Observatorio Astronómico de CórdobaUNC
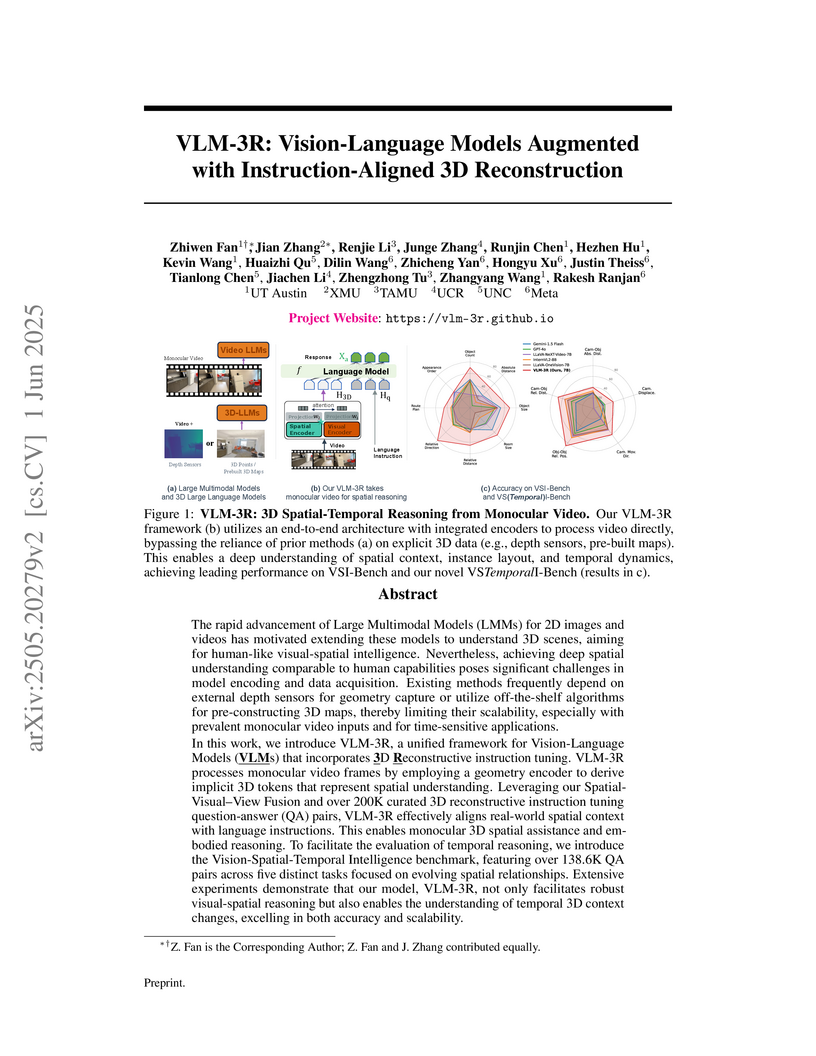
VLM-3R enhances Vision-Language Models' spatial and spatio-temporal reasoning by implicitly integrating 3D reconstruction directly from monocular video input. The framework achieves leading performance on static 3D spatial reasoning benchmarks and a newly introduced temporal 3D reasoning benchmark, VSTemporalI-Bench.
Benchmarks shape progress in AI research. A useful benchmark should be both difficult and realistic: questions should challenge frontier models while also reflecting real-world usage. Yet, current paradigms face a difficulty-realism tension: exam-style benchmarks are often made artificially difficult with limited real-world value, while benchmarks based on real user interaction often skew toward easy, high-frequency problems. In this work, we explore a radically different paradigm: assessing models on unsolved questions. Rather than a static benchmark scored once, we curate unsolved questions and evaluate models asynchronously over time with validator-assisted screening and community verification. We introduce UQ, a testbed of 500 challenging, diverse questions sourced from Stack Exchange, spanning topics from CS theory and math to sci-fi and history, probing capabilities including reasoning, factuality, and browsing. UQ is difficult and realistic by construction: unsolved questions are often hard and naturally arise when humans seek answers, thus solving them yields direct real-world value. Our contributions are threefold: (1) UQ-Dataset and its collection pipeline combining rule-based filters, LLM judges, and human review to ensure question quality (e.g., well-defined and difficult); (2) UQ-Validators, compound validation strategies that leverage the generator-validator gap to provide evaluation signals and pre-screen candidate solutions for human review; and (3) UQ-Platform, an open platform where experts collectively verify questions and solutions. The top model passes UQ-validation on only 15% of questions, and preliminary human verification has already identified correct answers among those that passed. UQ charts a path for evaluating frontier models on real-world, open-ended challenges, where success pushes the frontier of human knowledge. We release UQ at this https URL.
In this paper, we introduce Motion-Grounded Video Reasoning, a new motion
understanding task that requires generating visual answers (video segmentation
masks) according to the input question, and hence needs implicit spatiotemporal
reasoning and grounding. This task extends existing spatiotemporal grounding
work focusing on explicit action/motion grounding, to a more general format by
enabling implicit reasoning via questions. To facilitate the development of the
new task, we collect a large-scale dataset called GROUNDMORE, which comprises
1,715 video clips, 249K object masks that are deliberately designed with 4
question types (Causal, Sequential, Counterfactual, and Descriptive) for
benchmarking deep and comprehensive motion reasoning abilities. GROUNDMORE
uniquely requires models to generate visual answers, providing a more concrete
and visually interpretable response than plain texts. It evaluates models on
both spatiotemporal grounding and reasoning, fostering to address complex
challenges in motion-related video reasoning, temporal perception, and
pixel-level understanding. Furthermore, we introduce a novel baseline model
named Motion-Grounded Video Reasoning Assistant (MORA). MORA incorporates the
multimodal reasoning ability from the Multimodal LLM, the pixel-level
perception capability from the grounding model (SAM), and the temporal
perception ability from a lightweight localization head. MORA achieves
respectable performance on GROUNDMORE outperforming the best existing visual
grounding baseline model by an average of 21.5% relatively. We hope this novel
and challenging task will pave the way for future advancements in robust and
general motion understanding via video reasoning segmentation
24 Oct 2025
As large language models (LLMs) advance, the ultimate vision for their role in science is emerging: we could build an AI collaborator to effectively assist human beings throughout the entire scientific research process. We refer to this envisioned system as ResearchGPT. Given that scientific research progresses through multiple interdependent phases, achieving this vision requires rigorous benchmarks that evaluate the end-to-end workflow rather than isolated sub-tasks. To this end, we contribute CS-54k, a high-quality corpus of scientific Q&A pairs in computer science, built from 14k CC-licensed papers. It is constructed through a scalable, paper-grounded pipeline that combines retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with multi-stage quality control to ensure factual grounding. From this unified corpus, we derive two complementary subsets: CS-4k, a carefully curated benchmark for evaluating AI's ability to assist scientific research, and CS-50k, a large-scale training dataset. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CS-4k stratifies state-of-the-art LLMs into distinct capability tiers. Open models trained on CS-50k with supervised training and reinforcement learning demonstrate substantial improvements. Even 7B-scale models, when properly trained, outperform many larger proprietary systems, such as GPT-4.1, GPT-4o, and Gemini 2.5 Pro. This indicates that making AI models better research assistants relies more on domain-aligned training with high-quality data than on pretraining scale or general benchmark performance. We release CS-4k and CS-50k in the hope of fostering AI systems as reliable collaborators in CS research.
Single-image human mesh recovery is a challenging task due to the ill-posed nature of simultaneous body shape, pose, and camera estimation. Existing estimators work well on images taken from afar, but they break down as the person moves close to the camera. Moreover, current methods fail to achieve both accurate 3D pose and 2D alignment at the same time. Error is mainly introduced by inaccurate perspective projection heuristically derived from orthographic parameters. To resolve this long-standing challenge, we present our method BLADE which accurately recovers perspective parameters from a single image without heuristic assumptions. We start from the inverse relationship between perspective distortion and the person's Z-translation Tz, and we show that Tz can be reliably estimated from the image. We then discuss the important role of Tz for accurate human mesh recovery estimated from close-range images. Finally, we show that, once Tz and the 3D human mesh are estimated, one can accurately recover the focal length and full 3D translation. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks and real-world close-range images show that our method is the first to accurately recover projection parameters from a single image, and consequently attain state-of-the-art accuracy on 3D pose estimation and 2D alignment for a wide range of images. this https URL
This work introduces a principled, Bayesian thermodynamic framework using Active Inference to enable self-organization and adaptation in Multi-LLM systems. An agent embedded with this framework learned complex environment dynamics and exhibited strategic action selection, naturally transitioning from information-gathering exploration to goal-directed exploitation for an LLM-based agent.
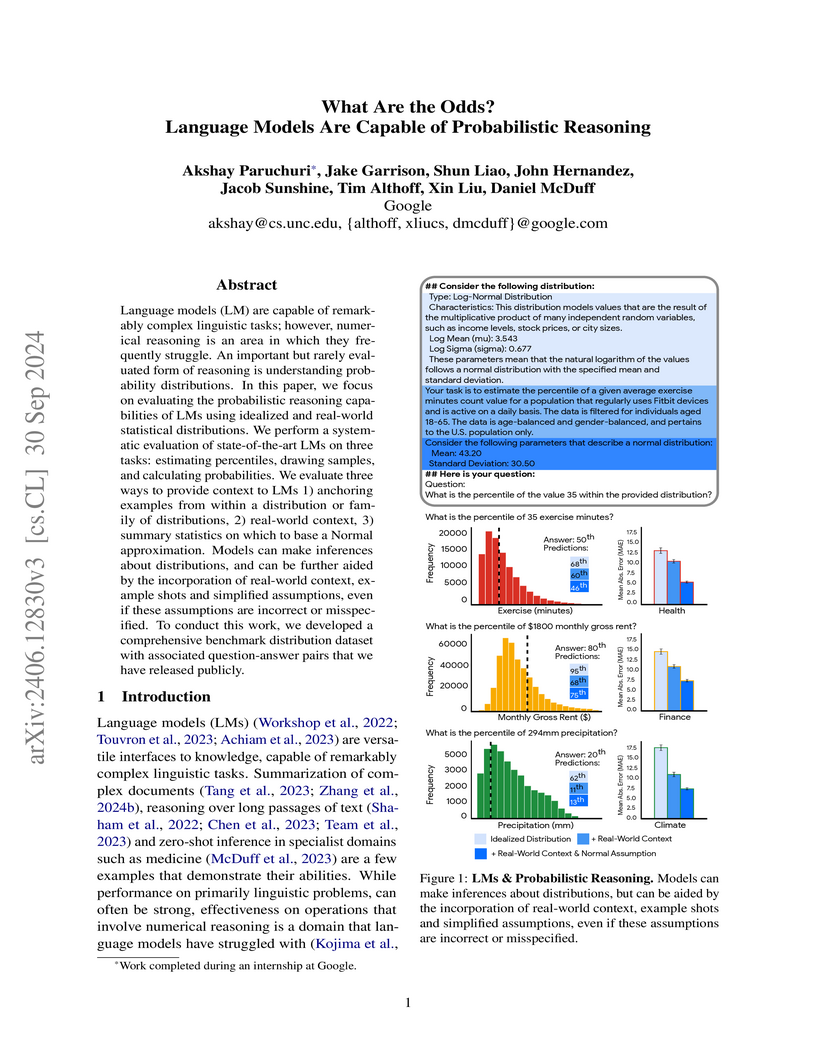
Large language models can perform probabilistic reasoning tasks, demonstrating varying accuracy across different distribution types and significantly improving performance with specific prompting strategies like in-context examples and simplified Normal approximations. This research from Google and UNC Chapel Hill provides a new benchmark dataset to evaluate these capabilities.
We find that CMB photons passing through local voids (z<0.03) are hotter
than expected at the 2.7−3.6σ level. Combined with earlier findings
showing a >5\sigma cooling of CMB photons in galactic filaments in the same
redshift range, we now have possible evidence for a negative Integrated
Sachs-Wolfe (ISW) effect in the very recent universe. In addition to having
opposite sign, the observed amplitude is an order of magnitude larger than the
predicted Rees-Sciama and ISW effects for the nearby universe. An altered
growth of gravitational potentials at very low redshift, as predicted by some
dark energy and modified gravity models, could give rise to the observed sign
change. We discuss the results in light of the latest Data Release 2 results of
the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) showing evidence for dynamical
dark energy. When removing the CMB quadrupole, we find the temperatures
measured in voids to a large degree uncorrelated with the temperature measured
in galaxies and the observed mean difference of 41μK between void and
galaxy temperatures is about 6.5σ larger than found in simulations.
21 Oct 2025
We use the TNG50 cosmological hydrodynamic simulation to study the accreted stellar component and stellar haloes of isolated galaxies spanning a wide range of masses ($10^8
Hybrid refractive-diffractive lenses combine the light efficiency of refractive lenses with the information encoding power of diffractive optical elements (DOE), showing great potential as the next generation of imaging systems. However, accurately simulating such hybrid designs is generally difficult, and in particular, there are no existing differentiable image formation models for hybrid lenses with sufficient accuracy.
In this work, we propose a new hybrid ray-tracing and wave-propagation (ray-wave) model for accurate simulation of both optical aberrations and diffractive phase modulation, where the DOE is placed between the last refractive surface and the image sensor, i.e. away from the Fourier plane that is often used as a DOE position. The proposed ray-wave model is fully differentiable, enabling gradient back-propagation for end-to-end co-design of refractive-diffractive lens optimization and the image reconstruction network. We validate the accuracy of the proposed model by comparing the simulated point spread functions (PSFs) with theoretical results, as well as simulation experiments that show our model to be more accurate than solutions implemented in commercial software packages like Zemax. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model through real-world experiments and show significant improvements in both aberration correction and extended depth-of-field (EDoF) imaging. We believe the proposed model will motivate further investigation into a wide range of applications in computational imaging, computational photography, and advanced optical design. Code will be released upon publication.
The properties of galaxies in low-density regions of the universe suggest an interplay between galaxy formation and environment. However, the specific reason why this particular large-scale environment influences the evolution of galaxies remains unclear. This paper examines the properties and evolutionary paths of galaxies within cosmic voids using the Illustris TNG300 simulation. The population of void galaxies at z = 0 has a higher star formation rate, a smaller stellar-to-halo-mass ratio, higher gas metallicity, and lower stellar metallicity in comparison with non-void galaxies at fixed stellar mass. Our analysis shows that these differences are mainly due to the characteristics of galaxies classified as satellites, for which the largest differences between void and non-void samples are found. Although the mean number of mergers is similar between void and non-void samples at a fixed stellar mass, void galaxies tend to experience mergers at later times, resulting in a more recent accumulation of accreted stellar mass. While the mean net accreted mass is comparable for high mass galaxies, low mass void galaxies tend to exhibit higher fractions of accreted stars than non-void galaxies. This finding challenges the common notion that void galaxies predominantly experience growth with infrequent mergers or interactions.
NSF’s NOIRLabInstituto de Astronomía Teórica y ExperimentalUniversidad Nacional de CórdobaGemini ObservatoryObservatorio Astronómico de CórdobaComisión Nacional de Actividades EspacialesUNSJConsejo de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas de la República ArgentinaInstituto de Ciencias Astrómicas, de la Tierra y el Espacio
Hot dust in the proximity of AGNs strongly emits in the Near Infrared producing a red excess that, in type 2 sources, can be modeled to measure its temperature. In the era of high spatial-resolution multi-wavelength data, mapping the hot dust around Supermassive Black Holes is important for the efforts to achieve a complete picture of the dust role and distribution around these compact objects.
In this work we propose a methodology to detect the hot dust emission in the proximity of Type 2 AGNs and measure its temperature using K-band spectra (λc = 2.2\,μm).
To achieve this, we have developed NIRDust, a Python package for modeling K-band spectra, estimate the dust temperature and characterize the involved uncertainties. We tested synthetic and real spectra in order to check the performance and suitability of the physical model over different types of data.
Our tests on synthetic spectra demonstrated that the obtained results are influenced by the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) of the input spectra. However, we accurately characterized the uncertainties, which remained below ∼150 K for an average S/N per pixel exceeding 20. Applying NIRDust to NGC 5128 (Centaurus A), observed with the Gemini South Telescope, we estimated a dust temperature of 662 and 667 K from Flamingos-2 spectra and 697 and 607 K from GNIRS spectra using two different approaches.
19 Jul 2016
 California Institute of Technology
California Institute of Technology University of Chicago
University of Chicago University of Oxford
University of Oxford ETH Zürich
ETH Zürich NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Space Telescope Science InstituteThe University of OklahomaSmithsonian Astrophysical ObservatoryUniversity of Maryland Baltimore CountyUniversidad Nacional de CórdobaInfrared Processing and Analysis CenterNASA HeadquartersObservatorio Astronómico de CórdobaKorea Aerospace Research Institute
Space Telescope Science InstituteThe University of OklahomaSmithsonian Astrophysical ObservatoryUniversity of Maryland Baltimore CountyUniversidad Nacional de CórdobaInfrared Processing and Analysis CenterNASA HeadquartersObservatorio Astronómico de CórdobaKorea Aerospace Research InstituteThe Disk Detective citizen science project aims to find new stars with 22 micron excess emission from circumstellar dust using data from NASA's WISE mission. Initial cuts on the AllWISE catalog provide an input catalog of 277,686 sources. Volunteers then view images of each source online in 10 different bands to identify false-positives (galaxies, background stars, interstellar matter, image artifacts, etc.). Sources that survive this online vetting are followed up with spectroscopy on the FLWO Tillinghast telescope. This approach should allow us to unleash the full potential of WISE for finding new debris disks and protoplanetary disks. We announce a first list of 37 new disk candidates discovered by the project, and we describe our vetting and follow-up process. One of these systems appears to contain the first debris disk discovered around a star with a white dwarf companion: HD 74389. We also report four newly discovered classical Be stars (HD 6612, HD 7406, HD 164137, and HD 218546) and a new detection of 22 micron excess around a previously known debris disk host star, HD 22128.
Bertsimas and Lo's seminal work established a foundational framework for addressing the implementation shortfall dilemma faced by large institutional investors. Their models emphasized the critical role of accurate knowledge of market microstructure and price/information dynamics in optimizing trades to minimize execution costs. However, this paper recognizes that perfect initial knowledge may not be a realistic assumption for new investors entering the market. Therefore, this study aims to bridge this gap by proposing an approach that iteratively derives OLS estimates of the market parameters from period to period. This methodology enables uninformed investors to engage in the market dynamically, adjusting their strategies over time based on evolving estimates, thus offering a practical solution for navigating the complexities of execution cost optimization without perfect initial knowledge.
06 Feb 2019
We present a near-infrared study of the Seyfert 2 galaxy NGC\,6300, based on subarcsecond images and long slit spectroscopy obtained with Flamingos-2 at Gemini South. We have found that the peak of the nuclear continuum emission in the Ks band and the surrounding nuclear disk are 25\,pc off-center with respect to the center of symmetry of the larger scale circumnuclear disk, suggesting that this black hole is still not fixed in the galaxy potential well. The molecular gas radial velocity curve yields a central black hole upper mass estimation of MSMBHupper=(6±2)×107\Msun. The Paβ emission line has a strongly asymmetric profile with a blueshifted broad component that we associate with a nuclear ionized gas outflow. We have found in the Ks-band spectra that the slope of the continuum becomes steeper with increasing radii, which can be explained as the presence of large amounts of hot dust not only in the nucleus but also in the circumnuclear region up to r=27\,pc. In fact, the nuclear red excess obtained after subtracting the stellar contribution resembles to that of a blackbody with temperatures around 1200\,K. This evidence supports the idea that absorbing material located around the nucleus, but not close enough to be the torus of the unified model, could be responsible for at least part of the nuclear obscuration in this Seyfert 2 nucleus.
Investigating the assembly history of the most massive and passive galaxies will enhance our understanding of why galaxies exhibit such a remarkable diversity in structure and morphology. In this paper, we simultaneously investigate the assembly history and redshift evolution of semi-analytically modelled galaxy properties of central galaxies between 0.56 < z < 4.15, alongside their connection to their halos as a function of large-scale environment. We extract sub-samples of galaxies from a mock catalogue representative for the BOSS-CMASS sample, which includes the most massive and passively evolving system known today. Utilising typical galaxy properties such as star formation rate, (g-i) colour, or cold gas-phase metallicity (Zcold), we track the redshift evolution of these properties across the main progenitor trees. We present results on galaxy and halo properties, including their growth and clustering functions. Our findings indicate that galaxies in the highest stellar and halo mass regimes are least metal-enriched (using Zcold as a proxy) and consistently exhibit significantly larger black hole masses and higher clustering amplitudes compared to sub-samples selected by e.g. colour or star formation rate. This population forms later and also retains large reservoirs of cold gas. In contrast, galaxies in the intermediate and lower stellar/halo mass regimes consume their cold gas at higher redshift and were among the earliest and quickest to assemble. We observe a clear trend where the clustering of the galaxies selected according to their Zcold-values (either low-Zcold or high-Zcold) depends on the density of their location within the large-scale environment. We assume that in particular galaxies in the low/high-Zcold sub-samples form and evolve through distinct evolutionary channels, which are predetermined by their location within the large-scale environment of the cosmic web.
14 Feb 2009
We use N-body/gasdynamical LambdaCDM cosmological simulations to examine the effect of the assembly of a central galaxy on the shape and mass profile of its dark halo. Two series of simulations are compared; one that follows only the evolution of the dark matter component and a second one where a baryonic component is added. These simulations include radiative cooling but neglect star formation and feedback, leading most baryons to collect at the halo center in a disk which is too small and too massive when compared with typical spiral. This unrealistic model allows us, nevertheless, to gauge the maximum effect that galaxies may have in transforming their dark halos. We find that the shape of the halo becomes more axisymmetric: halos are transformed from triaxial into essentially oblate systems, with well-aligned isopotential contours of roughly constant flattening (c/a ~ 0.85). Halos always contract as a result of galaxy assembly, but the effect is substantially less pronounced than predicted by the "adiabatic contraction" hypothesis. The reduced contraction helps to reconcile LambdaCDM halos with constraints on the dark matter content inside the solar circle and should alleviate the long-standing difficulty of matching simultaneously the scaling properties of galaxy disks and the luminosity function. The halo contraction is also less pronounced than found in earlier simulations, a disagreement that suggests that halo contraction is not solely a function of the initial and final distribution of baryons. Not only how much baryonic mass has been deposited at the center of a halo matters, but also the mode of its deposition. It might prove impossible to predict the halo response without a detailed understanding of a galaxy's assembly history. (Abriged)
29 Jan 2025
 University of Toronto
University of Toronto Kyoto University
Kyoto University University of CopenhagenUniversity of Ljubljana
University of CopenhagenUniversity of Ljubljana Columbia University
Columbia University Space Telescope Science InstituteYork University
Space Telescope Science InstituteYork University University of California, Davis
University of California, Davis University of GroningenNational Research Council of CanadaSaint Mary’s UniversityINAF – Osservatorio Astronomico di RomaObservatorio Astronómico de Córdoba
University of GroningenNational Research Council of CanadaSaint Mary’s UniversityINAF – Osservatorio Astronomico di RomaObservatorio Astronómico de CórdobaWe report the discovery of a z∼7 group of galaxies that contains two Little Red Dots (LRDs) just 3.3 kpc apart, along with three satellite galaxies, as part of the Canadian NIRISS Unbiased Cluster Survey (CANUCS). These LRDs are massive (M⋆∼1010M⊙) and dusty (A(V) >1 mag) whereas the three satellites are lower-mass objects (M⋆∼108−9M⊙) subject to low dust attenuations. The spectral energy distributions (SEDs) of this LRD pair show strong evidence for a Balmer Break, consistent with a recent (∼100 Myr) quenching of star formation. In contrast, the satellites are compatible with a recent-onset (∼100 Myr), ongoing burst of star formation. LRD1's SED is consistent with a dust-free AGN as the source of the UV excess in the galaxy. The optical continuum would be powered by the emission from an obscured post-starburst and the AGN at a subdominant level. LRD2's SED is more ambiguous to interpret, but it could also be indicative of a dust-free AGN. The proximity of the two LRDs suggests that their interaction may be responsible for their recent star formation histories, which can be interpreted as environmental bursting and quenching in the Epoch of Reionization.
Counterrotating stars in disk galaxies are a puzzling dynamical feature whose
origin has been ascribed to either satellite accretion events or to disk
instabilities triggered by deviations from axisymmetry. We use a cosmological
simulation of the formation of a disk galaxy to show that counterrotating
stellar disk components may arise naturally in hierarchically-clustering
scenarios even in the absence of merging. The simulated disk galaxy consists of
two coplanar, overlapping stellar components with opposite spins: an inner
counterrotating bar-like structure made up mostly of old stars surrounded by an
extended, rotationally-supported disk of younger stars. The opposite-spin
components originate from material accreted from two distinct filamentary
structures which at turn around, when their net spin is acquired, intersect
delineating a "V"-like structure. Each filament torques the other in opposite
directions; the filament that first drains into the galaxy forms the inner
counterrotating bar, while material accreted from the other filament forms the
outer disk. Mergers do not play a substantial role and most stars in the galaxy
are formed in situ; only 9% of all stars are contributed by accretion events.
The formation scenario we describe here implies a significant age difference
between the co- and counterrotating components, which may be used to
discriminate between competing scenarios for the origin of counterrotating
stars in disk galaxies.
Chaotic systems near black holes satisfy a universal bound, $\lambda \leq
\kappa_HlinkingtheLyapunovcoefficient\lambda$ associated with unstable
orbits to surface gravity κH of the event horizon. A natural question
is whether this bound is satisfied by unstable circular null geodesics in the
vicinity of black holes. However, there are known cases where this bound is
violated. It is intriguing to ask whether there exists an alternative universal
bound that is valid in such situations. We show that for any spherically
symmetric, static black hole that satisfies Einstein's equations and the
dominant energy condition, there exist other universal bounds relating the
Lyapunov coefficient to a generalized notion of surface gravity at the photon
sphere. As applications, we show how these bounds also constrain the imaginary
part of quasinormal modes in the eikonal regime and how the Lyapunov
coefficient relates to the shadow size and the entropy of the horizon.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.