Institute of High Performance Computing (IHPC)
This comprehensive survey systematically investigates and categorizes challenges in multimodal fusion with low-quality data found in real-world scenarios, proposing a novel data-centric taxonomy of noisy, incomplete, imbalanced, and quality-varying data. It reviews current solutions for each category, aiming to guide future research toward more robust and reliable multimodal AI systems.
A hierarchical extraction framework enables Large Language Models to construct knowledge graphs directly from unstructured text, addressing schema dependency and enhancing graph connectivity. This approach leverages coreference-aware prompting to build semantically rich KGs, demonstrating superior performance over existing methods and improving factual grounding for AI systems.
This paper introduces GMeLLo, a hybrid approach integrating Large Language Models with Knowledge Graphs to achieve accurate multi-hop question answering in evolving information environments. The system consistently outperforms existing knowledge editing methods, especially when managing a large volume of dynamic knowledge updates.
A mechanistic study of refusal in large language models using sparse autoencoders identifies distinct feature sets for harm and refusal, elucidating their causal relationship and explaining how adversarial jailbreaks suppress these features. Classifiers trained on these sparse refusal features outperform dense activation-based probes in detecting out-of-distribution adversarial prompts.
Despite extensive safety-tuning, large language models (LLMs) remain vulnerable to jailbreak attacks via adversarially crafted instructions, reflecting a persistent trade-off between safety and task performance. In this work, we propose Intent-FT, a simple and lightweight fine-tuning approach that explicitly trains LLMs to infer the underlying intent of an instruction before responding. By fine-tuning on a targeted set of adversarial instructions, Intent-FT enables LLMs to generalize intent deduction to unseen attacks, thereby substantially improving their robustness. We comprehensively evaluate both parametric and non-parametric attacks across open-source and proprietary models, considering harmfulness from attacks, utility, over-refusal, and impact against white-box threats. Empirically, Intent-FT consistently mitigates all evaluated attack categories, with no single attack exceeding a 50\% success rate -- whereas existing defenses remain only partially effective. Importantly, our method preserves the model's general capabilities and reduces excessive refusals on benign instructions containing superficially harmful keywords. Furthermore, models trained with Intent-FT accurately identify hidden harmful intent in adversarial attacks, and these learned intentions can be effectively transferred to enhance vanilla model defenses. We publicly release our code at this https URL.
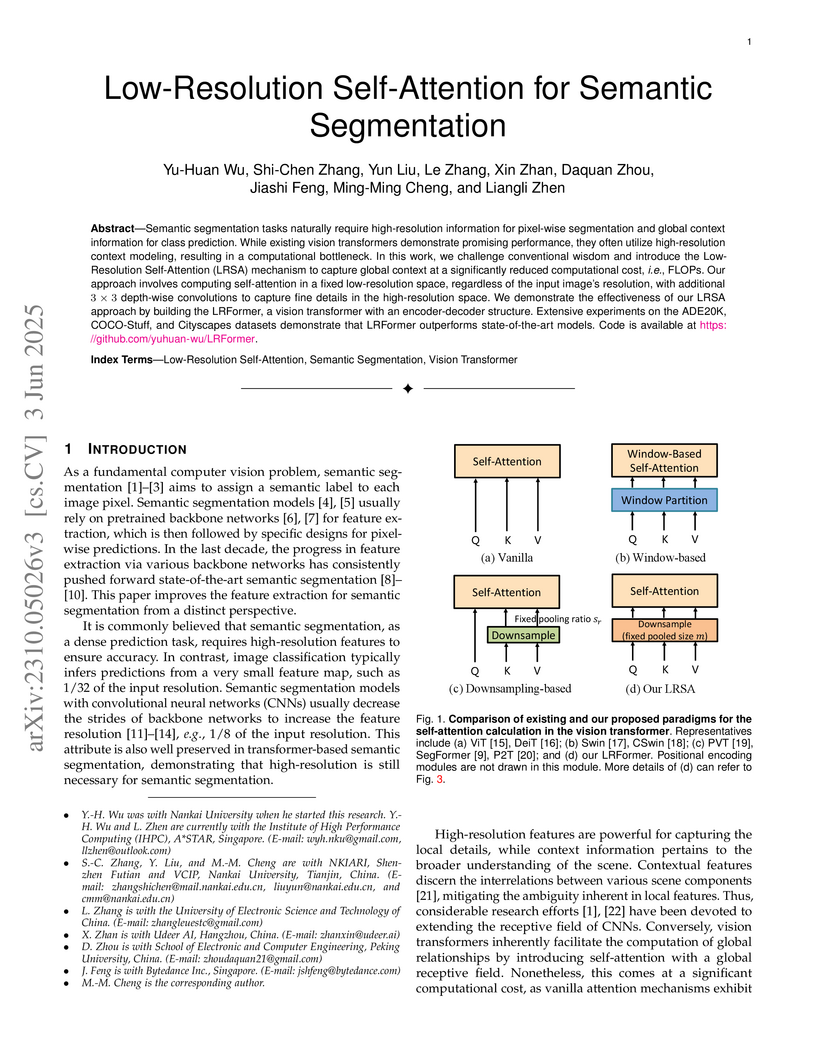
Semantic segmentation tasks naturally require high-resolution information for pixel-wise segmentation and global context information for class prediction. While existing vision transformers demonstrate promising performance, they often utilize high-resolution context modeling, resulting in a computational bottleneck. In this work, we challenge conventional wisdom and introduce the Low-Resolution Self-Attention (LRSA) mechanism to capture global context at a significantly reduced computational cost, i.e., FLOPs. Our approach involves computing self-attention in a fixed low-resolution space regardless of the input image's resolution, with additional 3x3 depth-wise convolutions to capture fine details in the high-resolution space. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our LRSA approach by building the LRFormer, a vision transformer with an encoder-decoder structure. Extensive experiments on the ADE20K, COCO-Stuff, and Cityscapes datasets demonstrate that LRFormer outperforms state-of-the-art models. Code is available at this https URL.
Researchers at A*STAR's Centre for Frontier AI Research and Institute of High Performance Computing are developing Super Tiny Language Models (STLMs) to improve the accessibility, sustainability, and deployability of language models. This work focuses on achieving high performance within 10M-100M parameters, with initial 50M parameter baselines demonstrating potential for basic linguistic understanding while highlighting embedding layers as the primary parameter bottleneck.
Vision Transformer has recently gained tremendous popularity in medical image segmentation task due to its superior capability in capturing long-range dependencies. However, transformer requires a large amount of labeled data to be effective, which hinders its applicability in annotation scarce semi-supervised learning scenario where only limited labeled data is available. State-of-the-art semi-supervised learning methods propose combinatorial CNN-Transformer learning to cross teach a transformer with a convolutional neural network, which achieves promising results. However, it remains a challenging task to effectively train the transformer with limited labeled data. In this paper, we propose an adversarial masked image modeling method to fully unleash the potential of transformer for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. The key challenge in semi-supervised learning with transformer lies in the lack of sufficient supervision signal. To this end, we propose to construct an auxiliary masked domain from original domain with masked image modeling and train the transformer to predict the entire segmentation mask with masked inputs to increase supervision signal. We leverage the original labels from labeled data and pseudo-labels from unlabeled data to learn the masked domain. To further benefit the original domain from masked domain, we provide a theoretical analysis of our method from a multi-domain learning perspective and devise a novel adversarial training loss to reduce the domain gap between the original and masked domain, which boosts semi-supervised learning performance. We also extend adversarial masked image modeling to CNN network. Extensive experiments on three public medical image segmentation datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, where our method outperforms existing methods significantly. Our code is publicly available at this https URL.
02 Dec 2025
Quantum channels function as the operational primitives of quantum theory, while superchannels describe the most general transformations acting upon them. Yet the prevailing framework for superchannels is both internally inconsistent, owing to the coexistence of distinct Choi operator constructions, and structurally incomplete, lacking the analogue of representations that ground channel theory. We resolve these issues by combining tensor-network methods with a generalized Occam's razor introduced here, establishing a unified foundation for superchannels. Our framework establishes the connections between competing Choi formulations, develops the Kraus, Stinespring, and Liouville representations for superchannels, and provides a simplified derivation of the realization theorem that identifies the minimal memory required to implement a given transformation. These structural tools also enable characterizations of superchannels that destroy quantum correlations or causal structure, opening a systematic route to non-Markovian quantum dynamics.
The performance of Federated Learning (FL) hinges on the effectiveness of
utilizing knowledge from distributed datasets. Traditional FL methods adopt an
aggregate-then-adapt framework, where clients update local models based on a
global model aggregated by the server from the previous training round. This
process can cause client drift, especially with significant cross-client data
heterogeneity, impacting model performance and convergence of the FL algorithm.
To address these challenges, we introduce FedAF, a novel aggregation-free FL
algorithm. In this framework, clients collaboratively learn condensed data by
leveraging peer knowledge, the server subsequently trains the global model
using the condensed data and soft labels received from the clients. FedAF
inherently avoids the issue of client drift, enhances the quality of condensed
data amid notable data heterogeneity, and improves the global model
performance. Extensive numerical studies on several popular benchmark datasets
show FedAF surpasses various state-of-the-art FL algorithms in handling
label-skew and feature-skew data heterogeneity, leading to superior global
model accuracy and faster convergence.
Visual Language Models such as CLIP excel in image recognition due to extensive image-text pre-training. However, applying the CLIP inference in zero-shot classification, particularly for medical image diagnosis, faces challenges due to: 1) the inadequacy of representing image classes solely with single category names; 2) the modal gap between the visual and text spaces generated by CLIP encoders. Despite attempts to enrich disease descriptions with large language models, the lack of class-specific knowledge often leads to poor performance. In addition, empirical evidence suggests that existing proxy learning methods for zero-shot image classification on natural image datasets exhibit instability when applied to medical datasets. To tackle these challenges, we introduce the Knowledge Proxy Learning (KPL) to mine knowledge from CLIP. KPL is designed to leverage CLIP's multimodal understandings for medical image classification through Text Proxy Optimization and Multimodal Proxy Learning. Specifically, KPL retrieves image-relevant knowledge descriptions from the constructed knowledge-enhanced base to enrich semantic text proxies. It then harnesses input images and these descriptions, encoded via CLIP, to stably generate multimodal proxies that boost the zero-shot classification performance. Extensive experiments conducted on both medical and natural image datasets demonstrate that KPL enables effective zero-shot image classification, outperforming all baselines. These findings highlight the great potential in this paradigm of mining knowledge from CLIP for medical image classification and broader areas.
The rapid growth of the financial sector and the rising focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations highlight the need for advanced NLP tools. However, open-source LLMs proficient in both finance and ESG domains remain scarce. To address this gap, we introduce SusGen-30K, a category-balanced dataset comprising seven financial NLP tasks and ESG report generation, and propose TCFD-Bench, a benchmark for evaluating sustainability report generation. Leveraging this dataset, we developed SusGen-GPT, a suite of models achieving state-of-the-art performance across six adapted and two off-the-shelf tasks, trailing GPT-4 by only 2% despite using 7-8B parameters compared to GPT-4's 1,700B. Based on this, we propose the SusGen system, integrated with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), to assist in sustainability report generation. This work demonstrates the efficiency of our approach, advancing research in finance and ESG.
In healthcare, federated learning (FL) is a widely adopted framework that enables privacy-preserving collaboration among medical institutions. With large foundation models (FMs) demonstrating impressive capabilities, using FMs in FL through cost-efficient adapter tuning has become a popular approach. Given the rapidly evolving healthcare environment, it is crucial for individual clients to quickly adapt to new tasks or diseases by tuning adapters while drawing upon past experiences. In this work, we introduce Federated Knowledge-Enhanced Initialization (FedKEI), a novel framework that leverages cross-client and cross-task transfer from past knowledge to generate informed initializations for learning new tasks with adapters. FedKEI begins with a global clustering process at the server to generalize knowledge across tasks, followed by the optimization of aggregation weights across clusters (inter-cluster weights) and within each cluster (intra-cluster weights) to personalize knowledge transfer for each new task. To facilitate more effective learning of the inter- and intra-cluster weights, we adopt a bi-level optimization scheme that collaboratively learns the global intra-cluster weights across clients and optimizes the local inter-cluster weights toward each client's task objective. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets of different modalities, including dermatology, chest X-rays, and retinal OCT, demonstrate FedKEI's advantage in adapting to new diseases compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are capable of generating persuasive Natural Language Explanations (NLEs) to justify their answers. However, the faithfulness of these explanations should not be readily trusted at face value. Recent studies have proposed various methods to measure the faithfulness of NLEs, typically by inserting perturbations at the explanation or feature level. We argue that these approaches are neither comprehensive nor correctly designed according to the established definition of faithfulness. Moreover, we highlight the risks of grounding faithfulness findings on out-of-distribution samples. In this work, we leverage a causal mediation technique called activation patching, to measure the faithfulness of an explanation towards supporting the explained answer. Our proposed metric, Causal Faithfulness quantifies the consistency of causal attributions between explanations and the corresponding model outputs as the indicator of faithfulness. We experimented across models varying from 2B to 27B parameters and found that models that underwent alignment tuning tend to produce more faithful and plausible explanations. We find that Causal Faithfulness is a promising improvement over existing faithfulness tests by taking into account the model's internal computations and avoiding out of distribution concerns that could otherwise undermine the validity of faithfulness assessments. We release the code in \url{this https URL}
In recent years, as various realistic face forgery techniques known as DeepFake improves by leaps and bounds,more and more DeepFake detection techniques have been proposed. These methods typically rely on detecting statistical differences between natural (i.e., real) and DeepFakegenerated images in both spatial and frequency domains. In this work, we propose to explicitly minimize the statistical differences to evade state-of-the-art DeepFake detectors. To this end, we propose a statistical consistency attack (StatAttack) against DeepFake detectors, which contains two main parts. First, we select several statistical-sensitive natural degradations (i.e., exposure, blur, and noise) and add them to the fake images in an adversarial way. Second, we find that the statistical differences between natural and DeepFake images are positively associated with the distribution shifting between the two kinds of images, and we propose to use a distribution-aware loss to guide the optimization of different degradations. As a result, the feature distributions of generated adversarial examples is close to the natural this http URL, we extend the StatAttack to a more powerful version, MStatAttack, where we extend the single-layer degradation to multi-layer degradations sequentially and use the loss to tune the combination weights jointly. Comprehensive experimental results on four spatial-based detectors and two frequency-based detectors with four datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed attack method in both white-box and black-box settings.
25 Aug 2025
A central goal in quantum error correction is to reduce the overhead of fault-tolerant quantum computing by increasing noise thresholds and reducing the number of physical qubits required to sustain a logical qubit. We introduce a potential path towards this goal based on a family of dynamically generated quantum error correcting codes that we call "hyperbolic Floquet codes.'' These codes are defined by a specific sequence of non-commuting two-body measurements arranged periodically in time that stabilize a topological code on a hyperbolic manifold with negative curvature. We focus on a family of lattices for n qubits that, according to our prescription that defines the code, provably achieve a finite encoding rate (1/8+2/n) while still requiring only two-body measurements. Similar to hyperbolic surface codes, the distance of the code at each time-step scales at most logarithmically in n. The family of lattices we choose indicates that this scaling is achievable in practice. We develop and benchmark an efficient matching-based decoder that provides evidence of a threshold near 0.1% in a phenomenological noise model and 0.25% in an entangling measurements noise model. Utilizing weight-two check operators and a qubit connectivity of 3, one of our hyperbolic Floquet codes uses 400 physical qubits to encode 52 logical qubits with a code distance of 8, i.e., it is a [[400,52,8]] code. At small error rates, comparable logical error suppression to this code requires 5x as many physical qubits (1924) when using the honeycomb Floquet code with the same noise model and decoder.
Aside from offering state-of-the-art performance in medical image generation, denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DPM) can also serve as a representation learner to capture semantic information and potentially be used as an image representation for downstream tasks, e.g., segmentation. However, these latent semantic representations rely heavily on labor-intensive pixel-level annotations as supervision, limiting the usability of DPM in medical image segmentation. To address this limitation, we propose an enhanced diffusion segmentation model, called TextDiff, that improves semantic representation through inexpensive medical text annotations, thereby explicitly establishing semantic representation and language correspondence for diffusion models. Concretely, TextDiff extracts intermediate activations of the Markov step of the reverse diffusion process in a pretrained diffusion model on large-scale natural images and learns additional expert knowledge by combining them with complementary and readily available diagnostic text information. TextDiff freezes the dual-branch multi-modal structure and mines the latent alignment of semantic features in diffusion models with diagnostic descriptions by only training the cross-attention mechanism and pixel classifier, making it possible to enhance semantic representation with inexpensive text. Extensive experiments on public QaTa-COVID19 and MoNuSeg datasets show that our TextDiff is significantly superior to the state-of-the-art multi-modal segmentation methods with only a few training samples.
In this work, we propose a method that leverages CLIP feature distillation, achieving efficient 3D segmentation through language guidance. Unlike previous methods that rely on multi-scale CLIP features and are limited by processing speed and storage requirements, our approach aims to streamline the workflow by directly and effectively distilling dense CLIP features, thereby achieving precise segmentation of 3D scenes using text. To achieve this, we introduce an adapter module and mitigate the noise issue in the dense CLIP feature distillation process through a self-cross-training strategy. Moreover, to enhance the accuracy of segmentation edges, this work presents a low-rank transient query attention mechanism. To ensure the consistency of segmentation for similar colors under different viewpoints, we convert the segmentation task into a classification task through label volume, which significantly improves the consistency of segmentation in color-similar areas. We also propose a simplified text augmentation strategy to alleviate the issue of ambiguity in the correspondence between CLIP features and text. Extensive experimental results show that our method surpasses current state-of-the-art technologies in both training speed and performance. Our code is available on: this https URL.
12 Nov 2024
Large language models (LLMs) often necessitate extensive labeled datasets and
training compute to achieve impressive performance across downstream tasks.
This paper explores a self-training paradigm, where the LLM autonomously
curates its own labels and selectively trains on unknown data samples
identified through a reference-free consistency method. Empirical evaluations
demonstrate significant improvements in reducing hallucination in generation
across multiple subjects. Furthermore, the selective training framework
mitigates catastrophic forgetting in out-of-distribution benchmarks, addressing
a critical limitation in training LLMs. Our findings suggest that such an
approach can substantially reduce the dependency on large labeled datasets,
paving the way for more scalable and cost-effective language model training.
14 Oct 2024
Large language models are increasingly being used to label or rate psychological features in text data. This approach helps address one of the limiting factors of digital trace data - their lack of an inherent target of measurement. However, this approach is also a form of psychological measurement (using observable variables to quantify a hypothetical latent construct). As such, these ratings are subject to the same psychometric considerations of reliability and validity as more standard psychological measures. Here we present a workflow for developing and evaluating large language model based measures of psychological features which incorporate these considerations. We also provide an example, attempting to measure the previously established constructs of attitude certainty, importance and moralization from text. Using a pool of prompts adapted from existing measurement instruments, we find they have good levels of internal consistency but only partially meet validity criteria.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.