Politecnico di Milano
We report on the development of a novel pixel charge readout system, Grid
Activated Multi-scale pixel readout (GAMPix), which is under development for
use in the GammaTPC gamma ray instrument concept. GammaTPC is being developed
to optimize the use of liquid argon time projection chamber technology for
gamma ray astrophysics, for which a fine grained low power charge readout is
essential. GAMPix uses a new architecture with coarse and fine scale
instrumented electrodes to solve the twin problems of loss of measured charge
after diffusion, and high readout power. Fundamentally, it enables low noise
and ultra low power charge readout at the spatial scale limited by diffusion in
a time projection chamber, and has other possibly applications, including
future DUNE modules.
Generative machine learning methods, such as diffusion models and flow matching, have shown great potential in modeling complex system behaviors and building efficient surrogate models. However, these methods typically learn the underlying physics implicitly from data. We propose Physics-Based Flow Matching (PBFM), a novel generative framework that explicitly embeds physical constraints, both PDE residuals and algebraic relations, into the flow matching objective. We also introduce temporal unrolling at training time that improves the accuracy of the final, noise-free sample prediction. Our method jointly minimizes the flow matching loss and the physics-based residual loss without requiring hyperparameter tuning of their relative weights. Additionally, we analyze the role of the minimum noise level, σmin, in the context of physical constraints and evaluate a stochastic sampling strategy that helps to reduce physical residuals. Through extensive benchmarks on three representative PDE problems, we show that our approach yields up to an 8× more accurate physical residuals compared to FM, while clearly outperforming existing algorithms in terms of distributional accuracy. PBFM thus provides a principled and efficient framework for surrogate modeling, uncertainty quantification, and accelerated simulation in physics and engineering applications.
AdaCLIP adapts the Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) model using hybrid learnable prompts and a Hybrid Semantic Fusion module to address zero-shot anomaly detection. This approach enables the system to identify anomalies in categories not seen during training, consistently outperforming existing zero-shot anomaly detection methods across 14 diverse real-world datasets.
 INFNJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchPolitecnico di MilanoUniversit`a di CataniaUniversit`a degli Studi di MilanoUniversit`a degli Studi Roma TreInstitute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of SciencesLaboratori Nazionali dell’INFN di FrascatiUniversit`a degli Studi di PerugiaUniversit`a degli Studi di FerraraUniversit´a di Milano-BicoccaUniversita' di Padova
INFNJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchPolitecnico di MilanoUniversit`a di CataniaUniversit`a degli Studi di MilanoUniversit`a degli Studi Roma TreInstitute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of SciencesLaboratori Nazionali dell’INFN di FrascatiUniversit`a degli Studi di PerugiaUniversit`a degli Studi di FerraraUniversit´a di Milano-BicoccaUniversita' di PadovaPrecise modeling of detector energy response is crucial for next-generation neutrino experiments which present computational challenges due to lack of analytical likelihoods. We propose a solution using neural likelihood estimation within the simulation-based inference framework. We develop two complementary neural density estimators that model likelihoods of calibration data: conditional normalizing flows and a transformer-based regressor. We adopt JUNO - a large neutrino experiment - as a case study. The energy response of JUNO depends on several parameters, all of which should be tuned, given their non-linear behavior and strong correlations in the calibration data. To this end, we integrate the modeled likelihoods with Bayesian nested sampling for parameter inference, achieving uncertainties limited only by statistics with near-zero systematic biases. The normalizing flows model enables unbinned likelihood analysis, while the transformer provides an efficient binned alternative. By providing both options, our framework offers flexibility to choose the most appropriate method for specific needs. Finally, our approach establishes a template for similar applications across experimental neutrino and broader particle physics.
We introduce a guide to help deep learning practitioners understand and
manipulate convolutional neural network architectures. The guide clarifies the
relationship between various properties (input shape, kernel shape, zero
padding, strides and output shape) of convolutional, pooling and transposed
convolutional layers, as well as the relationship between convolutional and
transposed convolutional layers. Relationships are derived for various cases,
and are illustrated in order to make them intuitive.
A new benchmark, AGENTSAFE, systematically evaluates the safety of embodied vision-language model (VLM) agents against hazardous instructions, revealing vulnerabilities primarily in the planning stage. The research introduces SAFE-AUDIT, a thought-level safety module that improves task success rate by 2.22% on normal instructions and achieves the lowest planning (3.52%) and task success rates (0.48%) for hazardous tasks.
Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) on chain-of-thought (CoT) data shows that a small amount of high-quality data can outperform massive datasets. Yet, what constitutes "quality" remains ill-defined. Existing reasoning methods rely on indirect heuristics such as problem difficulty or trace length, while instruction-tuning has explored a broader range of automated selection strategies, but rarely in the context of reasoning. We propose to define reasoning data quality using influence functions, which measure the causal effect of individual CoT examples on downstream accuracy, and introduce influence-based pruning, which consistently outperforms perplexity and embedding-based baselines on math reasoning within a model family.
We address the problem of uncertainty quantification in time series
forecasting by exploiting observations at correlated sequences. Relational deep
learning methods leveraging graph representations are among the most effective
tools for obtaining point estimates from spatiotemporal data and correlated
time series. However, the problem of exploiting relational structures to
estimate the uncertainty of such predictions has been largely overlooked in the
same context. To this end, we propose a novel distribution-free approach based
on the conformal prediction framework and quantile regression. Despite the
recent applications of conformal prediction to sequential data, existing
methods operate independently on each target time series and do not account for
relationships among them when constructing the prediction interval. We fill
this void by introducing a novel conformal prediction method based on graph
deep learning operators. Our approach, named Conformal Relational Prediction
(CoRel), does not require the relational structure (graph) to be known a priori
and can be applied on top of any pre-trained predictor. Additionally, CoRel
includes an adaptive component to handle non-exchangeable data and changes in
the input time series. Our approach provides accurate coverage and achieves
state-of-the-art uncertainty quantification in relevant benchmarks.
Language is a deep-rooted means of perpetration of stereotypes and discrimination. Large Language Models (LLMs), now a pervasive technology in our everyday lives, can cause extensive harm when prone to generating toxic responses. The standard way to address this issue is to align the LLM, which, however, dampens the issue without constituting a definitive solution. Therefore, testing LLM even after alignment efforts remains crucial for detecting any residual deviations with respect to ethical standards. We present EvoTox, an automated testing framework for LLMs' inclination to toxicity, providing a way to quantitatively assess how much LLMs can be pushed towards toxic responses even in the presence of alignment. The framework adopts an iterative evolution strategy that exploits the interplay between two LLMs, the System Under Test (SUT) and the Prompt Generator steering SUT responses toward higher toxicity. The toxicity level is assessed by an automated oracle based on an existing toxicity classifier. We conduct a quantitative and qualitative empirical evaluation using four state-of-the-art LLMs as evaluation subjects having increasing complexity (7-13 billion parameters). Our quantitative evaluation assesses the cost-effectiveness of four alternative versions of EvoTox against existing baseline methods, based on random search, curated datasets of toxic prompts, and adversarial attacks. Our qualitative assessment engages human evaluators to rate the fluency of the generated prompts and the perceived toxicity of the responses collected during the testing sessions. Results indicate that the effectiveness, in terms of detected toxicity level, is significantly higher than the selected baseline methods (effect size up to 1.0 against random search and up to 0.99 against adversarial attacks). Furthermore, EvoTox yields a limited cost overhead (from 22% to 35% on average).
 University of Washington
University of Washington Carnegie Mellon UniversityPolitecnico di Milano
Carnegie Mellon UniversityPolitecnico di Milano Technical University of MunichUniversity of North Carolinaunster
Technical University of MunichUniversity of North Carolinaunster Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyIstituto Nazionale di Fisica NucleareChulalongkorn UniversityMax Planck InstituteTriangle Universities Nuclear LaboratoryUniversity of Wuppertal* Czech Academy of SciencesUniversity of M":
Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyIstituto Nazionale di Fisica NucleareChulalongkorn UniversityMax Planck InstituteTriangle Universities Nuclear LaboratoryUniversity of Wuppertal* Czech Academy of SciencesUniversity of M":The KATRIN experiment delivers the most precise direct measurement of the effective electron antineutrino mass, establishing an upper limit of 0.45 eV at 90% confidence level based on 259 days of data. This result nearly doubles the precision of KATRIN's previous bound and provides a world-leading direct constraint on neutrino mass.
08 Sep 2025
Driven by the pursuit of gigabit-per-second data speeds for future 6G mobile networks, in addition to the support of sensing and artificial intelligence applications, the industry is expanding beyond crowded sub-6 GHz bands with innovative new spectrum allocations. In this paper, we chart a compelling vision for 6G within the frequency range 3 (FR3) spectrum, i.e. 7.125-24.25 \GHz, by delving into its key enablers and addressing the multifaceted challenges that lie ahead for these new frequency bands. Here we highlight the physical properties of this never-before used spectrum for cellular by reviewing recent channel measurements for outdoor and indoor environments, including path loss, delay and angular spreads, and material penetration loss, all which offer insights that underpin future 5G/6G wireless communication designs. Building on the fundamental knowledge of the channel properties, we explore FR3 spectrum agility strategies that balance coverage and capacity tradeoffs, while examining coexistence with incumbent systems, such as satellites, radio astronomy, and earth exploration. Moreover, we discuss the potential of massive multiple-input multiple-output technologies, challenges for commercial deployment, and potential solutions for FR3, including multiband sensing for FR3 integrated sensing and communications. Finally, we outline 6G standardization features that are likely to emerge from 3GPP radio frame innovations and open radio access network developments.
16 Jul 2025
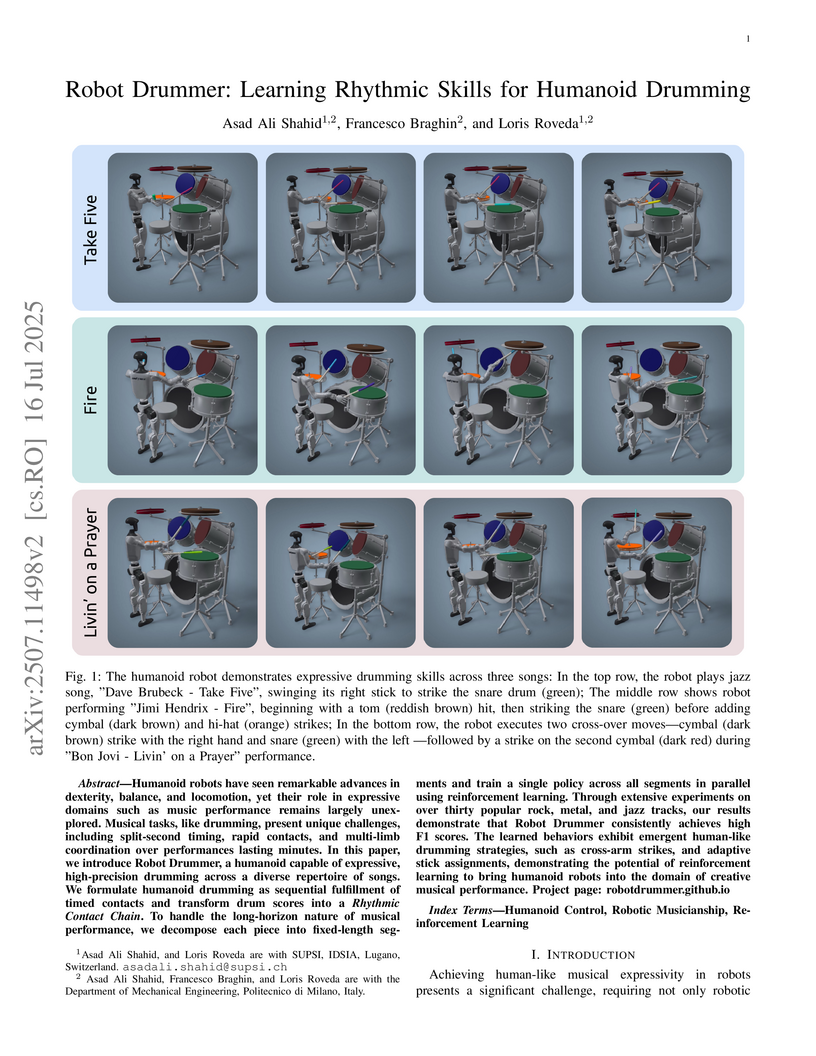
This research enables a full humanoid robot to perform complex, expressive drumming by interpreting standard musical scores. The work introduces a reinforcement learning framework that translates MIDI data into a Rhythmic Contact Chain and optimizes control policies using a dense, unified reward function, achieving high-precision drumming with emergent human-like strategies.
We study online learning in constrained Markov decision processes (CMDPs)
with adversarial losses and stochastic hard constraints, under bandit feedback.
We consider three scenarios. In the first one, we address general CMDPs, where
we design an algorithm attaining sublinear regret and cumulative positive
constraints violation. In the second scenario, under the mild assumption that a
policy strictly satisfying the constraints exists and is known to the learner,
we design an algorithm that achieves sublinear regret while ensuring that
constraints are satisfied at every episode with high probability. In the last
scenario, we only assume the existence of a strictly feasible policy, which is
not known to the learner, and we design an algorithm attaining sublinear regret
and constant cumulative positive constraints violation. Finally, we show that
in the last two scenarios, a dependence on the Slater's parameter is
unavoidable. To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first to study CMDPs
involving both adversarial losses and hard constraints. Thus, our algorithms
can deal with general non-stationary environments subject to requirements much
stricter than those manageable with existing ones, enabling their adoption in a
much wider range of applications.
25 Sep 2025
We propose a reduced-order modeling approach for nonlinear, parameter-dependent ordinary differential equations (ODE). Dimensionality reduction is achieved using nonlinear maps represented by autoencoders. The resulting low-dimensional ODE is then solved using standard integration in time schemes, and the high-dimensional solution is reconstructed from the low-dimensional one. We investigate the applicability of neural networks for constructing effective autoencoders with the property of reconstructing the input manifold with null representation error. We study the convergence of the reduced-order model to the high-fidelity one. Numerical experiments show the robustness and accuracy of our approach, highlighting its potential to accelerate complex dynamical simulations without sacrificing accuracy. Moreover, we examine how the reduction influences the stability properties of the reconstructed high-dimensional solution.
The whole is greater than the sum of its parts-even in 3D-text contrastive learning. We introduce SceneForge, a novel framework that enhances contrastive alignment between 3D point clouds and text through structured multi-object scene compositions. SceneForge leverages individual 3D shapes to construct multi-object scenes with explicit spatial relations, pairing them with coherent multi-object descriptions refined by a large language model. By augmenting contrastive training with these structured, compositional samples, SceneForge effectively addresses the scarcity of large-scale 3D-text datasets, significantly enriching data complexity and diversity. We systematically investigate critical design elements, such as the optimal number of objects per scene, the proportion of compositional samples in training batches, and scene construction strategies. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SceneForge delivers substantial performance gains across multiple tasks, including zero-shot classification on ModelNet, ScanObjNN, Objaverse-LVIS, and ScanNet, as well as few-shot part segmentation on ShapeNetPart. SceneForge's compositional augmentations are model-agnostic, consistently improving performance across multiple encoder architectures. Moreover, SceneForge improves 3D visual question answering on ScanQA, generalizes robustly to retrieval scenarios with increasing scene complexity, and showcases spatial reasoning capabilities by adapting spatial configurations to align precisely with textual instructions.
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have achieved remarkable success across various domains. However, recent theoretical advances have identified fundamental limitations in their information propagation capabilities, such as over-squashing, where distant nodes fail to effectively exchange information. While extensively studied in static contexts, this issue remains unexplored in Spatiotemporal GNNs (STGNNs), which process sequences associated with graph nodes. Nonetheless, the temporal dimension amplifies this challenge by increasing the information that must be propagated. In this work, we formalize the spatiotemporal over-squashing problem and demonstrate its distinct characteristics compared to the static case. Our analysis reveals that, counterintuitively, convolutional STGNNs favor information propagation from points temporally distant rather than close in time. Moreover, we prove that architectures that follow either time-and-space or time-then-space processing paradigms are equally affected by this phenomenon, providing theoretical justification for computationally efficient implementations. We validate our findings on synthetic and real-world datasets, providing deeper insights into their operational dynamics and principled guidance for more effective designs.
16 Sep 2025
In this work we exhibit a class of examples that show that the characterization of purification of quantum trajectories in terms of 'dark' subspaces that was proved for finite dimensional systems fails to hold in infinite dimensional ones. Moreover, we prove that the new phenomenon emerging in our class of models and preventing purification to happen is the only new possibility that emerges in infinite dimensional systems. Our proof strategy points out that the emergence of new phenomena in infinite dimensional systems is due to the fact that the set of orthogonal projections is not sequentially compact. Having in mind this insight, we are able to prove that the finite dimensional extends to a class of infinite dimensional models.
We study \emph{online episodic Constrained Markov Decision Processes} (CMDPs) under both stochastic and adversarial constraints. We provide a novel algorithm whose guarantees greatly improve those of the state-of-the-art best-of-both-worlds algorithm introduced by Stradi et al. (2025). In the stochastic regime, \emph{i.e.}, when the constraints are sampled from fixed but unknown distributions, our method achieves O(T) regret and constraint violation without relying on Slater's condition, thereby handling settings where no strictly feasible solution exists. Moreover, we provide guarantees on the stronger notion of \emph{positive} constraint violation, which does not allow to recover from large violation in the early episodes by playing strictly safe policies. In the adversarial regime, \emph{i.e.}, when the constraints may change arbitrarily between episodes, our algorithm ensures sublinear constraint violation without Slater's condition, and achieves sublinear α-regret with respect to the \emph{unconstrained} optimum, where α is a suitably defined multiplicative approximation factor. We further validate our results through synthetic experiments, showing the practical effectiveness of our algorithm.
Recent trends in deep learning (DL) have made hardware accelerators essential
for various high-performance computing (HPC) applications, including image
classification, computer vision, and speech recognition. This survey summarizes
and classifies the most recent developments in DL accelerators, focusing on
their role in meeting the performance demands of HPC applications. We explore
cutting-edge approaches to DL acceleration, covering not only GPU- and
TPU-based platforms but also specialized hardware such as FPGA- and ASIC-based
accelerators, Neural Processing Units, open hardware RISC-V-based accelerators,
and co-processors. This survey also describes accelerators leveraging emerging
memory technologies and computing paradigms, including 3D-stacked
Processor-In-Memory, non-volatile memories like Resistive RAM and Phase Change
Memories used for in-memory computing, as well as Neuromorphic Processing
Units, and Multi-Chip Module-based accelerators. Furthermore, we provide
insights into emerging quantum-based accelerators and photonics. Finally, this
survey categorizes the most influential architectures and technologies from
recent years, offering readers a comprehensive perspective on the rapidly
evolving field of deep learning acceleration.
Shallow Recurrent Decoder networks are a novel data-driven methodology able to provide accurate state estimation in engineering systems, such as nuclear reactors. This deep learning architecture is a robust technique designed to map the temporal trajectories of a few sparse measures to the full state space, including unobservable fields, which is agnostic to sensor positions and able to handle noisy data through an ensemble strategy, leveraging the short training times and without the need for hyperparameter tuning. Following its application to a novel reactor concept, this work investigates the performance of Shallow Recurrent Decoders when applied to a real system. The underlying model is represented by a fluid dynamics model of the TRIGA Mark II research reactor; the architecture will use both synthetic temperature data coming from the numerical model and leveraging experimental temperature data recorded during a previous campaign. The objective of this work is, therefore, two-fold: 1) assessing if the architecture can reconstruct the full state of the system (temperature, velocity, pressure, turbulence quantities) given sparse data located in specific, low-dynamics channels and 2) assessing the correction capabilities of the architecture (that is, given a discrepancy between model and data, assessing if sparse measurements can provide some correction to the architecture output). As will be shown, the accurate reconstruction of every characteristic field, using both synthetic and experimental data, in real-time makes this approach suitable for interpretable monitoring and control purposes in the framework of a reactor digital twin.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.