University of Dayton
Human pose estimation aims to locate the human body parts and build human body representation (e.g., body skeleton) from input data such as images and videos. It has drawn increasing attention during the past decade and has been utilized in a wide range of applications including human-computer interaction, motion analysis, augmented reality, and virtual reality. Although the recently developed deep learning-based solutions have achieved high performance in human pose estimation, there still remain challenges due to insufficient training data, depth ambiguities, and occlusion. The goal of this survey paper is to provide a comprehensive review of recent deep learning-based solutions for both 2D and 3D pose estimation via a systematic analysis and comparison of these solutions based on their input data and inference procedures. More than 250 research papers since 2014 are covered in this survey. Furthermore, 2D and 3D human pose estimation datasets and evaluation metrics are included. Quantitative performance comparisons of the reviewed methods on popular datasets are summarized and discussed. Finally, the challenges involved, applications, and future research directions are concluded. A regularly updated project page is provided: \url{this https URL}
A comprehensive survey maps the landscape of deep learning advancements since AlexNet in 2012, detailing architectural innovations and training techniques across supervised, unsupervised, and deep reinforcement learning. It consolidates key concepts and provides practical resources, including frameworks and benchmark datasets.
This expository paper introduces a simplified approach to image-based quality inspection in manufacturing using OpenAI's CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining) model adapted for few-shot learning. While CLIP has demonstrated impressive capabilities in general computer vision tasks, its direct application to manufacturing inspection presents challenges due to the domain gap between its training data and industrial applications. We evaluate CLIP's effectiveness through five case studies: metallic pan surface inspection, 3D printing extrusion profile analysis, stochastic textured surface evaluation, automotive assembly inspection, and microstructure image classification. Our results show that CLIP can achieve high classification accuracy with relatively small learning sets (50-100 examples per class) for single-component and texture-based applications. However, the performance degrades with complex multi-component scenes. We provide a practical implementation framework that enables quality engineers to quickly assess CLIP's suitability for their specific applications before pursuing more complex solutions. This work establishes CLIP-based few-shot learning as an effective baseline approach that balances implementation simplicity with robust performance, demonstrated in several manufacturing quality control applications.
Camouflaged object detection (COD) and camouflaged instance segmentation
(CIS) aim to recognize and segment objects that are blended into their
surroundings, respectively. While several deep neural network models have been
proposed to tackle those tasks, augmentation methods for COD and CIS have not
been thoroughly explored. Augmentation strategies can help improve models'
performance by increasing the size and diversity of the training data and
exposing the model to a wider range of variations in the data. Besides, we aim
to automatically learn transformations that help to reveal the underlying
structure of camouflaged objects and allow the model to learn to better
identify and segment camouflaged objects. To achieve this, we propose a
learnable augmentation method in the frequency domain for COD and CIS via the
Fourier transform approach, dubbed CamoFA. Our method leverages a conditional
generative adversarial network and cross-attention mechanism to generate a
reference image and an adaptive hybrid swapping with parameters to mix the
low-frequency component of the reference image and the high-frequency component
of the input image. This approach aims to make camouflaged objects more visible
for detection and segmentation models. Without bells and whistles, our proposed
augmentation method boosts the performance of camouflaged object detectors and
instance segmenters by large margins.
We introduce OpenEvents V1a large-scale benchmark dataset designed to advance event-centric vision-language understanding. Unlike conventional image captioning and retrieval datasets that focus on surface-level descriptions, OpenEvents V1 dataset emphasizes contextual and temporal grounding through three primary tasks: (1) generating rich, event-aware image captions, (2) retrieving event-relevant news articles from image queries, and (3) retrieving event-relevant images from narrative-style textual queries. The dataset comprises over 200,000 news articles and 400,000 associated images sourced from CNN and The Guardian, spanning diverse domains and time periods. We provide extensive baseline results and standardized evaluation protocols for all tasks. OpenEvents V1 establishes a robust foundation for developing multimodal AI systems capable of deep reasoning over complex real-world events. The dataset is publicly available at this https URL.
We present a comprehensive study on meaningfully evaluating sign language utterances in the form of human skeletal poses. The study covers keypoint distance-based, embedding-based, and back-translation-based metrics. We show tradeoffs between different metrics in different scenarios through automatic meta-evaluation of sign-level retrieval and a human correlation study of text-to-pose translation across different sign languages. Our findings and the open-source pose-evaluation toolkit provide a practical and reproducible way of developing and evaluating sign language translation or generation systems.
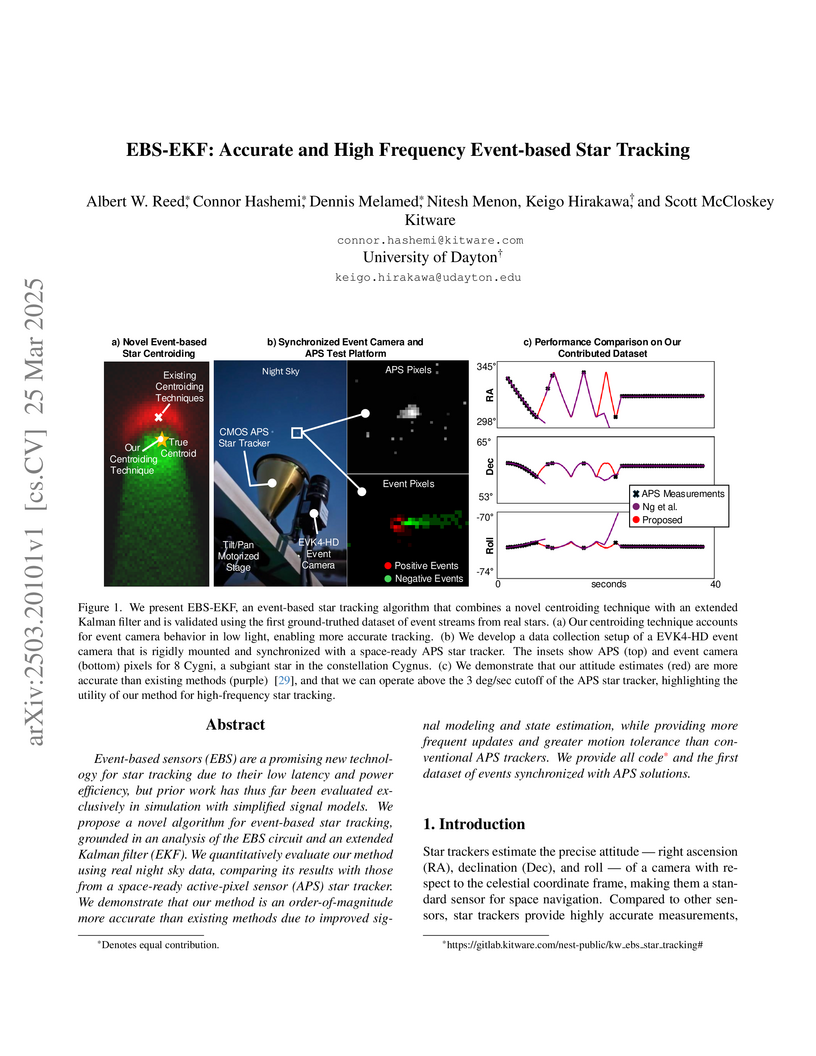
Researchers from Kitware and the University of Dayton developed EBS-EKF, an event-based star tracking algorithm, providing the first quantitative evaluation using real night sky data. The system achieves an order-of-magnitude accuracy improvement and superior motion tolerance compared to conventional systems, enabling high-frequency attitude estimation for agile spacecraft.
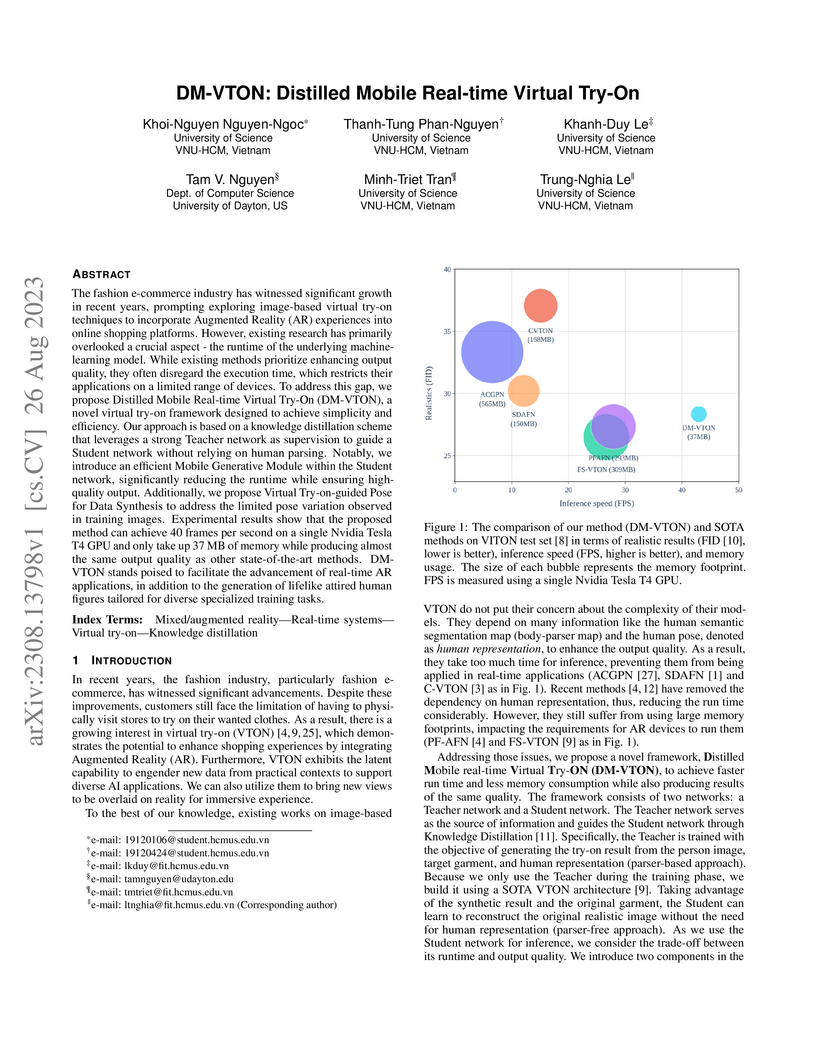
The fashion e-commerce industry has witnessed significant growth in recent years, prompting exploring image-based virtual try-on techniques to incorporate Augmented Reality (AR) experiences into online shopping platforms. However, existing research has primarily overlooked a crucial aspect - the runtime of the underlying machine-learning model. While existing methods prioritize enhancing output quality, they often disregard the execution time, which restricts their applications on a limited range of devices. To address this gap, we propose Distilled Mobile Real-time Virtual Try-On (DM-VTON), a novel virtual try-on framework designed to achieve simplicity and efficiency. Our approach is based on a knowledge distillation scheme that leverages a strong Teacher network as supervision to guide a Student network without relying on human parsing. Notably, we introduce an efficient Mobile Generative Module within the Student network, significantly reducing the runtime while ensuring high-quality output. Additionally, we propose Virtual Try-on-guided Pose for Data Synthesis to address the limited pose variation observed in training images. Experimental results show that the proposed method can achieve 40 frames per second on a single Nvidia Tesla T4 GPU and only take up 37 MB of memory while producing almost the same output quality as other state-of-the-art methods. DM-VTON stands poised to facilitate the advancement of real-time AR applications, in addition to the generation of lifelike attired human figures tailored for diverse specialized training tasks. this https URL
This paper offers a comprehensive review of sentiment-aware recommendation systems in e-commerce, focusing on academic advancements from 2023 to early 2025. It synthesizes how integrating Natural Language Processing techniques with recommender systems enhances personalization, prediction accuracy, and user satisfaction by leveraging nuanced opinions from free-text user feedback.
25 Jul 2025
MindFlow+, an agent developed by Xiaoduo AI Lab and the University of Dayton, specializes large language models for e-commerce customer service by fine-tuning on tool-augmented and reward-conditioned dialogue data. It achieved a 94.00% AI Contribution Ratio with the Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct model and demonstrated effective generalization across different product domains without retraining.
Recent few-shot object detection (FSOD) methods have focused on augmenting
synthetic samples for novel classes, show promising results to the rise of
diffusion models. However, the diversity of such datasets is often limited in
representativeness because they lack awareness of typical and hard samples,
especially in the context of foreground and background relationships. To tackle
this issue, we propose a Multi-Perspective Data Augmentation (MPAD) framework.
In terms of foreground-foreground relationships, we propose in-context learning
for object synthesis (ICOS) with bounding box adjustments to enhance the detail
and spatial information of synthetic samples. Inspired by the large margin
principle, support samples play a vital role in defining class boundaries.
Therefore, we design a Harmonic Prompt Aggregation Scheduler (HPAS) to mix
prompt embeddings at each time step of the generation process in diffusion
models, producing hard novel samples. For foreground-background relationships,
we introduce a Background Proposal method (BAP) to sample typical and hard
backgrounds. Extensive experiments on multiple FSOD benchmarks demonstrate the
effectiveness of our approach. Our framework significantly outperforms
traditional methods, achieving an average increase of 17.5% in nAP50 over
the baseline on PASCAL VOC. Code is available at
this https URL
Few-shot instance segmentation extends the few-shot learning paradigm to the instance segmentation task, which tries to segment instance objects from a query image with a few annotated examples of novel categories. Conventional approaches have attempted to address the task via prototype learning, known as point estimation. However, this mechanism depends on prototypes (\eg mean of K−shot) for prediction, leading to performance instability. To overcome the disadvantage of the point estimation mechanism, we propose a novel approach, dubbed MaskDiff, which models the underlying conditional distribution of a binary mask, which is conditioned on an object region and K−shot information. Inspired by augmentation approaches that perturb data with Gaussian noise for populating low data density regions, we model the mask distribution with a diffusion probabilistic model. We also propose to utilize classifier-free guided mask sampling to integrate category information into the binary mask generation process. Without bells and whistles, our proposed method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both base and novel classes of the COCO dataset while simultaneously being more stable than existing methods. The source code is available at: this https URL.
Researchers introduced the Camouflaged Object (CAMO) dataset and the Anabranch Network (ANet) to address the challenge of segmenting objects that blend with their surroundings. ANet integrates a classification stream to determine object presence with a segmentation stream, achieving improved accuracy over baseline models on the new datasets, particularly in realistic scenarios.
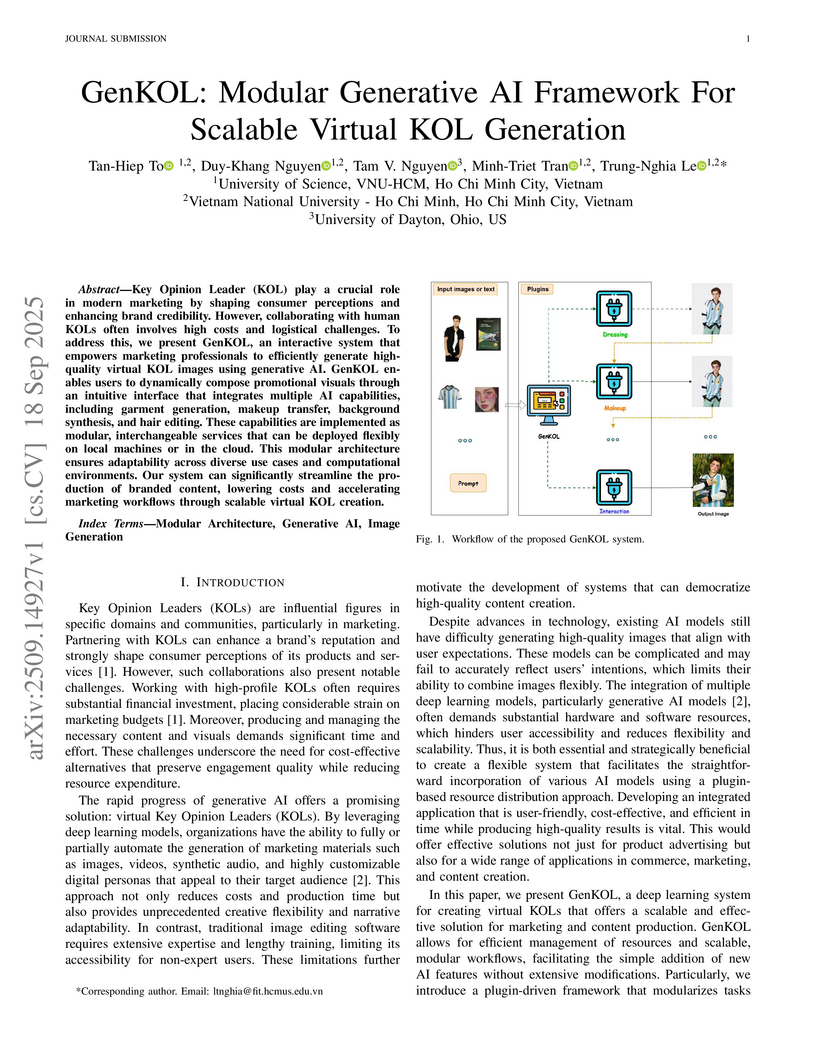
Key Opinion Leader (KOL) play a crucial role in modern marketing by shaping consumer perceptions and enhancing brand credibility. However, collaborating with human KOLs often involves high costs and logistical challenges. To address this, we present GenKOL, an interactive system that empowers marketing professionals to efficiently generate high-quality virtual KOL images using generative AI. GenKOL enables users to dynamically compose promotional visuals through an intuitive interface that integrates multiple AI capabilities, including garment generation, makeup transfer, background synthesis, and hair editing. These capabilities are implemented as modular, interchangeable services that can be deployed flexibly on local machines or in the cloud. This modular architecture ensures adaptability across diverse use cases and computational environments. Our system can significantly streamline the production of branded content, lowering costs and accelerating marketing workflows through scalable virtual KOL creation.
Automated analysis of endoscopic imagery is a critical yet underdeveloped component of ENT (ear, nose, and throat) care, hindered by variability in devices and operators, subtle and localized findings, and fine-grained distinctions such as laterality and vocal-fold state. In addition to classification, clinicians require reliable retrieval of similar cases, both visually and through concise textual descriptions. These capabilities are rarely supported by existing public benchmarks. To this end, we introduce ENTRep, the ACM Multimedia 2025 Grand Challenge on ENT endoscopy analysis, which integrates fine-grained anatomical classification with image-to-image and text-to-image retrieval under bilingual (Vietnamese and English) clinical supervision. Specifically, the dataset comprises expert-annotated images, labeled for anatomical region and normal or abnormal status, and accompanied by dual-language narrative descriptions. In addition, we define three benchmark tasks, standardize the submission protocol, and evaluate performance on public and private test splits using server-side scoring. Moreover, we report results from the top-performing teams and provide an insight discussion.
This study introduces a framework for evaluating consistency in large
language model (LLM) binary text classification, addressing the lack of
established reliability assessment methods. Adapting psychometric principles,
we determine sample size requirements, develop metrics for invalid responses,
and evaluate intra- and inter-rater reliability. Our case study examines
financial news sentiment classification across 14 LLMs (including
claude-3-7-sonnet, gpt-4o, deepseek-r1, gemma3, llama3.2, phi4, and
command-r-plus), with five replicates per model on 1,350 articles. Models
demonstrated high intra-rater consistency, achieving perfect agreement on
90-98% of examples, with minimal differences between expensive and economical
models from the same families. When validated against StockNewsAPI labels,
models achieved strong performance (accuracy 0.76-0.88), with smaller models
like gemma3:1B, llama3.2:3B, and claude-3-5-haiku outperforming larger
counterparts. All models performed at chance when predicting actual market
movements, indicating task constraints rather than model limitations. Our
framework provides systematic guidance for LLM selection, sample size planning,
and reliability assessment, enabling organizations to optimize resources for
classification tasks.
As generative AI ('GenAI') continues to evolve, educators face the challenge
of preparing students for a future where AI-assisted work is integral to
professional success. This paper introduces ChatISA, an in-house, multi-model
AI chatbot designed to support students and faculty in an Information Systems
and Analytics (ISA) department. ChatISA comprises four primary modules: Coding
Companion, Project Coach, Exam Ally, and Interview Mentor, each tailored to
enhance different aspects of the educational experience. Through iterative
development, student feedback, and leveraging open-source frameworks, we
created a robust tool that addresses coding inquiries, project management, exam
preparation, and interview readiness. The implementation of ChatISA provided
valuable insights and highlighted key challenges. Our findings demonstrate the
benefits of ChatISA for ISA education while underscoring the need for adaptive
pedagogy and proactive engagement with AI tools to fully harness their
educational potential. To support broader adoption and innovation, all code for
ChatISA is made publicly available on GitHub, enabling other institutions to
customize and integrate similar AI-driven educational tools within their
curricula.
Few-shot learning is proposed to tackle the problem of scarce training data in novel classes. However, prior works in instance-level few-shot learning have paid less attention to effectively utilizing the relationship between categories. In this paper, we exploit the hierarchical information to leverage discriminative and relevant features of base classes to effectively classify novel objects. These features are extracted from abundant data of base classes, which could be utilized to reasonably describe classes with scarce data. Specifically, we propose a novel superclass approach that automatically creates a hierarchy considering base and novel classes as fine-grained classes for few-shot instance segmentation (FSIS). Based on the hierarchical information, we design a novel framework called Soft Multiple Superclass (SMS) to extract relevant features or characteristics of classes in the same superclass. A new class assigned to the superclass is easier to classify by leveraging these relevant features. Besides, in order to effectively train the hierarchy-based-detector in FSIS, we apply the label refinement to further describe the associations between fine-grained classes. The extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on FSIS benchmarks. Code is available online.
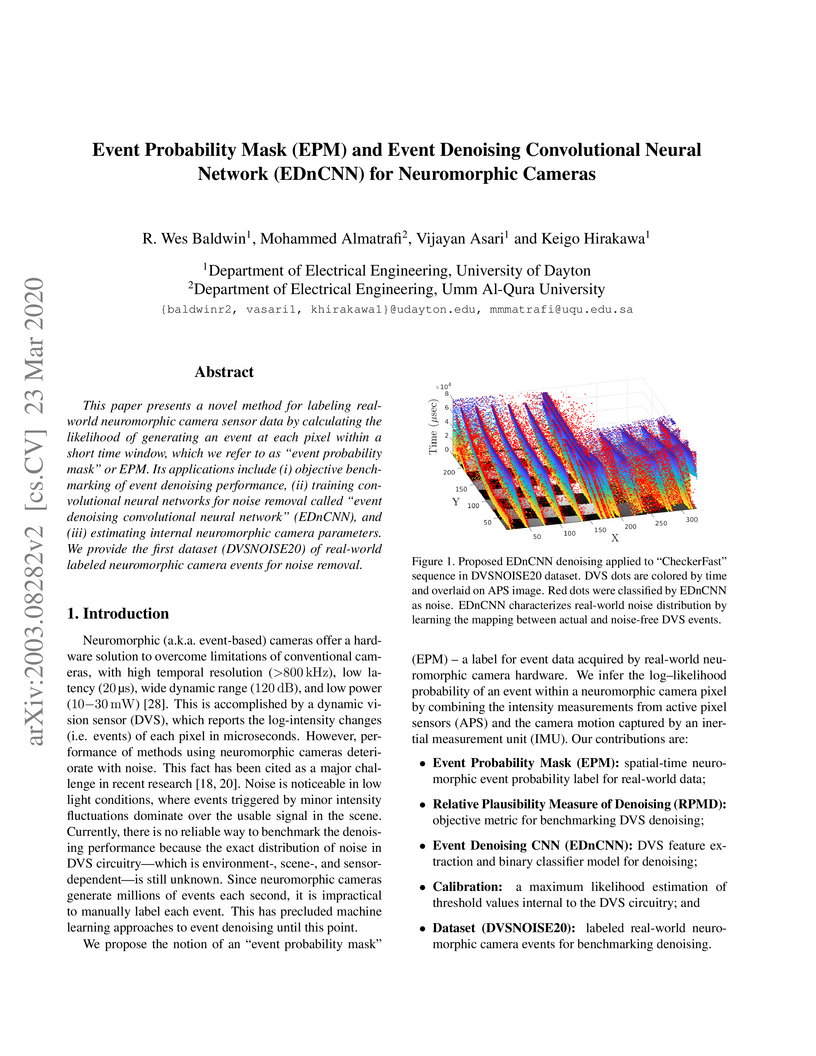
This paper presents a novel method for labeling real-world neuromorphic
camera sensor data by calculating the likelihood of generating an event at each
pixel within a short time window, which we refer to as "event probability mask"
or EPM. Its applications include (i) objective benchmarking of event denoising
performance, (ii) training convolutional neural networks for noise removal
called "event denoising convolutional neural network" (EDnCNN), and (iii)
estimating internal neuromorphic camera parameters. We provide the first
dataset (DVSNOISE20) of real-world labeled neuromorphic camera events for noise
removal.
Storytelling is a deeply personal and creative process, yet existing methods often treat users as passive consumers, offering generic plots with limited personalization. This undermines engagement and immersion, especially where individual style or appearance is crucial. We introduce TaleForge, a personalized story-generation system that integrates large language models (LLMs) and text-to-image diffusion to embed users' facial images within both narratives and illustrations. TaleForge features three interconnected modules: Story Generation, where LLMs create narratives and character descriptions from user prompts; Personalized Image Generation, merging users' faces and outfit choices into character illustrations; and Background Generation, creating scene backdrops that incorporate personalized characters. A user study demonstrated heightened engagement and ownership when individuals appeared as protagonists. Participants praised the system's real-time previews and intuitive controls, though they requested finer narrative editing tools. TaleForge advances multimodal storytelling by aligning personalized text and imagery to create immersive, user-centric experiences.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.