University of North Florida
This research systematically characterizes protoplanetary disk masses around a large sample of tight spectroscopic binaries, finding that these systems host significantly lower disk masses, reduced by approximately a factor of two, compared to single stars. The work provides robust observational evidence that tight binary companions negatively impact the reservoir of material available for planet formation.
3D object classification is a crucial problem due to its significant practical relevance in many fields, including computer vision, robotics, and autonomous driving. Although deep learning methods applied to point clouds sampled on CAD models of the objects and/or captured by LiDAR or RGBD cameras have achieved remarkable success in recent years, achieving high classification accuracy remains a challenging problem due to the unordered point clouds and their irregularity and noise. To this end, we propose a novel state-of-the-art (SOTA) 3D object classification technique that combines topological data analysis with various image filtration techniques to classify objects when they are represented using point clouds. We transform every point cloud into a voxelized binary 3D image to extract distinguishing topological features. Next, we train a lightweight one-dimensional Convolutional Neural Network (1D CNN) using the extracted feature set from the training dataset. Our framework, TACO-Net, sets a new state-of-the-art by achieving 99.05% and 99.52% accuracy on the widely used synthetic benchmarks ModelNet40 and ModelNet10, and further demonstrates its robustness on the large-scale real-world OmniObject3D dataset. When tested with ten different kinds of corrupted ModelNet40 inputs, the proposed TACO-Net demonstrates strong resiliency overall.
12 Sep 2025
 University of Toronto
University of Toronto University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign KU Leuven
KU Leuven Princeton UniversityUniversity of Colorado Boulder
Princeton UniversityUniversity of Colorado Boulder University of Virginia
University of Virginia Chalmers University of TechnologyUniversity of Wisconsin–MadisonUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoMoscow State UniversityNew Mexico State UniversityLeibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP)Universidad Católica del NorteUniversidad de La SerenaUniversity of North FloridaTexas Christian UniversityMax Planck Institut fr AstronomieUniversit
degli Studi di Firenze
Chalmers University of TechnologyUniversity of Wisconsin–MadisonUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoMoscow State UniversityNew Mexico State UniversityLeibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP)Universidad Católica del NorteUniversidad de La SerenaUniversity of North FloridaTexas Christian UniversityMax Planck Institut fr AstronomieUniversit
degli Studi di FirenzeWe present a first large-scale kinematic map of ∼50,000 young OB stars (Teff≥10,000 K), based on BOSS spectroscopy from the Milky Way Mapper OB program in the ongoing Sloan Digital Sky Survey V (SDSS-V). Using photogeometric distances, line-of-sight velocities and Gaia DR3 proper motions, we map 3D Galactocentric velocities across the Galactic plane to ∼5 kpc from the Sun, with a focus on radial motions (vR). Our results reveal mean radial motion with amplitudes of ±30 km/s that are coherent on kiloparsec scales, alternating between inward and outward motions. These vˉR amplitudes are considerably higher than those observed for older, red giant populations. These kinematic patterns show only a weak correlation with spiral arm over-densities. Age estimates, derived from MIST isochrones, indicate that 85% of the sample is younger than ∼300 Myr and that the youngest stars (≤30 Myr) align well with density enhancements. The age-dependent vˉR in Auriga makes it plausible that younger stars exhibits different velocity variations than older giants. The origin of the radial velocity features remains uncertain, and may result from a combination of factors, including spiral arm dynamics, the Galactic bar, resonant interactions, or phase mixing following a perturbation. The present analysis is based on approximately one-third of the full target sample. The completed survey will enable a more comprehensive investigation of these features and a detailed dynamical interpretation.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have made significant strides in Natural
Language Processing but remain vulnerable to fairness-related issues, often
reflecting biases inherent in their training data. These biases pose risks,
particularly when LLMs are deployed in sensitive areas such as healthcare,
finance, and law. This paper introduces a metamorphic testing approach to
systematically identify fairness bugs in LLMs. We define and apply a set of
fairness-oriented metamorphic relations (MRs) to assess the LLaMA and GPT
model, a state-of-the-art LLM, across diverse demographic inputs. Our
methodology includes generating source and follow-up test cases for each MR and
analyzing model responses for fairness violations. The results demonstrate the
effectiveness of MT in exposing bias patterns, especially in relation to tone
and sentiment, and highlight specific intersections of sensitive attributes
that frequently reveal fairness faults. This research improves fairness testing
in LLMs, providing a structured approach to detect and mitigate biases and
improve model robustness in fairness-sensitive applications.
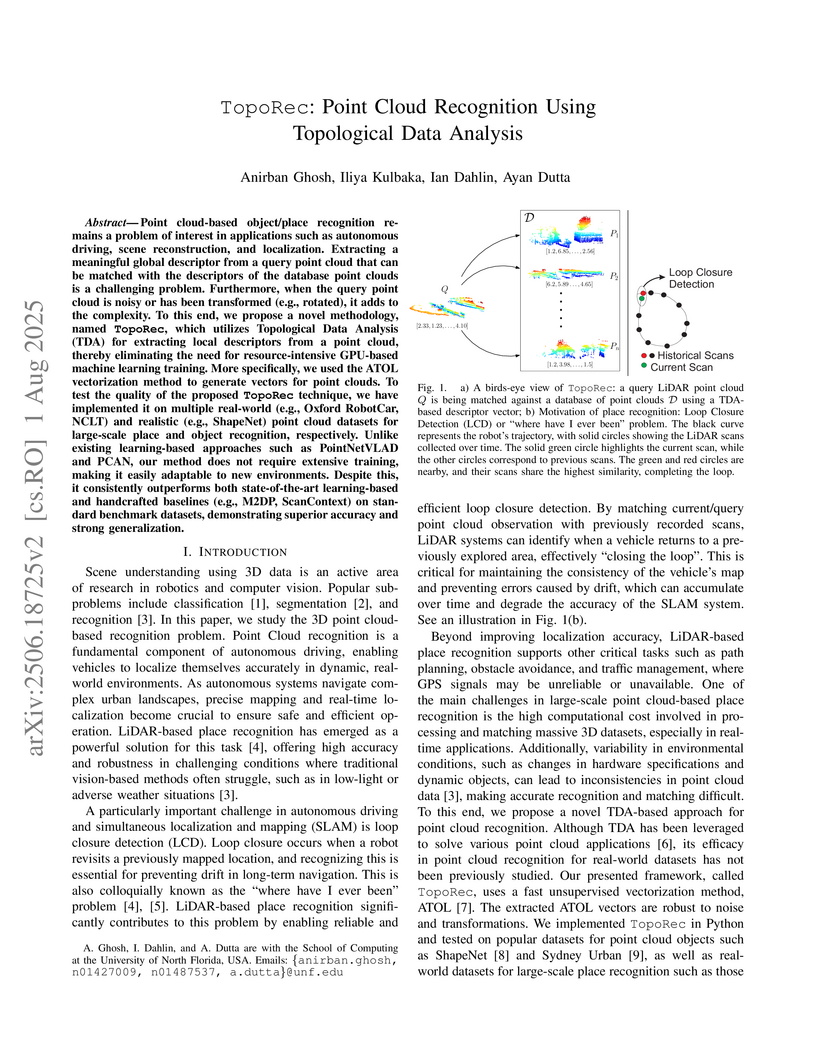
Point cloud-based object/place recognition remains a problem of interest in applications such as autonomous driving, scene reconstruction, and localization. Extracting a meaningful global descriptor from a query point cloud that can be matched with the descriptors of the database point clouds is a challenging problem. Furthermore, when the query point cloud is noisy or has been transformed (e.g., rotated), it adds to the complexity. To this end, we propose a novel methodology, named TopoRec, which utilizes Topological Data Analysis (TDA) for extracting local descriptors from a point cloud, thereby eliminating the need for resource-intensive GPU-based machine learning training. More specifically, we used the ATOL vectorization method to generate vectors for point clouds. To test the quality of the proposed TopoRec technique, we have implemented it on multiple real-world (e.g., Oxford RobotCar, NCLT) and realistic (e.g., ShapeNet) point cloud datasets for large-scale place and object recognition, respectively. Unlike existing learning-based approaches such as PointNetVLAD and PCAN, our method does not require extensive training, making it easily adaptable to new environments. Despite this, it consistently outperforms both state-of-the-art learning-based and handcrafted baselines (e.g., M2DP, ScanContext) on standard benchmark datasets, demonstrating superior accuracy and strong generalization.
This study presents the application of generative deep learning techniques to evaluate marine fog visibility nowcasting using the FATIMA (Fog and turbulence interactions in the marine atmosphere) campaign observations collected during July 2022 in the North Atlantic in the Grand Banks area and vicinity of Sable Island (SI), northeast of Canada. The measurements were collected using the Vaisala Forward Scatter Sensor model FD70 and Weather Transmitter model WXT50, and Gill R3A ultrasonic anemometer mounted on the Research Vessel Atlantic Condor. To perform nowcasting, the time series of fog visibility (Vis), wind speed, dew point depression, and relative humidity with respect to water were preprocessed to have lagged time step features. Generative nowcasting of Vis time series for lead times of 30 and 60 minutes were performed using conditional generative adversarial networks (cGAN) regression at visibility thresholds of Vis < 1 km and < 10 km. Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) was used as a baseline method for comparison against cGAN. At the 30 min lead time, Vis was best predicted with cGAN at Vis < 1 km (RMSE = 0.151 km) and with XGBoost at Vis < 10 km (RMSE = 2.821 km). At the 60 min lead time, Vis was best predicted with XGBoost at Vis < 1 km (RMSE = 0.167 km) and Vis < 10 km (RMSE = 3.508 km), but the cGAN RMSE was similar to XGBoost. Despite nowcasting Vis at 30 min being quite difficult, the ability of the cGAN model to track the variation in Vis at 1 km suggests that there is potential for generative analysis of marine fog visibility using observational meteorological parameters.
10 Dec 2021
Undergraduate physics education has greatly benefited from the introduction of computational activities. However, despite the benefits computation has delivered, we still lack a complete understanding of the computationally integrated learning experience from the student perspective. In particular, we are interested in investigating how students develop expert-like perceptions of computation as a practice within the professional physics community. To investigate this aspect of student development, we employ the Communities of Practice framework, which describes how students navigate through a professional community by appropriating the community's practices and goals as personally important. We introduce the construct of a COP-Model as a student's internal representation of a professional community that they develop as they navigate that community. We used this construct to formulate a set of research questions and semistructured interview protocols to explore how five physics students represent the use of computation in their mental models of the global physics community. We foreground these representations in the local academic community established by their instructors in three concurrent computationally integrated physics courses. We find that these students saw computation as a normal and valuable part of physics practice, identified benefits of using computation in alignment with the physics community, struggle with confidence with regards to computation, and demonstrate some expectations for computational proficiency that are misaligned with the physics community. We establish these themes with interview excerpts and discuss implications for instruction and future research.
11 Dec 2018
Digital advances have transformed the face of automatic music generation
since its beginnings at the dawn of computing. Despite the many breakthroughs,
issues such as the musical tasks targeted by different machines and the degree
to which they succeed remain open questions. We present a functional taxonomy
for music generation systems with reference to existing systems. The taxonomy
organizes systems according to the purposes for which they were designed. It
also reveals the inter-relatedness amongst the systems. This design-centered
approach contrasts with predominant methods-based surveys and facilitates the
identification of grand challenges to set the stage for new breakthroughs.
13 Nov 2023
Vanderbilt University University of Michigan
University of Michigan Boston University
Boston University MITWashington University in St. Louis
MITWashington University in St. Louis University of WarwickUniversity of Colorado BoulderJohns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory
University of WarwickUniversity of Colorado BoulderJohns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Harvard-Smithsonian Center for AstrophysicsEmbry-Riddle Aeronautical UniversityUniversity of North FloridaNational Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM)
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for AstrophysicsEmbry-Riddle Aeronautical UniversityUniversity of North FloridaNational Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM)
 University of Michigan
University of Michigan Boston University
Boston University MITWashington University in St. Louis
MITWashington University in St. Louis University of WarwickUniversity of Colorado BoulderJohns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory
University of WarwickUniversity of Colorado BoulderJohns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Harvard-Smithsonian Center for AstrophysicsEmbry-Riddle Aeronautical UniversityUniversity of North FloridaNational Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM)
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for AstrophysicsEmbry-Riddle Aeronautical UniversityUniversity of North FloridaNational Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM)One of the key research themes identified by the Astro2020 decadal survey is Worlds and Suns in Context. The Advanced X-ray Imaging Satellite (AXIS) is a proposed NASA APEX mission that will become the prime high-energy instrument for studying star-planet connections from birth to death. This work explores the major advances in this broad domain of research that will be enabled by the AXIS mission, through X-ray observations of stars in clusters spanning a broad range of ages, flaring M-dwarf stars known to host exoplanets, and young stars exhibiting accretion interactions with their protoplanetary disks. In addition, we explore the ability of AXIS to use planetary nebulae, white dwarfs, and the Solar System to constrain important physical processes from the microscopic (e.g., charge exchange) to the macroscopic (e.g., stellar wind interactions with the surrounding interstellar medium).
03 Nov 2025
We investigate the application of large language models (LLMs) to construct credit networks from firms' textual financial statements and to analyze the resulting network structures. We start with using LLMs to translate each firm's financial statement into a credit network that pertains solely to that firm. These networks are then aggregated to form a comprehensive credit network representing the whole financial system. During this process, the inconsistencies in financial statements are automatically detected and human intervention is involved. We demonstrate that this translation process is effective across financial statements corresponding to credit networks with diverse topological structures. We further investigate the reasoning capabilities of LLMs in analyzing credit networks and determining optimal strategies for executing financial operations to maximize network performance measured by the total assets of firms, which is an inherently combinatorial optimization challenge. To demonstrate this capability, we focus on two financial operations: portfolio compression and debt removal, applying them to both synthetic and real-world datasets. Our findings show that LLMs can generate coherent reasoning and recommend effective executions of these operations to enhance overall network performance.
01 Jul 2025
We introduce a nonperturbative approach to calculate the Rényi entropy of a single interval on the torus for single-character (meromorphic) conformal field theories. Our prescription uses the Wrońskian method of Mathur, Mukhi, and Sen [Nucl. Phys. B312, 15 (1989)], in which we construct differential equations for torus conformal blocks of the twist two-point function. As an illustrative example, we provide a detailed calculation of the second Rényi entropy for the E8,1 Wess-Zumino-Witten (WZW) model. We find that the Z2 cyclic orbifold of a meromorphic conformal field theory (CFT) results in a four-character CFT which realizes the toric code modular tensor category. The Z2 cyclic orbifold of the E8,1 WZW model, however, yields a three-character CFT since two of the characters coincide. We then compute the torus conformal blocks and find that the twist two-point function, and therefore the Rényi entropy, is two-periodic along each cycle of the torus. The second Rényi entropy for a single interval of the E8,1 WZW model has the universal logarithmic divergent behavior in the decompactification limit of the torus, as expected as well as the interval approaches the size of the cycle of the torus. Furthermore, we see that the q-expansion is UV finite, apart from the leading universal logarithmic divergence. We also find that there is a divergence as the size of the entangling interval approaches the cycle of the torus, suggesting that gluing two tori along an interval the size of a cycle is a singular limit.
30 Jan 2025
Context: Research software is essential for developing advanced tools and models to solve complex research problems and drive innovation across domains. Therefore, it is essential to ensure its correctness. Software testing plays a vital role in this task. However, testing research software is challenging due to the software's complexity and to the unique culture of the research software community. Aims: Building on previous research, this study provides an in-depth investigation of testing practices in research software, focusing on test case design, challenges with expected outputs, use of quality metrics, execution methods, tools, and desired tool features. Additionally, we explore whether demographic factors influence testing processes. Method: We survey research software developers to understand how they design test cases, handle output challenges, use metrics, execute tests, and select tools. Results: Research software testing varies widely. The primary challenges are test case design, evaluating test quality, and evaluating the correctness of test outputs. Overall, research software developers are not familiar with existing testing tools and have a need for new tools to support their specific needs. Conclusion: Allocating human resources to testing and providing developers with knowledge about effective testing techniques are important steps toward improving the testing process of research software. While many industrial testing tools exist, they are inadequate for testing research software due to its complexity, specialized algorithms, continuous updates, and need for flexible, custom testing approaches. Access to a standard set of testing tools that address these special characteristics will increase level of testing in research software development and reduce the overhead of distributing knowledge about software testing.
11 Jun 2025
Stellar accretion plays an important role in the early stages of stellar evolution, particularly in Classical T Tauri Stars (CTTSs). Accretion of a CTTS can be related to different physical parameters such as effective temperature (Teff), age, abundance of hydrogen, etc. We can infer how accretion works by examining it across different wavelength regions. Accretion can be traced using veiling, a parameter that measures how excess emission from accretion affects the photospheric spectrum of CTTS. In this study, we selected a sample of CTTSs, Weak-line T Tauri Stars (WTTSs), and field stars, observed as a part of the SDSS-V Milky Way Mapper using the BOSS spectrograph. We measured veiling for CTTSs through comparing them to theoretical spectra. Next, we assessed the effect of veiling on different stellar properties, including wavelength, Hα emission, effective temperature, and age. We investigated how veiling changes with these parameters and what the physical reasons behind the changes can be. Finally, we evaluated how our findings align with existing accretion shock models. This study highlights veiling as a critical diagnostic tool for understanding accretion in young stars.
22 Jul 2025
With billions of users and an immense volume of daily uploads, YouTube has become an attractive target for cybercriminals aiming to leverage its vast audience. The platform's openness and trustworthiness provide an ideal environment for deceptive campaigns that can operate under the radar of conventional security tools. This paper explores how cybercriminals exploit YouTube to disseminate malware, focusing on campaigns that promote free software or game cheats. It discusses deceptive video demonstrations and the techniques behind malware delivery. Additionally, the paper presents a new evasion technique that abuses YouTube's multilingual metadata capabilities to circumvent automated detection systems. Findings indicate that this method is increasingly being used in recent malicious videos to avoid detection and removal.
04 Nov 2024
We propose a distributed control law for a heterogeneous multi-robot coverage problem, where the robots could have different energy characteristics, such as capacity and depletion rates, due to their varying sizes, speeds, capabilities, and payloads. Existing energy-aware coverage control laws consider capacity differences but assume the battery depletion rate to be the same for all robots. In realistic scenarios, however, some robots can consume energy much faster than other robots; for instance, UAVs hover at different altitudes, and these changes could be dynamically updated based on their assigned tasks. Robots' energy capacities and depletion rates need to be considered to maximize the performance of a multi-robot system. To this end, we propose a new energy-aware controller based on Lloyd's algorithm to adapt the weights of the robots based on their energy dynamics and divide the area of interest among the robots accordingly. The controller is theoretically analyzed and extensively evaluated through simulations and real-world demonstrations in multiple realistic scenarios and compared with three baseline control laws to validate its performance and efficacy.
07 Oct 2024
Human movement analysis is crucial in health and sports biomechanics for understanding physical performance, guiding rehabilitation, and preventing injuries. However, existing tools are often proprietary, expensive, and function as "black boxes", limiting user control and customization. This paper introduces vailá-Versatile Anarcho Integrated Liberation Ánalysis in Multimodal Toolbox-an open-source, Python-based platform designed to enhance human movement analysis by integrating data from multiple biomechanical systems. vailá supports data from diverse sources, including retroreflective motion capture systems, inertial measurement units (IMUs), markerless video capture technology, electromyography (EMG), force plates, and GPS or GNSS systems, enabling comprehensive analysis of movement patterns. Developed entirely in Python 3.11.9, which offers improved efficiency and long-term support, and featuring a straightforward installation process, vailá is accessible to users without extensive programming experience. In this paper, we also present several workflow examples that demonstrate how vailá allows the rapid processing of large batches of data, independent of the type of collection method. This flexibility is especially valuable in research scenarios where unexpected data collection challenges arise, ensuring no valuable data point is lost. We demonstrate the application of vailá in analyzing sit-to-stand movements in pediatric disability, showcasing its capability to provide deeper insights even with unexpected movement patterns. By fostering a collaborative and open environment, vailá encourages users to innovate, customize, and freely explore their analysis needs, potentially contributing to the advancement of rehabilitation strategies and performance optimization.
12 Oct 2015
 CNRS
CNRS California Institute of TechnologySLAC National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversita di Pisa
California Institute of TechnologySLAC National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversita di Pisa Stanford University
Stanford University University of Maryland, College Park
University of Maryland, College Park NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Stockholm University
Stockholm University Aalto UniversityUniversity of TurkuDeutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESYICREAUniversity of IcelandHiroshima UniversityINAFClemson UniversityIstituto Nazionale di Fisica NucleareRikkyo UniversityNaval Research LaboratoryUniversit`a di Bologna
Aalto UniversityUniversity of TurkuDeutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESYICREAUniversity of IcelandHiroshima UniversityINAFClemson UniversityIstituto Nazionale di Fisica NucleareRikkyo UniversityNaval Research LaboratoryUniversit`a di Bologna University of California, Santa CruzUniversity of Maryland Baltimore CountyUniv. BordeauxCEA SaclayTuorla ObservatoryEureka Scientific Inc.University of North FloridaUniversit`a di Roma Tor VergataUniversit`a di TriesteAgenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI)Finnish Centre for Astronomy with ESO (FINCA)Universit`a degli Studi di PerugiaPurdue University CalumetUniversit`a e del Politecnico di BariUniversit\`a degli Studi di Bari Aldo MoroInstitut de Ci`encies de L’Espai (IEEC-CSIC)Centre d’Etude Spatiale des RayonnementsUniversit ́e Bordeaux 1Centre d’Etudes Nucl ́eaires de Bordeaux GradignanNYCB Real-Time Computing Inc.Universit´a di UdineLeopold-Franzens Universit¨at InnsbruckInstituto de Astrof
sica de CanariasMax-Planck-Institut f
ür RadioastronomieMax-Planck-Institut f
ur Physik`Ecole PolytechniqueUniversit
e Paris DiderotUniversita' di PadovaUniversit
´e Montpellier 2Universita' degli Studi di Torino
University of California, Santa CruzUniversity of Maryland Baltimore CountyUniv. BordeauxCEA SaclayTuorla ObservatoryEureka Scientific Inc.University of North FloridaUniversit`a di Roma Tor VergataUniversit`a di TriesteAgenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI)Finnish Centre for Astronomy with ESO (FINCA)Universit`a degli Studi di PerugiaPurdue University CalumetUniversit`a e del Politecnico di BariUniversit\`a degli Studi di Bari Aldo MoroInstitut de Ci`encies de L’Espai (IEEC-CSIC)Centre d’Etude Spatiale des RayonnementsUniversit ́e Bordeaux 1Centre d’Etudes Nucl ́eaires de Bordeaux GradignanNYCB Real-Time Computing Inc.Universit´a di UdineLeopold-Franzens Universit¨at InnsbruckInstituto de Astrof
sica de CanariasMax-Planck-Institut f
ür RadioastronomieMax-Planck-Institut f
ur Physik`Ecole PolytechniqueUniversit
e Paris DiderotUniversita' di PadovaUniversit
´e Montpellier 2Universita' degli Studi di TorinoWe report for the first time a gamma-ray and multi-wavelength nearly-periodic
oscillation in an active galactic nucleus. Using the Fermi Large Area Telescope
(LAT) we have discovered an apparent quasi-periodicity in the gamma-ray flux (E
>100 MeV) from the GeV/TeV BL Lac object PG 1553+113. The marginal significance
of the 2.18 +/-0.08 year-period gamma-ray cycle is strengthened by correlated
oscillations observed in radio and optical fluxes, through data collected in
the OVRO, Tuorla, KAIT, and CSS monitoring programs and Swift UVOT. The optical
cycle appearing in ~10 years of data has a similar period, while the 15 GHz
oscillation is less regular than seen in the other bands. Further long-term
multi-wavelength monitoring of this blazar may discriminate among the possible
explanations for this quasi-periodicity.
In this paper, we study the problem of coverage of an environment with an
energy-constrained robot in the presence of multiple charging stations. As the
robot's on-board power supply is limited, it might not have enough energy to
cover all the points in the environment with a single charge. Instead, it will
need to stop at one or more charging stations to recharge its battery
intermittently. The robot cannot violate the energy constraint, i.e., visit a
location with negative available energy. To solve this problem, we propose a
deep Q-learning framework that produces a policy to maximize the coverage and
minimize the budget violations. Our proposed framework also leverages the
memory of a recurrent neural network (RNN) to better suit this multi-objective
optimization problem. We have tested the presented framework within a 16 x 16
grid environment having charging stations and various obstacle configurations.
Results show that our proposed method finds feasible solutions and outperforms
a comparable existing technique.
Detecting spatial and temporal information of individual photons by using
single-photon-detector (SPD) arrays is critical to applications in
spectroscopy, communication, biological imaging, astronomical observation, and
quantum-information processing. Among the current SPDs1,detectors based on
superconducting nanowires have outstanding performance2, but are limited in
their ability to be integrated into large scale arrays due to the engineering
difficulty of high-bandwidth cryogenic electronic readout3-8. Here, we address
this problem by demonstrating a scalable single-photon imager using a single
continuous photon-sensitive superconducting nanowire microwave-plasmon
transmission line. By appropriately designing the nanowire's local
electromagnetic environment so that the nanowire guides microwave plasmons, the
propagating voltages signals generated by a photon-detection event were slowed
down to ~ 2% of the speed of light. As a result, the time difference between
arrivals of the signals at the two ends of the nanowire naturally encoded the
position and time of absorption of the photon. Thus, with only two readout
lines, we demonstrated that a 19.7-mm-long nanowire meandered across an area of
286 {\mu}m * 193 {\mu}m was capable of resolving ~590 effective pixels while
simultaneously recording the arrival times of photons with a temporal
resolution of 50 ps. The nanowire imager presents a scalable approach to
realizing high-resolution photon imaging in time and space.
Deterministic Rank Reduction Autoencoders (RRAEs) enforce by construction a regularization on the latent space by applying a truncated SVD. While this regularization makes Autoencoders more powerful, using them for generative purposes is counter-intuitive due to their deterministic nature. On the other hand, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) are well known for their generative abilities by learning a probabilistic latent space. In this paper, we present Variational Rank Reduction Autoencoders (VRRAEs), a model that leverages the advantages of both RRAEs and VAEs. Our claims and results show that when carefully sampling the latent space of RRAEs and further regularizing with the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence (similarly to VAEs), VRRAEs outperform RRAEs and VAEs. Additionally, we show that the regularization induced by the SVD not only makes VRRAEs better generators than VAEs, but also reduces the possibility of posterior collapse. Our results include a synthetic dataset of a small size that showcases the robustness of VRRAEs against collapse, and three real-world datasets; the MNIST, CelebA, and CIFAR-10, over which VRRAEs are shown to outperform both VAEs and RRAEs on many random generation and interpolation tasks based on the FID score. We developed an open-source implementation of VRRAEs in JAX (Equinox), available at this https URL.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.