Ask or search anything...
ETH Zürich and Tsinghua University researchers introduce OpenFunGraph, a framework that constructs functional 3D scene graphs by identifying interactive elements and their relationships in indoor spaces through foundation models, enabling richer scene understanding without requiring task-specific training data.
View blogThis survey comprehensively introduces and reviews Quantum-enhanced Computer Vision (QeCV), an emerging interdisciplinary field that applies quantum computational paradigms to address computational challenges in classical computer vision. It categorizes existing methods based on quantum annealing and gate-based quantum computing, detailing their application to a wide array of vision tasks.
View blogResearchers from DFKI, MPI for Informatics, and Snap Inc. developed DuetGen, a framework that generates synchronized and interactive two-person dance choreography directly from music. It employs a unified two-person motion representation, a hierarchical VQ-VAE for motion quantization, and two-stage masked transformers, achieving state-of-the-art realism and partner coordination on the DD100 dataset, with a 22% improvement in user study ratings over prior approaches.
View blogResearchers developed Continual Test-Time Adaptation (CoTTA), a method that enables deep learning models to continually adapt to evolving data distributions at inference time without requiring access to source data. CoTTA achieved a 16.2% error rate on CIFAR10C (standard setting) and improved semantic segmentation performance to 58.6% mIoU on Cityscapes-to-ACDC, outperforming prior test-time adaptation methods by mitigating error accumulation and catastrophic forgetting.
View blogResearchers from the University of Tübingen developed PhySIC, a framework reconstructing metric-scale 3D human and scene geometries, alongside dense vertex-level contact maps, from a single monocular image. The method reduces human pose error (PA-MPJPE) to 41.99mm on PROX and 46.50mm on RICH-100, while achieving contact F1-scores of 0.511 and 0.428 respectively, demonstrating robust physical plausibility and efficient reconstruction.
View blogResearchers at ETH Zürich developed "Roach," a high-performance reinforcement learning expert, to act as a coach for end-to-end imitation learning agents in urban driving simulations. This approach enables a camera-based agent to achieve state-of-the-art performance, with up to an 88% driving score in new towns and weather conditions, by learning from Roach's diverse supervision signals including action distributions, latent features, and value estimations.
View blogA State of the Art Report, this paper surveys advanced neural rendering methods, focusing on the paradigm shift towards learning 3D-consistent neural scene representations. It details how these methods, especially those influenced by Neural Radiance Fields, enable high-quality novel-view synthesis and controllable scene manipulation.
View blogSynthFun3D is a training-free framework for language-guided 3D scene synthesis that generates functionally-rich indoor environments with automatic, fine-grained part-level annotations. The framework addresses data scarcity for embodied AI, enabling a 2.12 mIoU improvement on the SceneFun3D benchmark when its synthetic data is used for pre-training.
View blogZegFormer introduces a decoupled approach to zero-shot semantic segmentation by separating class-agnostic grouping from segment-level classification, effectively integrating pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP. This method achieves state-of-the-art performance with a 73.3% harmonic mean mIoU on PASCAL VOC and 34.8% on COCO-Stuff, while also demonstrating robustness on the challenging ADE20k-Full benchmark with 275 unseen classes.
View blogPoseTrack introduces a large-scale benchmark for multi-person articulated pose estimation and tracking in unconstrained videos, providing 66,374 frames and 153,615 dense pose annotations. The benchmark reveals that top-performing methods achieve approximately 50% MOTA for tracking and 70% mAP for pose estimation, while highlighting challenges in dynamic, crowded scenes.
View blogResearchers from Max Planck Institute and ETH Zürich introduce the task of logical fallacy detection in natural language, constructing two novel datasets and proposing a structure-aware classification model. Their model achieved a 5.46% F1 score improvement over the best baseline on the LOGIC dataset and maintained a 5.66% F1 improvement on the challenging LOGICCLIMATE dataset for climate change claims, indicating enhanced logical reasoning.
View blog Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Stanford University
Stanford University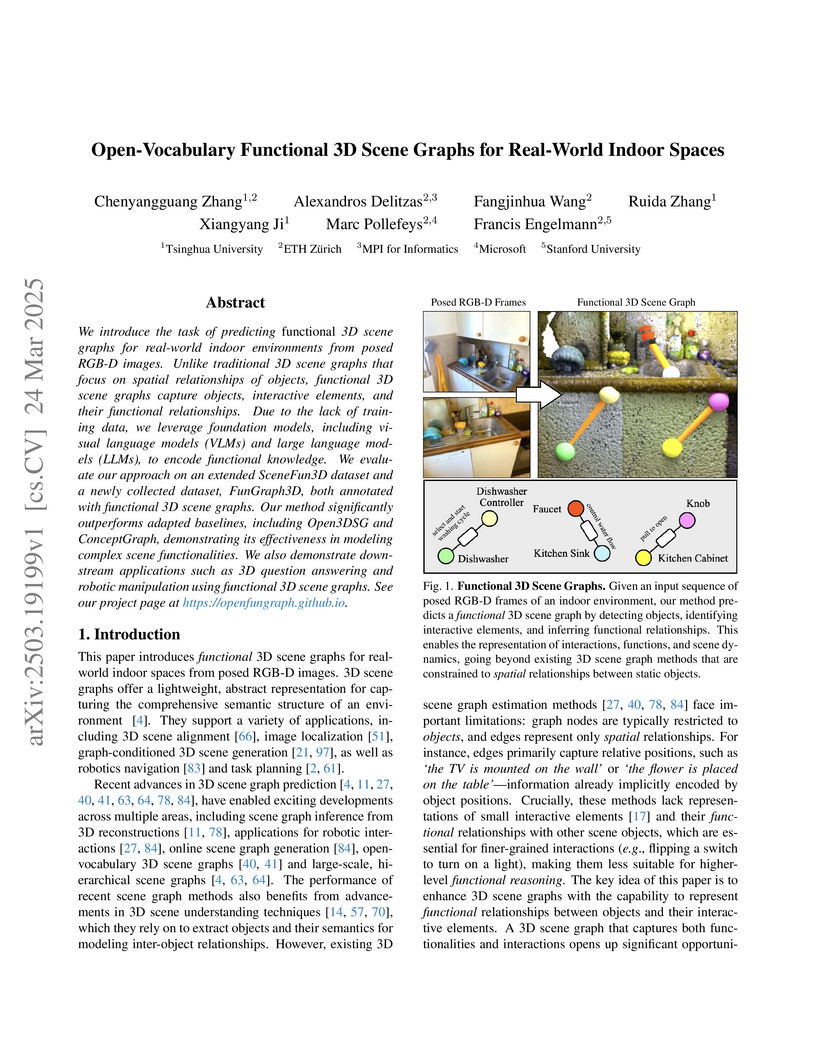
 Imperial College London
Imperial College London


 ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich EPFL
EPFL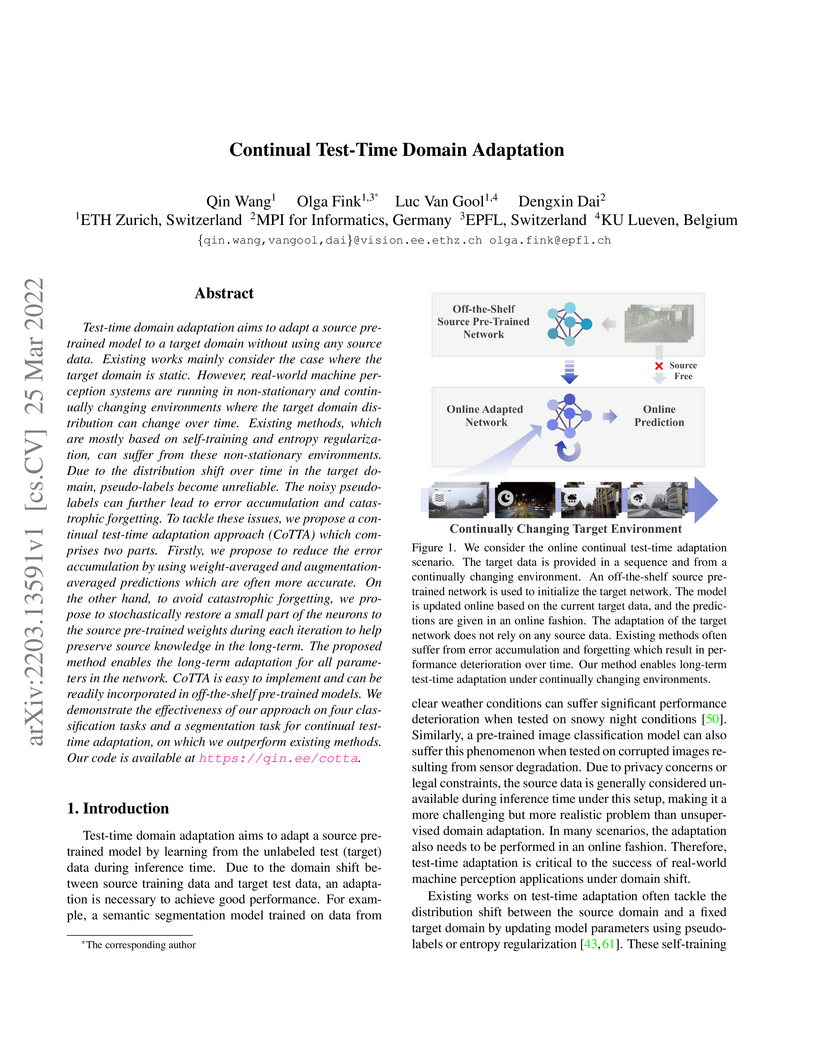

 Google
Google
 ETH Zürich
ETH Zürich KU Leuven
KU Leuven





 The University of Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong




 University of Michigan
University of Michigan
