Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications
Researchers at Beijing Language and Culture University, Tsinghua University, and collaborators introduce OMGEval, the first open-source multilingual generative evaluation benchmark that incorporates explicit cultural localization. This benchmark highlights a substantial performance gap between proprietary models like GPT-4 and open-source LLMs in understanding and generating culturally nuanced text across Chinese, Russian, French, Spanish, and Arabic.
22 Sep 2025
Researchers from Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Westlake University, and Zhejiang University, along with the OpenHelix Team, introduce VLA-Adapter, an efficient method to bridge vision-language representations to robotic actions. The approach enables state-of-the-art level performance with a tiny-scale 0.5B parameter backbone without robotic data pre-training, achieving a 97.3% average success rate on the LIBERO benchmark and providing a 3x faster inference speed (219.2 Hz) than comparable methods.
LightRAG integrates graph structures into text indexing and uses a dual-level retrieval paradigm to enhance Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. This approach improves contextual understanding, response diversity, retrieval efficiency, and adaptability to new data compared to existing RAG methods.
06 Dec 2025
 Monash UniversityCSIRO
Monash UniversityCSIRO Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University University of Manchester
University of Manchester Beihang University
Beihang University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology
ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology Beijing Jiaotong University
Beijing Jiaotong University Huawei
Huawei Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield
Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOM
TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOMA comprehensive synthesis of Large Language Models for automated software development covers the entire model lifecycle, from data curation to autonomous agents, and offers practical guidance derived from empirical experiments on pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, alongside a detailed analysis of challenges and future directions.
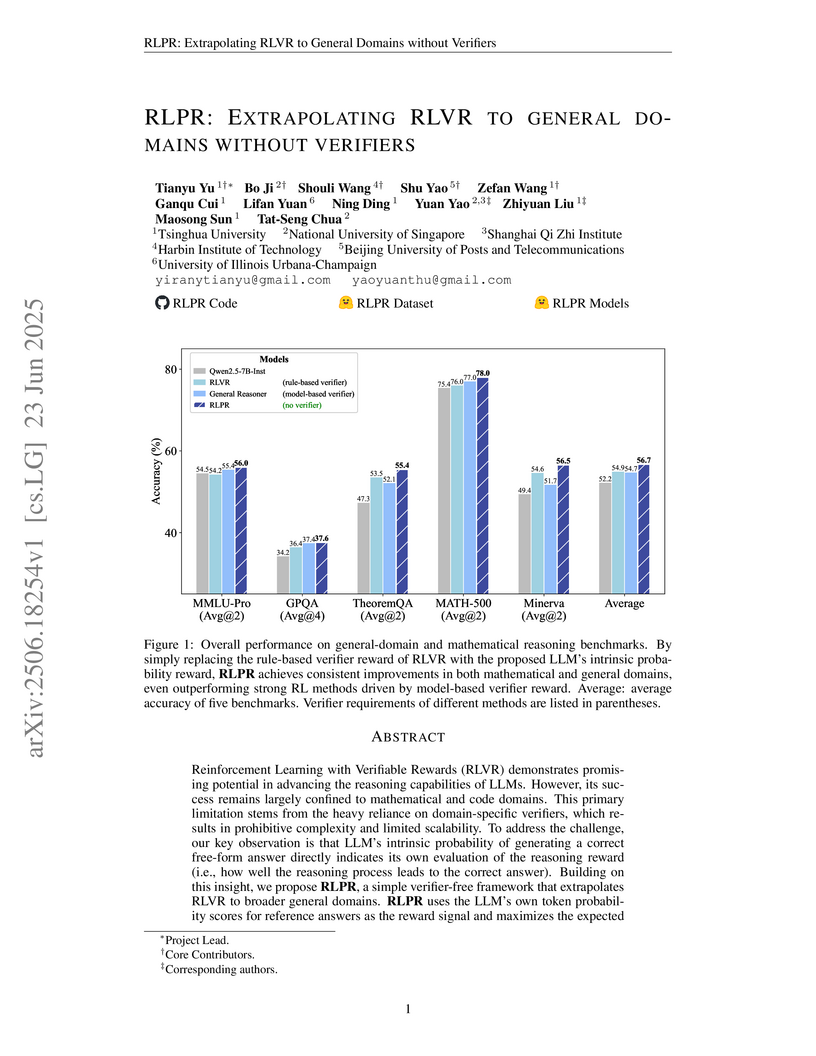
Researchers from Tsinghua University and NUS developed RLPR, a verifier-free reinforcement learning framework that enhances Large Language Model reasoning across general domains by using an intrinsic probability-based reward. This method achieved an average 24.9% improvement on general-domain benchmarks and consistently outperformed existing RLVR and concurrent verifier-free approaches by removing the need for external verification.
V-Thinker introduces a framework that empowers Large Multimodal Models with interactive, vision-centric reasoning capabilities by enabling them to autonomously modify and reflect on an image's visual state through code-driven tools. The system achieves an average accuracy improvement of 14.6% over baseline models on the new VTBench benchmark for interactive reasoning.
21 Oct 2025
Researchers from Tsinghua University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Siemens, and Tencent Robotics X developed "Puppeteer," a multi-agent framework that uses a centralized, learnable orchestrator to dynamically coordinate LLM-based agents. This approach, building on previous ChatDev work, achieves superior performance and reduced computational costs by adaptively evolving agent interaction topologies across diverse reasoning and generative tasks.
04 Oct 2025
Researchers at BIGAI and UniTree Robotics developed a unified policy for legged robots to control both position and contact force without relying on external force sensors. This policy enhanced imitation learning by generating force-aware data, leading to a 39.5% improvement in success rates for contact-rich manipulation tasks on quadrupedal and humanoid robots.
02 Oct 2025
Large language models (LLMs) have recently demonstrated strong capabilities as autonomous agents, showing promise in reasoning, tool use, and sequential decision-making. While prior benchmarks have evaluated LLM agents in domains such as software engineering and scientific discovery, the finance domain remains underexplored, despite its direct relevance to economic value and high-stakes decision-making. Existing financial benchmarks primarily test static knowledge through question answering, but they fall short of capturing the dynamic and iterative nature of trading. To address this gap, we introduce StockBench, a contamination-free benchmark designed to evaluate LLM agents in realistic, multi-month stock trading environments. Agents receive daily market signals -- including prices, fundamentals, and news -- and must make sequential buy, sell, or hold decisions. Performance is assessed using financial metrics such as cumulative return, maximum drawdown, and the Sortino ratio. Our evaluation of state-of-the-art proprietary (e.g., GPT-5, Claude-4) and open-weight (e.g., Qwen3, Kimi-K2, GLM-4.5) models shows that while most LLM agents struggle to outperform the simple buy-and-hold baseline, several models demonstrate the potential to deliver higher returns and manage risk more effectively. These findings highlight both the challenges and opportunities in developing LLM-powered financial agents, showing that excelling at static financial knowledge tasks does not necessarily translate into successful trading strategies. We release StockBench as an open-source resource to support reproducibility and advance future research in this domain.
30 May 2025
MemoryOS, developed by researchers at Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications and Tencent AI Lab, proposes a comprehensive operating system-inspired framework to manage long-term memory for AI agents, overcoming LLMs' context window limitations. This system significantly improves conversational coherence and personalization, achieving up to 49.11% F1 score improvement on ultra-long dialogues while reducing LLM calls by over 60% compared to baseline methods.
Time-R1 presents a reinforcement learning (RL) post-training framework for Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) to enhance temporal video grounding (TVG). The approach achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot performance on TVG benchmarks like Charades-STA and ActivityNet, demonstrating improved generalization and data efficiency by leveraging only 2.5K RL training samples.
09 Oct 2025
Kimi-Dev, an open-source 72B code LLM developed by Moonshot AI and academic collaborators, demonstrates that Agentless training can effectively serve as a structured skill prior to enhance multi-turn SWE-Agents. This approach achieves a state-of-the-art 60.4% resolve rate on SWE-bench Verified in Agentless mode and a competitive 48.6% pass@1 in agentic mode after minimal fine-tuning, while showing strong generalization to diverse benchmarks.
01 Nov 2025
Long-video understanding~(LVU) is a challenging problem in computer vision. Existing methods either downsample frames for single-pass reasoning, sacrificing fine-grained details, or depend on textual reasoning over task-agnostic representations, hindering task-specific perception and exploration. In this paper, we propose VideoExplorer, a framework grounded in the principle of ``thinking with video'', which naturally intertwines planning, temporal grounding, and scalable perception into a coherent reasoning process. Rather than reasoning over a static context, VideoExplorer iteratively formulates sub-questions, locates relevant moments, and performs task-oriented, temporally scalable video understanding until reaching the final answer, enabling faithful, efficient, and interpretable reasoning. To address the lack of LVU training resources, we construct a long-video reasoning dataset using difficulty-adaptive sampling to ensure high-quality trajectories on complex tasks. Building on this dataset, we design a two-stage training pipeline: supervised trajectory initialization followed by trajectory-level preference optimization, encouraging adaptive temporal grounding and iterative information integration guided by downstream rewards. Extensive evaluations on popular long-video understanding and reasoning benchmarks demonstrate VideoExplorer's significant advantage over existing baselines, highlighting its robustness, adaptability, and efficiency. Our code is made publicly available in this repository(this https URL).
29 Jul 2025
GRAPH-R1 introduces an agentic GraphRAG framework that employs end-to-end reinforcement learning for multi-turn interaction with lightweight knowledge hypergraphs. This approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across various RAG benchmarks, improving reasoning accuracy, retrieval efficiency, and generation quality while demonstrating strong out-of-distribution generalizability.
Researchers from Alibaba Group and USTC developed Live Avatar, an algorithm-system co-designed framework for real-time, high-fidelity, and infinite-length audio-driven avatar generation using a 14-billion-parameter diffusion model. The system achieves 20.88 FPS and demonstrates visual consistency for over 10,000 seconds, significantly advancing practical applications.
Researchers from Tsinghua University developed ChatDev, a chat-powered framework that enables specialized Large Language Model agents to collaboratively create software from design to testing using multi-turn dialogues. This framework produced software with an executability score of 0.8800 and a quality score of 0.3953 on the SRDD dataset, outperforming single-agent and statically-instructed multi-agent baselines.
The MM-HELIX framework evaluates and enhances multimodal large language models' long-chain reflective reasoning through a novel benchmark and an adaptive hybrid policy optimization strategy. This approach achieved an 18.6% accuracy improvement on its own benchmark and a 5.7% gain in generalization across other mathematical and logic tasks.
Researchers from Tsinghua University and Zhipu AI introduce ImageReward, a general-purpose human preference reward model, and Reward Feedback Learning (ReFL), a method for directly optimizing text-to-image diffusion models. ImageReward accurately predicts human aesthetic and alignment preferences, while ReFL leverages this feedback to improve generated image quality and human alignment.
25 Aug 2025
RepoMaster: Autonomous Exploration and Understanding of GitHub Repositories for Complex Task Solving
RepoMaster: Autonomous Exploration and Understanding of GitHub Repositories for Complex Task Solving
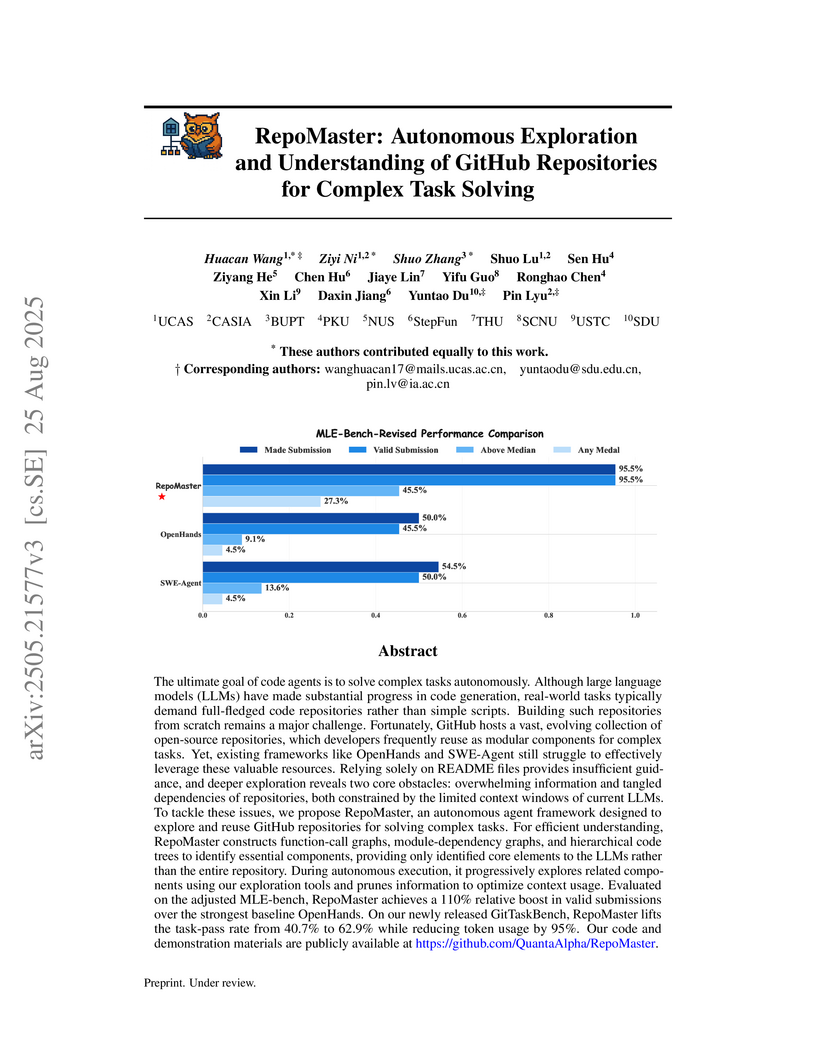
RepoMaster enables LLM-based agents to autonomously explore and understand complex GitHub repositories for task solving by intelligently reusing and adapting existing codebases. It significantly improves task success rates by up to 110% and reduces token consumption by approximately 95% compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
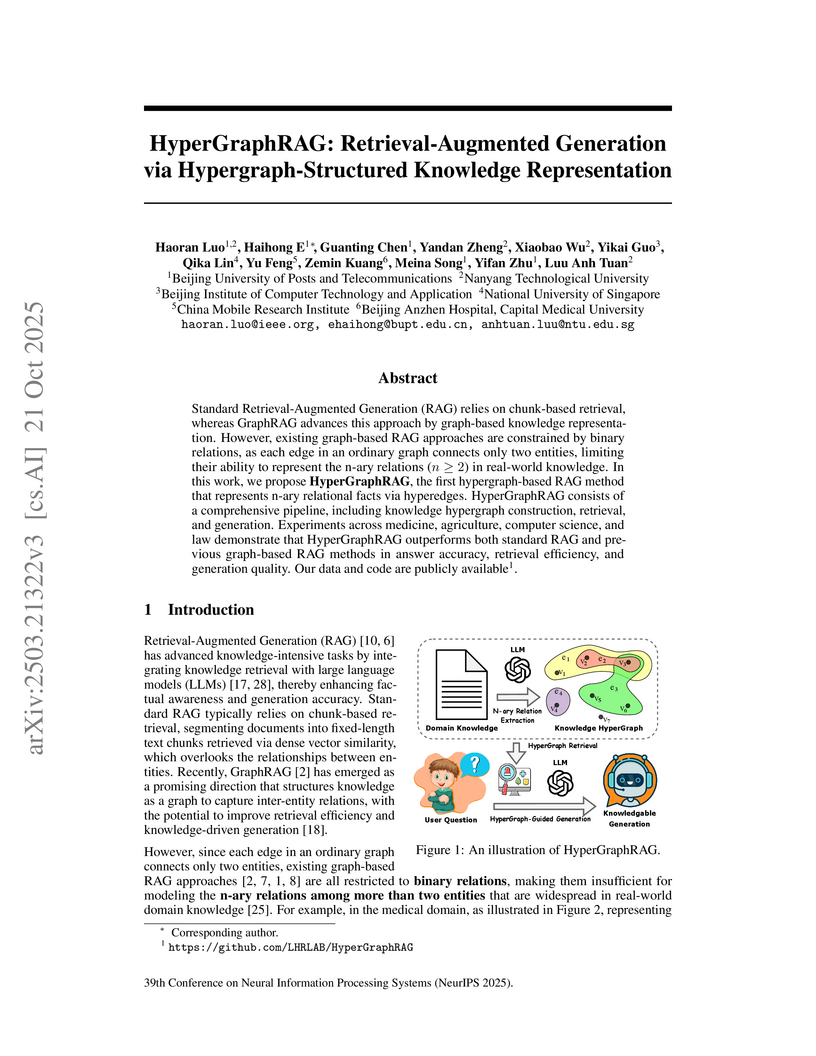
HyperGraphRAG introduces a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system that represents knowledge using hypergraphs to capture complex n-ary relations. The method consistently outperforms existing binary graph-based RAGs and standard RAG across diverse knowledge-intensive domains, demonstrating improvements in answer accuracy, retrieval relevance, and generation quality.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.