Aerospace Information Research InstituteHenan Academy of Sciences
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and collaborating institutions developed InstructSAM, a training-free framework for instruction-oriented remote sensing object counting, detection, and segmentation. It combines large vision-language models, SAM2, and CLIP with a novel counting-constrained mask-label matching, enabling robust performance on diverse tasks and reducing inference time by over 32% compared to generative VLM methods.
03 Feb 2025
Gravitational-wave (GW) ringdown signals from black holes (BHs) encode crucial information about the gravitational dynamics in the strong-field regime, which offers unique insights into BH properties. In the future, the improving sensitivity of GW detectors is to enable the extraction of multiple quasi-normal modes (QNMs) from ringdown signals. However, incorporating multiple modes drastically enlarges the parameter space, posing computational challenges to data analysis. Inspired by the F-statistic method in the continuous GW searches, we develope an algorithm, dubbed as FIREFLY, for accelerating the ringdown signal analysis. FIREFLY analytically marginalizes the amplitude and phase parameters of QNMs to reduce the computational cost and speed up the full-parameter inference from hours to minutes, while achieving consistent posterior and evidence. The acceleration becomes more significant when more QNMs are considered. Rigorously based on the principle of Bayesian inference and importance sampling, our method is statistically interpretable, flexible in prior choice, and compatible with various advanced sampling techniques, providing a new perspective for accelerating future GW data analysis.
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Fudan University
Fudan University University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityAerospace Information Research InstituteInstitute of Trustworthy Embodied AI, Fudan UniversityKey Laboratory of Target Cognition and Application Technology, Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityAerospace Information Research InstituteInstitute of Trustworthy Embodied AI, Fudan UniversityKey Laboratory of Target Cognition and Application Technology, Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of SciencesResearchers from Fudan University and Shanghai Jiao Tong University established a spatial retrieval augmented autonomous driving paradigm, integrating offline geographic images to enhance autonomous vehicle robustness. This approach boosted online mapping performance by up to 11.9% mAP and reduced collision rates in planning, particularly under challenging conditions.
Landslides are among the most common natural disasters globally, posing
significant threats to human society. Deep learning (DL) has proven to be an
effective method for rapidly generating landslide inventories in large-scale
disaster areas. However, DL models rely heavily on high-quality labeled
landslide data for strong feature extraction capabilities. And landslide
detection using DL urgently needs a benchmark dataset to evaluate the
generalization ability of the latest models. To solve the above problems, we
construct a Large-scale Multi-source High-resolution Landslide Dataset (LMHLD)
for Landslide Detection based on DL. LMHLD collects remote sensing images from
five different satellite sensors across seven study areas worldwide: Wenchuan,
China (2008); Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (2011); Gorkha, Nepal (2015); Jiuzhaigou,
China (2015); Taiwan, China (2018); Hokkaido, Japan (2018); Emilia-Romagna,
Italy (2023). The dataset includes a total of 25,365 patches, with different
patch sizes to accommodate different landslide scales. Additionally, a training
module, LMHLDpart, is designed to accommodate landslide detection tasks at
varying scales and to alleviate the issue of catastrophic forgetting in
multi-task learning. Furthermore, the models trained by LMHLD is applied in
other datasets to highlight the robustness of LMHLD. Five dataset quality
evaluation experiments designed by using seven DL models from the U-Net family
demonstrate that LMHLD has the potential to become a benchmark dataset for
landslide detection. LMHLD is open access and can be accessed through the link:
this https URL This dataset provides a strong
foundation for DL models, accelerates the development of DL in landslide
detection, and serves as a valuable resource for landslide prevention and
mitigation efforts.
PolSAR data presents unique challenges due to its rich and complex characteristics. Existing data representations, such as complex-valued data, polarimetric features, and amplitude images, are widely used. However, these formats often face issues related to usability, interpretability, and data integrity. Most feature extraction networks for PolSAR are small, limiting their ability to capture features effectively. To address these issues, We propose the Polarimetric Scattering Mechanism-Informed SAM (PolSAM), an enhanced Segment Anything Model (SAM) that integrates domain-specific scattering characteristics and a novel prompt generation strategy. PolSAM introduces Microwave Vision Data (MVD), a lightweight and interpretable data representation derived from polarimetric decomposition and semantic correlations. We propose two key components: the Feature-Level Fusion Prompt (FFP), which fuses visual tokens from pseudo-colored SAR images and MVD to address modality incompatibility in the frozen SAM encoder, and the Semantic-Level Fusion Prompt (SFP), which refines sparse and dense segmentation prompts using semantic information. Experimental results on the PhySAR-Seg datasets demonstrate that PolSAM significantly outperforms existing SAM-based and multimodal fusion models, improving segmentation accuracy, reducing data storage, and accelerating inference time. The source code and datasets will be made publicly available at this https URL.
28 Sep 2025
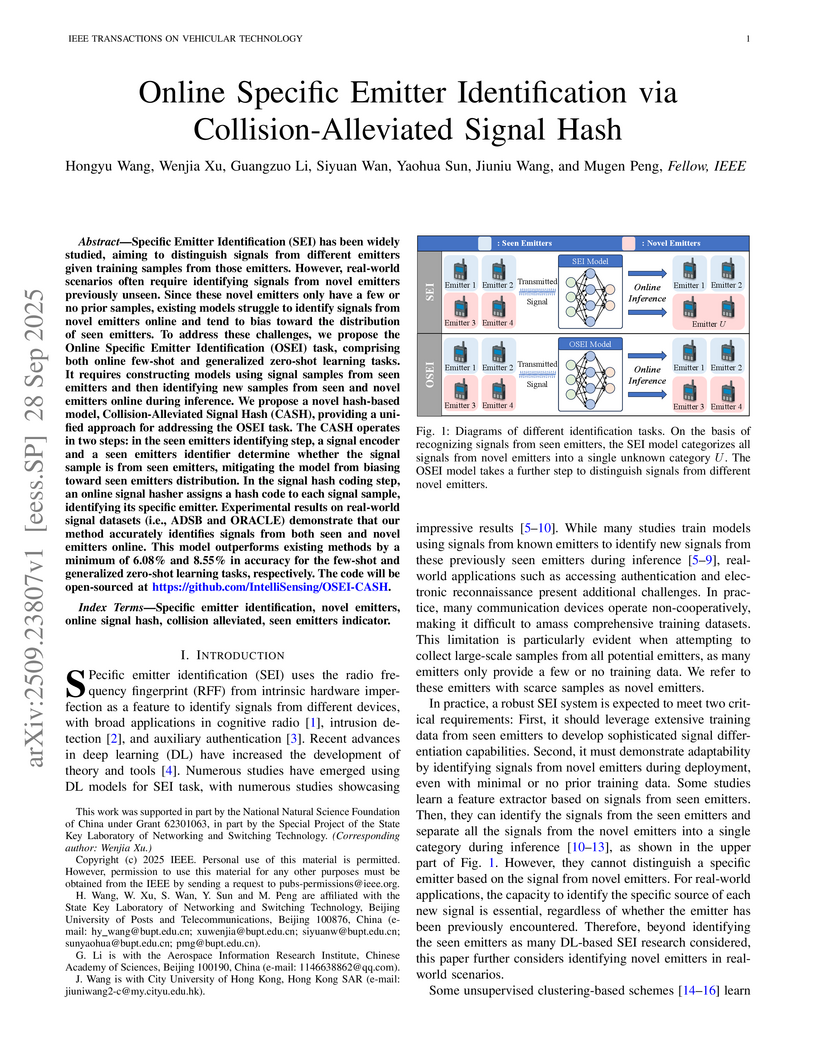
Specific Emitter Identification (SEI) has been widely studied, aiming to distinguish signals from different emitters given training samples from those emitters. However, real-world scenarios often require identifying signals from novel emitters previously unseen. Since these novel emitters only have a few or no prior samples, existing models struggle to identify signals from novel emitters online and tend to bias toward the distribution of seen emitters. To address these challenges, we propose the Online Specific Emitter Identification (OSEI) task, comprising both online \revise{few-shot and generalized zero-shot} learning tasks. It requires constructing models using signal samples from seen emitters and then identifying new samples from seen and novel emitters online during inference. We propose a novel hash-based model, Collision-Alleviated Signal Hash (CASH), providing a unified approach for addressing the OSEI task. The CASH operates in two steps: in the seen emitters identifying step, a signal encoder and a seen emitters identifier determine whether the signal sample is from seen emitters, mitigating the model from biasing toward seen emitters distribution. In the signal hash coding step, an online signal hasher assigns a hash code to each signal sample, identifying its specific emitter. Experimental results on real-world signal datasets (i.e., ADSB and ORACLE) demonstrate that our method accurately identifies signals from both seen and novel emitters online. This model outperforms existing methods by a minimum of 6.08\% and 8.55\% in accuracy for the few-shot and \revise{generalized zero-shot learning }tasks, respectively. The code will be open-sourced at \href{this https URL}{this https URL}.
Inverse problems governed by partial differential equations (PDEs) play a crucial role in various fields, including computational science, image processing, and engineering. Particularly, Darcy flow equation is a fundamental equation in fluid mechanics, which plays a crucial role in understanding fluid flow through porous media. Bayesian methods provide an effective approach for solving PDEs inverse problems, while their numerical implementation requires numerous evaluations of computationally expensive forward solvers. Therefore, the adoption of surrogate models with lower computational costs is essential. However, constructing a globally accurate surrogate model for high-dimensional complex problems demands high model capacity and large amounts of data. To address this challenge, this study proposes an efficient locally accurate surrogate that focuses on the high-probability regions of the true likelihood in inverse problems, with relatively low model complexity and few training data requirements. Additionally, we introduce a sequential Bayesian design strategy to acquire the proposed surrogate since the high-probability region of the likelihood is unknown. The strategy treats the posterior evolution process of sequential Bayesian design as a Gaussian process, enabling algorithmic acceleration through one-step ahead prior. The complete algorithmic framework is referred to as Sequential Bayesian design for locally accurate surrogate (SBD-LAS). Finally, three experiments based the Darcy flow equation demonstrate the advantages of the proposed method in terms of both inversion accuracy and computational speed.
13 Mar 2024
Recently, multiple pulsar timing array collaborations have presented
compelling evidence for a stochastic signal at nanohertz frequencies,
potentially originating from cosmic strings. Cosmic strings are linear
topological defects that can arise during phase transitions in the early
Universe or as fundamental strings in superstring theory. This paper focuses on
investigating the detection capabilities of Taiji, a planned space-based
gravitational wave detector, for the gravitational wave background generated by
cosmic strings. By analyzing simulated Taiji data and utilizing comprehensive
Bayesian parameter estimation techniques, we demonstrate a significant
improvement in precision compared to the NANOGrav 15-year data, surpassing it
by an order of magnitude. This highlights the enhanced measurement capabilities
of Taiji. Consequently, Taiji can serve as a valuable complementary tool to
pulsar timing arrays in validating and exploring the physics of cosmic strings
in the early Universe.
The cosmic distance duality relation (CDDR) is a fundamental and practical condition in observational cosmology that connects the luminosity distance and angular diameter distance. Testing its validity offers a powerful tool to probe new physics beyond the standard cosmological model. In this work, for the first time, we present a novel consistency test of CDDR by combining HII galaxy data with a comprehensive set of Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) measurements. The BAO measurements include two-dimensional (2D) BAO and three-dimensional (3D) BAO, as well as the latest 3D BAO data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) Data Release 2 (DR2). We adopt four different parameterizations of the CDDR parameter, η(z), to investigate possible deviations and their evolution with cosmic time. To ensure accurate redshift matching across datasets, we reconstruct the distance measures through a model-independent Artificial Neural Network (ANN) approach. Our analysis uniquely examines two distinct approaches: i) marginalization over the BAO sound horizon rd, and ii) fixing rd to specific values. We find no significant deviation from the CDDR (less than 68% confidence level) in either the marginalized rd or the rd=147.05 Mpc scenario. However, a slight deviation at the 68% confidence level is found when applying 2D-BAO data with rd=139.5 Mpc. Furthermore, our analysis shows that all BAO data considered in this work support the validity of the CDDR, where 3D-DESI BAO provides the tightest constraints. We find no tension between 2D and 3D BAO measurements, which confirms their mutual consistency. In addition, the treatment of the sound horizon rd significantly impacts η(z) constraints, which proves its importance in CDDR tests. Finally, the consistency of our results supports the standard CDDR and demonstrates the robustness of our analytical approach.
Vision transformers (ViTs) have been trending in image classification tasks due to their promising performance when compared to convolutional neural networks (CNNs). As a result, many researchers have tried to incorporate ViTs in hyperspectral image (HSI) classification tasks. To achieve satisfactory performance, close to that of CNNs, transformers need fewer parameters. ViTs and other similar transformers use an external classification (CLS) token which is randomly initialized and often fails to generalize well, whereas other sources of multimodal datasets, such as light detection and ranging (LiDAR) offer the potential to improve these models by means of a CLS. In this paper, we introduce a new multimodal fusion transformer (MFT) network which comprises a multihead cross patch attention (mCrossPA) for HSI land-cover classification. Our mCrossPA utilizes other sources of complementary information in addition to the HSI in the transformer encoder to achieve better generalization. The concept of tokenization is used to generate CLS and HSI patch tokens, helping to learn a {distinctive representation} in a reduced and hierarchical feature space. Extensive experiments are carried out on {widely used benchmark} datasets {i.e.,} the University of Houston, Trento, University of Southern Mississippi Gulfpark (MUUFL), and Augsburg. We compare the results of the proposed MFT model with other state-of-the-art transformers, classical CNNs, and conventional classifiers models. The superior performance achieved by the proposed model is due to the use of multihead cross patch attention. The source code will be made available publicly at \url{this https URL}.}
Strong gravitational lensing time-delay measurements, together with the distance sum rule (DSR), offer a model-independent approach to probe the geometry and expansion of the universe without relying on a fiducial cosmological model. In this work, we perform a cosmographic analysis by combining the latest Type Ia supernova datasets (PantheonPlus, DESY5, and Union3), baryon acoustic oscillation data from DESI-DR2, and updated time-delay distances from strong lensing systems. The analyses using SGL with individual SNIa datasets (SGL+PantheonPlus, SGL+DESY5, and SGL+Union3) indicate a preference for an open universe, though they remain consistent with spatially flat universe at the 95 confidence level. When DESI-DR2 data is included in each combination, the constraints tighten and shift slightly toward a closed universe, while flatness remains supported at the 68 confidence level. The best-fit values of q0 and j0 agree with ΛCDM expectations within 95 or 99 confidence depending on the dataset, whereas s0 remains weakly constrained in all cases. This work is the first in a series of two companion papers on cosmography with DESI-DR2 and strong lensing.
02 Oct 2025
Zhengzhou UniversityHenan Academy of SciencesZhengzhou University of Light IndustryChangchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of SciencesInstitute of Quantum Materials and Physics, Henan Academy of SciencesHenan Key Laboratory of Diamond Materials and DevicesSchool of Electronics and Information, Academy for Quantum Science and Technology, Zhengzhou University of Light IndustryState Key Laboratory of Luminescence and Applications, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Fiber-integrated nitrogen-vacancy (NV) magnetometers possess high sensitivity, integration, and flexibility, and thus have been explored extensively for industrial applications. While most studies have focused on the optimization of the quantum sensing head, less attention has been paid to the frequently employed professional, expensive, and bulky electronics, which hinder their practical applications. In this article, we fabricate a fiber-integrated NV magnetometer and develop a low-cost microcontroller-based software lock-in technique. In this technique, a microcontroller coordinates efficiently a microwave source chip and an analog-to-digital converter, and a program mimicking the lock-in mechanism realizes microwave frequency-modulated optically detected magnetic resonance of NV centers. As a result, with our setup and technique, we have realized the detection of weak magnetic field with a sensitivity of 93 nT/Hz^{1/2}, which is comparable to what obtained with bulky and professional devices. Furthermore, we demonstrated real-time magnetic field detection, achieving a standard deviation of 488 nT. Our work provides a novel and cost-effective technique for electronic miniaturization, thereby potentially accelerating the industrial application of NV magnetometers.
In a previous paper arXiv:2507.21691, we have carried out one-loop renormalization of the type-I seesaw model in the modified minimal-subtraction (MS) scheme. In the present one, we continue to renormalize the type-I seesaw model in the on-shell scheme. Such an investigation is mainly motivated by the fact that the on-shell scheme has been widely adopted in the renormalization of the standard electroweak theory and implemented for its precision tests. We first specify the physical parameters in the on-shell scheme, and then fix the corresponding counterterms through on-shell renormalization conditions. In the presence of massive Majorana neutrinos, we propose a practical method to determine gauge-independent counterterms for the lepton flavor mixing matrix. With the explicit counterterms in both the MS and on-shell schemes, we establish the matching relations of the electric charge, physical masses and flavor mixing matrix elements between these two schemes. Our results in the present and previous papers lay the foundation for precision calculations in the type-I seesaw model.
23 Feb 2025
Much research effort has been devoted to interfacial or two-dimensional (2D)
superconductors, but the underlying pairing mechanisms and pairing symmetries
are highly controversial in most cases. Here we propose an innovative approach
to probe the pairing symmetry of 2D superconductors, based on a van der Waals
heterostructure consisting of a prototypical 2D Ising superconductor coupled
with a 2D hole gas through an insulating spacer. We first show that, by tuning
the Coulomb attraction between the superconducting and hole layers, the gap of
the corresponding indirect exciton insulators is tuned as well, resulting in
contrasting manifestations of the distinct superconducting channels with
spin-singlet (s-, extended s-, and d-wave) and spin-triplet (p- and f-wave)
pairings. Strikingly, we find that the application of in-plane magnetic fields
can suppress all other channels while selecting the spin-triplet p-wave channel
to be the pure superconducting state, thus providing an ideal and practical
platform for realizing highly desirable topological superconductivity. Such an
approach can also be readily extended to other types of superconducting
systems, offering unprecedented opportunities to probe the microscopic
mechanisms of unconventional superconductivity.
20 May 2025
We derive the kinematic numerator factors for heavy-mass effective field
theory from the field theory limit of the string theory vertex operator
kinematic algebra introduced in arXiv:1806.09584. The kinematic numerators are
derived as correlators of nested commutators of gluon vertex operators
evaluated between massive tachyonic vertex operators. The resulting numerators
are given by products of structure constants of the vertex operator algebra
which yield gauge invariant expressions. The computation of the nested
commutators leads to a natural organisation in the form of rooted trees,
endowed with an order that facilitates the enumeration of the various
contributions. This kinematic algebra gives a string theory understanding of
the field theory fusion rules for constructing the heavy-mass effective field
theory numerator of arXiv:2104.11206 and arXiv:2111.15649.
Northwestern Polytechnical University Chinese Academy of SciencesChongqing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsAerospace Information Research InstituteAerospace Information Research Institute, CASShenzhen Research Institute of Northwestern Polytechnical UniversityAerospace Information Technology UniversitySuzhou Aerospace Information Research InstituteNational Key Laboratory of Microwave Imaging
Chinese Academy of SciencesChongqing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsAerospace Information Research InstituteAerospace Information Research Institute, CASShenzhen Research Institute of Northwestern Polytechnical UniversityAerospace Information Technology UniversitySuzhou Aerospace Information Research InstituteNational Key Laboratory of Microwave Imaging
 Chinese Academy of SciencesChongqing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsAerospace Information Research InstituteAerospace Information Research Institute, CASShenzhen Research Institute of Northwestern Polytechnical UniversityAerospace Information Technology UniversitySuzhou Aerospace Information Research InstituteNational Key Laboratory of Microwave Imaging
Chinese Academy of SciencesChongqing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsAerospace Information Research InstituteAerospace Information Research Institute, CASShenzhen Research Institute of Northwestern Polytechnical UniversityAerospace Information Technology UniversitySuzhou Aerospace Information Research InstituteNational Key Laboratory of Microwave ImagingResearchers from Northwestern Polytechnical University developed KINN, a Knowledge-Informed Neural Network, to address the representation trilemma in complex-valued Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) image recognition. The model achieved state-of-the-art accuracy with significantly fewer parameters, demonstrating strong generalization and tangible interpretability in data-scarce and out-of-distribution scenarios.
15 Apr 2025
Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) are highly energetic millisecond-duration astrophysical phenomena typically categorized as repeaters or non-repeaters. However, observational limitations may result in misclassifications, potentially leading to a higher proportion of repeaters than currently identified. In this study, we leverage unsupervised machine learning techniques to classify FRBs using data from the CHIME/FRB catalogs, including both the first catalog and a recent repeater catalog. By employing Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for dimensionality reduction and clustering algorithms (k-means and Hierarchical Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise), we successfully segregate repeaters and non-repeaters into distinct clusters, identifying over 100 potential repeater candidates. Our analysis reveals several empirical relations within the clusters, including the logΔtsc−logΔtrw, logΔtsc−logTB, and r−γ correlations, where Δtsc,Δtrw,TB,r,γ represent scattering time, rest-frame width, brightness temperature, spectral running, and spectral index, respectively. The Chow test results reveal that while some repeaters and non-repeaters share similar empirical relationships, the overall distinctions between the two groups remain significant, reinforcing the classification of FRBs into repeaters and non-repeaters. These findings provide new insights into the physical properties and emission mechanisms of FRBs. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of unsupervised learning in classifying FRBs and identifying potential repeaters, paving the way for more precise investigations into their origins and applications in cosmology. Future improvements in observational data and machine learning methodologies are expected to further enhance our understanding of FRBs.
Any-shot image classification allows to recognize novel classes with only a
few or even zero samples. For the task of zero-shot learning, visual attributes
have been shown to play an important role, while in the few-shot regime, the
effect of attributes is under-explored. To better transfer attribute-based
knowledge from seen to unseen classes, we argue that an image representation
with integrated attribute localization ability would be beneficial for
any-shot, i.e. zero-shot and few-shot, image classification tasks. To this end,
we propose a novel representation learning framework that jointly learns
discriminative global and local features using only class-level attributes.
While a visual-semantic embedding layer learns global features, local features
are learned through an attribute prototype network that simultaneously
regresses and decorrelates attributes from intermediate features. Furthermore,
we introduce a zoom-in module that localizes and crops the informative regions
to encourage the network to learn informative features explicitly. We show that
our locality augmented image representations achieve a new state-of-the-art on
challenging benchmarks, i.e. CUB, AWA2, and SUN. As an additional benefit, our
model points to the visual evidence of the attributes in an image, confirming
the improved attribute localization ability of our image representation. The
attribute localization is evaluated quantitatively with ground truth part
annotations, qualitatively with visualizations, and through well-designed user
studies.
22 Oct 2025
Elucidating the catalytic descriptor that accurately characterizes the structure-activity relationships of typical catalysts for various important heterogeneous catalytic reactions is pivotal for designing high-efficient catalytic systems. Here, an interpretable machine learning technique was employed to identify the key determinants governing the nitrate reduction reaction (NO3RR) performance across 286 single-atom catalysts (SACs) with the active sites anchored on double-vacancy BC3 monolayers. Through Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) analysis with reliable predictive accuracy, we quantitatively demonstrated that, favorable NO3RR activity stems from a delicate balance among three critical factors: low NV, moderate DN, and specific doping patterns. Building upon these insights, we established a descriptor (ψ) that integrates the intrinsic catalytic properties and the intermediate O-N-H angle (θ), effectively capturing the underlying structure-activity relationship. Guided by this, we further identified 16 promising catalysts with predicted low limiting potential (UL). Importantly, these catalysts are composed of cost-effective non-precious metal elements and are predicted to surpass most reported catalysts, with the best-performing Ti-V-1N1 is predicted to have an ultra-low UL of −0.10 V.
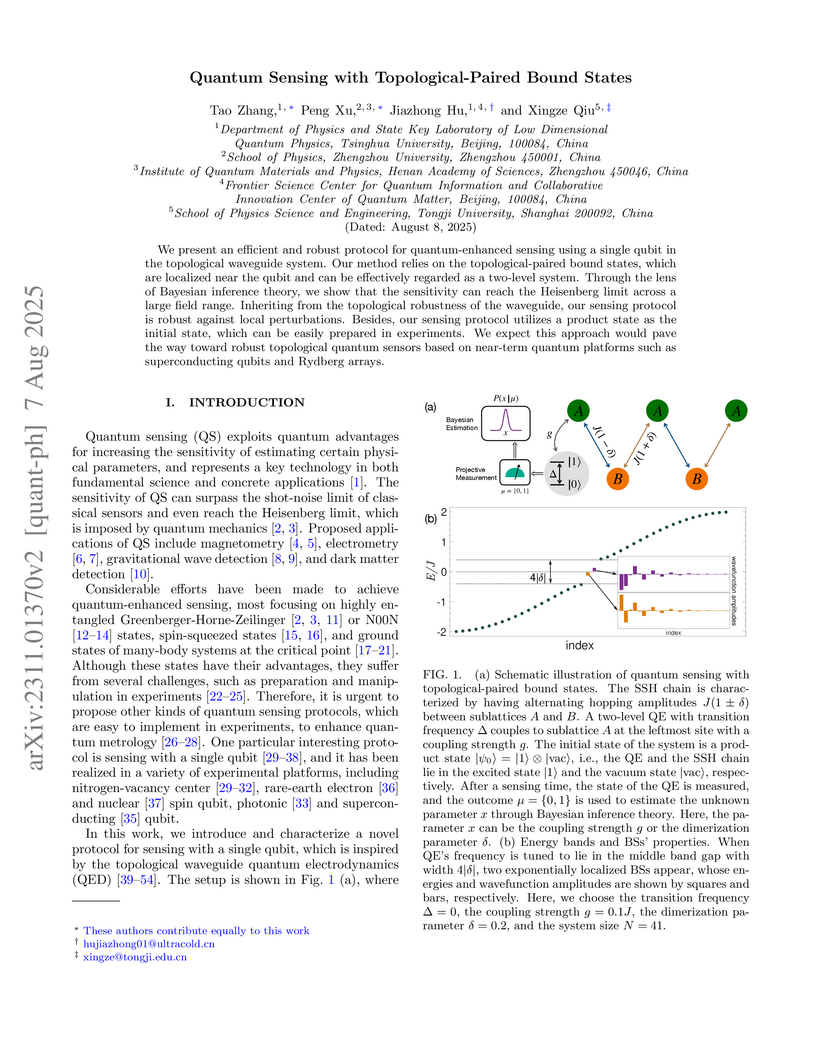
We present an efficient and robust protocol for quantum-enhanced sensing using a single qubit in the topological waveguide system. Our method relies on the topological-paired bound states, which are localized near the qubit and can be effectively regarded as a two-level system. Through the lens of Bayesian inference theory, we show that the sensitivity can reach the Heisenberg limit across a large field range. Inheriting from the topological robustness of the waveguide, our sensing protocol is robust against local perturbations. Besides, our sensing protocol utilizes a product state as the initial state, which can be easily prepared in experiments. We expect this approach would pave the way toward robust topological quantum sensors based on near-term quantum platforms such as superconducting qubits and Rydberg arrays.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.