Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation
Researchers from NTT Nanophotonics Center developed an optoelectronic recurrent neural network that leverages the resistive-capacitive (RC) delay of optical-electrical-optical converters. This inherent delay, traditionally seen as a limitation, is shown to compensate for optical loop losses, improving training accuracy and gradient stability across various circuit scales and datasets.
M2D-CLAP introduces a general-purpose audio-language representation that synergistically combines masked modeling with contrastive language-audio pre-training. This framework achieves state-of-the-art performance across diverse conventional audio tasks and audio-language tasks by efficiently leveraging LLM-based sentence embeddings through a multi-stage training strategy.
This paper presents Masked Modeling Duo (M2D), a refined self-supervised learning approach that improves upon masked prediction by having the target network encode only masked input patches, preventing information contamination. The extended M2D-X framework enables specialized representation learning for diverse audio applications, achieving state-of-the-art performance on a medical respiratory sound classification task and strong results in general audio and speech domains.
Recently, Ainsworth et al. showed that using weight matching (WM) to minimize
the L2 distance in a permutation search of model parameters effectively
identifies permutations that satisfy linear mode connectivity (LMC), where the
loss along a linear path between two independently trained models with
different seeds remains nearly constant. This paper analyzes LMC using WM,
which is useful for understanding stochastic gradient descent's effectiveness
and its application in areas like model merging. We first empirically show that
permutations found by WM do not significantly reduce the L2 distance between
two models, and the occurrence of LMC is not merely due to distance reduction
by WM itself. We then demonstrate that permutations can change the directions
of the singular vectors, but not the singular values, of the weight matrices in
each layer. This finding shows that permutations found by WM primarily align
the directions of singular vectors associated with large singular values across
models. This alignment brings the singular vectors with large singular values,
which determine the model's functionality, closer between the original and
merged models, allowing the merged model to retain functionality similar to the
original models, thereby satisfying LMC. This paper also analyzes activation
matching (AM) in terms of singular vectors and finds that the principle of AM
is likely the same as that of WM. Finally, we analyze the difference between WM
and the straight-through estimator (STE), a dataset-dependent permutation
search method, and show that WM can be more advantageous than STE in achieving
LMC among three or more models.
09 Apr 2019
A method is presented for crossmodal voice conversion, synthesizing speech tailored to a target face image, and for generating face images consistent with input speech, by learning implicit correlations between faces and voices without requiring explicit attribute labels. The proposed approach achieves voice conversion performance comparable to a strong attribute-conditioned baseline.
Building multisensory AI systems that learn from multiple sensory inputs such as text, speech, video, real-world sensors, wearable devices, and medical data holds great promise for impact in many scientific areas with practical benefits, such as in supporting human health and well-being, enabling multimedia content processing, and enhancing real-world autonomous agents. By synthesizing a range of theoretical frameworks and application domains, this thesis aims to advance the machine learning foundations of multisensory AI. In the first part, we present a theoretical framework formalizing how modalities interact with each other to give rise to new information for a task. These interactions are the basic building blocks in all multimodal problems, and their quantification enables users to understand their multimodal datasets, design principled approaches to learn these interactions, and analyze whether their model has succeeded in learning. In the second part, we study the design of practical multimodal foundation models that generalize over many modalities and tasks, which presents a step toward grounding large language models to real-world sensory modalities. We introduce MultiBench, a unified large-scale benchmark across a wide range of modalities, tasks, and research areas, followed by the cross-modal attention and multimodal transformer architectures that now underpin many of today's multimodal foundation models. Scaling these architectures on MultiBench enables the creation of general-purpose multisensory AI systems, and we discuss our collaborative efforts in applying these models for real-world impact in affective computing, mental health, cancer prognosis, and robotics. Finally, we conclude this thesis by discussing how future work can leverage these ideas toward more general, interactive, and safe multisensory AI.
This paper proposes a non-autoregressive extension of our previously proposed
sequence-to-sequence (S2S) model-based voice conversion (VC) methods. S2S
model-based VC methods have attracted particular attention in recent years for
their flexibility in converting not only the voice identity but also the pitch
contour and local duration of input speech, thanks to the ability of the
encoder-decoder architecture with the attention mechanism. However, one of the
obstacles to making these methods work in real-time is the autoregressive (AR)
structure. To overcome this obstacle, we develop a method to obtain a model
that is free from an AR structure and behaves similarly to the original S2S
models, based on a teacher-student learning framework. In our method, called
"FastS2S-VC", the student model consists of encoder, decoder, and attention
predictor. The attention predictor learns to predict attention distributions
solely from source speech along with a target class index with the guidance of
those predicted by the teacher model from both source and target speech. Thanks
to this structure, the model is freed from an AR structure and allows for
parallelization. Furthermore, we show that FastS2S-VC is suitable for real-time
implementation based on a sliding-window approach, and describe how to make it
run in real-time. Through speaker-identity and emotional-expression conversion
experiments, we confirmed that FastS2S-VC was able to speed up the conversion
process by 70 to 100 times compared to the original AR-type S2S-VC methods,
without significantly degrading the audio quality and similarity to target
speech. We also confirmed that the real-time version of FastS2S-VC can be run
with a latency of 32 ms when run on a GPU.
Pre-trained models are essential as feature extractors in modern machine
learning systems in various domains. In this study, we hypothesize that
representations effective for general audio tasks should provide multiple
aspects of robust features of the input sound. For recognizing sounds
regardless of perturbations such as varying pitch or timbre, features should be
robust to these perturbations. For serving the diverse needs of tasks such as
recognition of emotions or music genres, representations should provide
multiple aspects of information, such as local and global features. To
implement our principle, we propose a self-supervised learning method:
Bootstrap Your Own Latent (BYOL) for Audio (BYOL-A, pronounced "viola"). BYOL-A
pre-trains representations of the input sound invariant to audio data
augmentations, which makes the learned representations robust to the
perturbations of sounds. Whereas the BYOL-A encoder combines local and global
features and calculates their statistics to make the representation provide
multi-aspect information. As a result, the learned representations should
provide robust and multi-aspect information to serve various needs of diverse
tasks. We evaluated the general audio task performance of BYOL-A compared to
previous state-of-the-art methods, and BYOL-A demonstrated generalizability
with the best average result of 72.4% and the best VoxCeleb1 result of 57.6%.
Extensive ablation experiments revealed that the BYOL-A encoder architecture
contributes to most performance, and the final critical portion resorts to the
BYOL framework and BYOL-A augmentations. Our code is available online at
this https URL for future studies.
To reduce the need for skilled clinicians in heart sound interpretation, recent studies on automating cardiac auscultation have explored deep learning approaches. However, despite the demands for large data for deep learning, the size of the heart sound datasets is limited, and no pre-trained model is available. On the contrary, many pre-trained models for general audio tasks are available as general-purpose audio representations. This study explores the potential of general-purpose audio representations pre-trained on large-scale datasets for transfer learning in heart murmur detection. Experiments on the CirCor DigiScope heart sound dataset show that the recent self-supervised learning Masked Modeling Duo (M2D) outperforms previous methods with the results of a weighted accuracy of 0.832 and an unweighted average recall of 0.713. Experiments further confirm improved performance by ensembling M2D with other models. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of general-purpose audio representation in processing heart sounds and open the way for further applications. Our code is available online which runs on a 24 GB consumer GPU at this https URL
28 Dec 2020
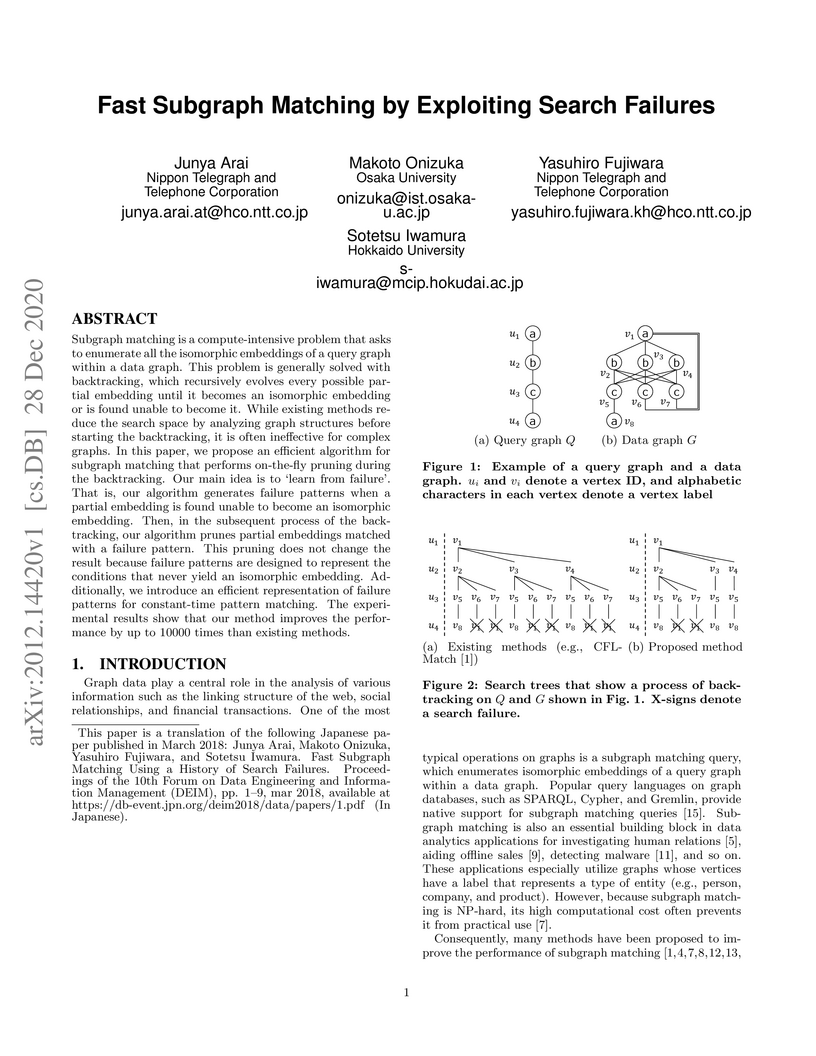
Subgraph matching is a compute-intensive problem that asks to enumerate all
the isomorphic embeddings of a query graph within a data graph. This problem is
generally solved with backtracking, which recursively evolves every possible
partial embedding until it becomes an isomorphic embedding or is found unable
to become it. While existing methods reduce the search space by analyzing graph
structures before starting the backtracking, it is often ineffective for
complex graphs. In this paper, we propose an efficient algorithm for subgraph
matching that performs on-the-fly pruning during the backtracking. Our main
idea is to `learn from failure'. That is, our algorithm generates failure
patterns when a partial embedding is found unable to become an isomorphic
embedding. Then, in the subsequent process of the backtracking, our algorithm
prunes partial embeddings matched with a failure pattern. This pruning does not
change the result because failure patterns are designed to represent the
conditions that never yield an isomorphic embedding. Additionally, we introduce
an efficient representation of failure patterns for constant-time pattern
matching. The experimental results show that our method improves the
performance by up to 10000 times than existing methods.
In this paper, we propose a non-parallel any-to-many voice conversion (VC)
method termed VoiceGrad. Inspired by WaveGrad, a recently introduced novel
waveform generation method, VoiceGrad is based upon the concepts of score
matching and Langevin dynamics. It uses weighted denoising score matching to
train a score approximator, a fully convolutional network with a U-Net
structure designed to predict the gradient of the log density of the speech
feature sequences of multiple speakers, and performs VC by using annealed
Langevin dynamics to iteratively update an input feature sequence towards the
nearest stationary point of the target distribution based on the trained score
approximator network. Thanks to the nature of this concept, VoiceGrad enables
any-to-many VC, a VC scenario in which the speaker of input speech can be
arbitrary, and allows for non-parallel training, which requires no parallel
utterances or transcriptions.
We propose a non-learning depth completion method for a sparse depth map
captured using a light detection and ranging (LiDAR) sensor guided by a pair of
stereo images. Generally, conventional stereo-aided depth completion methods
have two limiations. (i) They assume the given sparse depth map is accurately
aligned to the input image, whereas the alignment is difficult to achieve in
practice. (ii) They have limited accuracy in the long range because the depth
is estimated by pixel disparity. To solve the abovementioned limitations, we
propose selective stereo matching (SSM) that searches the most appropriate
depth value for each image pixel from its neighborly projected LiDAR points
based on an energy minimization framework. This depth selection approach can
handle any type of mis-projection. Moreover, SSM has an advantage in terms of
long-range depth accuracy because it directly uses the LiDAR measurement rather
than the depth acquired from the stereo. SSM is a discrete process; thus, we
apply variational smoothing with binary anisotropic diffusion tensor (B-ADT) to
generate a continuous depth map while preserving depth discontinuity across
object boundaries. Experimentally, compared with the previous state-of-the-art
stereo-aided depth completion, the proposed method reduced the mean absolute
error (MAE) of the depth estimation to 0.65 times and demonstrated
approximately twice more accurate estimation in the long range. Moreover, under
various LiDAR-camera calibration errors, the proposed method reduced the depth
estimation MAE to 0.34-0.93 times from previous depth completion methods.
Recent work [4] analyses the local convergence of Adam in a neighbourhood of
an optimal solution for a twice-differentiable function. It is found that the
learning rate has to be sufficiently small to ensure local stability of the
optimal solution. The above convergence results also hold for AdamW. In this
work, we propose a new adaptive optimisation method by extending AdamW in two
aspects with the purpose to relax the requirement on small learning rate for
local stability, which we refer to as Aida. Firstly, we consider tracking the
2nd moment r_t of the pth power of the gradient-magnitudes. r_t reduces to v_t
of AdamW when p=2. Suppose {m_t} is the first moment of AdamW. It is known that
the update direction m_{t+1}/(v_{t+1}+epsilon)^0.5 (or
m_{t+1}/(v_{t+1}^0.5+epsilon) of AdamW (or Adam) can be decomposed as the sign
vector sign(m_{t+1}) multiplied elementwise by a vector of magnitudes
|m_{t+1}|/(v_{t+1}+epsilon)^0.5 (or |m_{t+1}|/(v_{t+1}^0.5+epsilon)). Aida is
designed to compute the qth power of the magnitude in the form of
|m_{t+1}|^q/(r_{t+1}+epsilon)^(q/p) (or |m_{t+1}|^q/((r_{t+1})^(q/p)+epsilon)),
which reduces to that of AdamW when (p,q)=(2,1).
Suppose the origin 0 is a local optimal solution of a twice-differentiable
function. It is found theoretically that when q>1 and p>1 in Aida, the origin 0
is locally stable only when the weight-decay is non-zero. Experiments are
conducted for solving ten toy optimisation problems and training Transformer
and Swin-Transformer for two deep learning (DL) tasks. The empirical study
demonstrates that in a number of scenarios (including the two DL tasks), Aida
with particular setups of (p,q) not equal to (2,1) outperforms the setup
(p,q)=(2,1) of AdamW.
NTT Communication Science Laboratories assessed five audio foundation models for analyzing heart and respiratory sounds, finding that general-purpose models can achieve competitive performance on clean clinical datasets but show significant degradation on noisy data. General audio models pre-trained on diverse datasets surprisingly outperformed specialized models for respiratory sound classification.
Artificial objects often subjectively look eerie when their appearance to some extent resembles a human, which is known as the uncanny valley phenomenon. From a cognitive psychology perspective, several explanations of the phenomenon have been put forth, two of which are object categorization and realism inconsistency. Recently, MacDorman and Chattopadhyay (2016) reported experimental data as evidence in support of the latter. In our estimation, however, their results are still consistent with categorization-based stranger avoidance. In this Discussions paper, we try to describe why categorization-based stranger avoidance remains a viable explanation, despite the evidence of MacDorman and Chattopadhyay, and how it offers a more inclusive explanation of the impression of eeriness in the uncanny valley phenomenon.
This paper explores the problem of 3D human pose estimation from only low-level acoustic signals. The existing active acoustic sensing-based approach for 3D human pose estimation implicitly assumes that the target user is positioned along a line between loudspeakers and a microphone. Because reflection and diffraction of sound by the human body cause subtle acoustic signal changes compared to sound obstruction, the existing model degrades its accuracy significantly when subjects deviate from this line, limiting its practicality in real-world scenarios. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel method composed of a position discriminator and reverberation-resistant model. The former predicts the standing positions of subjects and applies adversarial learning to extract subject position-invariant features. The latter utilizes acoustic signals before the estimation target time as references to enhance robustness against the variations in sound arrival times due to diffraction and reflection. We construct an acoustic pose estimation dataset that covers diverse human locations and demonstrate through experiments that our proposed method outperforms existing approaches.
We make contributions towards improving adaptive-optimizer performance. Our
improvements are based on suppression of the range of adaptive stepsizes in the
AdaBelief optimizer. Firstly, we show that the particular placement of the
parameter epsilon within the update expressions of AdaBelief reduces the range
of the adaptive stepsizes, making AdaBelief closer to SGD with momentum.
Secondly, we extend AdaBelief by further suppressing the range of the adaptive
stepsizes. To achieve the above goal, we perform mutual layerwise vector
projections between the gradient g_t and its first momentum m_t before using
them to estimate the second momentum. The new optimization method is referred
to as Aida. Thirdly, extensive experimental results show that Aida outperforms
nine optimizers when training transformers and LSTMs for NLP, and VGG and
ResNet for image classification over CIAF10 and CIFAR100 while matching the
best performance of the nine methods when training WGAN-GP models for image
generation tasks. Furthermore, Aida produces higher validation accuracies than
AdaBelief for training ResNet18 over ImageNet. Code is available at this URL
28 Jan 2025
We experimentally demonstrate the decomposition of entropy production during free-energy generation in a nanometer-scale dot transitioning to a non-equilibrium steady state via single-electron counting statistics. An alternating-current signal driving a reservoir that injects multiple electrons into the dot makes it non-equilibrium, leading to free-energy generation, heat dissipation, and Shannon-entropy production. By analyzing the time-domain probability distributions of multiple electron states of the dot, we quantitatively decompose the heat dissipation into housekeeping and excess heats, revealing the correlation between the free energy and the decomposed components of heat dissipation. This correlation suggests that the ratio of the generated free energy to the work applied to the dot, can potentially reach 0.5 under far-from-equilibrium conditions induced by a large signal, while an efficiency of 0.25 was experimentally achieved. Our results, providing the theoretical and experimental efficiencies from the relation between decomposed heat dissipation and free-energy generation, promise to connect non-equilibrium thermodynamics perspectives to electronic devices.
26 Mar 2025
Data center networks (DCNs) require a low-cost, low-power optical transceiver
to handle increased traffic from generative artificial intelligence, video
streaming services, and more. Improving the required signal-to-noise ratio
(RSNR) by digital signal processing such as forward error correction (FEC)
mitigates the requirements for electrical and optical components. The optical
transceivers in DCNs exploit a low-complexity soft-decision (SD) FEC,
consisting of short block-length linear error-correcting codes and a
low-complexity SD decoder (SDD), such as a Chase decoder and ordered
statistical decoding. The low complexity SDD efficiently approaches a maximum
likelihood decoding (MLD). However, the decoding performance of MLD is limited
by its finite block length. In this paper, we describe the detail of our
proposed channel-polarized multilevel coding with iterative decoding
(CP-MLC-ID), which improves the decoding performance. The 19.5%-OH CP-MLC-ID
128-bit extended Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem (eBCH) and KP4 codes outperform the
concatenated eBCH and KP4 codes with a net coding gain of 0.25 and 0.40 dB for
the same and double the number of SDDs, respectively. We also investigate the
dependency of the decoding performance on the size of a bit interleaver. The
performance degradation of CP-MLC-ID using an 8-bit interleaver is about 0.1 dB
compared to using the large-bit interleaver. Our results indicate that even a
weak connection by exclusive-OR between codewords improves the decoding
performance, compared to simple concatenated codes in the DCNs.
The non-commutative harmonic oscillator (NCHO) was introduced as a specific Hamiltonian operator on L2(R)⊗C2 by Parmeggiani and Wakayama. Then it was proved by Ochiai and Wakayama that the eigenvalue problem for NCHO is reduced to a Heun differential equation. In this article, we consider some generalization of NCHO for L2(Rn)⊗Cp as a rotation-invariant differential equation. Then by applying a representation theory of sl(2,R)≃su(1,1), we check that its restriction to the space of products of radial functions and homogeneous harmonic polynomials is reduced to a holomorphic differential equation on the unit disk, which is generically Fuchsian.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.