National Institute of Technology Calicut
The redshifted 21-cm signal from the dark ages offers a powerful probe of cosmological models and the underlying dark matter microphysics. We investigate deviations from the standard ΛCDM prediction, an absorption trough of approximately −40.6mK at redshift z≃85.6, in the context of co-SIMP dark matter. The strength of co-SIMP interactions, quantified by the parameter Cint, enhances the absorption depth and shifts the trough to higher redshifts. For example, a model with Cint=1.0 produces a minimum brightness temperature of −50.6mK at z≃86.2. The 21-cm power spectrum increases with Cint in addition to the global signal. We assess the detectability of these signatures using signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and Fisher matrix forecasts. The maximum SNR reaches ∼15.7 for Cint=1.0 for the global signal. Fisher forecast for 1,000 hours of integration time shows that this model can be distinguished from a null-signal at 4.3σ and from the ΛCDM model case at 1.6σ, with order-of-magnitude improvements for 100,000 hours of integration. For the 21-cm power spectrum, our forecasts reveal complementary trends; with a modest setup (collecting area of 5km2 and 1,000 hours of integration time), the Cint=1.0 model can be detected at 4.63σ and differentiated from the standard scenario at 1.78σ. These findings highlight the potential of the 21-cm cosmology to probe the properties of dark matter and demonstrate that upcoming dark ages experiments, particularly space-based and lunar observations, can offer a promising avenue to test co-SIMP models.
The process of pooling vertices involves the creation of a new vertex, which becomes adjacent to all the vertices that were originally adjacent to the endpoints of the vertices being pooled. After this, the endpoints of these vertices and all edges connected to them are removed. In this document, we introduce a formal framework for the concept of fuzzy vertex pooling (FVP) and provide an overview of its key properties with its applications to neural networks. The pooling model demonstrates remarkable efficiency in minimizing loss rapidly while maintaining competitive accuracy, even with fewer hidden layer neurons. However, this advantage diminishes over extended training periods or with larger datasets, where the model's performance tends to degrade. This study highlights the limitations of pooling in later stages of deep learning training, rendering it less effective for prolonged or large-scale applications. Consequently, pooling is recommended as a strategy for early-stage training in advanced deep learning models to leverage its initial efficiency.
It is thought that the Universe went through an early period known as the Dark Ages, during which primeval density fluctuations grew to form the first luminous objects, marking the beginning of Cosmic Dawn around 100 million years after the Big Bang. The 21-cm line of hydrogen atoms is the most promising probe of these epochs, with extensive observational efforts underway. We combine hydrodynamical simulations with a large-scale grid in order to precisely calculate the effect of non-linear structure formation on the global (sky-averaged) 21-cm radio intensity. We show that it presents a potential opportunity to probe the properties of dark matter in a new regime, corresponding to a length-scale of only 150,000 light years and a mass-scale of 20 million Solar masses. This effect can in principle be detected unambiguously during the Dark Ages, where the weak signal requires an array of global signal antennae. During Cosmic Dawn, when stellar radiation boosts the signal, a single global antenna suffices, but the clumping effect must then be separated from the effect of the stars. Our findings open new avenues for testing the nature of dark matter as well as non-standard cosmological models.
Researchers from multiple institutions conducted a comparative analysis of fine-tuning and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) approaches for conversational AI in doctor-patient dialogues within mixed medical domains. The study found that fine-tuned GPT excelled in fluency and structural coherence, while Llama-2 with RAG achieved superior semantic accuracy and relevance, significantly outperforming an LSTM baseline.
The process of pooling vertices involves the creation of a new vertex, which becomes adjacent to all the vertices that were originally adjacent to the endpoints of the vertices being pooled. After this, the endpoints of these vertices and all edges connected to them are removed. In this document, we introduce a formal framework for the concept of fuzzy vertex pooling (FVP) and provide an overview of its key properties with its applications to neural networks. The pooling model demonstrates remarkable efficiency in minimizing loss rapidly while maintaining competitive accuracy, even with fewer hidden layer neurons. However, this advantage diminishes over extended training periods or with larger datasets, where the model's performance tends to degrade. This study highlights the limitations of pooling in later stages of deep learning training, rendering it less effective for prolonged or large-scale applications. Consequently, pooling is recommended as a strategy for early-stage training in advanced deep learning models to leverage its initial efficiency.
30 Jul 2025
We accomplish the quantization of a few classical constrained systems à la (modified) Faddeev-Jackiw formalism. We analyze the constraint structure and obtain basic brackets of the theory. In addition, we disclose the gauge symmetries within the symplectic framework. We also provide new interpretation for Lagrange multipliers and outline a MATLAB implementation algorithm for symplectic formulation.
18 Oct 2024
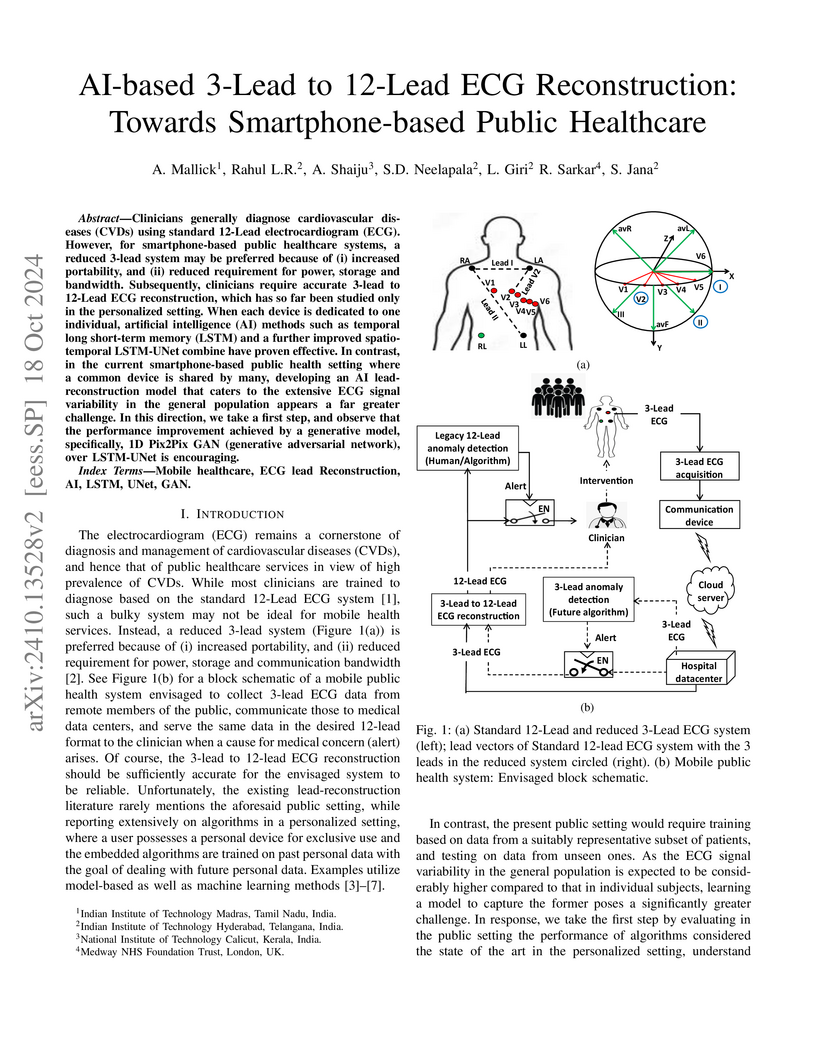
Clinicians generally diagnose cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) using standard 12-Lead electrocardiogram (ECG). However, for smartphone-based public healthcare systems, a reduced 3-lead system may be preferred because of (i) increased portability, and (ii) reduced requirement for power, storage and bandwidth. Subsequently, clinicians require accurate 3-lead to 12-Lead ECG reconstruction, which has so far been studied only in the personalized setting. When each device is dedicated to one individual, artificial intelligence (AI) methods such as temporal long short-term memory (LSTM) and a further improved spatio-temporal LSTM-UNet combine have proven effective. In contrast, in the current smartphone-based public health setting where a common device is shared by many, developing an AI lead-reconstruction model that caters to the extensive ECG signal variability in the general population appears a far greater challenge. In this direction, we take a first step, and observe that the performance improvement achieved by a generative model, specifically, 1D Pix2Pix GAN (generative adversarial network), over LSTM-UNet is encouraging.
Tree-based Long short term memory (LSTM) network has become state-of-the-art for modeling the meaning of language texts as they can effectively exploit the grammatical syntax and thereby non-linear dependencies among words of the sentence. However, most of these models cannot recognize the difference in meaning caused by a change in semantic roles of words or phrases because they do not acknowledge the type of grammatical relations, also known as typed dependencies, in sentence structure. This paper proposes an enhanced LSTM architecture, called relation gated LSTM, which can model the relationship between two inputs of a sequence using a control input. We also introduce a Tree-LSTM model called Typed Dependency Tree-LSTM that uses the sentence dependency parse structure as well as the dependency type to embed sentence meaning into a dense vector. The proposed model outperformed its type-unaware counterpart in two typical NLP tasks - Semantic Relatedness Scoring and Sentiment Analysis, in a lesser number of training epochs. The results were comparable or competitive with other state-of-the-art models. Qualitative analysis showed that changes in the voice of sentences had little effect on the model's predicted scores, while changes in nominal (noun) words had a more significant impact. The model recognized subtle semantic relationships in sentence pairs. The magnitudes of learned typed dependencies embeddings were also in agreement with human intuitions. The research findings imply the significance of grammatical relations in sentence modeling. The proposed models would serve as a base for future researches in this direction.
13 Apr 2025
Observations of the Epoch of Reionization (EoR) have the potential to answer
long-standing questions of astrophysical interest regarding the nature of the
first luminous sources and their effects on the intergalactic medium (IGM). We
present astrophysical constraints from a Neural Density Estimation-Accelerated
Bayesian joint analysis of constraints deriving from Cosmic Microwave
Background power spectrum measurements from Planck and SPT, IGM neutral
fraction measurements from Lyman-line-based data sets and 21-cm power spectrum
upper limits from HERA, LOFAR and the MWA. In the context of the model
employed, the data is found to be consistent with galaxies forming from
predominantly atomic-cooled hydrogen gas in dark matter halos, with masses
Mmin≳2.6×109 M⊙((1+z)/10)21
at 95% credibility (Vc≳50 km s−1) being the
dominant galactic population driving reionization. These galaxies reionize the
neutral hydrogen in the IGM over a narrow redshift interval ($\Delta
z_\mathrm{re} < 1.8$ at 95% credibility), with the midpoint of reionization
(when the sky-averaged IGM neutral fraction is 50%) constrained to $z_{50} =
7.16^{+0.15}_{-0.12}$. Given the parameter posteriors from our joint analysis,
we find that the posterior predictive distribution of the global 21-cm signal
is reduced in amplitude and shifted to lower redshifts relative to the model
prior. We caution, however, that our inferences are model-dependent. Future
work incorporating updated, mass-dependent star formation efficiencies in
atomic cooling halos, informed by the latest UV luminosity function constraints
from the James Webb Space Telescope, promises to refine these inferences
further and enhance our understanding of cosmic reionization.
Rigid registration of multi-view and multi-platform LiDAR scans is a fundamental problem in 3D mapping, robotic navigation, and large-scale urban modeling applications. Data acquisition with LiDAR sensors involves scanning multiple areas from different points of view, thus generating partially overlapping point clouds of the real world scenes. Traditionally, ICP (Iterative Closest Point) algorithm is used to register the acquired point clouds together to form a unique point cloud that captures the scanned real world scene. Conventional ICP faces local minima issues and often needs a coarse initial alignment to converge to the optimum. In this work, we present an algorithm for registering multiple, overlapping LiDAR scans. We introduce a geometric metric called Transformation Compatibility Measure (TCM) which aids in choosing the most similar point clouds for registration in each iteration of the algorithm. The LiDAR scan most similar to the reference LiDAR scan is then transformed using simplex technique. An optimization of the transformation using gradient descent and simulated annealing techniques are then applied to improve the resulting registration. We evaluate the proposed algorithm on four different real world scenes and experimental results shows that the registration performance of the proposed method is comparable or superior to the traditionally used registration methods. Further, the algorithm achieves superior registration results even when dealing with outliers.
 CNRS
CNRS UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley The University of Texas at AustinUniversidad Autónoma de Madrid
The University of Texas at AustinUniversidad Autónoma de Madrid Université Paris-Saclay
Université Paris-Saclay Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryThe University of ManchesterUniversity of SussexUniversity of NottinghamLeibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP)Chosun UniversityNational Institute of Technology CalicutMax Planck Institut fr AstronomieUniversit
de StrasbourgZentrum fr Astronomie der Universitt Heidelberg
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryThe University of ManchesterUniversity of SussexUniversity of NottinghamLeibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP)Chosun UniversityNational Institute of Technology CalicutMax Planck Institut fr AstronomieUniversit
de StrasbourgZentrum fr Astronomie der Universitt HeidelbergThe thermal Sunyaev-Zel'dovich (tSZ) effect arises from inverse Compton scattering of low energy photons onto thermal electrons, proportional to the integrated electron pressure, and is usually observed from galaxy clusters. However, we can expect that the Epoch of Reionization (EoR) also contributes to this signal, but that contribution has not been previously evaluated. In this work we analyse a suite of fully-coupled radiation-hydrodynamics simulations based on RAMSES-CUDATON to calculate and study the tSZ signal from the Reionization Epoch. We construct lightcones of the electron pressure in the intergalactic medium for $6
Class Activation Maps (CAMs) are one of the important methods for visualizing regions used by deep learning models. Yet their robustness to different noise remains underexplored. In this work, we evaluate and report the resilience of various CAM methods for different noise perturbations across multiple architectures and datasets. By analyzing the influence of different noise types on CAM explanations, we assess the susceptibility to noise and the extent to which dataset characteristics may impact explanation stability. The findings highlight considerable variability in noise sensitivity for various CAMs. We propose a robustness metric for CAMs that captures two key properties: consistency and responsiveness. Consistency reflects the ability of CAMs to remain stable under input perturbations that do not alter the predicted class, while responsiveness measures the sensitivity of CAMs to changes in the prediction caused by such perturbations. The metric is evaluated empirically across models, different perturbations, and datasets along with complementary statistical tests to exemplify the applicability of our proposed approach.
We consider the problem of optimizing Quality of Experience (QoE) of clients streaming real-time video, served by networks managed by different operators that can share bandwidth with each other. The abundance of real-time video traffic is evident in the popularity of applications like video conferencing and video streaming of live events, which have increased significantly since the recent pandemic. We model the problem as a joint optimization of resource allocation for the clients and bandwidth sharing across the operators, with special attention to how the resource allocation impacts clients' perceived video quality. We propose an online policy as a solution, which involves dynamically sharing a portion of one operator's bandwidth with another operator. We provide strong theoretical optimality guarantees for the policy. We also use extensive simulations to demonstrate the policy's substantial performance improvements (of up to ninety percent), and identify insights into key system parameters (e.g., imbalance in arrival rates or channel conditions of the operators) that dictate the improvements.
17 Dec 2024
This article investigates the convergence properties of s-numbers of certain truncations of bounded linear operators between Banach spaces. We prove a generalized version of a known convergence result for the approximation numbers of truncations of operators, removing the restrictive assumption of separability from the underlying spaces. This generalization extends several existing results in the literature and establishes a close connection between two significant problems concerning approximation numbers. By exploring the relationships between approximation numbers and other prominent s-numbers, we also derive results on the convergence of s-numbers of truncations to those of the original operator, as applications of the generalized convergence result.
With a fleet of exploratory space missions on the horizon, the study of target specific biospheres is crucial for accurately determining the probability of the existence of microbial life on various planetary bodies and prioritising targets accordingly. Although previous studies have compared the potential habitability of objects in our solar system by bulk characteristics, it is less common that precise qualitative methods are developed for ranking candidates hospitable to microbial life on a local environment basis. In this review we create a planetary environmental database and use it to motivate a list of primary habitability candidates and essential criteria for microbial survival. We then propose a new method, the Microbial Habitability Index (MHI) which uses a metric of microbial survival factor values in target environments compared with appropriate Earth analogues to assess their potential for life. We arrive at a selection of eight primary candidates and from this set conclude that Europa, Mars, and Enceladus have the highest potential for facilitating microbial survival.
Confined spin-wave modes are a promising object for studying nonlinear
effects and future quantum technologies. Here, using micromagnetic simulations,
we use a microwave magnetic field from a coplanar waveguide (CPW) to pump a
standing spin-wave confined in the cavity of magnonic crystal. We find that the
frequency of the fundamental cavity mode is equal to the ferromagnetic
resonance frequency of the plane film and overlaps with the magnonic bandgap,
allowing high magnetic field tunability. Multi-frequency harmonics of the
cavity mode are generated once the microwave amplitude surpasses a certain
threshold. Specifically, the second and third harmonics at 0.5 T equate to 48.6
and 72.9 GHz with wavelengths of 44 and 22 nm respectively, which propagate
into the crystal. This effect reaches saturation when the CPW covers the entire
cavity, making the system feasible for realization. These processes show
potential for the advancement of magnonics at high-frequencies and very
short-wavelengths.
The dark ages 21-cm signal is a powerful tool for precision cosmology and probing new physics. We study two non-standard models: an excess radio background (ERB) model (possibly generated by dark matter decay) and the millicharged dark matter (mDM) model. These models were inspired by the possible EDGES detection of a strong global 21-cm absorption during cosmic dawn, but more generally they provide a way to anticipate the potential discovery space. During the dark ages the 21-cm global signal in the ERB model reaches a saturated form for an amplitude Ar=0.4, where Ar is the radio background intensity at cosmic dawn relative to the cosmic microwave background. This amplitude is one-fifth of the minimum required to explain the EDGES signal, and corresponds to just 0.1% of the observed extragalactic background; it would give a signal that can be detected at 5.9σ significance (compared to 4.1σ for the standard signal) and can be distinguished from the standard (no ERB) signal at 8.5σ, all with a 1,000 hr global signal measurement. The 21-cm power spectrum has potentially more information, but far greater resources would be required for comparable constraints. For the mDM model, over a range of viable parameters, the global signal detection significance would be 4.7−7.2σ, and it could be distinguished from the standard at 2.2−9.3σ. With an array of global signal antennas achieving an effective 100,000 hr integration, the significance would be 10× better. Our analysis helps motivate the development of lunar and space-based dark ages experiments.
Recursive neural networks (Tree-RNNs) based on dependency trees are
ubiquitous in modeling sentence meanings as they effectively capture semantic
relationships between non-neighborhood words. However, recognizing semantically
dissimilar sentences with the same words and syntax is still a challenge to
Tree-RNNs. This work proposes an improvement to Dependency Tree-RNN (DT-RNN)
using the grammatical relationship type identified in the dependency parse. Our
experiments on semantic relatedness scoring (SRS) and recognizing textual
entailment (RTE) in sentence pairs using SICK (Sentence Involving Compositional
Knowledge) dataset show encouraging results. The model achieved a 2%
improvement in classification accuracy for the RTE task over the DT-RNN model.
The results show that Pearson's and Spearman's correlation measures between the
model's predicted similarity scores and human ratings are higher than those of
standard DT-RNNs.
02 Aug 2023
Identifying the structural dependence between the cryptocurrencies and predicting market trend are fundamental for effective portfolio management in cryptocurrency trading. In this paper, we present a unified Bayesian framework based on potential field theory and Gaussian Process to characterize the structural dependency of various cryptocurrencies, using historic price information. The following are our significant contributions: (i) Proposed a novel model for cryptocurrency price movements as a trajectory of a dynamical system governed by a time-varying non-linear potential field. (ii) Validated the existence of the non-linear potential function in cryptocurrency market through Lyapunov stability analysis. (iii) Developed a Bayesian framework for inferring the non-linear potential function from observed cryptocurrency prices. (iv) Proposed that attractors and repellers inferred from the potential field are reliable cryptocurrency market indicators, surpassing existing attributes, such as, mean, open price or close price of an observation window, in the literature. (v) Analysis of cryptocurrency market during various Bitcoin crash durations from April 2017 to November 2021, shows that attractors captured the market trend, volatility, and correlation. In addition, attractors aids explainability and visualization. (vi) The structural dependence inferred by the proposed approach was found to be consistent with results obtained using the popular wavelet coherence approach. (vii) The proposed market indicators (attractors and repellers) can be used to improve the prediction performance of state-of-art deep learning price prediction models. As, an example, we show improvement in Litecoin price prediction up to a horizon of 12 days.
Beyond fifth-generation (B5G) networks aim to support high data rates, low-latency applications, and massive machine communications. Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML) can help to improve B5G network performance and efficiency. However, dynamic service demands of B5G use cases cause AI/ML model performance degradation, resulting in Service Level Agreements (SLA) violations, over- or under-provisioning of resources, etc. Retraining is essential to address the performance degradation of the AI/ML models. Existing threshold and periodic retraining approaches have potential disadvantages, such as SLA violations and inefficient resource utilization for setting a threshold parameter in a dynamic environment. This paper proposes a novel approach that predicts when to retrain AI/ML models using Generative Artificial Intelligence. The proposed predictive approach is evaluated for a Quality of Service Prediction use case on the Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Software Community platform and compared to the predictive approach based on the classifier and a threshold approach. Also, a realtime dataset from the Colosseum testbed is considered to evaluate Network Slicing (NS) use case with the proposed predictive approach. The results show that the proposed predictive approach outperforms both the classifier-based predictive and threshold approaches.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.