OPPO
The PainterNet framework enables adaptive image inpainting that achieves high semantic consistency for local edits and accommodates diverse mask inputs. This is accomplished through a dual-branch architecture, local textual prompts, and an Actual-Token Attention Loss, resulting in superior performance on new benchmark datasets.
06 Dec 2025
 Monash UniversityCSIRO
Monash UniversityCSIRO Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University University of Manchester
University of Manchester Beihang University
Beihang University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology
ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology Beijing Jiaotong University
Beijing Jiaotong University Huawei
Huawei Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield
Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOM
TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOMA comprehensive synthesis of Large Language Models for automated software development covers the entire model lifecycle, from data curation to autonomous agents, and offers practical guidance derived from empirical experiments on pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, alongside a detailed analysis of challenges and future directions.
We introduce OpenIllumination, a real-world dataset containing over 108K images of 64 objects with diverse materials, captured under 72 camera views and a large number of different illuminations. For each image in the dataset, we provide accurate camera parameters, illumination ground truth, and foreground segmentation masks. Our dataset enables the quantitative evaluation of most inverse rendering and material decomposition methods for real objects. We examine several state-of-the-art inverse rendering methods on our dataset and compare their performances. The dataset and code can be found on the project page: this https URL.
06 Aug 2025
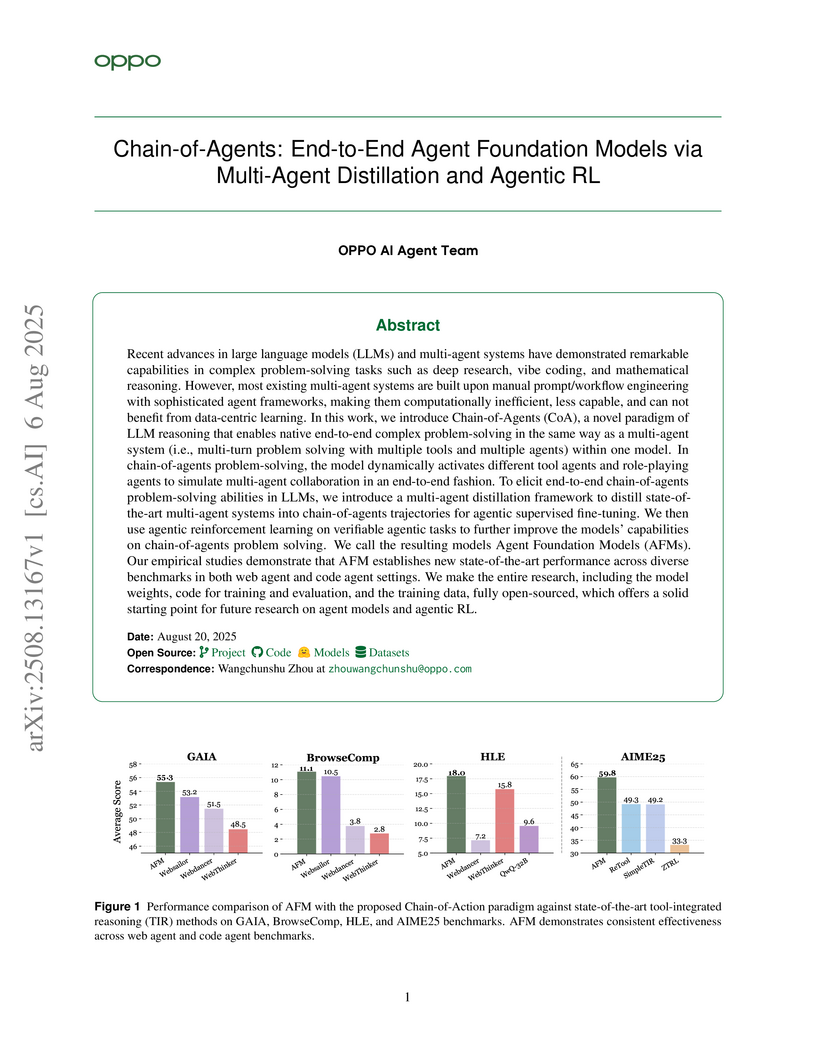
The OPPO AI Agent Team developed Chain-of-Agents (CoA), a paradigm enabling a single large language model (LLM) to perform end-to-end complex problem-solving by simulating multi-agent collaboration. This approach, trained via multi-agent distillation and agentic reinforcement learning, achieves state-of-the-art performance across various agentic tasks while reducing inference cost by 84.6% compared to traditional multi-agent systems.
27 Oct 2025
AGENT KB is a universal memory infrastructure that facilitates the sharing of problem-solving experiences across diverse AI agent frameworks. It demonstrated consistent performance improvements, including an 18.7 percentage point gain on the GAIA benchmark and up to a 21.0 percentage point increase on SWE-bench Lite.
01 Dec 2025
The OPPO AI Agent Team developed FINDER, a human-curated benchmark, and DEFT, the first failure taxonomy, to systematically evaluate and diagnose Deep Research Agents (DRAs). Evaluations using these tools revealed that current DRAs exhibit significant struggles with evidence integration, verification, and reasoning resilience, often engaging in strategic content fabrication rather than solely initial task comprehension.
03 Nov 2025
A framework called Multi-Agent Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (MARFT) is introduced to optimize Large Language Model-based Multi-Agent Systems (LaMAS) using reinforcement learning techniques. It leverages a Flexible Markov Game formulation and achieves performance improvements on agentic tasks like mathematical problem-solving and coding, with MARFT-A increasing episodic return by approximately 18.45% on the MATH dataset and 14.75% in coding benchmarks.
M+ extends the MemoryLLM architecture, enabling Large Language Models to retain and recall information over sequence lengths exceeding 160,000 tokens, a substantial improvement over MemoryLLM's previous 20,000 token limit. This is achieved through a scalable long-term memory mechanism and a co-trained retriever that efficiently retrieves relevant hidden states, while maintaining competitive GPU memory usage.
23 Jun 2025
The OPPO AI Agent Team systematically investigated design choices for language agents, developing the open-source OAgents framework that incorporates effective components and achieves a 73.93% score on the GAIA benchmark. This work also revealed significant reproducibility issues in existing agent research and established a more robust evaluation protocol.
24 Jul 2025
A systematic empirical analysis by the OPPO AI Agent Team quantifies the efficiency-effectiveness trade-off in LLM-driven agent systems, leading to the "Efficient Agents" framework. This framework reduces operational costs by 28.4% compared to previous methods, achieving 96.7% of leading agent performance on the GAIA benchmark.
29 Sep 2025
A collaboration from OPPO, Zhejiang University, M-A-P, and 2077.AI introduces the first benchmark and evaluation framework for personalized deep research agents (DRAs), enabling assessment of how agents integrate user profiles into complex research tasks. The work demonstrates that open-source DRAs excel in personalization but lack factual reliability, while commercial DRAs prioritize quality and reliability over advanced personalization.
21 Oct 2025
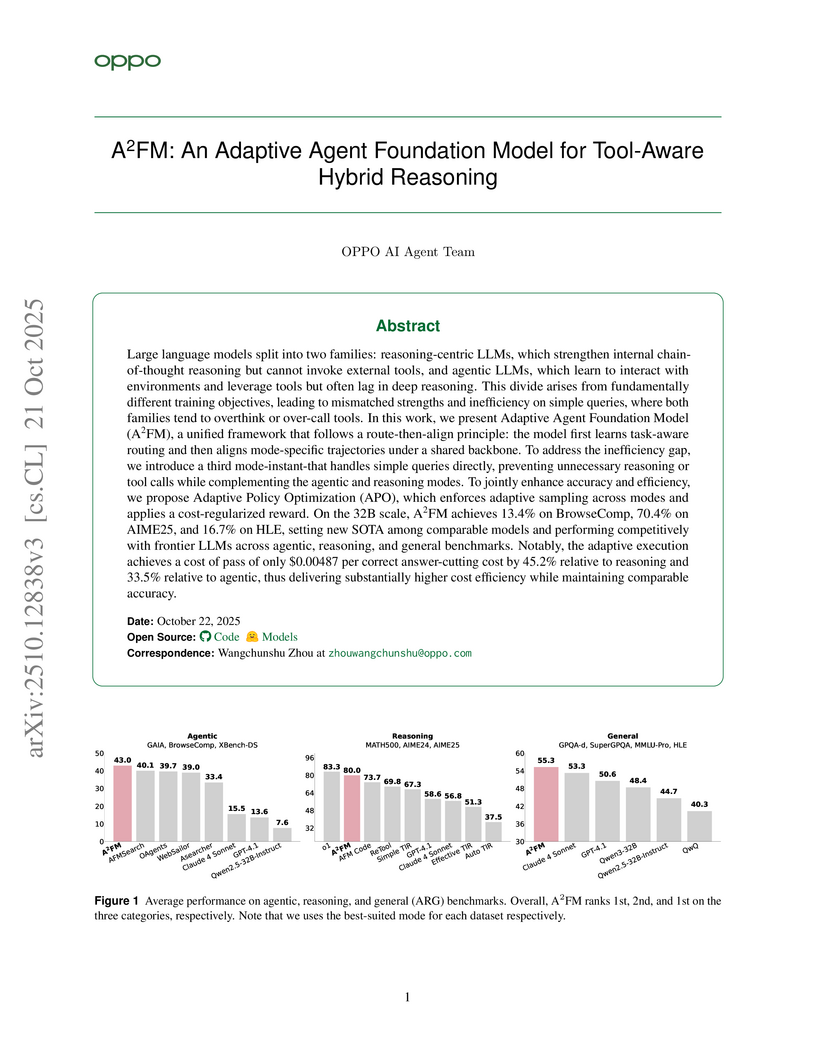
Large language models split into two families: reasoning-centric LLMs, which strengthen internal chain-of-thought reasoning but cannot invoke external tools, and agentic LLMs, which learn to interact with environments and leverage tools but often lag in deep reasoning. This divide arises from fundamentally different training objectives, leading to mismatched strengths and inefficiency on simple queries, where both families tend to overthink or over-call tools. In this work, we present Adaptive Agent Foundation Model (A2FM), a unified framework that follows a route-then-align principle: the model first learns task-aware routing and then aligns mode-specific trajectories under a shared backbone. To address the inefficiency gap, we introduce a third mode-instant-that handles simple queries directly, preventing unnecessary reasoning or tool calls while complementing the agentic and reasoning modes. To jointly enhance accuracy and efficiency, we propose Adaptive Policy Optimization (APO), which enforces adaptive sampling across modes and applies a cost-regularized reward. On the 32B scale, A2FM achieves 13.4% on BrowseComp, 70.4% on AIME25, and 16.7% on HLE, setting new SOTA among comparable models and performing competitively with frontier LLMs across agentic, reasoning, and general benchmarks. Notably, the adaptive execution achieves a cost of pass of only $0.00487 per correct answer-cutting cost by 45.2% relative to reasoning and 33.5% relative to agentic, thus delivering substantially higher cost efficiency while maintaining comparable accuracy.
OSEDiff, developed by researchers at The Hong Kong Polytechnic University and OPPO Research Institute, introduces a one-step effective diffusion network for real-world image super-resolution. This method achieves high perceptual quality by directly starting the diffusion process from the low-quality image's latent representation, resulting in a significant inference speedup, being approximately 105 times faster than StableSR and 39 times faster than SeeSR, while also reducing output uncertainty.
21 Jul 2025
MobileUse introduces a GUI agent featuring hierarchical reflection and proactive exploration to enhance autonomous mobile operation. It achieved a state-of-the-art 62.9% success rate on AndroidWorld, a 3.4% improvement over the previous best, and a 44.2% success rate on AndroidLab.
VisualQuality-R1 is a no-reference image quality assessment model that uses a reasoning-induced approach trained via Reinforcement Learning to Rank, outperforming existing models in generalization and multi-dataset settings while generating detailed, human-aligned quality explanations.
06 Aug 2025
This survey paper consolidates the rapidly expanding field of OS Agents, which utilize (Multimodal) Large Language Models to automate tasks across general computing devices, by providing a comprehensive taxonomy, reviewing construction methodologies, and outlining evaluation standards. The work from Zhejiang University and collaborators aims to structure the domain and guide future research towards robust, safe, and personalized AI assistants.
D3, a training-free method from Xi'an Jiaotong University and OPPO, detects AI-generated videos by analyzing second-order temporal features derived from Newtonian mechanics, which current generative models struggle to simulate accurately. The approach achieved a mean Average Precision of 98.46% on the GenVideo dataset, outperforming the previous state-of-the-art method by 10.39% mean AP, while also demonstrating superior computational efficiency and robustness to post-processing.
The paper introduces VideoVerse, a new benchmark designed to evaluate Text-to-Video (T2V) models based on their “world model” capabilities, assessing understanding of complex temporal causality and implicit world knowledge. It utilizes 300 curated prompts and a VLM-based evaluation protocol, revealing that current T2V generators, particularly open-source ones, are significantly limited in reasoning about real-world dynamics.
TaskCraft, developed by the OPPO AI Agent Team, introduces an automated method for generating difficulty-scalable, multi-tool, and verifiable agentic tasks complete with ground-truth execution trajectories. This approach addresses the data scarcity for training AI agents that interact with external tools, and fine-tuning on its synthetic data improves model performance on multi-hop question answering benchmarks.
Researchers from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University and OPPO Research Institute developed DP²O-SR, a direct perceptual preference optimization framework that refines large-scale generative models for real-world image super-resolution by leveraging their inherent stochasticity. This approach achieves state-of-the-art perceptual quality on the RealSR benchmark, improves the worst-case output quality, and is strongly preferred by users over existing methods, without requiring human annotation.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.