Westlake University
Westlake University22 Sep 2025
Researchers from Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Westlake University, and Zhejiang University, along with the OpenHelix Team, introduce VLA-Adapter, an efficient method to bridge vision-language representations to robotic actions. The approach enables state-of-the-art level performance with a tiny-scale 0.5B parameter backbone without robotic data pre-training, achieving a 97.3% average success rate on the LIBERO benchmark and providing a 3x faster inference speed (219.2 Hz) than comparable methods.
TTT3R improves the length generalization of recurrent 3D reconstruction models by integrating a test-time training (TTT) approach with a confidence-aware state update rule. This method maintains constant memory and real-time inference, achieving a 2x improvement in global pose estimation accuracy for long sequences on datasets like ScanNet and TUM-D compared to prior RNN-based baselines.
LUFFY introduces a framework that enhances Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) by integrating off-policy guidance into Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR). This approach enables LRMs to acquire new reasoning capabilities from stronger external policies, achieving state-of-the-art performance on math benchmarks, superior generalization on out-of-distribution tasks, and successfully training weaker foundation models where on-policy methods fail.
30 Sep 2025
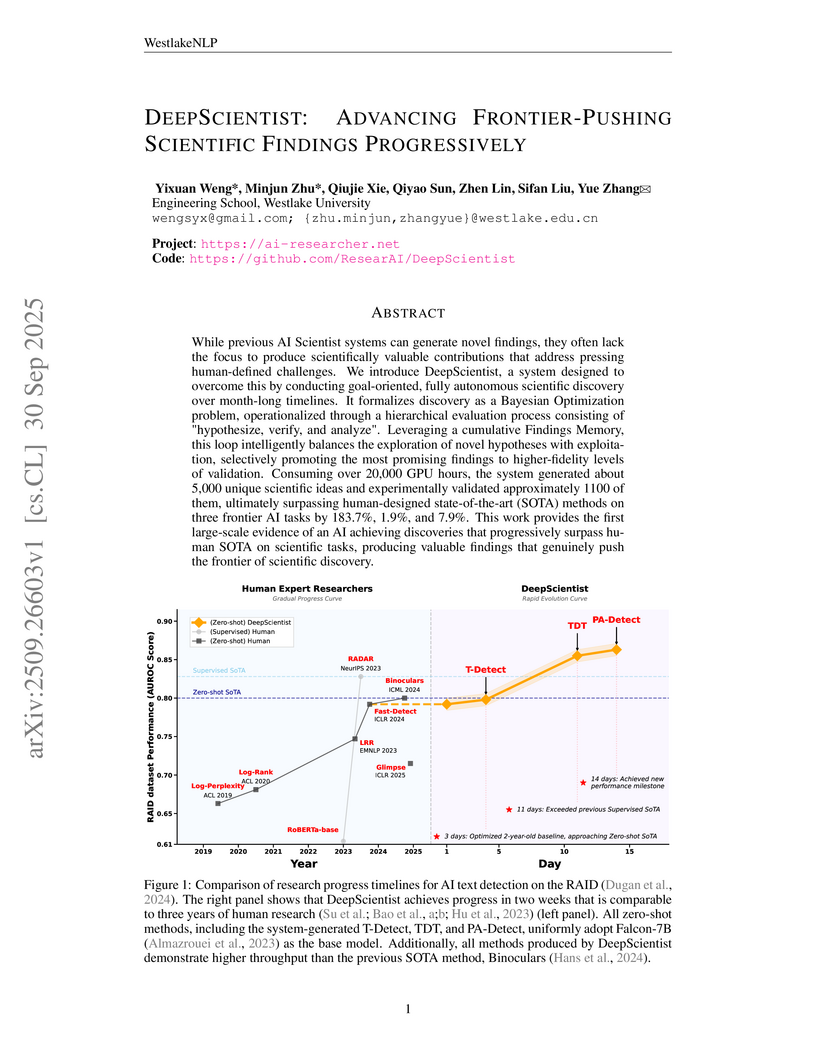
DeepScientist, developed by WestlakeNLP, is an autonomous AI system that successfully surpassed human state-of-the-art on three frontier AI tasks within a month-long cycle, including a 142.8% improvement in agent failure attribution and a 7.9% higher AUROC for AI text detection. The system employs a goal-driven Bayesian optimization approach and a multi-agent architecture to conduct large-scale, iterative scientific exploration and validate findings.
13 Oct 2025
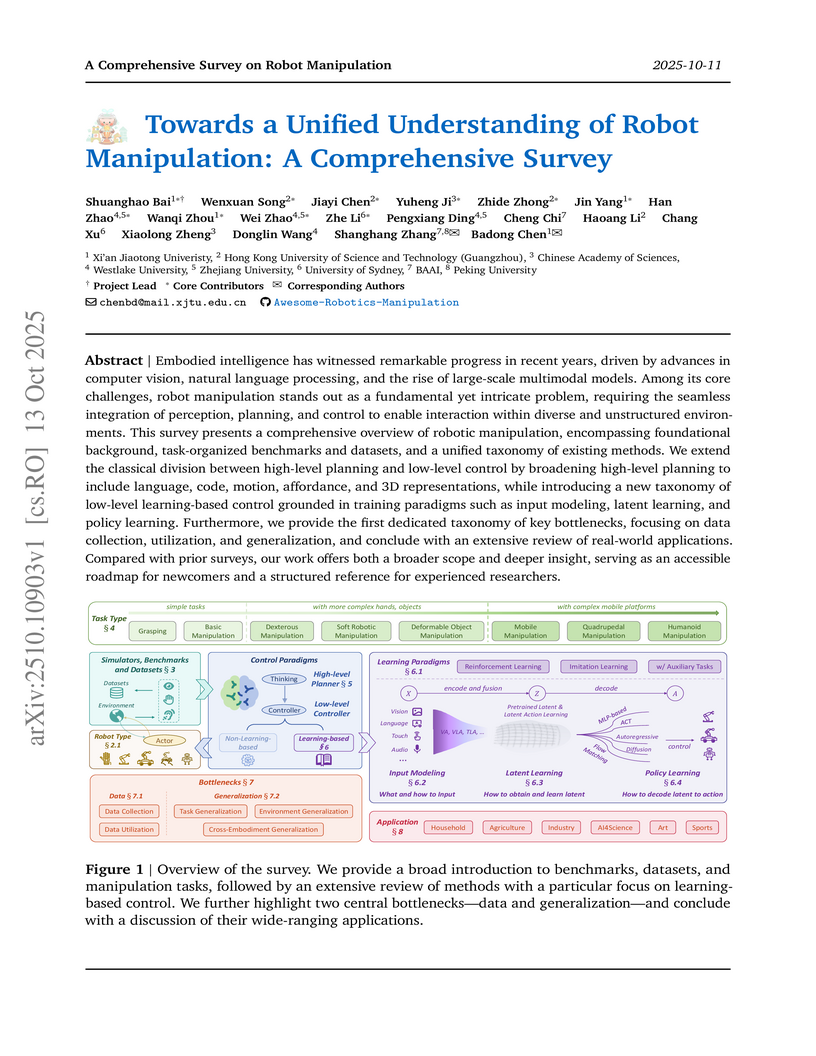
This survey synthesizes the extensive and fragmented field of robot manipulation, providing a comprehensive overview that unifies diverse methodologies and challenges under novel classification systems. It structures the landscape by introducing new taxonomies for high-level planning, low-level learning-based control, and key bottlenecks, while outlining future research directions.
HUMAN3R presents a unified, feed-forward framework for online 4D human-scene reconstruction from monocular video. The system jointly estimates multi-person global human motions, dense 3D scene geometry, and camera parameters in real-time at 15 FPS, outperforming or matching prior methods on various reconstruction benchmarks while consuming only 8 GB of GPU memory.
The notion of chiral-induced spin selectivity (CISS) has attracted intensive
research interest recently. However, the practical applications of the CISS
effects face challenges due to relatively low spin polarization. In this
Letter, we propose a non-perturbative theory illustrating how circularly
polarized (CP) light enhances CISS effects through strong light-matter
interactions. We introduce a Floquet electronic friction model to study the
nonadiabatic dynamics and spin transport through a chiral molecule in a
molecule junction subjected to external driving. Our results show that the
interplay of the nonadiabatic effects and light-matter interactions can
significantly (>90%) enhance electron spin polarization under CP light. Our
predictions can be very useful in experiments for using CP light to control
spin current in chiral molecular junctions.
Researchers from Westlake and Zhejiang Universities introduced VLA-RFT, a framework for fine-tuning Vision-Language-Action policies by interacting with a learned world model to generate verified rewards. This method enhanced robustness to environmental perturbations and improved average task success rates by 4.5 percentage points on the LIBERO benchmark with significantly fewer training iterations.
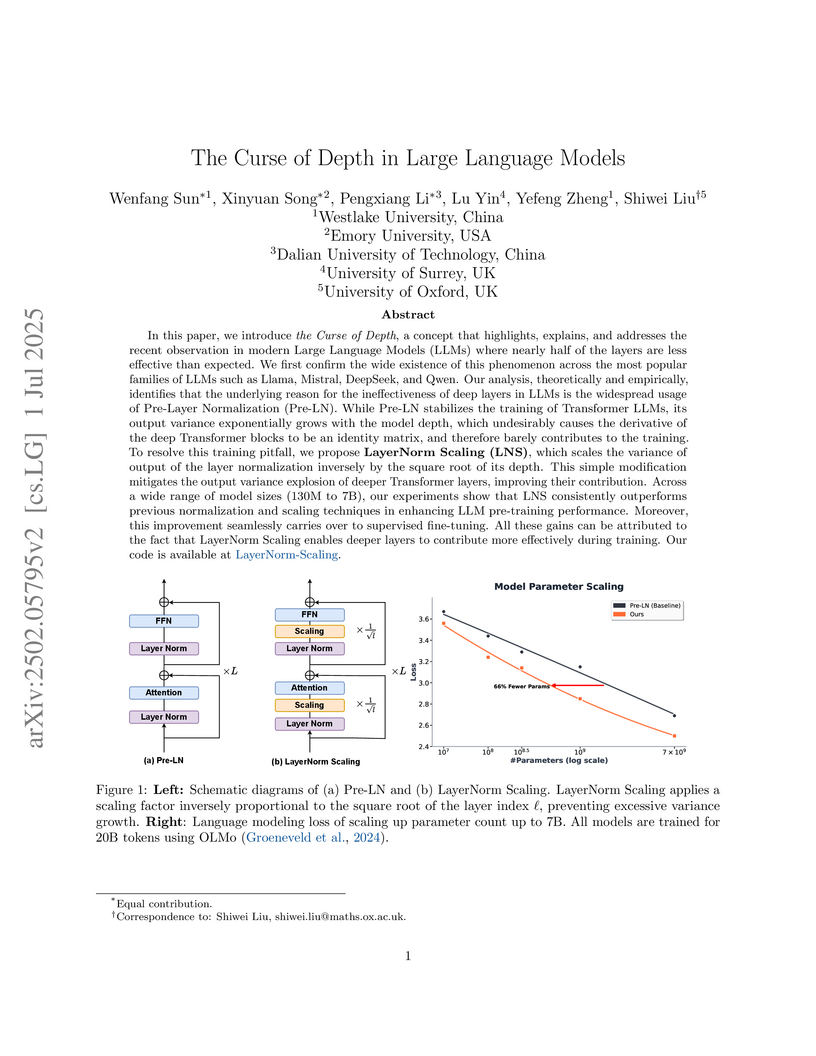
Researchers at Westlake University, Emory University, Dalian University of Technology, University of Surrey, and University of Oxford investigated the 'Curse of Depth' in large language models, demonstrating that Pre-Layer Normalization leads to exponential output variance growth, rendering deep layers ineffective. They propose LayerNorm Scaling (LNS), a hyperparameter-free method that reduces variance growth to a polynomial rate, leading to improved pre-training perplexity and an average 1.8% gain on downstream tasks across various LLM scales.
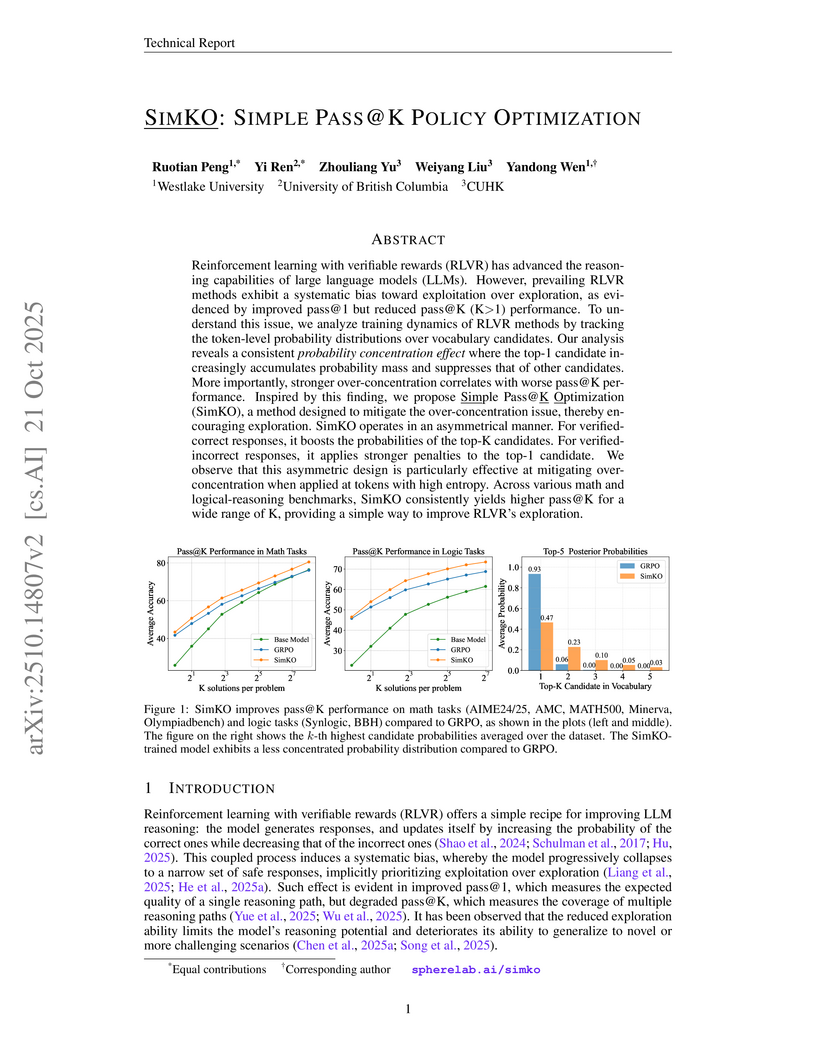
SimKO is a method that improves Large Language Models trained with Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards by mitigating a phenomenon called "probability over-concentration" during token generation. The approach employs asymmetric gradient redistribution to enhance `pass@K` performance while also improving `pass@1` on various math and logical reasoning tasks, consistently outperforming existing RLVR techniques.
WORLDFORGE presents a training-free guidance framework that enables video diffusion models to achieve precise 3D/4D camera trajectory control while preserving their pre-trained generative priors. This framework consistently outperforms existing baselines, reducing FID to 96.08 for 3D static scenes and FVD to 93.17 for 4D dynamic scenes, and supports various video post-production tasks.
A comprehensive survey systematically reviews advancements in feed-forward 3D reconstruction and view synthesis since 2020, categorizing methods by underlying scene representations such as NeRF, pointmaps, and 3D Gaussian Splatting. It details how deep learning has enabled significantly faster and more generalizable 3D vision, highlighting diverse applications and critical open research challenges.
DeepReview proposes a multi-stage framework that simulates a human expert's deep thinking process for LLM-based paper reviews, decomposing the task into novelty assessment, multi-dimensional evaluation, and reliability verification. The resulting DeepReviewer-14B model, trained on a synthesized 13K dataset, achieves notable improvements in review rating accuracy and ranking quality over larger baseline models.
This survey provides the first systematic review of multimodal long-context token compression, categorizing techniques across images, videos, and audio by both modality and algorithmic mechanism. It reveals how diverse compression strategies address the quadratic complexity of self-attention in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), improving efficiency and enabling new applications like real-time robotic perception and high-resolution medical image analysis.
WebVoyager is an end-to-end web agent framework that utilizes Large Multimodal Models to perform complex tasks by interacting directly with real-world websites. It achieved a 59.1% task success rate on a new benchmark of real-world web tasks, outperforming text-only and "All Tools" baselines, and introduces a reliable GPT-4V-powered automatic evaluation protocol.
TrustJudge introduces a probabilistic framework to systematically mitigate two fundamental inconsistencies—score-comparison and pairwise transitivity—within LLM-as-a-judge evaluation. The method significantly reduces conflict ratios and non-transitivity rates by employing distribution-sensitive scoring and likelihood-aware aggregation, while maintaining or enhancing evaluation accuracy across various large language models and tasks.
11 Oct 2025
Researchers from Zhejiang University, Ant Group, and others introduced ENVIRONMENT TUNING, a training paradigm for Large Language Model (LLM) agents that focuses on modifying the learning environment itself. This method enables agents to achieve robust generalization and stability in complex, multi-turn tool-use tasks despite extreme data scarcity, significantly boosting performance on benchmarks like BFCL V3 by up to 18.50% and improving out-of-distribution generalization where supervised fine-tuning models collapse.
Diffusion-based large language models (dLLMs) have emerged as a promising alternative to autoregressive (AR) LLMs, leveraging denoising-based generation to enable inherent parallelism. Even more and more open-sourced dLLM models emerge, yet their widespread adoption remains constrained by the lack of a standardized and efficient inference framework. We present dInfer, an efficient and extensible framework for dLLM inference. dInfer decomposes the inference pipeline into four modular components--model, diffusion iteration manager, decoding strategy, and KV-cache manager--and integrates novel algorithms for each component alongside system-level optimizations. Through this combination of algorithmic innovations and system enhancements, dInfer achieves substantial efficiency gains without compromising output quality on LLaDA-MoE. At batch size 1, it surpasses 1,100 tokens per second on HumanEval and averages over 800 tokens per second across six benchmarks on 8× H800 GPUs. Compared to prior systems, dInfer delivers a 10× speedup over Fast-dLLM while maintaining similar model performance. Even compared to the AR model (with a comparable number of activation parameters and performance) QWen2.5-3B, which is highly optimized with the latest vLLM inference engine, dInfer still delivers a 2-3× speedup. The implementation of dInfer is open-sourced at this https URL.
HoliTom introduces a training-free, holistic token merging framework for Video Large Language Models, synergistically combining outer-LLM spatio-temporal compression with inner-LLM merging. This approach reduces computational costs to 6.9% of original FLOPs while retaining 99.1% of performance and accelerating inference by 2.28 times.
Easi3R introduces a training-free framework that extracts disentangled motion from dynamic videos by interpreting the attention mechanisms of a pre-trained static 3D foundation model like DUSt3R. The method achieves state-of-the-art performance in dynamic object segmentation, camera pose estimation, and 4D reconstruction without requiring any additional training or fine-tuning on dynamic datasets.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.