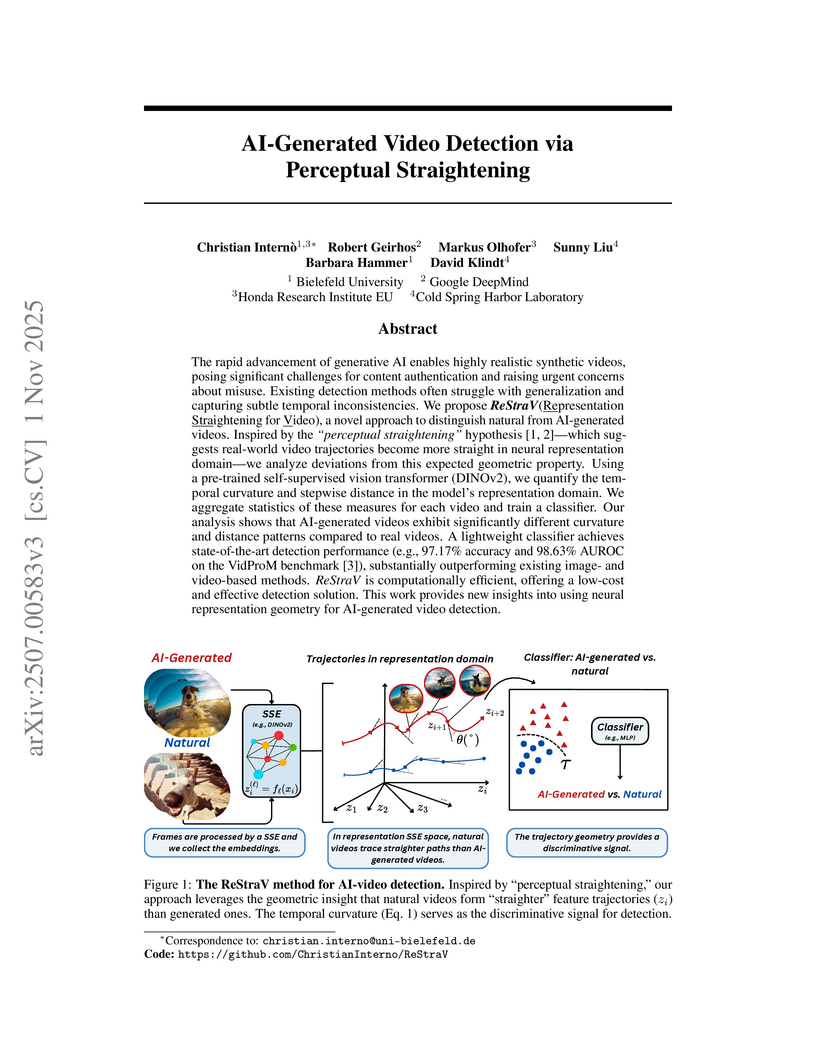
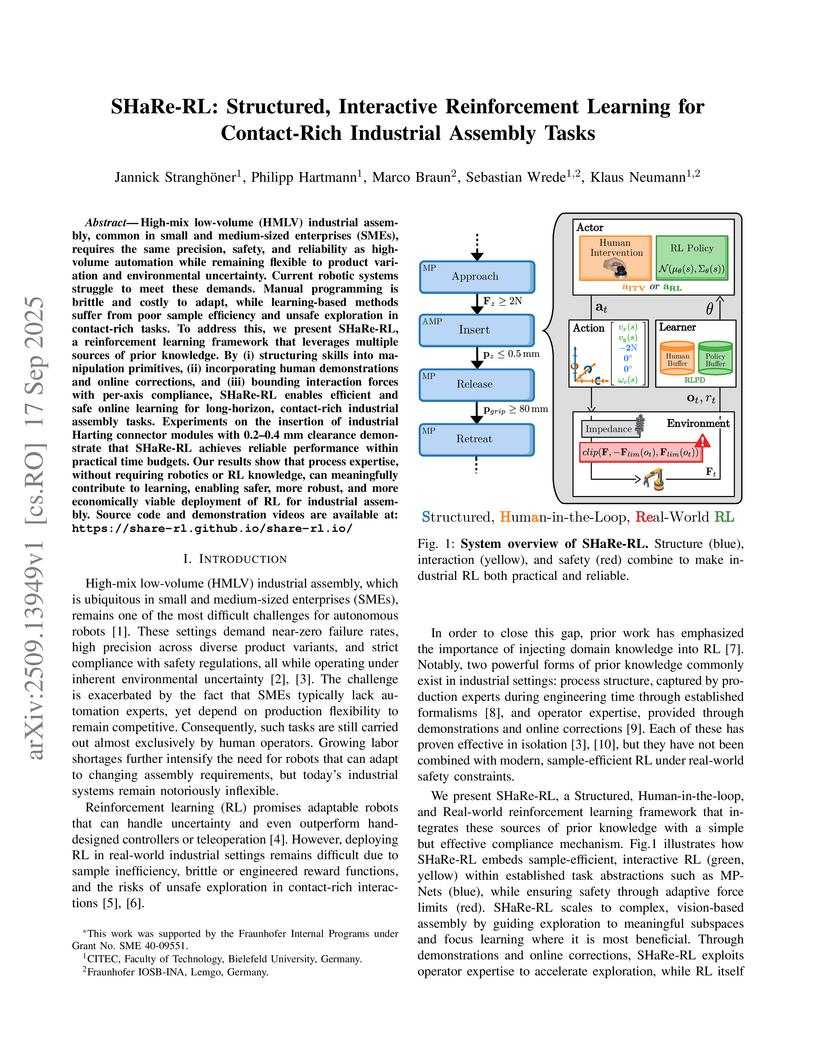
Bielefeld University
ReStraV, a method inspired by the 'perceptual straightening' hypothesis from biological vision, distinguishes AI-generated videos from natural ones by quantifying geometric properties of video trajectories in a frozen neural representation space. It achieves high accuracy and robust generalization to diverse and unseen generative models, providing an efficient and model-agnostic detection solution.
This survey from Bielefeld University, UBC, and the University of Waterloo offers a structured overview of video diffusion models, detailing their core principles, architectural choices, and diverse applications. It highlights how these models address the complexities of temporal consistency in video generation and identifies key challenges and future directions, including their emerging role in intelligent decision-making.
Graphusion introduces a three-step Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework that leverages Large Language Models to construct scientific knowledge graphs from free text by moving beyond local extraction to integrate a global perspective. The framework incorporates a novel fusion step for entity merging, conflict resolution, and novel triplet inference, achieving higher entity and relation quality in human evaluation and demonstrating improved accuracy on a new educational question-answering benchmark for scientific domains.
Large Language Models (LLMs) do not reliably simulate human psychology, demonstrating a critical failure to generalize based on semantic meaning when confronted with subtly reworded scenarios. This work shows LLMs react primarily to textual similarities rather than deep conceptual understanding, unlike human participants who adjust judgments based on meaningful distinctions.
Modern foundational models increasingly reflect not just world knowledge, but patterns of human preference embedded in their training data. We hypothesize that recursive alignment-via human feedback and model-generated corpora-induces a social desirability bias, nudging models to favor agreeable or flattering responses over objective reasoning. We refer to it as the Narcissus Hypothesis and test it across 31 models using standardized personality assessments and a novel Social Desirability Bias score. Results reveal a significant drift toward socially conforming traits, with profound implications for corpus integrity and the reliability of downstream inferences. We then offer a novel epistemological interpretation, tracing how recursive bias may collapse higher-order reasoning down Pearl's Ladder of Causality, culminating in what we refer to as the Rung of Illusion.
Generating bitmap graphics from text has gained considerable attention, yet
for scientific figures, vector graphics are often preferred. Given that vector
graphics are typically encoded using low-level graphics primitives, generating
them directly is difficult. To address this, we propose the use of TikZ, a
well-known abstract graphics language that can be compiled to vector graphics,
as an intermediate representation of scientific figures. TikZ offers
human-oriented, high-level commands, thereby facilitating conditional language
modeling with any large language model. To this end, we introduce DaTikZ, the
first large-scale TikZ dataset consisting of 120k TikZ drawings aligned with
captions. We fine-tune LLaMA on DaTikZ, as well as our new model CLiMA, which
augments LLaMA with multimodal CLIP embeddings. In both human and automatic
evaluation, CLiMA and LLaMA outperform commercial GPT-4 and Claude 2 in terms
of similarity to human-created figures, with CLiMA additionally improving
text-image alignment. Our detailed analysis shows that all models generalize
well and are not susceptible to memorization. GPT-4 and Claude 2, however, tend
to generate more simplistic figures compared to both humans and our models. We
make our framework, AutomaTikZ, along with model weights and datasets, publicly
available.
Water distribution systems (WDSs) are an important part of critical
infrastructure becoming increasingly significant in the face of climate change
and urban population growth. We propose a robust and scalable surrogate deep
learning (DL) model to enable efficient planning, expansion, and rehabilitation
of WDSs. Our approach incorporates an improved graph neural network
architecture, an adapted physics-informed algorithm, an innovative training
scheme, and a physics-preserving data normalization method. Evaluation results
on a number of WDSs demonstrate that our model outperforms the current
state-of-the-art DL model. Moreover, our method allows us to scale the model to
bigger and more realistic WDSs. Furthermore, our approach makes the model more
robust to out-of-distribution input features (demands, pipe diameters). Hence,
our proposed method constitutes a significant step towards bridging the
simulation-to-real gap in the use of artificial intelligence for WDSs.
The IM-IAD benchmark establishes a comprehensive evaluation framework for industrial image anomaly detection, addressing the gap between academic performance and real-world manufacturing demands by evaluating algorithms across various supervision levels, data constraints, and efficiency metrics. Extensive experiments reveal no single algorithm excels universally across accuracy, speed, and memory usage, highlighting the need for context-specific solutions.
A survey by researchers from SUSTech, University of Surrey, and Tencent provides a comprehensive review of deep learning techniques for industrial image anomaly detection, systematically classifying methods by architecture and supervision level. The paper highlights that memory bank-based approaches excel in image-level classification, while reconstruction methods are more effective for pixel-level localization, and identifies critical challenges for real-world deployment, such as data realism and model generalization.
We propose a novel diffusion-based framework for reconstructing 3D geometry of hand-held objects from monocular RGB images by leveraging hand-object interaction as geometric guidance. Our method conditions a latent diffusion model on an inpainted object appearance and uses inference-time guidance to optimize the object reconstruction, while simultaneously ensuring plausible hand-object interactions. Unlike prior methods that rely on extensive post-processing or produce low-quality reconstructions, our approach directly generates high-quality object geometry during the diffusion process by introducing guidance with an optimization-in-the-loop design. Specifically, we guide the diffusion model by applying supervision to the velocity field while simultaneously optimizing the transformations of both the hand and the object being reconstructed. This optimization is driven by multi-modal geometric cues, including normal and depth alignment, silhouette consistency, and 2D keypoint reprojection. We further incorporate signed distance field supervision and enforce contact and non-intersection constraints to ensure physical plausibility of hand-object interaction. Our method yields accurate, robust and coherent reconstructions under occlusion while generalizing well to in-the-wild scenarios.
17 Sep 2025
SHaRe-RL is a framework that makes robotic automation for complex, contact-rich industrial assembly tasks both efficient and safe enough for real-world deployment in Small and Medium-sized Enterprises. It achieves a 95% success rate and a 5.4-second cycle time on a challenging connector insertion, outperforming human expert baselines.
Water distribution systems (WDS) are an integral part of critical infrastructure which is pivotal to urban development. As 70% of the world's population will likely live in urban environments in 2050, efficient simulation and planning tools for WDS play a crucial role in reaching UN's sustainable developmental goal (SDG) 6 - "Clean water and sanitation for all". In this realm, we propose a novel and efficient machine learning emulator, more precisely, a physics-informed deep learning (DL) model, for hydraulic state estimation in WDS. Using a recursive approach, our model only needs a few graph convolutional neural network (GCN) layers and employs an innovative algorithm based on message passing. Unlike conventional machine learning tasks, the model uses hydraulic principles to infer two additional hydraulic state features in the process of reconstructing the available ground truth feature in an unsupervised manner. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first DL approach to emulate the popular hydraulic simulator EPANET, utilizing no additional information. Like most DL models and unlike the hydraulic simulator, our model demonstrates vastly faster emulation times that do not increase drastically with the size of the WDS. Moreover, we achieve high accuracy on the ground truth and very similar results compared to the hydraulic simulator as demonstrated through experiments on five real-world WDS datasets.
This paper introduces RouteFinder, a comprehensive foundation model framework to tackle different Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) variants. Our core idea is that a foundation model for VRPs should be able to represent variants by treating each as a subset of a generalized problem equipped with different attributes. We propose a unified VRP environment capable of efficiently handling any combination of these attributes. The RouteFinder model leverages a modern transformer-based encoder and global attribute embeddings to improve task representation. Additionally, we introduce two reinforcement learning techniques to enhance multi-task performance: mixed batch training, which enables training on different variants at once, and multi-variant reward normalization to balance different reward scales. Finally, we propose efficient adapter layers that enable fine-tuning for new variants with unseen attributes. Extensive experiments on 48 VRP variants show RouteFinder outperforms recent state-of-the-art learning methods. Our code is publicly available at this https URL.
23 Sep 2025
We study mean-field games of optimal stopping (OS-MFGs) and introduce an entropy-regularized framework to enable learning-based solution methods. By utilizing randomized stopping times, we reformulate the OS-MFG as a mean-field game of singular stochastic controls (SC-MFG) with entropy regularization. We establish the existence of equilibria and prove their stability as the entropy parameter vanishes. Fictitious play algorithms tailored for the regularized setting are introduced, and we show their convergence under both Lasry-Lions monotonicity and supermodular assumptions on the reward functional. Our work lays the theoretical foundation for model-free learning approaches to OS-MFGs.
While automatic subjective speech quality assessment has witnessed much progress, an open question is whether an automatic quality assessment at frame resolution is possible. This would be highly desirable, as it adds explainability to the assessment of speech synthesis systems. Here, we take first steps towards this goal by identifying issues of existing quality predictors that prevent sensible frame-level prediction. Further, we define criteria that a frame-level predictor should fulfill. We also suggest a chunk-based processing that avoids the impact of a localized distortion on the score of neighboring frames. Finally, we measure in experiments with localized artificial distortions the localization performance of a set of frame-level quality predictors and show that they can outperform detection performance of human annotations obtained from a crowd-sourced perception experiment.
Data augmentation is a promising technique for unsupervised anomaly detection in industrial applications, where the availability of positive samples is often limited due to factors such as commercial competition and sample collection difficulties. In this paper, how to effectively select and apply data augmentation methods for unsupervised anomaly detection is studied. The impact of various data augmentation methods on different anomaly detection algorithms is systematically investigated through experiments. The experimental results show that the performance of different industrial image anomaly detection (termed as IAD) algorithms is not significantly affected by the specific data augmentation method employed and that combining multiple data augmentation methods does not necessarily yield further improvements in the accuracy of anomaly detection, although it can achieve excellent results on specific methods. These findings provide useful guidance on selecting appropriate data augmentation methods for different requirements in IAD.
Backchannels and fillers are important linguistic expressions in dialogue, but are under-represented in modern transformer-based language models (LMs). Our work studies the representation of them in language models using three fine-tuning strategies. The models are trained on three dialogue corpora in English and Japanese, where backchannels and fillers are preserved and annotated, to investigate how fine-tuning can help LMs learn their representations. We first apply clustering analysis to the learnt representation of backchannels and fillers, and have found increased silhouette scores in representations from fine-tuned models, which suggests that fine-tuning enables LMs to distinguish the nuanced semantic variation in different backchannel and filler use. We also use natural language generation (NLG) metrics to confirm that the utterances generated by fine-tuned language models resemble human-produced utterances more closely. Our findings suggest the potentials of transforming general LMs into conversational LMs that are more capable of producing human-like languages adequately.
Language-image pre-training (LIP) enables the development of vision-language models capable of zero-shot classification, localization, multimodal retrieval, and semantic understanding. Various explanation methods have been proposed to visualize the importance of input image-text pairs on the model's similarity outputs. However, popular saliency maps are limited by capturing only first-order attributions, overlooking the complex cross-modal interactions intrinsic to such encoders. We introduce faithful interaction explanations of LIP models (FIxLIP) as a unified approach to decomposing the similarity in vision-language encoders. FIxLIP is rooted in game theory, where we analyze how using the weighted Banzhaf interaction index offers greater flexibility and improves computational efficiency over the Shapley interaction quantification framework. From a practical perspective, we propose how to naturally extend explanation evaluation metrics, such as the pointing game and area between the insertion/deletion curves, to second-order interaction explanations. Experiments on the MS COCO and ImageNet-1k benchmarks validate that second-order methods, such as FIxLIP, outperform first-order attribution methods. Beyond delivering high-quality explanations, we demonstrate the utility of FIxLIP in comparing different models, e.g. CLIP vs. SigLIP-2.
GeoSceneGraph, developed by Huawei Technologies and Bielefeld University, introduces a diffusion model leveraging geometric scene graphs and equivariant graph neural networks for text-guided 3D indoor scene synthesis. The method demonstrates competitive performance in scene quality and controllability, notably achieving 40.89% iRecall on dining room generation and robust results in zero-shot unconditional synthesis.
We investigate the task of missing value estimation in graphs as given by water distribution systems (WDS) based on sparse signals as a representative machine learning challenge in the domain of critical infrastructure. The underlying graphs have a comparably low node degree and high diameter, while information in the graph is globally relevant, hence graph neural networks face the challenge of long-term dependencies. We propose a specific architecture based on message passing which displays excellent results for a number of benchmark tasks in the WDS domain. Further, we investigate a multi-hop variation, which requires considerably less resources and opens an avenue towards big WDS graphs.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.