University of Adelaide
16 Sep 2025
NavFoM, an embodied navigation foundation model, achieves cross-task and cross-embodiment generalization by leveraging a dual-branch architecture that integrates multimodal inputs with an LLM. This model demonstrates state-of-the-art or competitive performance across seven diverse benchmarks, including VLN, object searching, tracking, and autonomous driving, achieving a 5.6% increase in success rate on single-view VLN-CE RxR and a 78% success rate in real-world VLN tasks.
OCRBench v2 offers an improved benchmark for evaluating Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) on visual text localization and reasoning. It presents 23 tasks across 31 diverse scenarios with 10,000 human-validated instruction-response pairs and a private test set, revealing that current LMMs perform poorly on fine-grained spatial perception, complex layout understanding, and structured element parsing tasks, despite advances in basic text recognition.
NaVid is a video-based Vision-Language Model that enables navigation in continuous environments using only monocular RGB video streams. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on R2R Val-Unseen with 35.9% SPL and demonstrates a 66% success rate in real-world scenarios, eliminating reliance on depth, odometry, or maps.
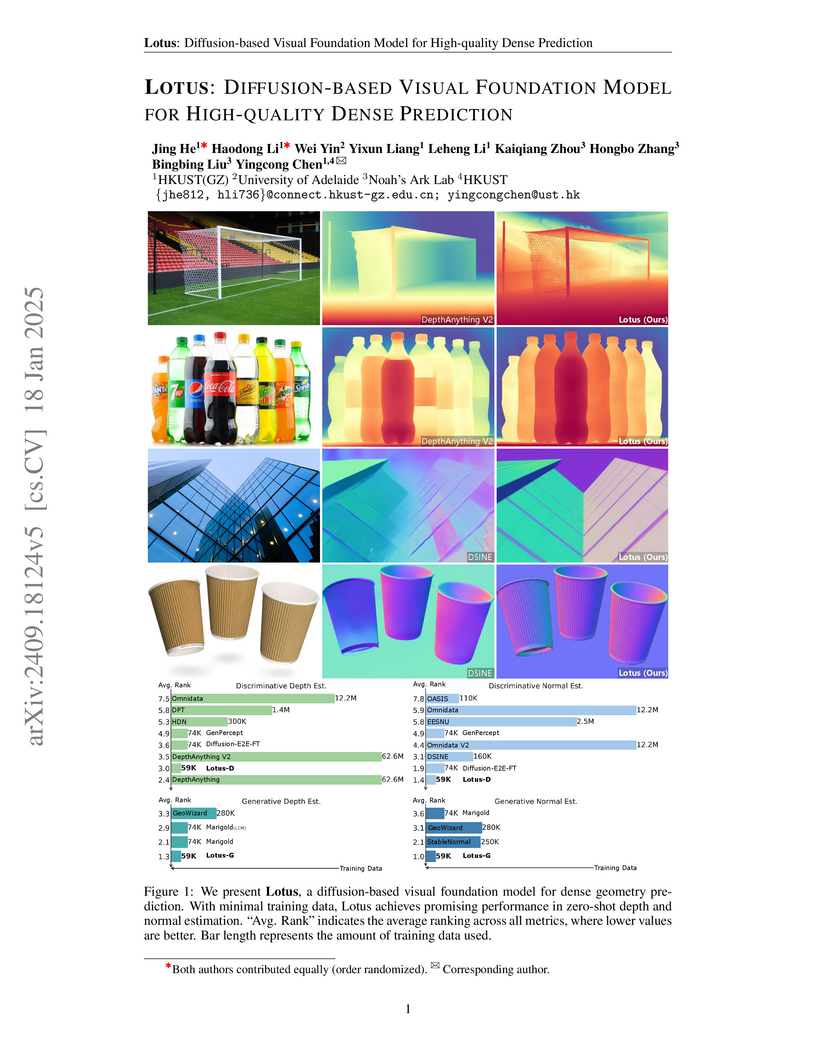
Lotus introduces a diffusion-based visual foundation model that re-engineers the standard diffusion formulation for high-quality dense geometry prediction, achieving strong zero-shot generalization. It demonstrates competitive performance against state-of-the-art discriminative methods while training on significantly less data and offering hundreds of times faster inference speeds than prior diffusion-based approaches.
SayPlan enables scalable robot task planning in large-scale, multi-room environments by grounding Large Language Models with 3D Scene Graphs. The framework leverages an LLM-guided semantic search for efficient information management and an iterative replanning loop with a scene graph simulator to ensure generated plans are physically executable.
Researchers from Australian National University and University of Adelaide, among others, introduce the Matterport3D Simulator and the Room-to-Room (R2R) dataset to benchmark Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) in real-world indoor environments. Their baseline sequence-to-sequence models achieve a 20.4% success rate in unseen environments, revealing a substantial performance drop compared to seen environments (38.6% success), highlighting a significant generalization challenge.
A comprehensive survey reviews Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) research, detailing the integration of foundation models like LLMs and VLMs into VLN systems and outlining the resulting progress, opportunities, and challenges in the field. The paper highlights how these models enhance multimodal comprehension, reasoning, and generalization across various VLN tasks, particularly through improved world modeling, human instruction interpretation, and agent planning capabilities.
This survey comprehensively introduces and reviews Quantum-enhanced Computer Vision (QeCV), an emerging interdisciplinary field that applies quantum computational paradigms to address computational challenges in classical computer vision. It categorizes existing methods based on quantum annealing and gate-based quantum computing, detailing their application to a wide array of vision tasks.
Modern deep neural networks, particularly recent large language models, come
with massive model sizes that require significant computational and storage
resources. To enable the deployment of modern models on resource-constrained
environments and accelerate inference time, researchers have increasingly
explored pruning techniques as a popular research direction in neural network
compression. However, there is a dearth of up-to-date comprehensive review
papers on pruning. To address this issue, in this survey, we provide a
comprehensive review of existing research works on deep neural network pruning
in a taxonomy of 1) universal/specific speedup, 2) when to prune, 3) how to
prune, and 4) fusion of pruning and other compression techniques. We then
provide a thorough comparative analysis of eight pairs of contrast settings for
pruning and explore emerging topics, including pruning for large language
models, large multimodal models, post-training pruning, and different
supervision levels for pruning to shed light on the commonalities and
differences of existing methods and lay the foundation for further method
development. To facilitate future research, we build a curated collection of
datasets, networks, and evaluations on different applications. Finally, we
provide valuable recommendations on selecting pruning methods and prospect
several promising research directions. We build a repository at
this https URL
Researchers at the University of Sydney, University of Adelaide, Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence, and Carnegie Mellon University developed the "Flow" framework to enable dynamic workflow refinement in multi-agent Large Language Model systems. By representing workflows as Activity-on-Vertex (AOV) graphs and emphasizing modular design, Flow achieved a 93% average success rate and 3.54/4 human rating, consistently outperforming static workflow baselines in complex coding tasks and demonstrating enhanced error tolerance.
AerialVLN introduces a new vision-and-language navigation task for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in complex, continuous outdoor city environments. The associated dataset and simulator enable training agents to follow natural language instructions, revealing a substantial performance gap between current AI models (1.0-1.6% success rate) and human pilots (80.8% success rate).
NavGPT-2 introduces a framework for Vision-and-Language Navigation that leverages Large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to achieve performance competitive with specialized models while simultaneously preserving the VLM's ability to generate human-interpretable navigational reasoning. This approach demonstrates strong results on the R2R dataset and enhanced generalization to unseen environments and instructions, addressing the trade-off between performance and transparency in embodied AI.
25 Apr 2025
EmoDubber is an AI system for movie dubbing that generates high-quality, emotion-controllable speech, accurately synchronizing with lip movements and maintaining clear pronunciation. The system, developed by researchers from institutions including the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Macquarie University, achieves superior lip sync error metrics (e.g., LSE-C 8.09, LSE-D 6.96 on Chem dataset) and pronunciation (WER 11.72-12.81% on Chem dataset) through a novel architecture incorporating duration-level contrastive learning and flow-based emotion control with guidance mechanisms.
Researchers developed a systematic framework to define, quantify, and mitigate "counting hallucinations" in Diffusion Probabilistic Models, introducing the CountHalluSet benchmark and revealing inconsistent correlations between perceptual quality metrics like FID and factual accuracy. Their proposed Joint-Diffusion Model, which integrates structural constraints, demonstrably reduced these factual inconsistencies in generated images.
03 Aug 2025
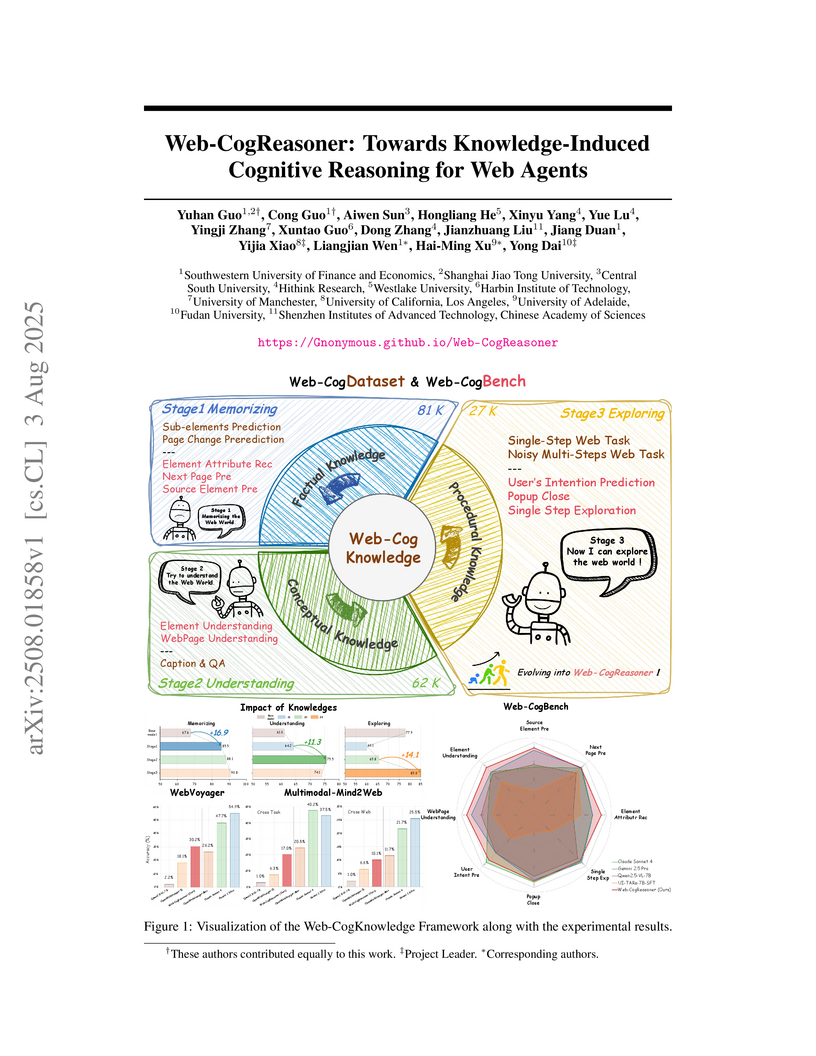
A framework called Web-CogReasoner enables web agents to learn and apply factual, conceptual, and procedural knowledge through a human-inspired curriculum. This structured approach, using the Qwen2.5-VL-7B LMM, leads to an 84.4% accuracy on cognitive reasoning tasks and establishes a new state-of-the-art for open-source agents on the WebVoyager benchmark with a 30.2% success rate.
Researchers from Monash University, Tsinghua University, UC Santa Cruz, University of Adelaide, and Bytedance Seed developed VQ-VA WORLD, a data-driven framework to enable open-source models to perform Visual Question-Visual Answering (VQ-VA). The framework introduces a large-scale, knowledge-rich dataset curated by an agentic pipeline and a new human-curated benchmark, resulting in an open-source model outperforming existing open-weight counterparts and significantly closing the performance gap with proprietary systems on VQ-VA tasks.
16 Jun 2024
Physically Embodied Gaussian Splatting develops a real-time, self-correcting world model for robotics by coupling 3D Gaussians for visual representation with particles for physics simulation. This approach tracks and predicts dynamic scenes at 30 Hz, achieving lower tracking error than physics-only or visual-only baselines in diverse manipulation and interaction scenarios.
BEVBert proposes a topo-metric map pre-training framework for Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN), moving beyond discrete panoramic views to provide agents with explicit spatial understanding. The approach achieves state-of-the-art results across multiple VLN benchmarks, including 73 SR and 62 SPL on R2R and 64.4 SR on RxR unseen test splits.
Researchers from Shenzhen MSU-BIT University and the University of Adelaide introduce Online Video Grounding with Hybrid-modal Queries (OVG-HQ), a task enabling real-time video segment localization using combined text, image, and video queries. Their OVG-HQ-Unify framework, featuring a Parametric Memory Block and a hybrid distillation strategy, outperforms existing online and adapted offline methods, achieving 45.95 FPS on an RTX 4090 GPU while improving oR^1_{0.5} by up to 8.98% for certain query types on their new QVHighlights-Unify dataset.
SmartWay: Enhanced Waypoint Prediction and Backtracking for Zero-Shot Vision-and-Language Navigation
SmartWay: Enhanced Waypoint Prediction and Backtracking for Zero-Shot Vision-and-Language Navigation
A framework for Vision-and-Language Navigation in Continuous Environments (VLN-CE), SmartWay enhances waypoint prediction via a DINOv2 encoder and occupancy-aware loss, while its zero-shot MLLM-based navigator incorporates a history-aware prompting system and a novel backtracking mechanism. The system achieves an Oracle Success Rate of 51% in simulated zero-shot VLN-CE and a Success Rate of 36% on a physical robot in real-world scenarios.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.