Booking.com
22 Jul 2024
We study a specific type of SCM, called a Dynamic Structural Causal Model (DSCM), whose endogenous variables represent functions of time, which is possibly cyclic and allows for latent confounding. As a motivating use-case, we show that certain systems of Stochastic Differential Equations (SDEs) can be appropriately represented with DSCMs. An immediate consequence of this construction is a graphical Markov property for systems of SDEs. We define a time-splitting operation, allowing us to analyse the concept of local independence (a notion of continuous-time Granger (non-)causality). We also define a subsampling operation, which returns a discrete-time DSCM, and which can be used for mathematical analysis of subsampled time-series. We give suggestions how DSCMs can be used for identification of the causal effect of time-dependent interventions, and how existing constraint-based causal discovery algorithms can be applied to time-series data.
This paper critically re-evaluates the paradigm of Learning Using Privileged Information (LUPI), finding that current methods like Generalized Distillation and TRAM do not consistently transfer knowledge from privileged information or yield performance benefits over adequately trained baseline models in real-world settings. The analysis suggests that reported gains in prior work often arise from experimental setup factors rather than the inherent value of privileged information transfer.
23 Oct 2017
There is an extensive literature about online controlled experiments, both on
the statistical methods available to analyze experiment results as well as on
the infrastructure built by several large scale Internet companies but also on
the organizational challenges of embracing online experiments to inform product
development. At Booking.com we have been conducting evidenced based product
development using online experiments for more than ten years. Our methods and
infrastructure were designed from their inception to reflect Booking.com
culture, that is, with democratization and decentralization of experimentation
and decision making in mind.
In this paper we explain how building a central repository of successes and
failures to allow for knowledge sharing, having a generic and extensible code
library which enforces a loose coupling between experimentation and business
logic, monitoring closely and transparently the quality and the reliability of
the data gathering pipelines to build trust in the experimentation
infrastructure, and putting in place safeguards to enable anyone to have end to
end ownership of their experiments have allowed such a large organization as
Booking.com to truly and successfully democratize experimentation.
A fundamental objective in intelligent robotics is to move towards lifelong learning robot that can learn and adapt to unseen scenarios over time. However, continually learning new tasks would introduce catastrophic forgetting problems due to data distribution shifts. To mitigate this, we store a subset of data from previous tasks and utilize it in two manners: leveraging experience replay to retain learned skills and applying a novel Retrieval-based Local Adaptation technique to restore relevant knowledge. Since a lifelong learning robot must operate in task-free scenarios, where task IDs and even boundaries are not available, our method performs effectively without relying on such information. We also incorporate a selective weighting mechanism to focus on the most "forgotten" skill segment, ensuring effective knowledge restoration. Experimental results across diverse manipulation tasks demonstrate that our framework provides a scalable paradigm for lifelong learning, enhancing robot performance in open-ended, task-free scenarios.
10 Oct 2025
Causal Machine Learning has emerged as a powerful tool for flexibly estimating causal effects from observational data in both industry and academia. However, causal inference from observational data relies on untestable assumptions about the data-generating process, such as the absence of unobserved confounders. When these assumptions are violated, causal effect estimates may become biased, undermining the validity of research findings. In these contexts, sensitivity analysis plays a crucial role, by enabling data scientists to assess the robustness of their findings to plausible violations of unconfoundedness. This paper introduces sensitivity analysis and demonstrates its practical relevance through a (simulated) data example based on a use case at this http URL. We focus our presentation on a recently proposed method by Chernozhukov et al. (2023), which derives general non-parametric bounds on biases due to omitted variables, and is fully compatible with (though not limited to) modern inferential tools of Causal Machine Learning. By presenting this use case, we aim to raise awareness of sensitivity analysis and highlight its importance in real-world scenarios.
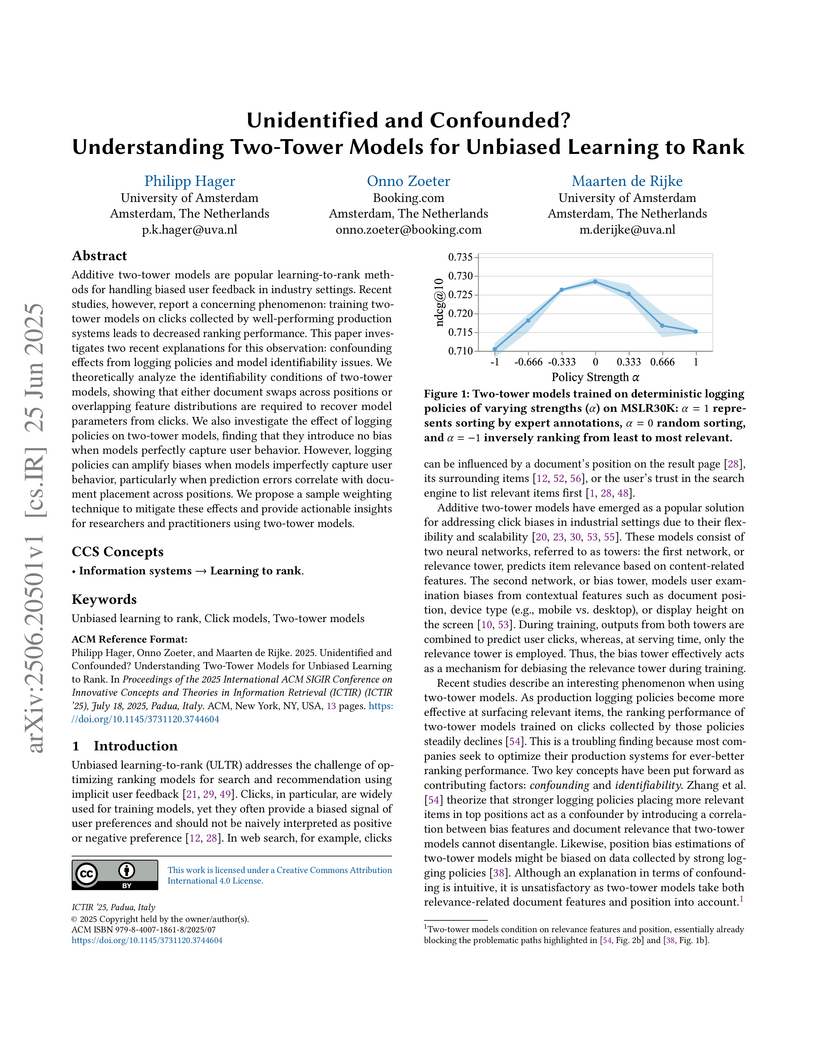
Researchers from the University of Amsterdam and Booking.com clarify how two-tower models for unbiased learning to rank are affected by data collection policies. The work demonstrates that logging policies amplify model bias primarily when the models are misspecified, and establishes that identifiability can arise from either explicit document swaps or sufficient overlap in feature distributions, with a proposed sample weighting technique effectively mitigating policy-induced bias.
Unbiased learning-to-rank (ULTR) is a well-established framework for learning
from user clicks, which are often biased by the ranker collecting the data.
While theoretically justified and extensively tested in simulation, ULTR
techniques lack empirical validation, especially on modern search engines. The
Baidu-ULTR dataset released for the WSDM Cup 2023, collected from Baidu's
search engine, offers a rare opportunity to assess the real-world performance
of prominent ULTR techniques. Despite multiple submissions during the WSDM Cup
2023 and the subsequent NTCIR ULTRE-2 task, it remains unclear whether the
observed improvements stem from applying ULTR or other learning techniques.
In this work, we revisit and extend the available experiments on the
Baidu-ULTR dataset. We find that standard unbiased learning-to-rank techniques
robustly improve click predictions but struggle to consistently improve ranking
performance, especially considering the stark differences obtained by choice of
ranking loss and query-document features. Our experiments reveal that gains in
click prediction do not necessarily translate to enhanced ranking performance
on expert relevance annotations, implying that conclusions strongly depend on
how success is measured in this benchmark.
This paper studies grading algorithms for randomized exams. In a randomized
exam, each student is asked a small number of random questions from a large
question bank. The predominant grading rule is simple averaging, i.e.,
calculating grades by averaging scores on the questions each student is asked,
which is fair ex-ante, over the randomized questions, but not fair ex-post, on
the realized questions. The fair grading problem is to estimate the average
grade of each student on the full question bank. The maximum-likelihood
estimator for the Bradley-Terry-Luce model on the bipartite student-question
graph is shown to be consistent with high probability when the number of
questions asked to each student is at least the cubed-logarithm of the number
of students. In an empirical study on exam data and in simulations, our
algorithm based on the maximum-likelihood estimator significantly outperforms
simple averaging in prediction accuracy and ex-post fairness even with a small
class and exam size.
Uplift modeling is a key technique for promotion optimization in recommender systems, but standard methods typically fail to account for interference, where treating one item affects the outcomes of others. This violation of the Stable Unit Treatment Value Assumption (SUTVA) leads to suboptimal policies in real-world marketplaces. Recent developments in interference-aware estimators such as Additive Inverse Propensity Weighting (AddIPW) have not found their way into the uplift modeling literature yet, and optimising policies using these estimators is not well-established. This paper proposes a practical methodology to bridge this gap. We use the AddIPW estimator as a differentiable learning objective suitable for gradient-based optimization. We demonstrate how this framework can be integrated with proven response transformation techniques to directly optimize for economic outcomes like incremental profit. Through simulations, we show that our approach significantly outperforms interference-naive methods, especially as interference effects grow. Furthermore, we find that adapting profit-centric uplift strategies within our framework can yield superior performance in identifying the highest-impact interventions, offering a practical path toward more profitable incentive personalization.
Reasoning about fairness through correlation-based notions is rife with pitfalls. The 1973 University of California, Berkeley graduate school admissions case from Bickel et. al. (1975) is a classic example of one such pitfall, namely Simpson's paradox. The discrepancy in admission rates among males and female applicants, in the aggregate data over all departments, vanishes when admission rates per department are examined. We reason about the Berkeley graduate school admissions case through a causal lens. In the process, we introduce a statistical test for causal hypothesis testing based on Pearl's instrumental-variable inequalities (Pearl 1995). We compare different causal notions of fairness that are based on graphical, counterfactual and interventional queries on the causal model, and develop statistical tests for these notions that use only observational data. We study the logical relations between notions, and show that while notions may not be equivalent, their corresponding statistical tests coincide for the case at hand. We believe that a thorough case-based causal analysis helps develop a more principled understanding of both causal hypothesis testing and fairness.
Controlling the length of generated text can be crucial in various
text-generation tasks, including summarization. Existing methods often require
complex model alterations, limiting compatibility with pre-trained models. We
address these limitations by developing a simple approach for controlling the
length of automatic text summaries by increasing the importance of correctly
predicting the EOS token in the cross-entropy loss computation. The proposed
methodology is agnostic to architecture and decoding algorithms and orthogonal
to other inference-time techniques to control the generation length. We tested
it with encoder-decoder and modern GPT-style LLMs, and show that this method
can control generation length, often without affecting the quality of the
summary.
We study the generalization capabilities of Group Convolutional Neural
Networks (GCNNs) with ReLU activation function by deriving upper and lower
bounds for their Vapnik-Chervonenkis (VC) dimension. Specifically, we analyze
how factors such as the number of layers, weights, and input dimension affect
the VC dimension. We further compare the derived bounds to those known for
other types of neural networks. Our findings extend previous results on the VC
dimension of continuous GCNNs with two layers, thereby providing new insights
into the generalization properties of GCNNs, particularly regarding the
dependence on the input resolution of the data.
In this paper, we investigate properties and limitations of invariance learned by neural networks from the data compared to the genuine invariance achieved through invariant weight-tying. To do so, we adopt a group theoretical perspective and analyze invariance learning in neural networks without weight-tying constraints. We demonstrate that even when a network learns to correctly classify samples on a group orbit, the underlying decision-making in such a model does not attain genuine invariance. Instead, learned invariance is strongly conditioned on the input data, rendering it unreliable if the input distribution shifts. We next demonstrate how to guide invariance learning toward genuine invariance by regularizing the invariance of a model at the training. To this end, we propose several metrics to quantify learned invariance: (i) predictive distribution invariance, (ii) logit invariance, and (iii) saliency invariance similarity. We show that the invariance learned with the invariance error regularization closely reassembles the genuine invariance of weight-tying models and reliably holds even under a severe input distribution shift. Closer analysis of the learned invariance also reveals the spectral decay phenomenon, when a network chooses to achieve the invariance to a specific transformation group by reducing the sensitivity to any input perturbation.
Booking.com researchers developed a structured maturity framework for assessing and enhancing Machine Learning (ML) system quality, implemented across hundreds of production ML systems. This framework led to consistent increases in ML quality scores and significantly improved various quality attributes, directly impacting business value and operational efficiency.
We propose an adaptation of the curriculum training framework, applicable to
state-of-the-art meta learning techniques for few-shot classification.
Curriculum-based training popularly attempts to mimic human learning by
progressively increasing the training complexity to enable incremental concept
learning. As the meta-learner's goal is learning how to learn from as few
samples as possible, the exact number of those samples (i.e. the size of the
support set) arises as a natural proxy of a given task's difficulty. We define
a simple yet novel curriculum schedule that begins with a larger support size
and progressively reduces it throughout training to eventually match the
desired shot-size of the test setup. This proposed method boosts the learning
efficiency as well as the generalization capability. Our experiments with the
MAML algorithm on two few-shot image classification tasks show significant
gains with the curriculum training framework. Ablation studies corroborate the
independence of our proposed method from the model architecture as well as the
meta-learning hyperparameters
Uplift modeling is a collection of machine learning techniques for estimating causal effects of a treatment at the individual or subgroup levels. Over the last years, causality and uplift modeling have become key trends in personalization at online e-commerce platforms, enabling the selection of the best treatment for each user in order to maximize the target business metric. Uplift modeling can be particularly useful for personalized promotional campaigns, where the potential benefit caused by a promotion needs to be weighed against the potential costs. In this tutorial we will cover basic concepts of causality and introduce the audience to state-of-the-art techniques in uplift modeling. We will discuss the advantages and the limitations of different approaches and dive into the unique setup of constrained uplift modeling. Finally, we will present real-life applications and discuss challenges in implementing these models in production.
Promotions play a crucial role in e-commerce platforms, and various cost structures are employed to drive user engagement. This paper focuses on promotions with response-dependent costs, where expenses are incurred only when a purchase is made. Such promotions include discounts and coupons. While existing uplift model approaches aim to address this challenge, these approaches often necessitate training multiple models, like meta-learners, or encounter complications when estimating profit due to zero-inflated values stemming from non-converted individuals with zero cost and profit.
To address these challenges, we introduce Incremental Profit per Conversion (IPC), a novel uplift measure of promotional campaigns' efficiency in unit economics. Through a proposed response transformation, we demonstrate that IPC requires only converted data, its propensity, and a single model to be estimated. As a result, IPC resolves the issues mentioned above while mitigating the noise typically associated with the class imbalance in conversion datasets and biases arising from the many-to-one mapping between search and purchase data. Lastly, we validate the efficacy of our approach by presenting results obtained from a synthetic simulation of a discount coupon campaign.
Fraud detection and prevention play an important part in ensuring the sustained operation of any e-commerce business. Machine learning (ML) often plays an important role in these anti-fraud operations, but the organizational context in which these ML models operate cannot be ignored. In this paper, we take an organization-centric view on the topic of fraud detection by formulating an operational model of the anti-fraud departments in e-commerce organizations. We derive 6 research topics and 12 practical challenges for fraud detection from this operational model. We summarize the state of the literature for each research topic, discuss potential solutions to the practical challenges, and identify 22 open research challenges.
Privacy in Social Network Sites (SNSs) like Facebook or Instagram is closely related to people's self-disclosure decisions and their ability to foresee the consequences of sharing personal information with large and diverse audiences. Nonetheless, online privacy decisions are often based on spurious risk judgements that make people liable to reveal sensitive data to untrusted recipients and become victims of social engineering attacks. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in combination with persuasive mechanisms like nudging is a promising approach for promoting preventative privacy behaviour among the users of SNSs. Nevertheless, combining behavioural interventions with high levels of personalization can be a potential threat to people's agency and autonomy even when applied to the design of social engineering countermeasures. This paper elaborates on the ethical challenges that nudging mechanisms can introduce to the development of AI-based countermeasures, particularly to those addressing unsafe self-disclosure practices in SNSs. Overall, it endorses the elaboration of personalized risk awareness solutions as i) an ethical approach to counteract social engineering, and ii) as an effective means for promoting reflective privacy decisions.
14 Dec 2024
A well-known problem when learning from user clicks are inherent biases
prevalent in the data, such as position or trust bias. Click models are a
common method for extracting information from user clicks, such as document
relevance in web search, or to estimate click biases for downstream
applications such as counterfactual learning-to-rank, ad placement, or fair
ranking. Recent work shows that the current evaluation practices in the
community fail to guarantee that a well-performing click model generalizes well
to downstream tasks in which the ranking distribution differs from the training
distribution, i.e., under covariate shift. In this work, we propose an
evaluation metric based on conditional independence testing to detect a lack of
robustness to covariate shift in click models. We introduce the concept of
debiasedness in click modeling and derive a metric for measuring it. In
extensive semi-synthetic experiments, we show that our proposed metric helps to
predict the downstream performance of click models under covariate shift and is
useful in an off-policy model selection setting.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.