Alibaba
06 Dec 2025
 Monash UniversityCSIRO
Monash UniversityCSIRO Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University University of Manchester
University of Manchester Beihang University
Beihang University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology
ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology Beijing Jiaotong University
Beijing Jiaotong University Huawei
Huawei Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield
Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOM
TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOMA comprehensive synthesis of Large Language Models for automated software development covers the entire model lifecycle, from data curation to autonomous agents, and offers practical guidance derived from empirical experiments on pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, alongside a detailed analysis of challenges and future directions.
Alibaba's HumanAIGC Team developed WAN-ANIMATE, a unified framework for character animation and replacement that delivers high-fidelity results. The open-sourced model outperforms existing open-source alternatives and is preferred over commercial products like Runway's Act-two and Bytedance's DreamActor-M1 in human evaluations across metrics like identity consistency and expression accuracy.
OpenHands is an open-source platform facilitating the development, evaluation, and deployment of generalist AI agents that interact with digital environments by writing code, using command lines, and browsing the web. Its CodeAct agent achieved competitive performance across 15 diverse benchmarks, including software engineering, web browsing, and general assistance tasks, without task-specific modifications.
Efficient processing of long contexts has been a persistent pursuit in Natural Language Processing. With the growing number of long documents, dialogues, and other textual data, it is important to develop Long Context Language Models (LCLMs) that can process and analyze extensive inputs in an effective and efficient way. In this paper, we present a comprehensive survey on recent advances in long-context modeling for large language models. Our survey is structured around three key aspects: how to obtain effective and efficient LCLMs, how to train and deploy LCLMs efficiently, and how to evaluate and analyze LCLMs comprehensively. For the first aspect, we discuss data strategies, architectural designs, and workflow approaches oriented with long context processing. For the second aspect, we provide a detailed examination of the infrastructure required for LCLM training and inference. For the third aspect, we present evaluation paradigms for long-context comprehension and long-form generation, as well as behavioral analysis and mechanism interpretability of LCLMs. Beyond these three key aspects, we thoroughly explore the diverse application scenarios where existing LCLMs have been deployed and outline promising future development directions. This survey provides an up-to-date review of the literature on long-context LLMs, which we wish to serve as a valuable resource for both researchers and engineers. An associated GitHub repository collecting the latest papers and repos is available at: \href{this https URL}{\color[RGB]{175,36,67}{LCLM-Horizon}}.
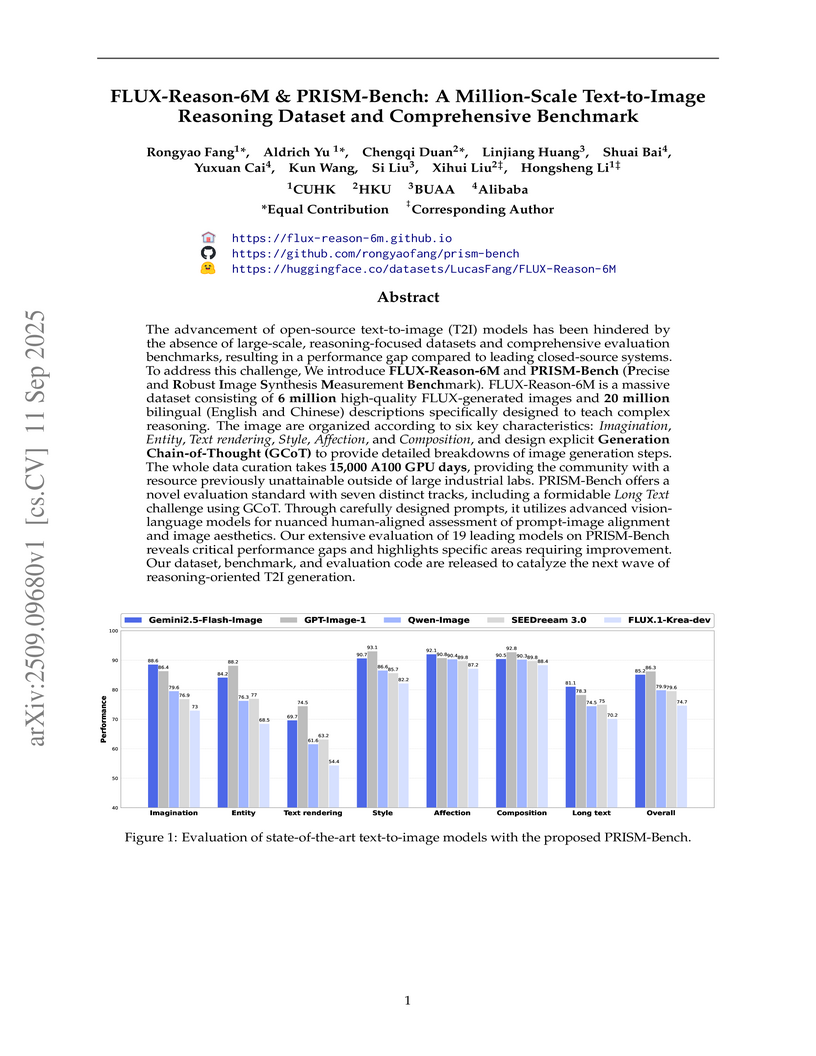
Researchers from CUHK, HKU, Beihang University, and Alibaba introduced FLUX-Reason-6M, a 6-million-image, reasoning-focused text-to-image dataset, and PRISM-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating T2I models. This work provides an open-source resource with 20 million bilingual captions, including Generation Chain-of-Thought prompts, aiming to advance T2I reasoning capabilities and offering a robust evaluation of 19 leading models, highlighting persistent challenges in text rendering and long instruction following.
06 Jun 2025
Alibaba Group's ROLL is a comprehensive framework designed for large-scale Reinforcement Learning (RL) training of Large Language Models (LLMs), capable of supporting models over 200 billion parameters. It demonstrated robust scalability by training an MoE model on thousands of GPUs for two weeks uninterrupted and achieved significant performance improvements on RLVR and agentic RL tasks.
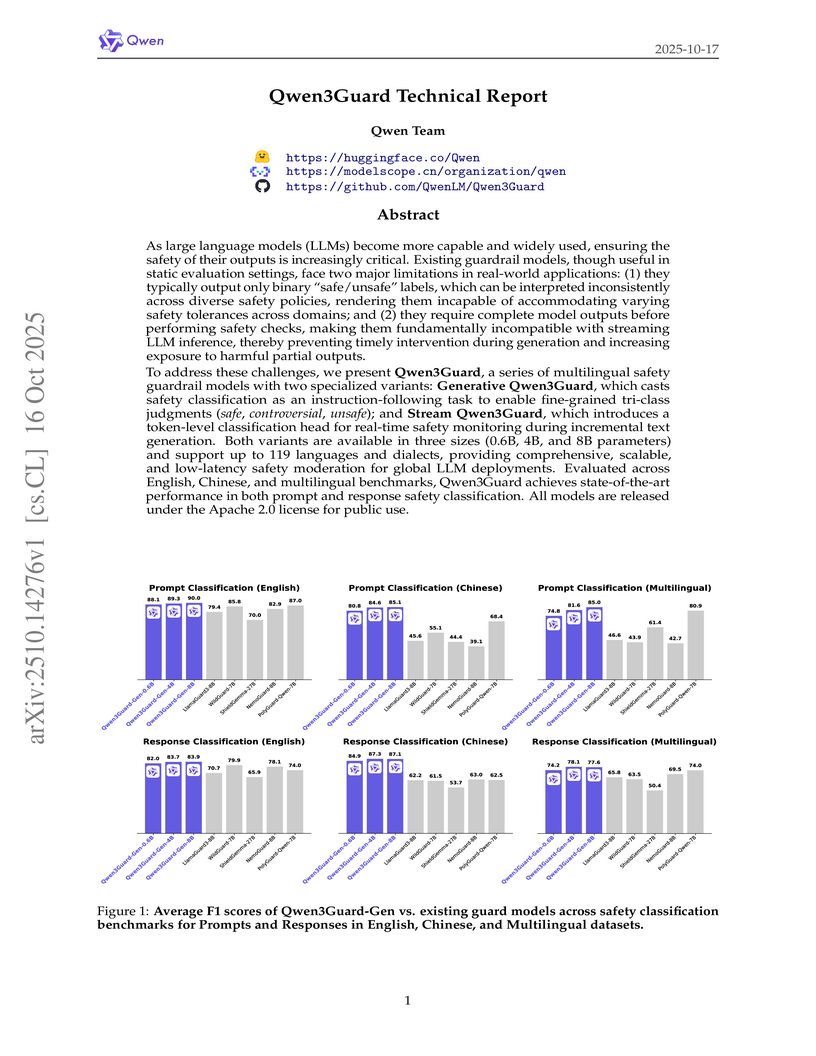
The Qwen Team introduced Qwen3Guard, a suite of multilingual safety guardrail models available in Generative and Stream variants, to enable more flexible, real-time moderation of large language models. The Generative model achieved top performance on 8 out of 14 public English benchmarks, while the Stream variant precisely detected unsafe content at the token level, with an approximate 86% hit rate for the first unsafe token.
WAN-S2V, from Alibaba's HumanAIGC Team, generates audio-driven human videos that achieve cinematic quality, producing expressive character movements, dynamic camera work, and long-term consistency. The model significantly outperforms existing methods across qualitative and quantitative benchmarks, demonstrating superior visual quality, identity preservation, and motion richness in complex scenarios.
Researchers at Alibaba developed a Multi-Attribution Learning (MAL) framework that integrates diverse attribution signals to improve Conversion Rate (CVR) prediction. Deployed on Taobao, the system achieved a +2.7% increase in Gross Merchandise Volume (GMV), +1.2% in orders, and +2.6% in Return on Investment (ROI) in online A/B tests.
HealthGPT presents a Medical Large Vision-Language Model that unifies both visual comprehension and generation capabilities by adapting pre-trained large language models with heterogeneous knowledge. The model achieves state-of-the-art results across various medical visual question answering, report generation, super-resolution, and modality conversion tasks.
27 Oct 2025
Query-product relevance prediction is a core task in e-commerce search. BERT-based models excel at semantic matching but lack complex reasoning capabilities. While Large Language Models (LLMs) are explored, most still use discriminative fine-tuning or distill to smaller models for deployment. We propose a framework to directly deploy LLMs for this task, addressing key challenges: Chain-of-Thought (CoT) error accumulation, discriminative hallucination, and deployment feasibility. Our framework, TaoSR1, involves three stages: (1) Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with CoT to instill reasoning; (2) Offline sampling with a pass@N strategy and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to improve generation quality; and (3) Difficulty-based dynamic sampling with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to mitigate discriminative hallucination. Additionally, post-CoT processing and a cumulative probability-based partitioning method enable efficient online deployment. TaoSR1 significantly outperforms baselines on offline datasets and achieves substantial gains in online side-by-side human evaluations, introducing a novel paradigm for applying CoT reasoning to relevance classification.
RecIS is a PyTorch-native training framework developed by Alibaba that unifies sparse and dense computations for industrial-grade recommendation models. It achieves up to 2x faster training throughput compared to existing solutions and enables the processing of user behavior sequences with up to 1 million interactions.
A new alignment pipeline, MM-RLHF, enhances Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by improving visual perception, reasoning, dialogue, and trustworthiness. This approach leads to an average 11% gain in conversational abilities and a 57% reduction in unsafe behaviors across various models.
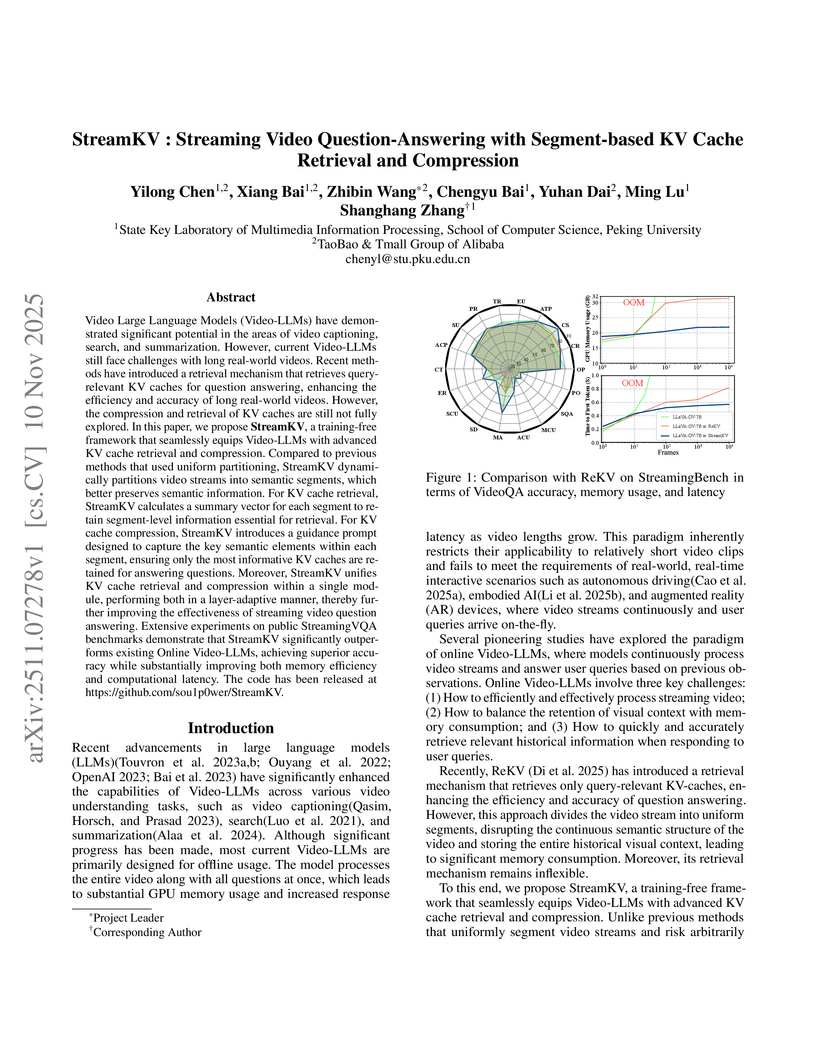
Researchers from Peking University and Alibaba developed StreamKV, a training-free framework that enables Video Large Language Models (Video-LLMs) to perform efficient and accurate question-answering in real-time streaming video environments. The framework achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on the StreamingBench benchmark, demonstrating robust performance even with up to 90% KV cache compression while substantially reducing memory consumption and latency.
The "Global Compression Commander" (GlobalCom²) framework accelerates inference for High-Resolution Large Vision-Language Models (HR-LVLMs) and VideoLLMs by intelligently compressing visual tokens using a global-to-local guidance strategy. It achieves a 90.9% reduction in FLOPs, a 40.0% decrease in peak GPU memory, and a 1.8x inference throughput boost at 10% token retention, while maintaining over 90% of original model performance.
Video generation has emerged as a promising tool for world simulation, leveraging visual data to replicate real-world environments. Within this context, egocentric video generation, which centers on the human perspective, holds significant potential for enhancing applications in virtual reality, augmented reality, and gaming. However, the generation of egocentric videos presents substantial challenges due to the dynamic nature of egocentric viewpoints, the intricate diversity of actions, and the complex variety of scenes encountered. Existing datasets are inadequate for addressing these challenges effectively. To bridge this gap, we present EgoVid-5M, the first high-quality dataset specifically curated for egocentric video generation. EgoVid-5M encompasses 5 million egocentric video clips and is enriched with detailed action annotations, including fine-grained kinematic control and high-level textual descriptions. To ensure the integrity and usability of the dataset, we implement a sophisticated data cleaning pipeline designed to maintain frame consistency, action coherence, and motion smoothness under egocentric conditions. Furthermore, we introduce EgoDreamer, which is capable of generating egocentric videos driven simultaneously by action descriptions and kinematic control signals. The EgoVid-5M dataset, associated action annotations, and all data cleansing metadata will be released for the advancement of research in egocentric video generation.
Researchers from Alibaba, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, and other institutions developed LLaVA-MoD, a framework that leverages Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture and progressive knowledge distillation to create efficient small-scale Multimodal Large Language Models (s-MLLMs). The resulting 2-billion-parameter model achieves state-of-the-art performance among similarly sized models and significantly reduces hallucination, even surpassing larger teacher models and RLHF-based systems, while using only 0.3% of the training data compared to some large MLLMs.
09 May 2020
Machine-learning (ML) hardware and software system demand is burgeoning. Driven by ML applications, the number of different ML inference systems has exploded. Over 100 organizations are building ML inference chips, and the systems that incorporate existing models span at least three orders of magnitude in power consumption and five orders of magnitude in performance; they range from embedded devices to data-center solutions. Fueling the hardware are a dozen or more software frameworks and libraries. The myriad combinations of ML hardware and ML software make assessing ML-system performance in an architecture-neutral, representative, and reproducible manner challenging. There is a clear need for industry-wide standard ML benchmarking and evaluation criteria. MLPerf Inference answers that call. In this paper, we present our benchmarking method for evaluating ML inference systems. Driven by more than 30 organizations as well as more than 200 ML engineers and practitioners, MLPerf prescribes a set of rules and best practices to ensure comparability across systems with wildly differing architectures. The first call for submissions garnered more than 600 reproducible inference-performance measurements from 14 organizations, representing over 30 systems that showcase a wide range of capabilities. The submissions attest to the benchmark's flexibility and adaptability.
This survey provides a comprehensive and up-to-date review of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) applied to time series analysis tasks, including forecasting, classification, anomaly detection, and imputation. The paper introduces a unified taxonomy for categorizing GNN-based approaches and highlights key architectural trends, dependency modeling strategies, and critical future research directions in the field.
26 Nov 2025
Researchers from the National University of Singapore and collaborators introduced a framework for Multi-Scale Temporal Prediction (MSTP) in dynamic scenes, formalizing the task and creating a new benchmark. Their Incremental Generation and Multi-agent Collaboration (IG-MC) method achieved improved accuracy and consistency in forecasting future states across varying temporal and hierarchical scales, demonstrating robust performance in both general human actions and complex surgical workflows.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.