Hong Kong Polytechnic University
This comprehensive survey from a large multi-institutional collaboration examines "Latent Reasoning" in Large Language Models, an emerging paradigm that performs multi-step inference entirely within the model's high-bandwidth continuous hidden states to overcome the limitations of natural language-based explicit reasoning. It highlights the significant bandwidth advantage of latent representations (approximately 2700x higher) and provides a unified taxonomy of current methodologies.
Machine unlearning (MU) is gaining increasing attention due to the need to remove or modify predictions made by machine learning (ML) models. While training models have become more efficient and accurate, the importance of unlearning previously learned information has become increasingly significant in fields such as privacy, security, and fairness. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of MU, covering current state-of-the-art techniques and approaches, including data deletion, perturbation, and model updates. In addition, commonly used metrics and datasets are also presented. The paper also highlights the challenges that need to be addressed, including attack sophistication, standardization, transferability, interpretability, training data, and resource constraints. The contributions of this paper include discussions about the potential benefits of MU and its future directions. Additionally, the paper emphasizes the need for researchers and practitioners to continue exploring and refining unlearning techniques to ensure that ML models can adapt to changing circumstances while maintaining user trust. The importance of unlearning is further highlighted in making Artificial Intelligence (AI) more trustworthy and transparent, especially with the increasing importance of AI in various domains that involve large amounts of personal user data.
Researchers demonstrated that Large Language Models (LLMs) encode problem difficulty in their internal representations, localizing this mechanism to specific attention heads and showing it can be linearly probed. This allows for automatic difficulty annotation and offers insights into adaptive reasoning, revealing differences from token-level entropy.
A new Retrieval-Augmented Generation framework, LinearRAG, constructs a relation-free hierarchical graph and utilizes a two-stage retrieval process to enhance accuracy and efficiency for large-scale corpora. It consistently surpasses existing GraphRAG methods in generation accuracy and indexing speed, achieving zero LLM token consumption and up to 15.1x faster indexing on large datasets.
By reformulating multi-head attention to reveal an intrinsic FFN-like structure, UMoE introduces a unified Mixture-of-Experts architecture that integrates shared experts across both attention and FFN layers. This approach consistently improves language modeling perplexity and zero-shot performance across various tasks, while enhancing parameter efficiency in large language models.
Although large language models (LLMs) have significant potential to advance chemical discovery, current LLMs lack core chemical knowledge, produce unreliable reasoning trajectories, and exhibit suboptimal performance across diverse chemical tasks. To address these challenges, we propose Chem-R, a generalizable Chemical Reasoning model designed to emulate the deliberative processes of chemists. Chem-R is trained through a three-phase framework that progressively builds advanced reasoning capabilities, including: 1) Chemical Foundation Training, which establishes core chemical knowledge. 2) Chemical Reasoning Protocol Distillation, incorporating structured, expert-like reasoning traces to guide systematic and reliable problem solving. 3) Multi-task Group Relative Policy Optimization that optimizes the model for balanced performance across diverse molecular- and reaction-level tasks. This structured pipeline enables Chem-R to achieve state-of-the-art performance on comprehensive benchmarks, surpassing leading large language models, including Gemini-2.5-Pro and DeepSeek-R1, by up to 32% on molecular tasks and 48% on reaction tasks. Meanwhile, Chem-R also consistently outperforms the existing chemical foundation models across both molecular and reaction level tasks. These results highlight Chem-R's robust generalization, interpretability, and potential as a foundation for next-generation AI-driven chemical discovery. The code and model are available at this https URL.
Researchers at Zhejiang University and Xiaohongshu Inc., among others, discovered a "Refusal Cliff" where large reasoning models internally detect harmful prompts but then suppress these safety intentions before generating unsafe outputs. They identified specific "Refusal Suppression Heads" responsible for this suppression and developed "Cliff-as-a-Judge," an alignment method that achieves comparable safety performance with 98.3% less training data.
NVIDIA researchers introduce Eagle2, a groundbreaking vision-language model that achieves state-of-the-art performance while using just 9B parameters, matching the capabilities of models up to 70B parameters through novel data strategies and training methods that are fully documented and shared with the research community.
We introduce CMPhysBench, designed to assess the proficiency of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Condensed Matter Physics, as a novel Benchmark. CMPhysBench is composed of more than 520 graduate-level meticulously curated questions covering both representative subfields and foundational theoretical frameworks of condensed matter physics, such as magnetism, superconductivity, strongly correlated systems, etc. To ensure a deep understanding of the problem-solving process,we focus exclusively on calculation problems, requiring LLMs to independently generate comprehensive solutions. Meanwhile, leveraging tree-based representations of expressions, we introduce the Scalable Expression Edit Distance (SEED) score, which provides fine-grained (non-binary) partial credit and yields a more accurate assessment of similarity between prediction and ground-truth. Our results show that even the best models, Grok-4, reach only 36 average SEED score and 28% accuracy on CMPhysBench, underscoring a significant capability gap, especially for this practical and frontier domain relative to traditional physics. The code anddataset are publicly available at this https URL.
GuardAgent introduces a framework for safeguarding Large Language Model (LLM) agents against safety and privacy violations by leveraging knowledge-enabled reasoning and code generation for deterministic policy enforcement. The system significantly outperforms existing text-based guardrails and hardcoded approaches in accuracy while maintaining the target agent's original task performance, validated on newly created healthcare access control and web safety benchmarks.
StreamingThinker introduces a paradigm for Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning that enables concurrent input processing and thinking, inspired by human cognition. This approach reduces token-to-first-token (TTFT) latency by approximately 80% and overall time-level latency by over 60% while maintaining reasoning accuracy across various tasks.
31 Mar 2024
RQ-RAG introduces a framework that trains Large Language Models to dynamically refine search queries through rewriting, decomposition, and disambiguation before retrieval. This approach improved accuracy for complex and ambiguous questions, outperforming Llama2-7B by 33.5% and existing RAG methods like SAIL-7B and Self-RAG by 20.3% and 1.9% respectively on question answering benchmarks.
19 Nov 2025
Researchers from Griffith University and collaborators introduce ARG-DESIGNER, an autoregressive graph generation model that designs customized multi-agent system communication topologies from scratch. The model achieves state-of-the-art performance across six benchmarks, including MMLU and HumanEval, while simultaneously reducing token consumption by approximately 50% compared to previous learning-based methods.
The research introduces ReasonEmbed, a text embedding model tailored for reasoning-intensive document retrieval that achieves state-of-the-art performance on relevant benchmarks. ReasonEmbed-Qwen3-8B reached an nDCG@10 of 38.1 on the BRIGHT benchmark, an improvement of nearly 10 points over leading baselines, while also demonstrating strong out-of-domain generalization on the R2MED benchmark.
This survey provides a comprehensive, industry-informed analysis of map evolution in autonomous driving, categorizing it into High-Definition (HD), Lightweight (Lite), and Implicit maps. It identifies key challenges and solutions across these stages, asserting that maps, in various forms, remain indispensable for autonomous systems.
Researchers at the Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence (BAAI) developed Video-XL-2, a multimodal large language model that uses task-aware Key-Value sparsification to efficiently understand very long videos. The model processes over 10,000 frames on a single 80GB A100 GPU, achieving state-of-the-art performance on various benchmarks while significantly reducing computational and memory costs.
Recommender systems have become an essential component of many online platforms, providing personalized recommendations to users. A crucial aspect is embedding techniques that convert the high-dimensional discrete features, such as user and item IDs, into low-dimensional continuous vectors, which can enhance the recommendation performance. Embedding techniques have revolutionized the capture of complex entity relationships, generating significant research interest. This survey presents a comprehensive analysis of recent advances in recommender system embedding techniques. We examine centralized embedding approaches across matrix, sequential, and graph structures. In matrix-based scenarios, collaborative filtering generates embeddings that effectively model user-item preferences, particularly in sparse data environments. For sequential data, we explore various approaches including recurrent neural networks and self-supervised methods such as contrastive and generative learning. In graph-structured contexts, we analyze techniques like node2vec that leverage network relationships, along with applicable self-supervised methods. Our survey addresses critical scalability challenges in embedding methods and explores innovative directions in recommender systems. We introduce emerging approaches, including AutoML, hashing techniques, and quantization methods, to enhance performance while reducing computational complexity. Additionally, we examine the promising role of Large Language Models (LLMs) in embedding enhancement. Through detailed discussion of various architectures and methodologies, this survey aims to provide a thorough overview of state-of-the-art embedding techniques in recommender systems, while highlighting key challenges and future research directions.
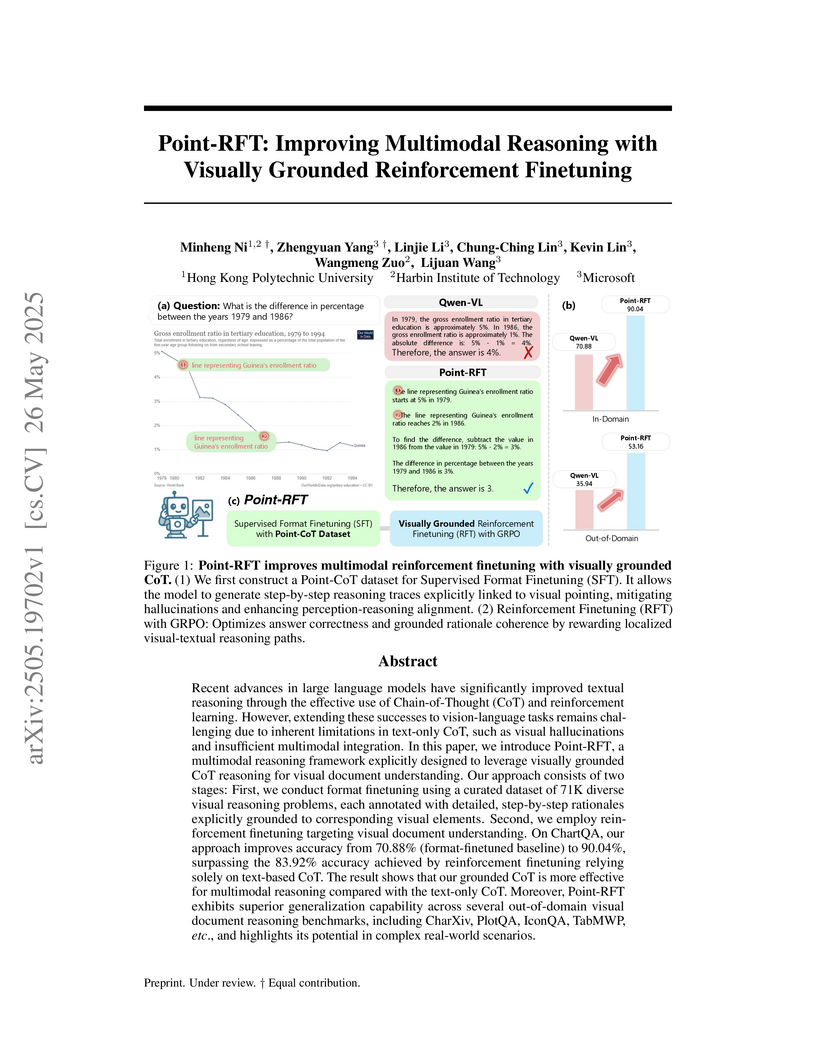
Point-RFT is a framework for multimodal reasoning that explicitly grounds Chain-of-Thought (CoT) steps to specific visual coordinates, enhancing reasoning accuracy and interpretability. This approach achieves 90.04% accuracy on the ChartQA dataset, outperforming previous methods and generalizing well to out-of-domain visual reasoning tasks.
Think2Sing introduces an LLM-assisted diffusion-based framework to generate expressive 3D head animations specifically for singing performances. It infers structured "motion subtitles" from lyrics and acoustics, then uses these subtitles to guide a diffusion model, achieving superior realism, temporal coherence, and emotional expressiveness compared to prior audio-driven methods.
Reinforcement learning has powered many of the recent breakthroughs in large language models, especially for tasks where rewards can be computed automatically, such as code generation. However, these methods deteriorate in open-ended domains like medical consultation, where feedback is inherently ambiguous, highly context-dependent, and cannot be reduced to a reliable scalar signal. In such settings, RL must either rely on supervision-intensive reward models that often fail to generalize, or it falls into pathological behaviors such as reward hacking - an especially troubling risk for high-stakes medical dialogue. To address these limitations, we introduce ORBIT, an open-ended rubric-based incremental training framework for high-stakes medical dialogue. ORBIT integrates synthetic dialogue generation with dynamically constructed rubrics that serve as adaptive guides for incremental RL. Instead of relying on external medical knowledge bases or handcrafted rule sets, ORBIT uses rubric-driven feedback to steer the learning process. Its judge component can be instantiated with general-purpose instruction-following LLMs, removing the need for any task-specific fine-tuning. Applied to the Qwen3-4B-Instruct model, ORBIT raises the HealthBench-Hard score from 7.0 to 27.5 using only 2k training samples, achieving SOTA performance for models at this scale. With larger rubric datasets, ORBIT-trained models further compete with the strongest open-source baselines on HealthBench-Hard. Our analysis shows that rubric-guided RL consistently improves consultation quality across diverse medical scenarios. We also apply such rubric generation and training pipeline to InfoBench, where ORBIT enhances instruction-following performance, highlighting the generality of rubric-based feedback.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.