StepFun
06 Dec 2025
 Monash UniversityCSIRO
Monash UniversityCSIRO Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University University of Manchester
University of Manchester Beihang University
Beihang University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology
ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology Beijing Jiaotong University
Beijing Jiaotong University Huawei
Huawei Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield
Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOM
TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOMA comprehensive synthesis of Large Language Models for automated software development covers the entire model lifecycle, from data curation to autonomous agents, and offers practical guidance derived from empirical experiments on pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, alongside a detailed analysis of challenges and future directions.
03 Nov 2025
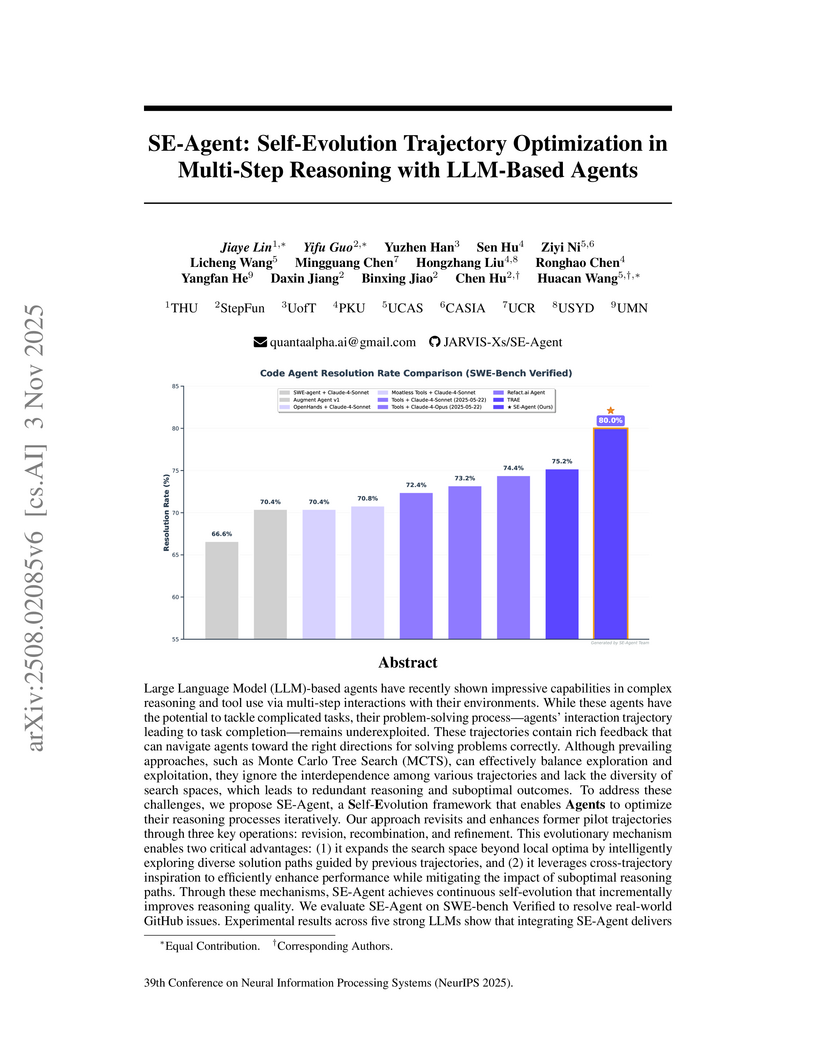
A collaborative effort introduces SE-Agent, a self-evolutionary framework for LLM-based agents that optimizes multi-step reasoning trajectories via iterative revision, recombination, and refinement. This approach achieved state-of-the-art performance on SWE-bench Verified, improving Pass@1 by up to 112% for Llama-3.1-70b-Instruct and reaching 61.2% with Claude-3.7-Sonnet.
Researchers from Fudan University and StepFun developed "WithAnyone," a framework that enables controllable and ID-consistent image generation, effectively resolving the prevalent "copy-paste" artifact in existing models. The framework introduces a large-scale paired multi-person dataset and a comprehensive benchmark, achieving high identity fidelity while allowing flexible control over pose and expression, and outperforming state-of-the-art methods across various metrics.
27 Aug 2025
Step-Audio 2 is a multi-modal large language model designed for end-to-end audio understanding and expressive speech conversation. It achieves state-of-the-art performance by deeply integrating paralinguistic information and leveraging retrieval-augmented generation with a unique audio search tool.
Step1X-Edit introduces a state-of-the-art open-source image editing framework that processes natural language instructions to generate high-fidelity visual outputs, achieving competitive performance with leading proprietary models like GPT-4o and Gemini2 Flash. The framework includes a data generation pipeline producing over 1 million high-quality image-instruction triplets and a new evaluation standard, GEdit-Bench, based on genuine user requests.
NextStep-1, developed by StepFun, advances autoregressive image generation by processing continuous image tokens with a causal transformer and flow matching head. It achieves state-of-the-art performance in its category and competes with leading diffusion models in text-to-image synthesis and editing tasks.
25 Aug 2025
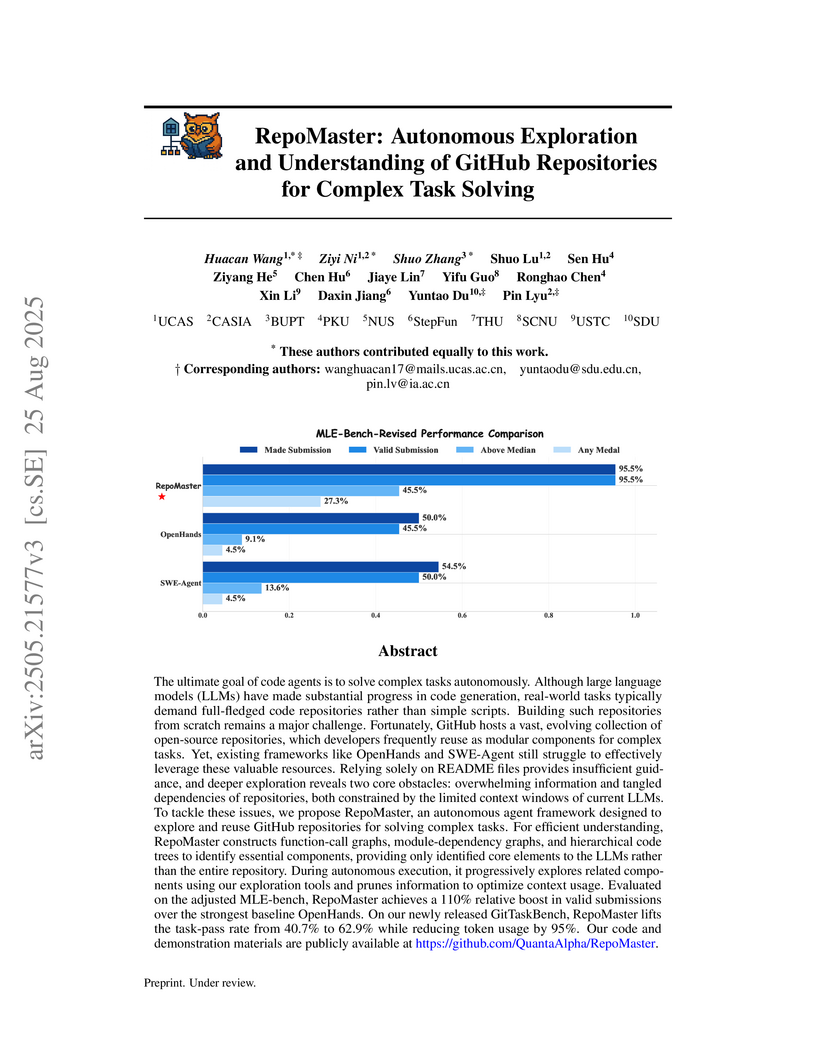
RepoMaster: Autonomous Exploration and Understanding of GitHub Repositories for Complex Task Solving
RepoMaster: Autonomous Exploration and Understanding of GitHub Repositories for Complex Task Solving
RepoMaster enables LLM-based agents to autonomously explore and understand complex GitHub repositories for task solving by intelligently reusing and adapting existing codebases. It significantly improves task success rates by up to 110% and reduces token consumption by approximately 95% compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
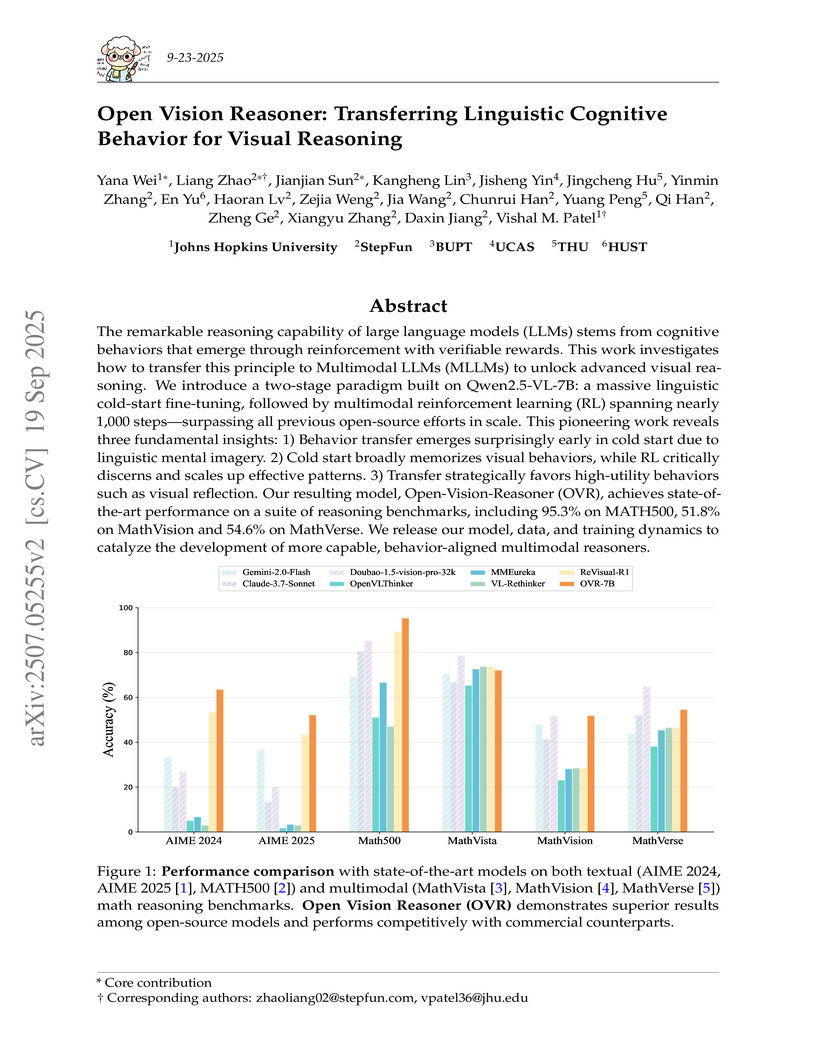
The remarkable reasoning capability of large language models (LLMs) stems from cognitive behaviors that emerge through reinforcement with verifiable rewards. This work investigates how to transfer this principle to Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) to unlock advanced visual reasoning. We introduce a two-stage paradigm built on Qwen2.5-VL-7B: a massive linguistic cold-start fine-tuning, followed by multimodal reinforcement learning (RL) spanning nearly 1,000 steps, surpassing all previous open-source efforts in scale. This pioneering work reveals three fundamental insights: 1) Behavior transfer emerges surprisingly early in cold start due to linguistic mental imagery. 2) Cold start broadly memorizes visual behaviors, while RL critically discerns and scales up effective patterns. 3) Transfer strategically favors high-utility behaviors such as visual reflection. Our resulting model, Open-Vision-Reasoner (OVR), achieves state-of-the-art performance on a suite of reasoning benchmarks, including 95.3% on MATH500, 51.8% on MathVision and 54.6% on MathVerse. We release our model, data, and training dynamics to catalyze the development of more capable, behavior-aligned multimodal reasoners.
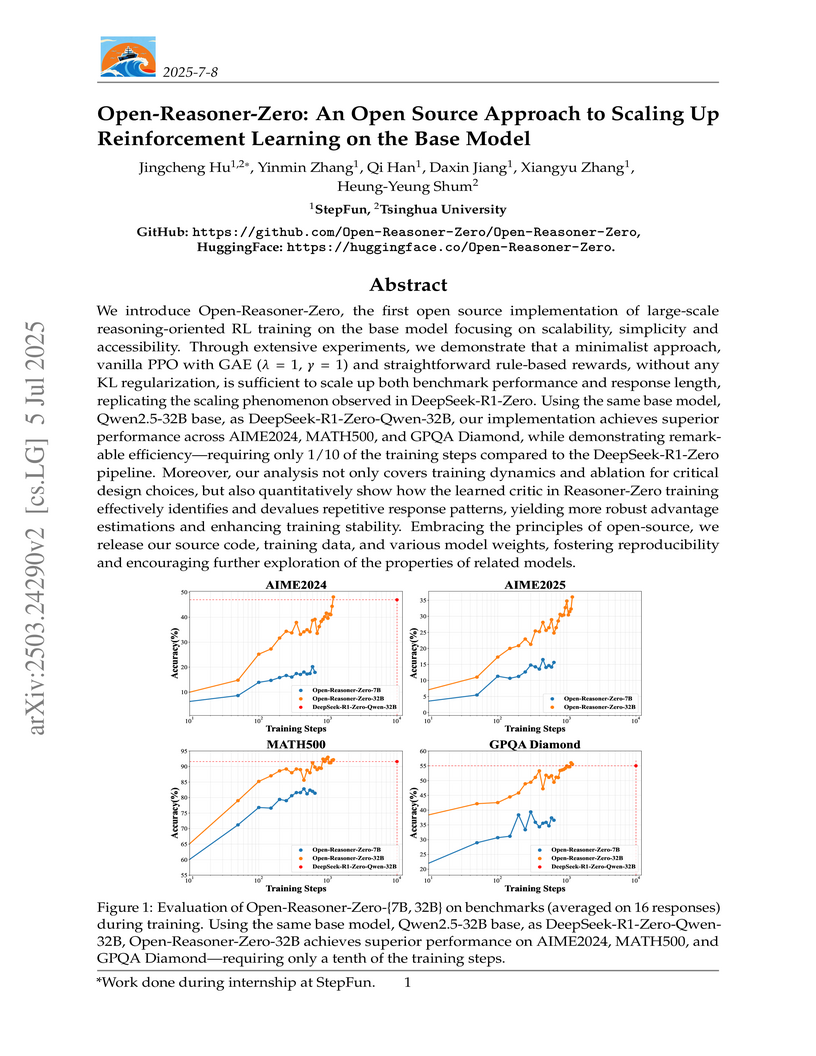
This research from StepFun and Tsinghua University presents Open-Reasoner-Zero (ORZ), the first comprehensive open-source implementation for scaling reinforcement learning directly on base large language models for reasoning tasks. ORZ demonstrates that a minimalist PPO setup, utilizing specific GAE parameters and no KL regularization, can achieve state-of-the-art reasoning performance while requiring significantly fewer training steps than comparable methods.
Researchers demonstrate a reinforcement learning framework that enhances the visual perception capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs), achieving state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks including a 31.9% AP on COCO2017val object detection - the first time a pure MLLM has surpassed the 30% threshold.
Reconstructive Visual Instruction Tuning (ROSS) enhances Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) by introducing a vision-centric denoising objective, improving fine-grained visual comprehension and significantly reducing hallucinations. The approach achieves state-of-the-art performance with a single visual encoder, often surpassing models that rely on multiple aggregated visual experts and even commercial LMMs.
The General OCR Theory (GOT) model proposes an OCR-2.0 paradigm, providing a unified end-to-end architecture to recognize diverse artificial optical characters beyond text. This model achieves state-of-the-art results on standard benchmarks and processes non-textual elements like formulas and music notation at a fraction of the computational cost of large vision-language models.
14 Sep 2025
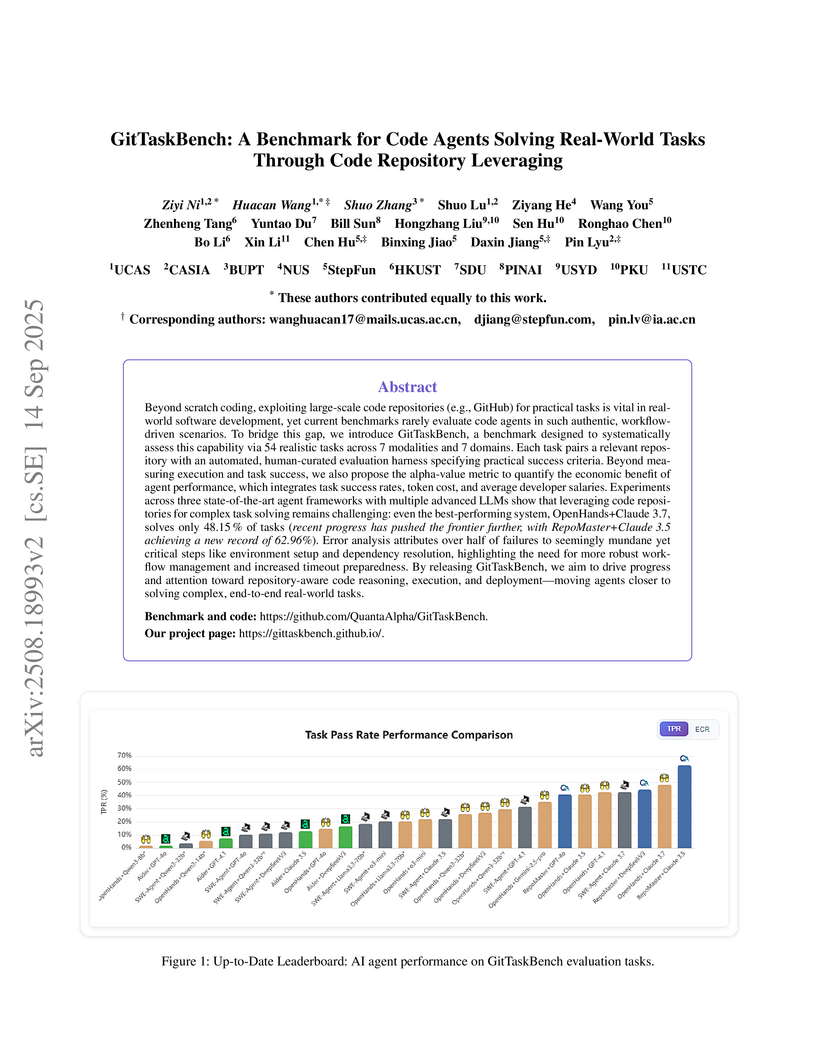
Beyond scratch coding, exploiting large-scale code repositories (e.g., GitHub) for practical tasks is vital in real-world software development, yet current benchmarks rarely evaluate code agents in such authentic, workflow-driven scenarios. To bridge this gap, we introduce GitTaskBench, a benchmark designed to systematically assess this capability via 54 realistic tasks across 7 modalities and 7 domains. Each task pairs a relevant repository with an automated, human-curated evaluation harness specifying practical success criteria. Beyond measuring execution and task success, we also propose the alpha-value metric to quantify the economic benefit of agent performance, which integrates task success rates, token cost, and average developer salaries. Experiments across three state-of-the-art agent frameworks with multiple advanced LLMs show that leveraging code repositories for complex task solving remains challenging: even the best-performing system, OpenHands+Claude 3.7, solves only 48.15% of tasks (recent progress has pushed the frontier further, with RepoMaster+Claude 3.5 achieving a new record of 62.96%). Error analysis attributes over half of failures to seemingly mundane yet critical steps like environment setup and dependency resolution, highlighting the need for more robust workflow management and increased timeout preparedness. By releasing GitTaskBench, we aim to drive progress and attention toward repository-aware code reasoning, execution, and deployment -- moving agents closer to solving complex, end-to-end real-world tasks. The benchmark and code are open-sourced at this https URL.
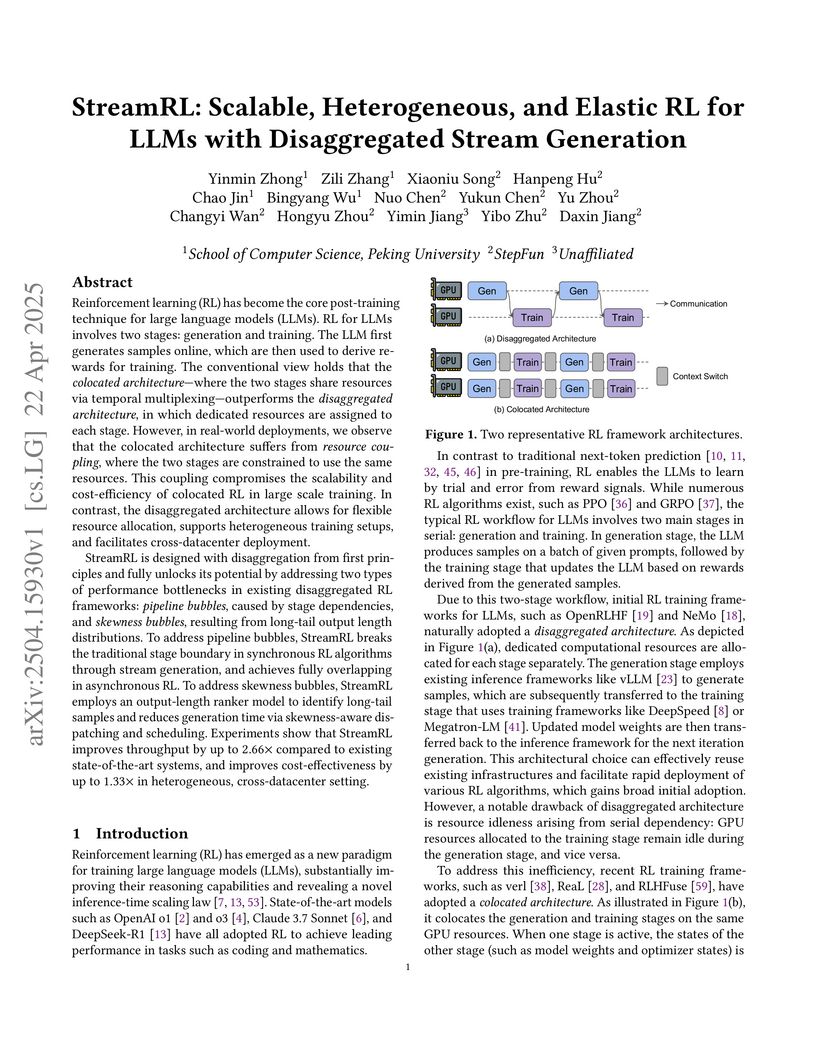
StreamRL introduces a disaggregated architecture for reinforcement learning in large language models that achieves 2.66x throughput improvement over existing systems by separating generation and training stages, enabling flexible resource allocation and heterogeneous hardware utilization across datacenters while addressing pipeline and skewness bottlenecks.
The impressive capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) across diverse tasks are now well established, yet their effective deployment necessitates careful hyperparameter optimization. Although existing methods have explored the influence of hyperparameters on model performance, a principled and generalizable framework across model architectures and data recipes remains absent. In this study, we conduct an unprecedented empirical investigation training over 3,700 LLMs from scratch across 100 trillion tokens, consuming nearly one million NVIDIA H800 GPU hours to establish a universal Scaling Law for hyperparameter optimization in LLM Pre-training, called Step Law. We empirically observe that, under fixed model size (N) and dataset size (D), the hyperparameter landscape exhibits convexity with a broad optimum, substantially reducing the complexity of hyperparameter search. Building on this insight, we formally define and empirically validate the Step Law: The optimal learning rate follows a power-law relationship with N and D, while the optimal batch size is primarily influenced by D and remains largely invariant to N.Notably, our estimated optima deviate from the global best performance found via exhaustive search by merely 0.094\% on the test set. To our best known, Step Law is the first that unifies different model shapes and structures, such as Mixture-of-Experts models and dense transformers, as well as establishes optimal hyperparameter scaling laws across diverse data recipes. We contribute a universal, plug-and-play optimal hyperparameter tool for the community, which is expected to advance efficient LLM training at scale. All experimental code, data and checkpoints are publicly available at this https URL
WMAct introduces a framework for enhancing world model reasoning in LLMs through active, multi-turn interaction, moving away from rigid reasoning structures. The approach achieves superior performance on grid-world tasks like Sokoban (78.57% success), Maze (88.14%), and Taxi (62.16%), outperforming larger proprietary models, and shows improved generalization across diverse reasoning benchmarks.
Researchers from Fudan University, CUHK, and StepFun introduce FAVOR-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating fine-grained video motion understanding in multimodal large language models, along with a training dataset of 17,152 videos that enables significant improvements in motion analysis capabilities across multiple evaluation frameworks.
Researchers from NUS and Sea AI Lab introduced "Quokka," the first large-scale scaling law for Diffusion Language Models (DLMs), demonstrating that DLMs require 2-5 times more training data than autoregressive models for equivalent compute and providing optimal allocation strategies for parameters and data across various resource constraints. The work also identified effective architectural and training choices, such as the superiority of masked diffusion and the transferability of AR-derived batch size and learning rate laws.
CoSER presents a comprehensive dataset derived from renowned literary works and a novel "Given-Circumstance Acting" (GCA) evaluation protocol for role-playing language agents. This framework enabled the training of CoSER 8B and 70B models, which achieve strong performance in simulating established characters with high fidelity across multi-turn interactions, outperforming existing models on various benchmarks.
Researchers at Yongliang Wu and collaborators developed KRIS-Bench, the first comprehensive benchmark to evaluate how well instruction-based image editing models understand and apply real-world knowledge. Their evaluation of 10 state-of-the-art models reveals a consistent gap between following instructions and generating knowledge-plausible edits, with closed-source models generally performing better but all models struggling with procedural knowledge tasks.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.