Tencent
Tencent09 Oct 2025
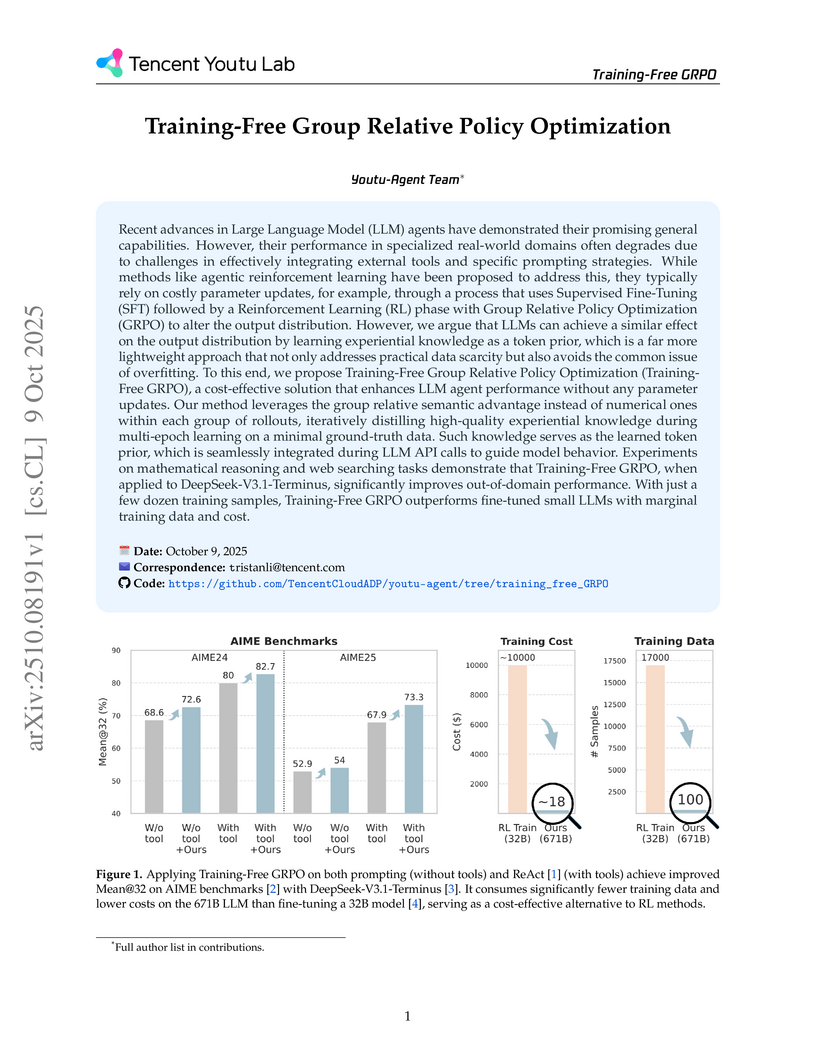
Researchers from Tencent Youtu Lab developed Training-Free Group Relative Policy Optimization, a method that enhances LLM agent performance in specialized tasks by learning and integrating experiential knowledge as a token prior without modifying model parameters. This approach achieved substantial performance gains on mathematical reasoning and web searching benchmarks with significantly reduced data and computational costs, leveraging the full capabilities of frozen large LLMs.
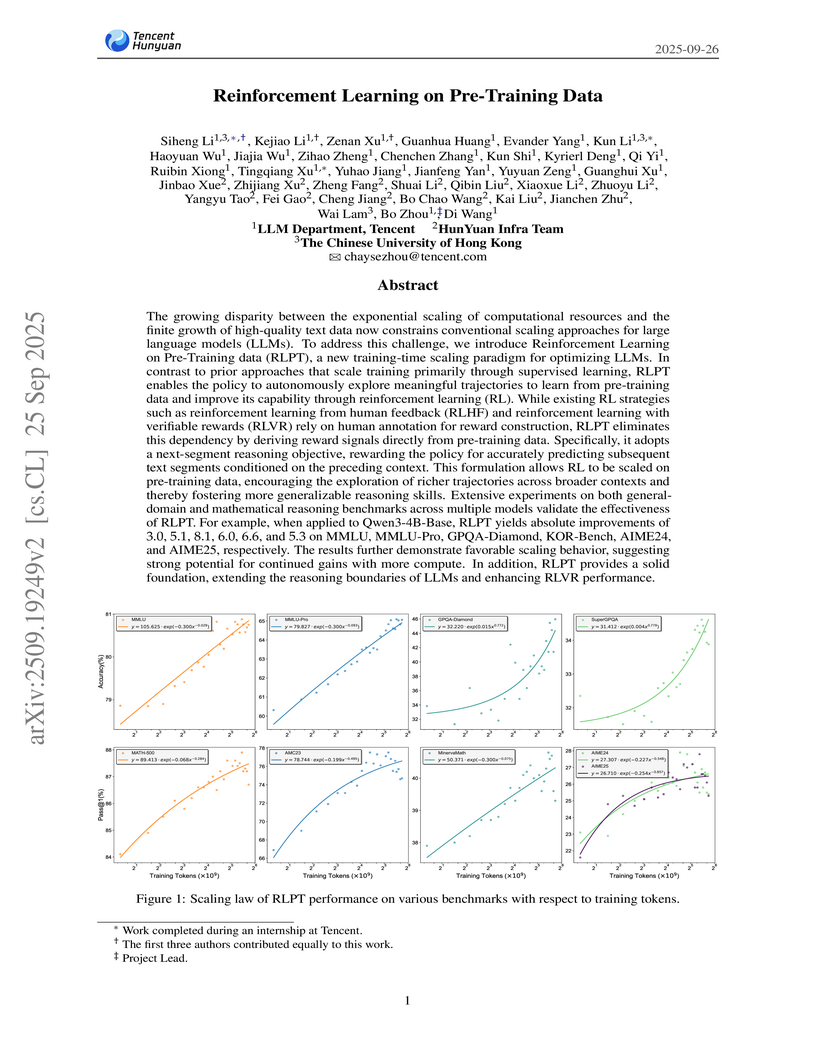
Tencent's LLM Department, HunYuan Infra Team, and CUHK developed Reinforcement Learning on Pre-Training data (RLPT), a framework applying reinforcement learning directly to unlabeled pre-training data. This approach addresses data scarcity and fosters deeper reasoning skills, showing absolute improvements of 3.0 on MMLU and 8.1 on GPQA-Diamond for Qwen3-4B-Base models.
FlashSloth, developed by researchers from Xiamen University, Tencent Youtu Lab, and Shanghai AI Laboratory, introduces a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) architecture that significantly improves efficiency through embedded visual compression. The approach reduces visual tokens by 80-89% and achieves 2-5 times faster response times, while maintaining highly competitive performance across various vision-language benchmarks.
Single-stream Policy Optimization (SPO) introduces a group-free approach for enhancing Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning, overcoming inefficiencies in existing group-based reinforcement learning methods. The Tencent-authored work demonstrates superior performance, achieving a +3.4 percentage point improvement in `maj@32` score and a 4.35x speedup in agentic training throughput compared to GRPO, alongside more stable learning signals.
06 Dec 2025
 Monash UniversityCSIRO
Monash UniversityCSIRO Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University University of Manchester
University of Manchester Beihang University
Beihang University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology
ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology Beijing Jiaotong University
Beijing Jiaotong University Huawei
Huawei Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield
Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOM
TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOMA comprehensive synthesis of Large Language Models for automated software development covers the entire model lifecycle, from data curation to autonomous agents, and offers practical guidance derived from empirical experiments on pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, alongside a detailed analysis of challenges and future directions.
01 Feb 2024
Recommender systems with cascading architecture play an increasingly significant role in online recommendation platforms, where the approach to dealing with negative feedback is a vital issue. For instance, in short video platforms, users tend to quickly slip away from candidates that they feel aversive, and recommender systems are expected to receive these explicit negative feedbacks and make adjustments to avoid these recommendations. Considering recency effect in memories, we propose a forgetting model based on Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve to cope with negative feedback. In addition, we introduce a Pareto optimization solver to guarantee a better trade-off between recency and model performance. In conclusion, we propose Pareto-based Multi-Objective Recommender System with forgetting curve (PMORS), which can be applied to any multi-objective recommendation and show sufficiently superiority when facing explicit negative feedback. We have conducted evaluations of PMORS and achieved favorable outcomes in short-video scenarios on both public dataset and industrial dataset. After being deployed on an online short video platform named WeChat Channels in May, 2023, PMORS has not only demonstrated promising results for both consistency and recency but also achieved an improvement of up to +1.45% GMV.
This survey provides a comprehensive synthesis of the rapidly evolving field of Multimodal Large Language Models, detailing their common architectures, multi-stage training paradigms, and diverse evaluation methodologies. It highlights the importance of data quality for instruction tuning and addresses key challenges, including the pervasive issue of multimodal hallucination.
We present HunyuanImage 3.0, a native multimodal model that unifies multimodal understanding and generation within an autoregressive framework, with its image generation module publicly available. The achievement of HunyuanImage 3.0 relies on several key components, including meticulous data curation, advanced architecture design, a native Chain-of-Thoughts schema, progressive model pre-training, aggressive model post-training, and an efficient infrastructure that enables large-scale training and inference. With these advancements, we successfully trained a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model comprising over 80 billion parameters in total, with 13 billion parameters activated per token during inference, making it the largest and most powerful open-source image generative model to date. We conducted extensive experiments and the results of automatic and human evaluation of text-image alignment and visual quality demonstrate that HunyuanImage 3.0 rivals previous state-of-the-art models. By releasing the code and weights of HunyuanImage 3.0, we aim to enable the community to explore new ideas with a state-of-the-art foundation model, fostering a dynamic and vibrant multimodal ecosystem. All open source assets are publicly available at this https URL
Tencent's Hunyuan Foundation Model Team developed HunyuanVideo, an open-source framework for large video generative models that achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source solutions. The 13-billion-parameter model excels in human evaluations for motion dynamics and visual quality, supported by a systematic framework for data, architecture, and efficient training.
This research from Tencent and Tsinghua University provides the first formal proof that integrating external tools strictly expands a Large Language Model's problem-solving capabilities, overcoming the limitations of pure-text reasoning within practical token budgets. It also introduces an algorithm, ASPO, that stably guides LLMs to proactively leverage tools, demonstrating emergent cognitive patterns for complex tasks.
25 Aug 2025
Proximal Supervised Fine-Tuning (PSFT) introduces a PPO-inspired clipped objective to stabilize large language model fine-tuning, preventing entropy collapse and catastrophic forgetting. This approach yields a more robust and generalized base model, serving as a superior "cold start" for subsequent reinforcement learning from human feedback or direct preference optimization, which ultimately leads to enhanced performance across various tasks.
Efficient processing of long contexts has been a persistent pursuit in Natural Language Processing. With the growing number of long documents, dialogues, and other textual data, it is important to develop Long Context Language Models (LCLMs) that can process and analyze extensive inputs in an effective and efficient way. In this paper, we present a comprehensive survey on recent advances in long-context modeling for large language models. Our survey is structured around three key aspects: how to obtain effective and efficient LCLMs, how to train and deploy LCLMs efficiently, and how to evaluate and analyze LCLMs comprehensively. For the first aspect, we discuss data strategies, architectural designs, and workflow approaches oriented with long context processing. For the second aspect, we provide a detailed examination of the infrastructure required for LCLM training and inference. For the third aspect, we present evaluation paradigms for long-context comprehension and long-form generation, as well as behavioral analysis and mechanism interpretability of LCLMs. Beyond these three key aspects, we thoroughly explore the diverse application scenarios where existing LCLMs have been deployed and outline promising future development directions. This survey provides an up-to-date review of the literature on long-context LLMs, which we wish to serve as a valuable resource for both researchers and engineers. An associated GitHub repository collecting the latest papers and repos is available at: \href{this https URL}{\color[RGB]{175,36,67}{LCLM-Horizon}}.
This paper introduces "Diffusion of Thought (DoT)", a method for integrating Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning into diffusion language models. The approach demonstrates high accuracy and significant efficiency gains on reasoning tasks, outperforming autoregressive counterparts while offering a flexible computation-accuracy trade-off.
PREF-GRPO introduces a novel training method for text-to-image (T2I) models that stabilizes reinforcement learning against reward hacking by utilizing pairwise preference rewards. The accompanying UNIGENBENCH offers a fine-grained, MLLM-powered framework for comprehensive and diagnostic evaluation of T2I models.
Tencent's Hunyuan3D 2.0 system introduces an open-source, large-scale foundational model for generating high-resolution textured 3D assets from images. The system leverages a two-stage diffusion pipeline, including a novel shape encoder and a multi-view consistent texture synthesis module, demonstrating superior performance in geometry detail, texture quality, and condition alignment compared to previous methods.
 University of WashingtonWuhan University
University of WashingtonWuhan University University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign UCLA
UCLA Chinese Academy of SciencesShanghai AI Laboratory
Chinese Academy of SciencesShanghai AI Laboratory New York University
New York University National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore Fudan University
Fudan University Georgia Institute of Technology
Georgia Institute of Technology University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Zhejiang UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of China
Zhejiang UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of China Renmin University of China
Renmin University of China The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Peking UniversityGriffith University
Peking UniversityGriffith University Nanyang Technological University
Nanyang Technological University Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University The University of Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong The Pennsylvania State UniversityA*STARShanghai UniversityUniversity of Illinois at ChicagoSingapore Management University
The Pennsylvania State UniversityA*STARShanghai UniversityUniversity of Illinois at ChicagoSingapore Management University Southern University of Science and Technology
Southern University of Science and Technology HKUST
HKUST TencentTeleAISquirrel Ai LearningHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)The University of North Carolina at Chapel HillBen Gurion UniversityCenter for Applied Scientific Computing
TencentTeleAISquirrel Ai LearningHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)The University of North Carolina at Chapel HillBen Gurion UniversityCenter for Applied Scientific ComputingThis survey paper defines and applies a 'full-stack' safety concept for Large Language Models (LLMs), systematically analyzing safety concerns across their entire lifecycle from data to deployment and commercialization. The collaboration synthesizes findings from over 900 papers, providing a unified taxonomy of attacks and defenses while identifying key insights and future research directions for LLM and LLM-agent safety.
FlashWorld enables high-quality 3D scene generation from a single image or text prompt within seconds, achieving a 10-100x speedup over previous methods while delivering superior visual fidelity and consistent 3D structures. The model recovers intricate details and produces realistic backgrounds even for complex scenes, demonstrating strong performance across image-to-3D and text-to-3D tasks.
The 'Yan' framework provides a unified approach for interactive video generation, achieving real-time 1080P/60FPS AAA-level simulations with accurate physics. It supports multi-modal content generation guided by prompts and enables dynamic, multi-granularity editing of both structure and style during interaction.
Tencent Hunyuan3D developed Hunyuan3D Studio, an end-to-end AI pipeline that automates the generation of game-ready 3D assets from text or image prompts. This system integrates multiple AI modules to produce high-fidelity models with optimized geometry, PBR textures, and animatable rigs, drastically reducing production time and complexity.
The LaSeR framework enables Large Language Models to efficiently perform self-verification and enhance their reasoning capabilities by deriving a 'last-token self-rewarding score' directly from the final predicted token's probability distribution. This approach integrates self-assessment at nearly zero additional inference cost, improving reasoning performance while achieving high F1 scores for distinguishing correct from incorrect solutions.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.