating that the 'mask-as-embedding' paradigm can be extended without architectural changes.
Researchers from The Chinese University of Hong Kong, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, SmartMore, and Kuaishou Technology developed Jenga, a training-free inference pipeline that accelerates video Diffusion Transformer models. It achieves up to 8.83x speedup on models like HunyuanVideo while maintaining or enhancing generation quality, by dynamically carving attention and progressively generating video resolutions.
Researchers from The Chinese University of Hong Kong developed ControlNeXt, an efficient and powerful method for controllable image and video generation. The approach significantly reduces computational overhead and improves training stability by selectively fine-tuning a small subset of a pre-trained diffusion model's parameters and introducing a novel Cross Normalization technique, demonstrating strong performance across diverse tasks and backbones with over 90% fewer learnable parameters than ControlNet.
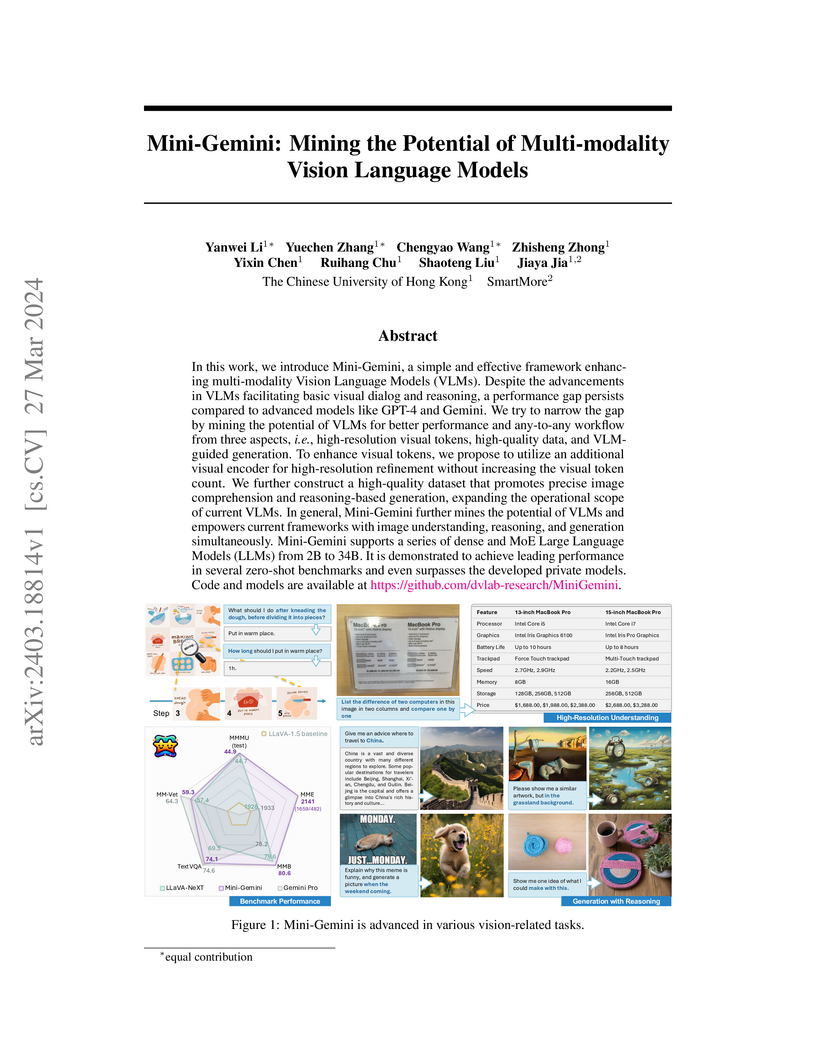
In this work, we introduce Mini-Gemini, a simple and effective framework
enhancing multi-modality Vision Language Models (VLMs). Despite the
advancements in VLMs facilitating basic visual dialog and reasoning, a
performance gap persists compared to advanced models like GPT-4 and Gemini. We
try to narrow the gap by mining the potential of VLMs for better performance
and any-to-any workflow from three aspects, i.e., high-resolution visual
tokens, high-quality data, and VLM-guided generation. To enhance visual tokens,
we propose to utilize an additional visual encoder for high-resolution
refinement without increasing the visual token count. We further construct a
high-quality dataset that promotes precise image comprehension and
reasoning-based generation, expanding the operational scope of current VLMs. In
general, Mini-Gemini further mines the potential of VLMs and empowers current
frameworks with image understanding, reasoning, and generation simultaneously.
Mini-Gemini supports a series of dense and MoE Large Language Models (LLMs)
from 2B to 34B. It is demonstrated to achieve leading performance in several
zero-shot benchmarks and even surpasses the developed private models. Code and
models are available at https://github.com/dvlab-research/MiniGemini.
Knowledge distillation transfers knowledge from the teacher network to the
student one, with the goal of greatly improving the performance of the student
network. Previous methods mostly focus on proposing feature transformation and
loss functions between the same level's features to improve the effectiveness.
We differently study the factor of connection path cross levels between teacher
and student networks, and reveal its great importance. For the first time in
knowledge distillation, cross-stage connection paths are proposed. Our new
review mechanism is effective and structurally simple. Our finally designed
nested and compact framework requires negligible computation overhead, and
outperforms other methods on a variety of tasks. We apply our method to
classification, object detection, and instance segmentation tasks. All of them
witness significant student network performance improvement. Code is available
at this https URL
The RL-GPT framework, developed by researchers from The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Peking University, and SmartMore, integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning (RL) to enable embodied agents to master complex tasks in open-world environments like Minecraft. The system leverages LLMs to strategically orchestrate RL for low-level skill acquisition, demonstrating up to a 6.7x improvement over pure RL and a 1.9x improvement over pure code-based approaches in various tasks, including successfully obtaining a diamond in Minecraft.
Few-shot semantic segmentation (FSS) aims to form class-agnostic models segmenting unseen classes with only a handful of annotations. Previous methods limited to the semantic feature and prototype representation suffer from coarse segmentation granularity and train-set overfitting. In this work, we design Hierarchically Decoupled Matching Network (HDMNet) mining pixel-level support correlation based on the transformer architecture. The self-attention modules are used to assist in establishing hierarchical dense features, as a means to accomplish the cascade matching between query and support features. Moreover, we propose a matching module to reduce train-set overfitting and introduce correlation distillation leveraging semantic correspondence from coarse resolution to boost fine-grained segmentation. Our method performs decently in experiments. We achieve 50.0% mIoU on \coco~dataset one-shot setting and 56.0% on five-shot segmentation, respectively.
This paper introduces Lyra, an efficient framework for multi-modal language models that emphasizes speech integration with other modalities like vision and text
The research introduces Distribution-aware Interference-free Knowledge Integration (DIKI), a framework for parameter-efficient continual learning of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) in Domain-Class Incremental Learning (DCIL) settings. DIKI preserves the VLM's pre-trained zero-shot generalization ability through an interference-free knowledge integration mechanism and dynamic calibration, achieving state-of-the-art performance with significant reductions in trainable parameters and computational requirements.
In this paper, we delve deeper into the Kullback-Leibler (KL) Divergence loss and mathematically prove that it is equivalent to the Decoupled Kullback-Leibler (DKL) Divergence loss that consists of 1) a weighted Mean Square Error (wMSE) loss and 2) a Cross-Entropy loss incorporating soft labels. Thanks to the decomposed formulation of DKL loss, we have identified two areas for improvement. Firstly, we address the limitation of KL/DKL in scenarios like knowledge distillation by breaking its asymmetric optimization property. This modification ensures that the wMSE component is always effective during training, providing extra constructive cues. Secondly, we introduce class-wise global information into KL/DKL to mitigate bias from individual samples. With these two enhancements, we derive the Improved Kullback-Leibler (IKL) Divergence loss and evaluate its effectiveness by conducting experiments on CIFAR-10/100 and ImageNet datasets, focusing on adversarial training, and knowledge distillation tasks. The proposed approach achieves new state-of-the-art adversarial robustness on the public leaderboard -- RobustBench and competitive performance on knowledge distillation, demonstrating the substantial practical merits. Our code is available at this https URL.
The paper introduces "Defect Spectrum," a meticulously re-annotated dataset featuring 125 distinct defect classes and detailed semantic pixel-level labels for industrial quality control. It also proposes "Defect-Gen," a two-stage diffusion model that synthesizes high-quality defective images and masks from limited real data, leading to improved defect segmentation performance.
19 Feb 2024
Empathetic response generation is increasingly significant in AI, necessitating nuanced emotional and cognitive understanding coupled with articulate response expression. Current large language models (LLMs) excel in response expression; however, they lack the ability to deeply understand emotional and cognitive nuances, particularly in pinpointing fine-grained emotions and their triggers. Conversely, small-scale empathetic models (SEMs) offer strength in fine-grained emotion detection and detailed emotion cause identification. To harness the complementary strengths of both LLMs and SEMs, we introduce a Hybrid Empathetic Framework (HEF). HEF regards SEMs as flexible plugins to improve LLM's nuanced emotional and cognitive understanding. Regarding emotional understanding, HEF implements a two-stage emotion prediction strategy, encouraging LLMs to prioritize primary emotions emphasized by SEMs, followed by other categories, substantially alleviates the difficulties for LLMs in fine-grained emotion detection. Regarding cognitive understanding, HEF employs an emotion cause perception strategy, prompting LLMs to focus on crucial emotion-eliciting words identified by SEMs, thus boosting LLMs' capabilities in identifying emotion causes. This collaborative approach enables LLMs to discern emotions more precisely and formulate empathetic responses. We validate HEF on the Empathetic-Dialogue dataset, and the findings indicate that our framework enhances the refined understanding of LLMs and their ability to convey empathetic responses.
Generative Video Propagation (GenProp), developed by researchers from CUHK, Adobe Research, and HKUST, presents a unified framework for diverse video editing tasks by consistently propagating modifications made to a single first frame across an entire video sequence. This approach achieved higher PSNR, CLIP-Text, and CLIP-Image scores on challenging video editing benchmarks, and was strongly preferred by users over competing baselines for visual quality and instruction alignment.
TGDPO integrates token-level reward guidance into the Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) framework, leading to enhanced Large Language Model alignment. This approach yields up to 7.5 points higher win rates on MT-Bench and improves training stability, requiring less hyperparameter tuning compared to traditional DPO.
We introduce a new image segmentation task, called Entity Segmentation (ES), which aims to segment all visual entities (objects and stuffs) in an image without predicting their semantic labels. By removing the need of class label prediction, the models trained for such task can focus more on improving segmentation quality. It has many practical applications such as image manipulation and editing where the quality of segmentation masks is crucial but class labels are less important. We conduct the first-ever study to investigate the feasibility of convolutional center-based representation to segment things and stuffs in a unified manner, and show that such representation fits exceptionally well in the context of ES. More specifically, we propose a CondInst-like fully-convolutional architecture with two novel modules specifically designed to exploit the class-agnostic and non-overlapping requirements of ES. Experiments show that the models designed and trained for ES significantly outperforms popular class-specific panoptic segmentation models in terms of segmentation quality. Moreover, an ES model can be easily trained on a combination of multiple datasets without the need to resolve label conflicts in dataset merging, and the model trained for ES on one or more datasets can generalize very well to other test datasets of unseen domains. The code has been released at this https URL.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.