Meituan Inc.
OneCAT, developed by Meituan Inc. and Shanghai Jiao Tong University, introduces a pure decoder-only, encoder-free, and VAE tokenizer-free multimodal model for unified understanding, generation, and editing. This architecture significantly improves inference efficiency, achieving up to 61% faster time-to-first-token for high-resolution understanding and approximately 10x faster image generation compared to diffusion-based models, while setting new state-of-the-art among unified models on various benchmarks.
26 Aug 2025
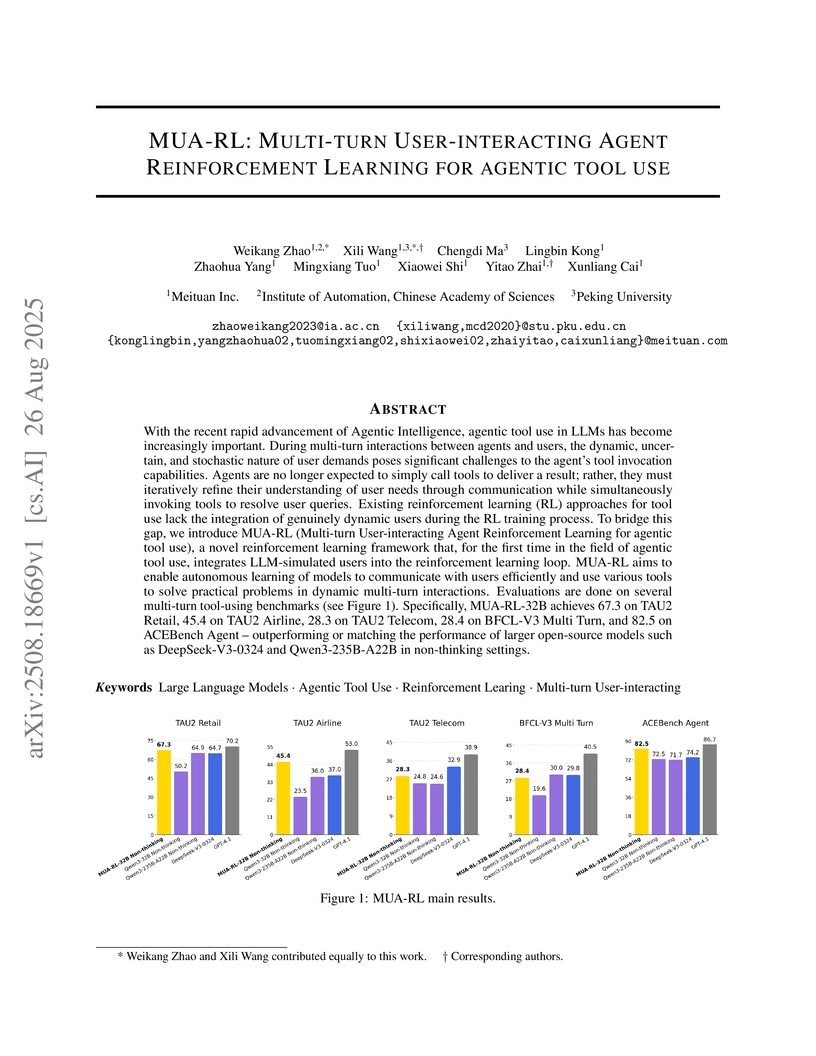
MUA-RL introduces a reinforcement learning framework that integrates LLM-simulated users directly into the training loop for agentic tool use, enabling agents to learn from dynamic multi-turn interactions. The method yields agents capable of robustly solving complex user queries and achieving performance comparable to or surpassing larger models on various benchmarks, including TAU-Bench and ACEBench.
Researchers systematically analyzed visual layer selection in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), demonstrating that integrating features from shallow, middle, and deep Vision Transformer layers via a simple concatenation fusion outperforms conventional deep-layer reliance and more complex fusion strategies.
Researchers from Sun Yat-sen University, Peng Cheng Laboratory, and Meituan Inc. developed X-SAM, a unified Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) framework capable of performing seven distinct image segmentation tasks. X-SAM achieves state-of-the-art results across various benchmarks, including new records on RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, RefCOCOg, and GCG datasets, while also introducing Visual Grounded (VGD) segmentation.
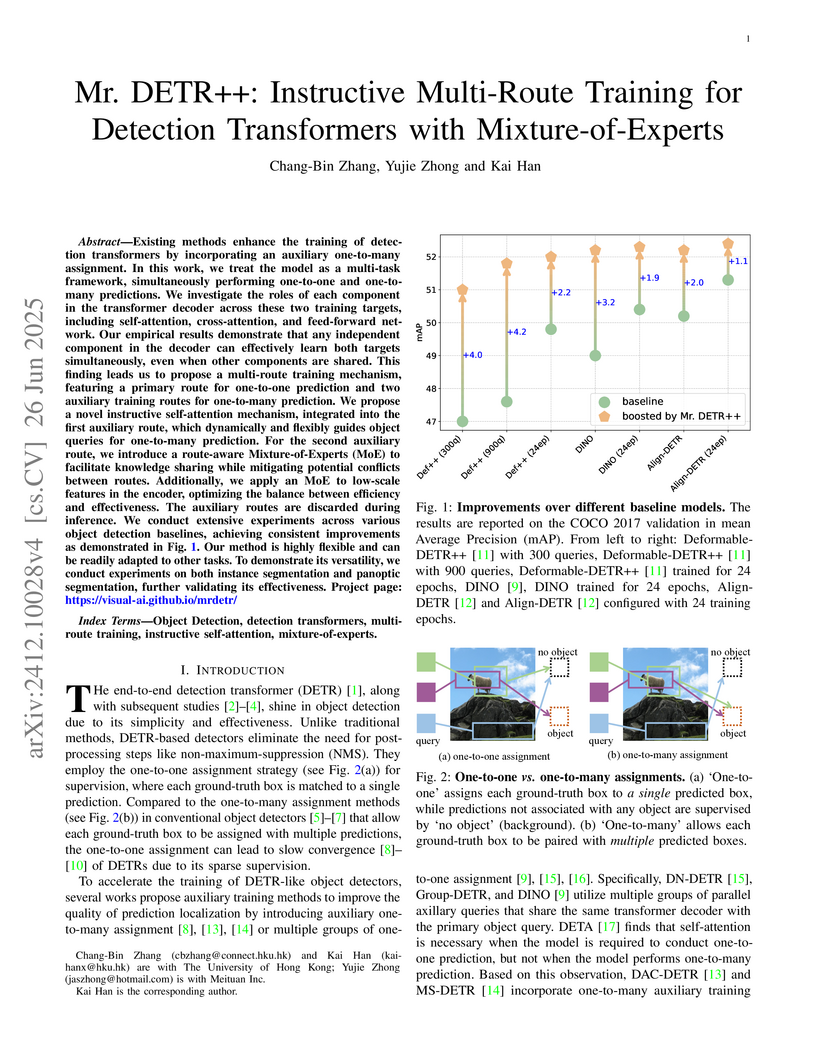
Mr. DETR++ introduces an instructive multi-route training framework for Detection Transformers, which addresses their slow training convergence by integrating one-to-one and one-to-many supervision signals. The approach, which includes novel Mixture-of-Experts designs and discards auxiliary routes during inference, achieves consistent performance gains of up to +4.0% mAP on COCO object detection while maintaining the baseline model's inference speed.
The AdaR framework teaches Large Language Models to perform adaptive mathematical reasoning by combining an automated data synthesis pipeline with a specialized reinforcement learning strategy. It achieved substantial performance gains, averaging +8.50 points across diverse benchmarks, by compelling models to rely on underlying problem-solving logic rather than superficial patterns.
The "thinking with images" paradigm represents a pivotal shift in the reasoning of Vision Language Models (VLMs), moving from text-dominant chain-of-thought to image-interactive reasoning. By invoking visual tools or generating intermediate visual representations, VLMs can iteratively attend to fine-grained regions, enabling deeper image understanding and more faithful multimodal reasoning. As an emerging paradigm, however, it still leaves substantial room for exploration in data construction accuracy, structural design, and broader application scenarios, which offer rich opportunities for advancing multimodal reasoning. To further advance this line of work, we present DeepSketcher, a comprehensive suite comprising both an image-text interleaved dataset and a self-contained model. The dataset contains 31k chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning trajectories with diverse tool calls and resulting edited images, covering a wide range of data types and manipulation instructions with high annotation accuracy. Building on this resource, we design a model that performs interleaved image-text reasoning and natively generates "visual thoughts" by operating directly in the visual embedding space, rather than invoking external tools and repeatedly re-encoding generated images. This design enables tool-free and more flexible "thinking with images". Extensive experiments on multimodal reasoning benchmarks demonstrate strong performance, validating both the utility of the dataset and the effectiveness of the model design.
04 Sep 2025
The MULTICONIR benchmark was developed to systematically evaluate information retrieval and reranking models on multi-condition natural language queries, revealing that current state-of-the-art models suffer significant performance degradation and lack robust relevance monotonicity and format invariance. Advanced general-purpose LLMs, such as GPT-4o, demonstrated superior capabilities in these complex retrieval scenarios.
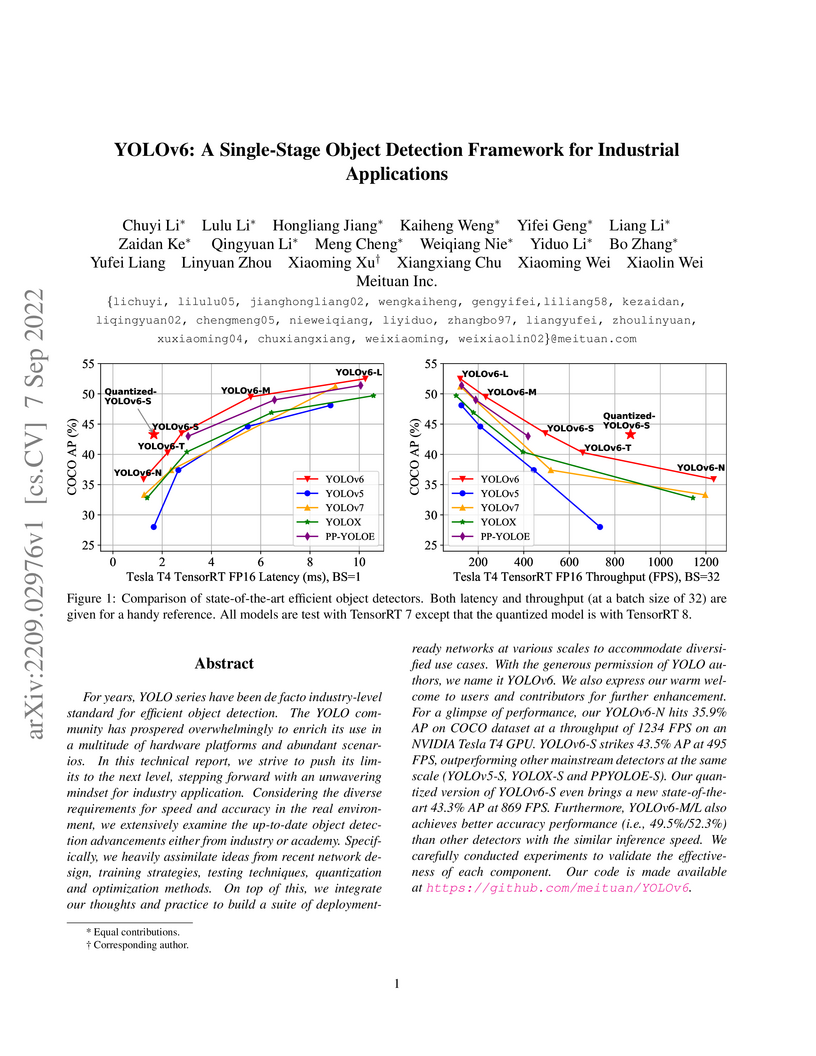
For years, the YOLO series has been the de facto industry-level standard for efficient object detection. The YOLO community has prospered overwhelmingly to enrich its use in a multitude of hardware platforms and abundant scenarios. In this technical report, we strive to push its limits to the next level, stepping forward with an unwavering mindset for industry application.
Considering the diverse requirements for speed and accuracy in the real environment, we extensively examine the up-to-date object detection advancements either from industry or academia. Specifically, we heavily assimilate ideas from recent network design, training strategies, testing techniques, quantization, and optimization methods. On top of this, we integrate our thoughts and practice to build a suite of deployment-ready networks at various scales to accommodate diversified use cases. With the generous permission of YOLO authors, we name it YOLOv6. We also express our warm welcome to users and contributors for further enhancement. For a glimpse of performance, our YOLOv6-N hits 35.9% AP on the COCO dataset at a throughput of 1234 FPS on an NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPU. YOLOv6-S strikes 43.5% AP at 495 FPS, outperforming other mainstream detectors at the same scale~(YOLOv5-S, YOLOX-S, and PPYOLOE-S). Our quantized version of YOLOv6-S even brings a new state-of-the-art 43.3% AP at 869 FPS. Furthermore, YOLOv6-M/L also achieves better accuracy performance (i.e., 49.5%/52.3%) than other detectors with a similar inference speed. We carefully conducted experiments to validate the effectiveness of each component. Our code is made available at this https URL.
This research provides a systematic analysis of visual feature integration in Multimodal Large Language Models, focusing on optimal layer selection and fusion strategies. It identifies that selecting specific layers from different stages of a visual encoder and employing an external direct fusion method consistently yield the best performance across various multimodal benchmarks.
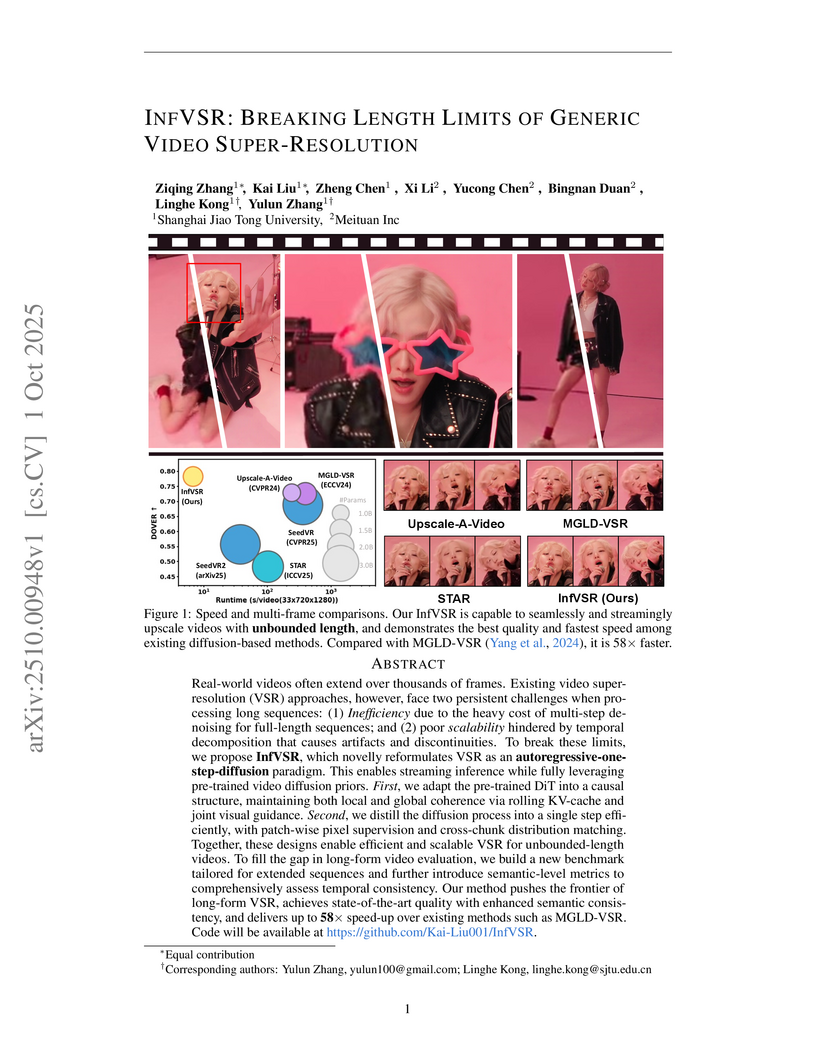
Real-world videos often extend over thousands of frames. Existing video super-resolution (VSR) approaches, however, face two persistent challenges when processing long sequences: (1) inefficiency due to the heavy cost of multi-step denoising for full-length sequences; and (2) poor scalability hindered by temporal decomposition that causes artifacts and discontinuities. To break these limits, we propose InfVSR, which novelly reformulates VSR as an autoregressive-one-step-diffusion paradigm. This enables streaming inference while fully leveraging pre-trained video diffusion priors. First, we adapt the pre-trained DiT into a causal structure, maintaining both local and global coherence via rolling KV-cache and joint visual guidance. Second, we distill the diffusion process into a single step efficiently, with patch-wise pixel supervision and cross-chunk distribution matching. Together, these designs enable efficient and scalable VSR for unbounded-length videos. To fill the gap in long-form video evaluation, we build a new benchmark tailored for extended sequences and further introduce semantic-level metrics to comprehensively assess temporal consistency. Our method pushes the frontier of long-form VSR, achieves state-of-the-art quality with enhanced semantic consistency, and delivers up to 58x speed-up over existing methods such as MGLD-VSR. Code will be available at this https URL.
We present MobileVLM, a competent multimodal vision language model (MMVLM) targeted to run on mobile devices. It is an amalgamation of a myriad of architectural designs and techniques that are mobile-oriented, which comprises a set of language models at the scale of 1.4B and 2.7B parameters, trained from scratch, a multimodal vision model that is pre-trained in the CLIP fashion, cross-modality interaction via an efficient projector. We evaluate MobileVLM on several typical VLM benchmarks. Our models demonstrate on par performance compared with a few much larger models. More importantly, we measure the inference speed on both a Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 CPU and an NVIDIA Jeston Orin GPU, and we obtain state-of-the-art performance of 21.5 tokens and 65.3 tokens per second, respectively. Our code will be made available at: this https URL.
TimeMarker from Meituan Inc. is a versatile Video-LLM that enhances video understanding across varying lengths and achieves superior temporal localization by integrating explicit Temporal Separator Tokens and an AnyLength mechanism. It demonstrated state-of-the-art performance, outperforming specialized supervised models on benchmarks like Charades-STA and ActivityNet Captions for temporal grounding.
08 Aug 2025
Meituan researchers developed RoboTron-Nav, a unified framework for language-guided visual navigation that integrates perception, planning, and prediction through multitask learning and adaptive memory. The framework achieved an 81.1% success rate on the challenging CHORES-S ObjectNav benchmark, representing a 9% absolute improvement over prior state-of-the-art methods.
04 Nov 2025
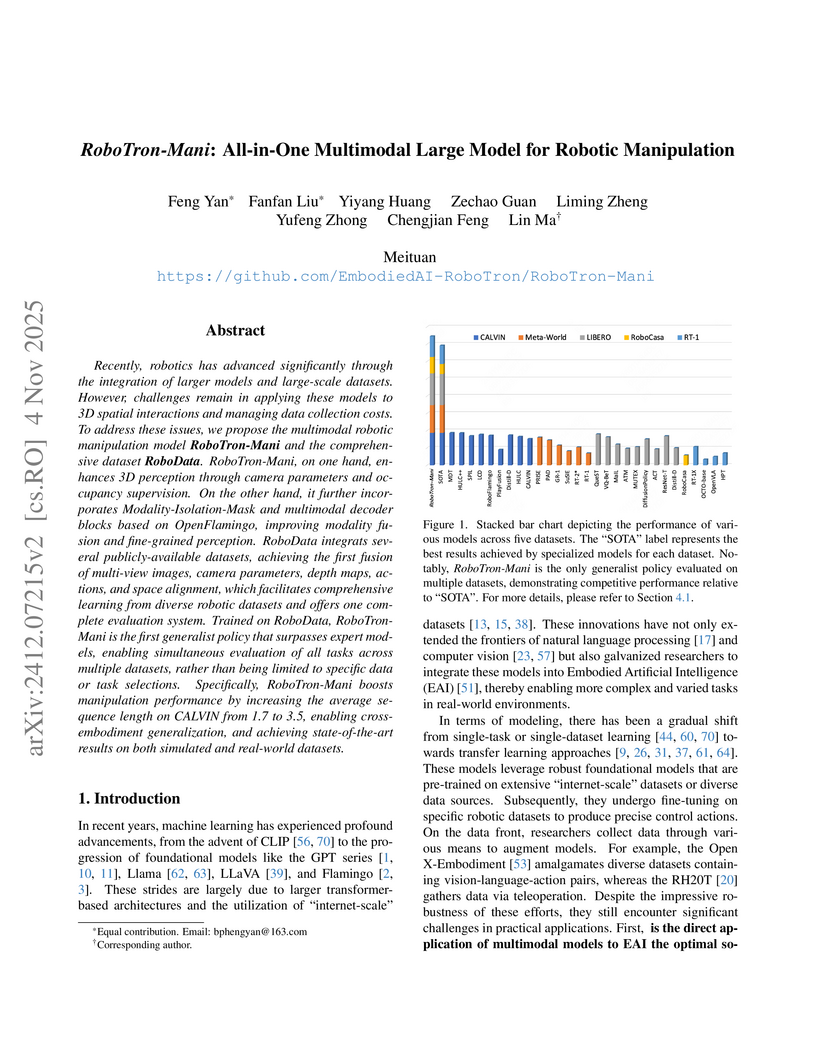
Recently, robotics has advanced significantly through the integration of larger models and large-scale datasets. However, challenges remain in applying these models to 3D spatial interactions and managing data collection costs. To address these issues, we propose the multimodal robotic manipulation model RoboTron-Mani and the comprehensive dataset RoboData. RoboTron-Mani, on one hand, enhances 3D perception through camera parameters and occupancy supervision. On the other hand, it further incorporates Modality-Isolation-Mask and multimodal decoder blocks based on OpenFlamingo, improving modality fusion and fine-grained perception. RoboData integrats several publicly-available datasets, achieving the first fusion of multi-view images, camera parameters, depth maps, actions, and space alignment, which facilitates comprehensive learning from diverse robotic datasets and offers one complete evaluation system. Trained on RoboData, RoboTron-Mani is the first generalist policy that surpasses expert models, enabling simultaneous evaluation of all tasks across multiple datasets, rather than being limited to specific data or task selections. Specifically, RoboTron-Mani boosts manipulation performance by increasing the average sequence length on CALVIN from 1.7 to 3.5, enabling cross-embodiment generalization, and achieving state-of-the-art results on both simulated and real-world datasets.
GRAM introduces a Generative Foundation Reward Model that leverages a two-stage training approach with unlabeled and labeled data, significantly improving reward model generalization and reducing reliance on extensive human preference annotations for LLM alignment. The model demonstrates superior out-of-distribution performance and efficient adaptation to new tasks.
Researchers from Eastern Institute of Technology, Tencent, and collaborators develop SkipGPT, a dynamic layer pruning framework that introduces token-aware global routing and decoupled pruning policies for MLP versus self-attention modules, achieving over 40% parameter reduction while maintaining or exceeding original model performance through a two-stage training paradigm that first tunes lightweight routers (0.01% parameters) then applies LoRA fine-tuning, with SkipGPT-RT retaining over 90% performance on LLaMA2-7B/13B at 25% pruning and over 95% on LLaMA3.1-8B while outperforming static methods like ShortGPT and dynamic approaches like MoD-D across commonsense reasoning benchmarks, revealing through routing behavior analysis that attention modules exhibit higher redundancy than MLPs and that computational needs shift contextually with later tokens requiring more attention but less MLP processing, challenging the fixed 1:1 attention-MLP architecture design while demonstrating that joint training of routers with pre-trained parameters causes instability compared to their stable disentangled optimization approach.
07 Mar 2025
This work demonstrates that Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) for LLM alignment can be framed as an imitation learning problem on preference data distributions. This insight leads to Direct Imitation Learning (DIL), an algorithm that improves performance across various benchmarks, including the UltraFeedback Binarized and Anthropic Helpful-Harmless datasets, by directly optimizing the imitation objective.
Researchers developed VisiPruner, a training-free framework that leverages a new understanding of how multimodal large language models process visual information discontinuously across layers. This approach significantly reduces computational overhead by up to 99% in visual-related attention and 53.9% in total FLOPs while preserving performance across various models and benchmarks.
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Meituan introduced NEEDLEINATABLE (NIAT), the first long-context tabular benchmark to evaluate large language models' (LLMs) fine-grained understanding of individual cells within structured tables. This work revealed significant performance gaps in locating cells by index and a "lost-in-the-middle-table" phenomenon, while a proposed data synthesis method improved models' average accuracy by 14.55% on downstream tabular benchmarks.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.