Leibniz-Institute of Photonic Technology
Optical microscopy is one of the most widely used techniques in research studies for life sciences and biomedicine. These applications require reliable experimental pipelines to extract valuable knowledge from the measured samples and must be supported by image quality assessment (IQA) to ensure correct processing and analysis of the image data. IQA methods are implemented with variable complexity. However, while most quality metrics have a straightforward implementation, they might be time consuming and computationally expensive when evaluating a large dataset. In addition, quality metrics are often designed for well-defined image features and may be unstable for images out of the ideal domain.
To overcome these limitations, recent works have proposed deep learning-based IQA methods, which can provide superior performance, increased generalizability and fast prediction. Our method, named μDeepIQA, is inspired by previous studies and applies a deep convolutional neural network designed for IQA on natural images to optical microscopy measurements. We retrained the same architecture to predict individual quality metrics and global quality scores for optical microscopy data. The resulting models provide fast and stable predictions of image quality by generalizing quality estimation even outside the ideal range of standard methods. In addition, μDeepIQA provides patch-wise prediction of image quality and can be used to visualize spatially varying quality in a single image. Our study demonstrates that optical microscopy-based studies can benefit from the generalizability of deep learning models due to their stable performance in the presence of outliers, the ability to assess small image patches, and rapid predictions.
07 Jul 2025
Large language models (LLMs) are revolutionizing self driving laboratories (SDLs) for materials research, promising unprecedented acceleration of scientific discovery. However, current SDL implementations rely on rigid protocols that fail to capture the adaptability and intuition of expert scientists in dynamic experimental settings. We introduce Artificially Intelligent Lab Assistant (AILA), a framework automating atomic force microscopy through LLM driven agents. Further, we develop AFMBench a comprehensive evaluation suite challenging AI agents across the complete scientific workflow from experimental design to results analysis. We find that state of the art models struggle with basic tasks and coordination scenarios. Notably, Claude 3.5 sonnet performs unexpectedly poorly despite excelling in materials domain question answering (QA) benchmarks, revealing that domain specific QA proficiency does not necessarily translate to effective agentic capabilities. Additionally, we observe that LLMs can deviate from instructions, raising safety alignment concerns for SDL applications. Our ablations reveal that multi agent frameworks outperform single-agent architectures. We also observe significant prompt fragility, where slight modifications in prompt structure cause substantial performance variations in capable models like GPT 4o. Finally, we evaluate AILA's effectiveness in increasingly advanced experiments AFM calibration, feature detection, mechanical property measurement, graphene layer counting, and indenter detection. Our findings underscore the necessity for rigorous benchmarking protocols and prompt engineering strategies before deploying AI laboratory assistants in scientific research environments.
16 Jan 2025
 CNRS
CNRS Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University University of Southern CaliforniaGhent University
University of Southern CaliforniaGhent University Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Stanford University
Stanford University Université Paris-Saclay
Université Paris-Saclay CEA
CEA Princeton UniversityNational Institute of Standards and TechnologyThe University of British ColumbiaNorth Carolina State UniversityUniversity of TrentoIMECÉcole Polytechnique Fédérale de LausanneNational Research CouncilNTT CorporationLeibniz-Institute of Photonic TechnologyLetiHewlett Packard LabsHewlett Packard EnterpriseSapienza UniversityInstitut FEMTO-STInstitut National de la Recherche Scientifique-Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications (IN)Université Franche Comte CNRSUniversit
Grenoble AlpesEnrico Fermi” Research CenterQueens
’ University
Princeton UniversityNational Institute of Standards and TechnologyThe University of British ColumbiaNorth Carolina State UniversityUniversity of TrentoIMECÉcole Polytechnique Fédérale de LausanneNational Research CouncilNTT CorporationLeibniz-Institute of Photonic TechnologyLetiHewlett Packard LabsHewlett Packard EnterpriseSapienza UniversityInstitut FEMTO-STInstitut National de la Recherche Scientifique-Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications (IN)Université Franche Comte CNRSUniversit
Grenoble AlpesEnrico Fermi” Research CenterQueens
’ UniversityThis roadmap consolidates recent advances while exploring emerging applications, reflecting the remarkable diversity of hardware platforms, neuromorphic concepts, and implementation philosophies reported in the field. It emphasizes the critical role of cross-disciplinary collaboration in this rapidly evolving field.
 ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich Chinese Academy of SciencesUniversity of Stuttgart
Chinese Academy of SciencesUniversity of Stuttgart National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore Stanford University
Stanford University City University of Hong Kong
City University of Hong Kong Peking UniversityJinan UniversitySoutheast University
Peking UniversityJinan UniversitySoutheast University Australian National UniversityKing Abdullah University of Science and TechnologyMax Planck Institute for Solid State ResearchPohang University of Science and TechnologyNational Cheng Kung UniversityUniversidade Federal de PernambucoUniversity of the WitwatersrandÉcole Polytechnique Fédérale de LausanneSamsungPohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH)ICREA-Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis AvançatsICFO-Institut de Ciencies Fotoniques, The Barcelona Institute of Science and TechnologyUniversity of RostockLeibniz-Institute of Photonic TechnologyUniversidad de La FronteraGraduate Center of the City University of New YorkChangchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of SciencesAdvanced Science Research Center, City University of New YorkLudwig-Maximilians-Universtität MünchenThe City College of New York (USA)RomaTre UniversityNational Yang Ming-Chiao Tung UniversityBeijing Institute of Technology
Australian National UniversityKing Abdullah University of Science and TechnologyMax Planck Institute for Solid State ResearchPohang University of Science and TechnologyNational Cheng Kung UniversityUniversidade Federal de PernambucoUniversity of the WitwatersrandÉcole Polytechnique Fédérale de LausanneSamsungPohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH)ICREA-Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis AvançatsICFO-Institut de Ciencies Fotoniques, The Barcelona Institute of Science and TechnologyUniversity of RostockLeibniz-Institute of Photonic TechnologyUniversidad de La FronteraGraduate Center of the City University of New YorkChangchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of SciencesAdvanced Science Research Center, City University of New YorkLudwig-Maximilians-Universtität MünchenThe City College of New York (USA)RomaTre UniversityNational Yang Ming-Chiao Tung UniversityBeijing Institute of TechnologyScientific research needs a new system that appropriately values science and scientists. Key innovations, within institutions and funding agencies, are driving better assessment of research, with open knowledge and FAIR (findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable) principles as central pillars. Furthermore, coalitions, agreements, and robust infrastructures have emerged to promote more accurate assessment metrics and efficient knowledge sharing. However, despite these efforts, the system still relies on outdated methods where standardized metrics such as h-index and journal impact factor dominate evaluations. These metrics have had the unintended consequence of pushing researchers to produce more outputs at the expense of integrity and reproducibility. In this community paper, we bring together a global community of researchers, funding institutions, industrial partners, and publishers from 14 different countries across the 5 continents. We aim at collectively envision an evolved knowledge sharing and research evaluation along with the potential positive impact on every stakeholder involved. We imagine these ideas to set the groundwork for a cultural change to redefine a more fair and equitable scientific landscape.
We demonstrate that the orbifold lattice Hamiltonian -- an approach known for
its efficiency in simulating SU(N) Yang-Mills theory and QCD on digital
quantum computers -- can reproduce the Kogut-Susskind Hamiltonian in a
controlled limit. While the original Kogut-Susskind approach faces significant
implementation challenges on quantum hardware, we show that it emerges
naturally as the infinite scalar mass limit of the orbifold lattice
formulation, even at finite lattice spacing. Our analysis provides both a
general analytical framework applicable to SU(N) gauge theories in arbitrary
dimensions and specific numerical evidence for (2+1)-dimensional SU(N)
Yang-Mills theories (N=2,3). Using Euclidean path integral methods, we
quantify the convergence rate by comparing the standard Wilson action with the
orbifold lattice action, matching lattice parameters, and systematically
extrapolating results as the bare scalar mass approaches infinity. This
reformulation resolves longstanding technical obstacles and offers a
straightforward implementation protocol for digital quantum simulation of the
Kogut-Susskind Hamiltonian with exponential speedup compared to classical
methods and previously known quantum methods.
When light propagates through a multimode optical fibre (MMF), the spatial information it carries is scrambled. Wavefront shaping can undo this scrambling, typically one spatial mode at a time - enabling deployment of MMFs as ultra-thin micro-endoscopes. In this work we go beyond serial wavefront shaping by showing how to simultaneously unscramble all spatial modes emerging from an MMF in parallel. We introduce a passive multiple-scattering element - crafted through the process of inverse design - that is complementary to an MMF and undoes its optical effects. This optical inverter makes possible both single-shot wide-field imaging and super-resolution imaging through MMFs. Our design consists of a cascade of diffractive elements, and can be understood from the perspective of both multi-plane light conversion, and as a physically inspired deep diffractive neural network. This physical architecture can outperform state-of-the-art electronic neural networks tasked with unscrambling light, as it preserves the phase and coherence information of the optical signals flowing through it. Here we demonstrate our MMF inversion concept through numerical simulations, and efficiently sort and unscramble up to ~400 step-index fibre modes, reforming incoherent images of scenes at arbitrary distances from the distal fibre facet. We also describe how our optical inverter can dynamically adapt to see through flexible fibres with a range of experimentally realistic TMs - made possible by moulding optical memory effects into the structure of our design. Although complex, our inversion scheme is based on current fabrication technology so could be realised in the near future. Beyond imaging through scattering media, these concepts open up a range of new avenues for optical multiplexing, communications and computation in the realms of classical and quantum photonics.
11 Feb 2020
We study the influence of a strong off-resonant driving signal to the energy levels of a superconducting flux qubit both experimentally and theoretically. In the experiment, we carry out a three-tone spectroscopy. This allows us to directly observe the modification of the qubit's energy levels by the dynamical Stark shift caused by the driving signal. A theoretical treatment including corrections from both, rotating and counter-rotating frame, allowed us to completely explain the observed experimental results and to reconstruct the influence of the strong driving to the dissipative dynamics as well as to the coupling constants of the qubit. As one potential application, the tunability of the minimal energy-level splitting of a superconducting qubit by a microwave induced dynamical Stark shift can help to overcome the parameter spread induced by the micro fabrication of superconducting artificial quantum circuits.
When light propagates through a multimode optical fibre (MMF), the spatial information it carries is scrambled. Wavefront shaping can undo this scrambling, typically one spatial mode at a time - enabling deployment of MMFs as ultra-thin micro-endoscopes. In this work we go beyond serial wavefront shaping by showing how to simultaneously unscramble all spatial modes emerging from an MMF in parallel. We introduce a passive multiple-scattering element - crafted through the process of inverse design - that is complementary to an MMF and undoes its optical effects. This optical inverter makes possible both single-shot wide-field imaging and super-resolution imaging through MMFs. Our design consists of a cascade of diffractive elements, and can be understood from the perspective of both multi-plane light conversion, and as a physically inspired deep diffractive neural network. This physical architecture can outperform state-of-the-art electronic neural networks tasked with unscrambling light, as it preserves the phase and coherence information of the optical signals flowing through it. Here we demonstrate our MMF inversion concept through numerical simulations, and efficiently sort and unscramble up to ~400 step-index fibre modes, reforming incoherent images of scenes at arbitrary distances from the distal fibre facet. We also describe how our optical inverter can dynamically adapt to see through flexible fibres with a range of experimentally realistic TMs - made possible by moulding optical memory effects into the structure of our design. Although complex, our inversion scheme is based on current fabrication technology so could be realised in the near future. Beyond imaging through scattering media, these concepts open up a range of new avenues for optical multiplexing, communications and computation in the realms of classical and quantum photonics.
The rapid expansion of chemistry literature poses significant challenges for researchers seeking to efficiently access domain-specific knowledge. To support advancements in chemistry-focused natural language processing (NLP), we present ChemRxivQuest, a curated dataset of 970 high-quality question-answer (QA) pairs derived from 155 ChemRxiv preprints across 17 subfields of chemistry. Each QA pair is explicitly linked to its source text segment to ensure traceability and contextual accuracy. ChemRxivQuest was constructed using an automated pipeline that combines optical character recognition (OCR), GPT-4o-based QA generation, and a fuzzy matching technique for answer verification. The dataset emphasizes conceptual, mechanistic, applied, and experimental questions, enabling applications in retrieval-based QA systems, search engine development, and fine-tuning of domain-adapted large language models. We analyze the dataset's structure, coverage, and limitations, and outline future directions for expansion and expert validation. ChemRxivQuest provides a foundational resource for chemistry NLP research, education, and tool development.
The knowledge of the exact structure of the optical system PSF enables a
high-quality image reconstruction in fluorescence microscopy. Accurate PSF
models account for the vector nature of light and the phase and amplitude
modifications. Most existing real-space-based PSF models fall into a sampling
pitfall near the centre position, yielding to the violation of the energy
conservation. In this work, we present novel, to the best of our knowledge,
Fourier-based techniques for computing vector PSF and compare them to the
state-of-the-art. Our methods are shown to satisfy the physical condition of
the imaging process. They are reproducible, computationally efficient, and easy
to implement and easy to modify to represent various imaging modalities.
14 Apr 2025
 University of Washington
University of Washington University of Pittsburgh
University of Pittsburgh University of ManchesterUniversity of Stuttgart
University of ManchesterUniversity of Stuttgart Tel Aviv University
Tel Aviv University UC BerkeleySungkyunkwan UniversityUniversity of Warsaw
UC BerkeleySungkyunkwan UniversityUniversity of Warsaw ETH Zürich
ETH Zürich University of California, San Diego
University of California, San Diego Northwestern University
Northwestern University University of Texas at Austin
University of Texas at Austin Nanyang Technological University
Nanyang Technological University Columbia UniversityAarhus University
Columbia UniversityAarhus University Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Purdue University
Purdue University Aalto University
Aalto University Virginia TechCase Western Reserve UniversityUniversity of SiegenITMO UniversityMax Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of MatterUniversity of Minho
Virginia TechCase Western Reserve UniversityUniversity of SiegenITMO UniversityMax Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of MatterUniversity of Minho University of Central Florida
University of Central Florida Chalmers University of TechnologyFlorida International UniversityUniversity of Regensburg
Chalmers University of TechnologyFlorida International UniversityUniversity of Regensburg University of BaselUniversity of Southern DenmarkNaval Research LaboratoryKing Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST)Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-RossendorfUniversity of GothenburgLinköping UniversityCNRCity College of New YorkColorado School of MinesPenn State UniversityWest Virginia UniversityUniversity of HasseltDonostia International Physics Center DIPCAGH University of Science and TechnologyIMDEA NanocienciaLeibniz-Institute of Photonic TechnologyNational Research Council (CNR)CIC nanoGUNENational Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)ICFOBrazilian Center for Research in PhysicsInstituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón (ICMA)RWTH Aachen UniversityNorwegian University of
Science and Technology
University of BaselUniversity of Southern DenmarkNaval Research LaboratoryKing Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST)Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-RossendorfUniversity of GothenburgLinköping UniversityCNRCity College of New YorkColorado School of MinesPenn State UniversityWest Virginia UniversityUniversity of HasseltDonostia International Physics Center DIPCAGH University of Science and TechnologyIMDEA NanocienciaLeibniz-Institute of Photonic TechnologyNational Research Council (CNR)CIC nanoGUNENational Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)ICFOBrazilian Center for Research in PhysicsInstituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón (ICMA)RWTH Aachen UniversityNorwegian University of
Science and TechnologyTriggered by the development of exfoliation and the identification of a wide
range of extraordinary physical properties in self-standing films consisting of
one or few atomic layers, two-dimensional (2D) materials such as graphene,
transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), and other van der Waals (vdW) crystals
currently constitute a wide research field protruding in multiple directions in
combination with layer stacking and twisting, nanofabrication, surface-science
methods, and integration into nanostructured environments. Photonics
encompasses a multidisciplinary collection of those directions, where 2D
materials contribute with polaritons of unique characteristics such as strong
spatial confinement, large optical-field enhancement, long lifetimes, high
sensitivity to external stimuli (e.g., electric and magnetic fields, heating,
and strain), a broad spectral range from the far infrared to the ultraviolet,
and hybridization with spin and momentum textures of electronic band
structures. The explosion of photonics with 2D materials as a vibrant research
area is producing breakthroughs, including the discovery and design of new
materials and metasurfaces with unprecedented properties as well as
applications in integrated photonics, light emission, optical sensing, and
exciting prospects for applications in quantum information, and nanoscale
thermal transport. This Roadmap summarizes the state of the art in the field,
identifies challenges and opportunities, and discusses future goals and how to
meet them through a wide collection of topical sections prepared by leading
practitioners.
06 Dec 2024
Powerful mid-infrared illumination combined with mechanical detection via force microscopy provides access to nanoscale spectroscopic imaging in Materials and Life Sciences. Photo-induced force microscopy (PiFM) employs pulsed illumination and noncontact force microscopy resulting in unprecedented spatial and high spectral resolution. The near-field-enhanced light absorption in the materials leads to thermal expansion affecting the distance-dependent weak van der Waals (VdW) force acting between the tip and the sample. We model the non-linear impact of material characteristics and surface shape on the tip-sample interaction, the heat generation from the presence of a photo-induced electric field, the associated thermal expansion under different illumination conditions including light polarization and the feedback to the dynamic tip motion due to the expansion. Comparison of the results with our experimental investigation of a polymer nanosphere shows good agreement, contributing new insights into the understanding required for a quantitative analysis of nanostructured materials imaged using PiFM.
26 Feb 2024
Quantum light sources are crucial foundational components for various quantum
technology applications. With the rapid development of quantum technology,
there has been a growing demand for materials with the capability of hosting
quantum emitters. One such material platform uses fluorescent defects in
hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) that can host deep sublevels within the bandgap.
The localized electron irradiation has shown its effectiveness in generating
deep sublevels to induce single emitters in hBN. The question is whether
localized (electron beam) irradiation is a reliable tool for creating emitters
in other wide bandgap materials and its uniqueness to hBN. Here, we investigate
and compare the fabrication of quantum emitters in hBN and exfoliated muscovite
mica flakes along with other 3D crystals, such as silicon carbide and gallium
nitride, which are known to host quantum emitters. We used our primary
fabrication technique of localized electron irradiation using a standard
scanning electron microscope. To complement our experimental work, we employed
density functional theory simulations to study the atomic structures of defects
in mica. While our fabrication technique allows one to create hBN quantum
emitters with a high yield and high single photon purity, it is unable to
fabricate single emitters in the other solid-state crystals under
investigation. This allows us to draw conclusions on the emitter fabrication
mechanism in hBN, which could rely on activating pre-existing defects by charge
state manipulation. Therefore, we provide an essential step toward the
identification of hBN emitters and their formation process.
Atomically thin molecular carbon nanomembranes (CNMs) with intrinsic sub-nanometer porosity are considered as promising candidates for next generation filtration and gas separation applications due to their extremely low thickness, energy efficiency and selectivity. CNMs are intrinsically porous which is advantageous over other 2D materials such as graphene and transition metal dichalcogenides where defects and pores need to be introduced after synthesis. It was already discovered that water and helium permeate through 4,4-terphenylthiol (TPT) CNM above the limit of detection. Additionally, the permeation of water vapour was nonlinear against its pressure and 1000 stronger than permeation of helium despite their similar kinetic diameters. However, there was no clear permeation mechanism which could explain permeation of both species. Here, we demonstrate that permeation of all gas species is defined by their adsorption. We performed gas permeation measurements through TPT CNM at different temperatures and found that all measured gases experienced an activation energy barrier which correlated with their kinetic diameters. Furthermore, we identified that entropy loss during adsorption and permeation is the fundamental reason of strong nonlinear permeation of water. Our results also demonstrated that adsorption plays a major role in permeation of all gases, not just water.
14 Oct 2024
The quantum Josephson voltage standard is well established across the metrology community for many years. It relies on the synchronisation of the flux tunneling in the S/I/S Josepson junctions (JJ) with the microwave radiation (MW). The phenomenon is called the Shapiro steps. Together with the Quantum Hall resistance standard, the voltage standard forms the foundation of electrostatic metrology. The current is then defined as the ratio of the voltage and resistance. Realisation of the quantum current standard, would close the electrostatic metrological triangle of voltage-resistance-current. The current quantisation, the inverse Shapiro steps, was recently shown using the superconducting nanowires and small JJ. The effect is a synchronization of the MW with the Cooper pair tunnelling. This paves the way to combine the JJ voltage and current standards on the same chip and demonstrate feasibility of the multi-standard operation. We show the voltage and current quantization on the same chip up to frequency of 10 GHz, corresponding to the amplitudes 0.021 mV and 3.23 nA respectively. The accuracy of the voltage and current quantisation, however, is relatively low, 35 ppk and 100 ppk respectively. We discuss measures to optimise the JJs, circuit and environment to boost the amplitude and accuracy of the standards.
Colloidal 2D semiconductor nanoplatelets are highly efficient light emitters, which exhibit large absorption and emission cross sections, and constitute promising laser gain media. However, if dispersed in solutions, such nanoplatelets lack a suitable optical platform for scalable and application-oriented integration into optical setups such as lasers. Here, we demonstrate the first successful integration of solution-processed 2D CdSe/CdS Core/Crown nanoplatelets in m-scale liquid core optical fibers. We compare the nanoplatelets' spectroscopic properties before and after filling them into the fibers and find that spontaneous emission is shifted and broadened. We even observe a first evidence of stimulated emission at high excitation energies. In conclusion, liquid core fibers constitute a novel and scalable platform for optical integration of nanoplatelets for applications as novel, highly reconfigurable laser gain medium.
02 Sep 2019
A classical way of describing a dielectric function employs sums of contributions from damped harmonic oscillators. Each term leads to a maximum in the imaginary part of the dielectric function at the transversal optical (TO) resonance frequency of the corresponding oscillator. In contrast, the peak maxima of the negative imaginary part of the inverse dielectric function are attributed to the so-called longitudinal optical (LO) oscillator frequencies. The shapes of the corresponding bands resemble those of the imaginary part of the dielectric function. Therefore, it seems natural to also employ sums of the contributions of damped harmonic oscillators to describe the imaginary part of the inverse dielectric function. In this contribution, we derive the corresponding dispersion relations to investigate and establish the relationship between the transversal and longitudinal optical oscillator strength, which can differ, according to experimental results, by up to three orders of magnitude. So far, these differences are not understood and prevent the longitudinal optical oscillator strengths from proper interpretation. We demonstrate that transversal and longitudinal oscillator strengths should be identical for a single oscillator and that the experimental differences are in this case due to the introduction of a dielectric background in the dispersion formula. For this effect we derive an exact correction. Based on this correction we further derive a modified Kramers-Kronig sum rule for the isotropic case as well as for the components of the inverse dielectric function tensor. For systems with more than one oscillator, our model for the isotropic case can be extended to yield oscillator strengths and LO resonance wavenumber for uncoupled LO modes with or without dielectric background...
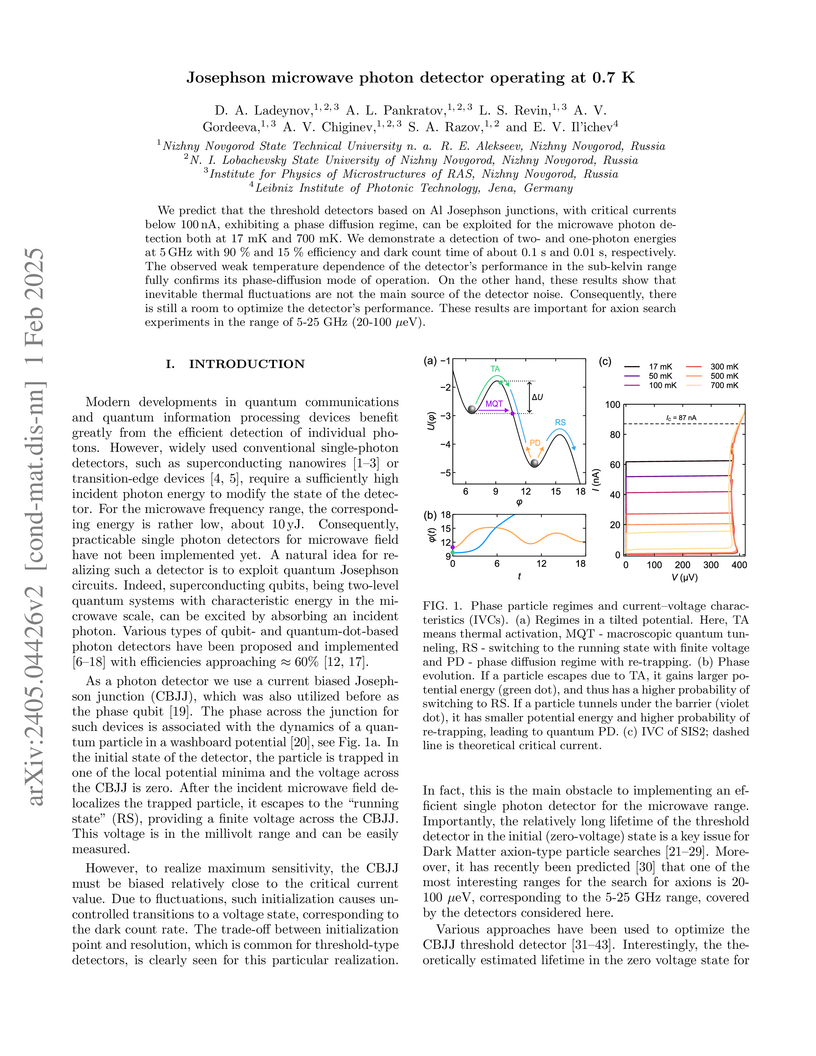
We predict that the threshold detectors based on Al Josephson junctions, with critical currents below 100 nA, exhibiting a phase diffusion regime, can be exploited for the microwave photon detection both at 17 mK and 700 mK. We demonstrate a detection of two- and one-photon energies at 5 GHz with 90% and 15% efficiency and dark count time of about 0.1 s and 0.01 s, respectively. The observed weak temperature dependence of the detector's performance in the sub-kelvin range fully confirms its phase-diffusion mode of operation. On the other hand, these results show that inevitable thermal fluctuations are not the main source of the detector noise. Consequently, there is still a room to optimize the detector's performance. These results are important for axion search experiments in the range of 5-25 GHz (20-100 μeV).
The power of photothermal spectroscopic imaging to visualize antimicrobial
interaction on the surface of individual bacteria cells has been demonstrated
on the model system Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis) and vancomycin using
mid-infrared photo-induced force microscopy (PiF-IR, also mid-IR PiFM).
High-resolution PiF contrasts obtained by merging subsequent PiF-IR scans at
two different illumination frequencies revealed chemical details of cell wall
destruction after 30 and 60 min incubation with vancomycin with a spatial
resolution of ≈5 nm. This approach compensates local intensity
variations induced by near-field coupling of the illuminating electric field
with nanostructured surfaces, which appear in single-frequency contrasts in
photothermal imaging methods, as shown by [Anindo et al., J. Phys. Chem C,
2025, 129, 4517]. Spectral shifts associated with hydrogen bond formation
between vancomycin and the N-acyl-D-Ala4-D-Ala5 termini in the peptidoglycan
cell wall have been observed in chemometrics of PiF-IR spectra from treated and
untreated B. subtilis harvested after 30 min from the same experiment. The
vancomyin interaction in the piecrust of a progressing septum is located with
≈10 nm resolution exemplarily using PiF contrasts of three selected
bands of a PiF-IR hyperspectral scan of an individual B. subtilis cell
harvested after 30 min incubation. Our results provide a new perspective for
visualizing the chemical interaction of antibiotics on the surface of microbes
with few nanometer resolution.
29 Mar 2024
We like and need Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) for data
processing. This is measureable in the exponential growth of data processed by
ICT, e.g. ICT for cryptocurrency mining and search engines. So far, the energy
demand for computing technology has increased by a factor of 1.38 every ten
years due to the exponentially increasing use of ICT systems as computing
devices. The energy consumption of ICT systems is expected to rise from 1500
TWh (8% of global electricity consumption) in 2010 to 5700 TWh (14% of global
electricity consumption) in 2030. A large part of this energy is required for
the continuous data transfer between the separated memory and processor units
which constitute the main components of ICT computing devices in von-Neumann
architecture. This at the same time massively slows down the computing power of
ICT systems in the von-Neumann architecture. In addition, due to the increasing
complexity of AI compute algorithms, since 2010 the AI training compute time
demand for computing technology increases tenfold every year, for example in
the period from 2010 to 2020 from 1x10^{-6} to 1x10^{+4} Petaflops/Day. It has
been theoretically predicted that ICT systems in the neuromorphic computer
architecture will circumvent all of this through the use of merged memory and
processor units. However, the core hardware element for this has not yet been
realized so far. In this work we discuss the prespectives for non-linear
resistive switches as the core hardware element for merged memory and processor
units in neuromorphic computers.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.