Ask or search anything...
EventGPT introduces the first multimodal large language model specifically for understanding event streams, enabling comprehensive scene summarization, reasoning, and question answering from asynchronous event camera data. The model consistently outperforms existing MLLMs in challenging high dynamic range and high-speed motion conditions through a novel architecture and progressive three-stage training.
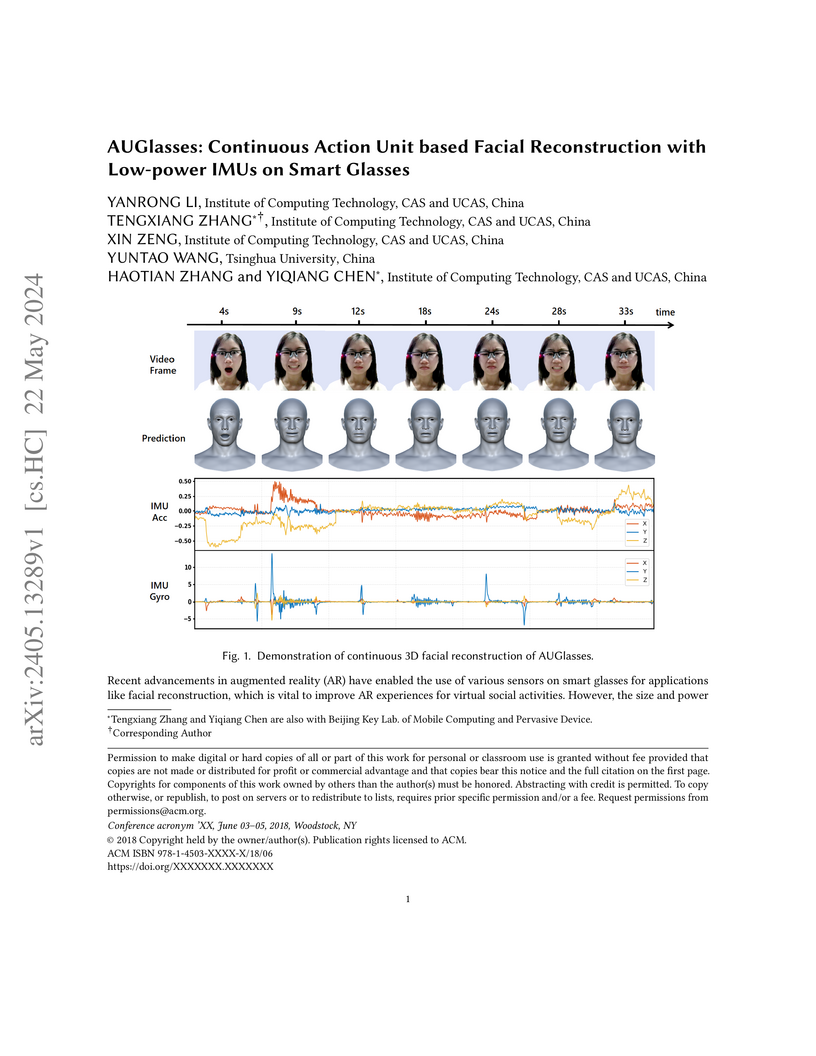
View blogResearchers at the Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Tsinghua University introduced AUGlasses, a low-power system integrated into smart glasses that uses Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) for continuous, privacy-preserving facial reconstruction. The system achieves real-time 3D facial animation with an average NME of 2.75% while consuming only 49.95 mW.
View blogResearchers introduced Video-R1, the first framework to apply a rule-based reinforcement learning paradigm for enhancing temporal reasoning capabilities in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for video. Video-R1, leveraging a new temporal-aware RL algorithm and dedicated video reasoning datasets, consistently outperforms previous state-of-the-art models, achieving 37.1% accuracy on VSI-Bench, surpassing GPT-4o's 34.0%.
View blogVMamba adapts the efficient Mamba State Space Model to computer vision, introducing a 2D-Selective-Scan (SS2D) module that achieves linear computational complexity and memory consumption with image resolution. The architecture demonstrates competitive or superior performance across image classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation benchmarks compared to CNNs and Vision Transformers, while offering significantly higher throughput.
View blogThe Grasp Any Region (GAR) framework introduces a multimodal large language model that achieves precise, context-aware pixel understanding by integrating global context with local details. It enables sophisticated interactions among multiple visual prompts and advanced compositional reasoning, establishing new state-of-the-art performance across diverse region-level understanding benchmarks, including a new GAR-Bench dataset.
View blogGeometric-Mean Policy Optimization (GMPO) stabilizes reinforcement learning for large language models (LLMs) by employing a geometric mean for token-level reward aggregation. This approach yielded an average 4.1% improvement in Pass@1 accuracy over GRPO on mathematical reasoning benchmarks and showed gains in multimodal and Mixture-of-Experts settings, demonstrating more stable training and enhanced policy exploration.
View blogThis survey by multiple institutions defines Deep Research (DR) as a paradigm enabling Large Language Models to perform complex, open-ended tasks through autonomous workflows and verifiable outputs. It systematically categorizes DR into a three-stage roadmap, dissects its four core components, and outlines optimization techniques and evaluation benchmarks.
View blogResearchers at Microsoft and collaborating universities developed DOCREWARD, a Document Reward Model designed to evaluate the visual structure and style professionalism of multi-page documents, independently of their textual content. The model achieved 89.22% human preference accuracy, a 19.45 percentage point improvement over GPT-5, and increased the win rate of AI-generated documents in human comparisons to 60.8% when used as a reward signal.
View blogImagerySearch, an adaptive test-time search strategy, and LDT-Bench, a new evaluation benchmark, are presented to enhance text-to-video generation for imaginative scenarios characterized by long-distance semantic prompts. This approach achieves an 8.83% improvement in overall ImageryQA score on LDT-Bench and demonstrates superior robustness to increasing semantic distance when compared to existing methods.
View blogResearchers at Peking University, UCAS, and Moonshot AI developed a novel reinforcement learning environment, VLM-Gym, to train Vision-Language Models (VLMs) for improved performance in interactive visual games. Their G1-7B models, trained with a perception-enhanced cold start and reinforcement learning, consistently achieve higher scores than leading proprietary VLMs, demonstrating how VLM perception and reasoning abilities can mutually reinforce each other through reward-driven interaction.
View blogEVEv2.0 introduces a family of encoder-free Vision-Language Models that efficiently learn visual perception from scratch, leveraging a "Divide-and-Conquer" architecture and a high-quality captioning engine. The model achieves competitive performance with mainstream encoder-based VLMs of similar capacity on various benchmarks while utilizing significantly less training data.
View blogResearchers from CASIA, UCAS, and ByteDance introduced TreeBench, a diagnostic benchmark that evaluates Large Multimodal Models' visual grounded reasoning by assessing fine-grained perception and traceable evidence through bounding box annotations. They also developed TreeVGR, a training paradigm that uses dual IoU rewards to enhance models' ability to generate explicit visual reasoning pathways, demonstrating substantial performance gains on VGR tasks, including a 13.4 point accuracy improvement on TreeBench over its base model.
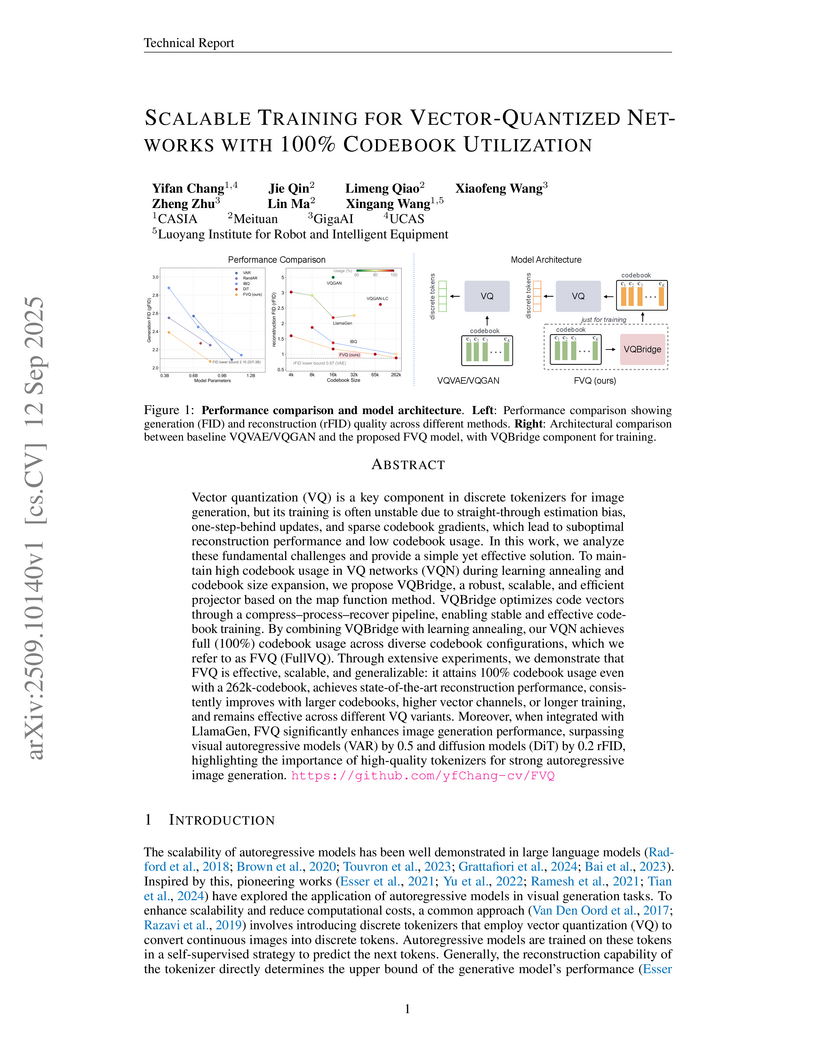
View blogResearchers from CASIA, Meituan, GigaAI, and other institutions developed FullVQ (FVQ), a scalable training method for vector-quantized networks that consistently achieves 100% codebook utilization by introducing a novel VQBridge projector. FVQ sets a new state-of-the-art for discrete tokenizers with an rFID of 0.88 and enables autoregressive models to surpass advanced diffusion models in image generation quality without incurring inference overhead.
View blogA new framework, Distribution Matching Variational AutoEncoder (DMVAE), explicitly aligns a VAE's aggregate latent distribution with a pre-defined reference distribution using score-based matching. The approach achieves a state-of-the-art gFID of 1.82 on ImageNet 256x256, demonstrating superior training efficiency for downstream generative models, particularly when utilizing Self-Supervised Learning features as the reference.
View blog Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University

 ByteDance
ByteDance


 CUHK
CUHK Microsoft
Microsoft
 Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University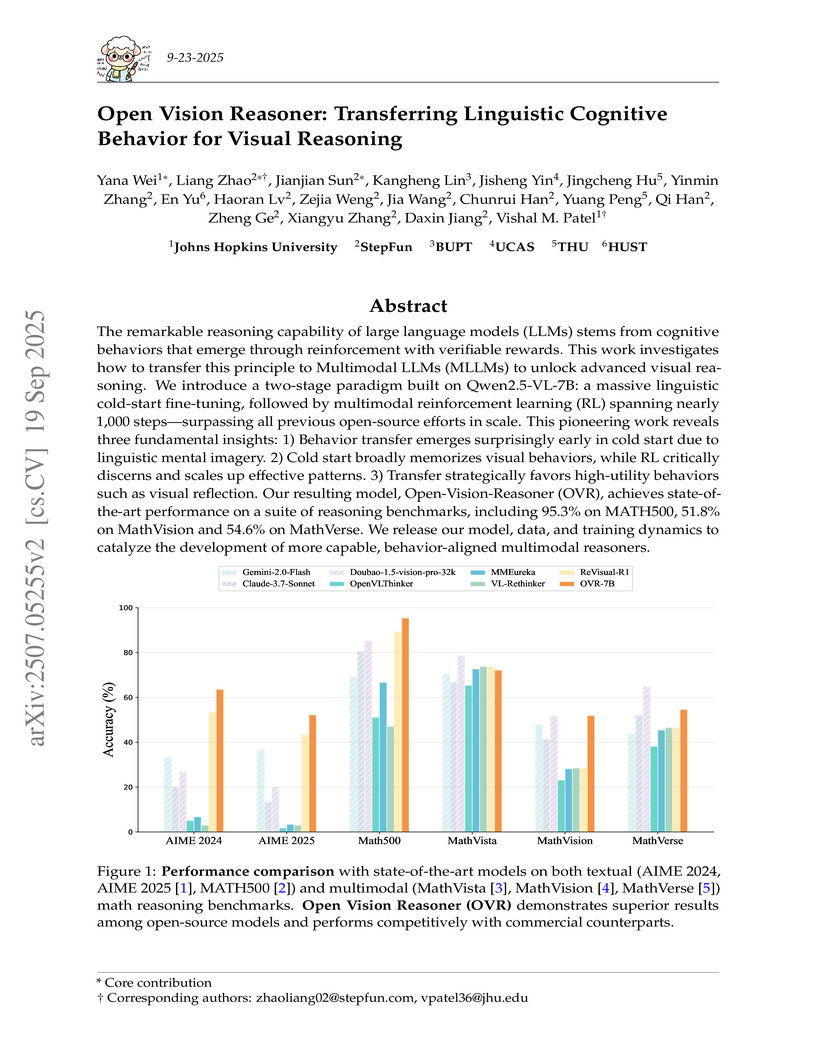

 University of Amsterdam
University of Amsterdam Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University
 MIT
MIT
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences
 Meta
Meta
 Alibaba Group
Alibaba Group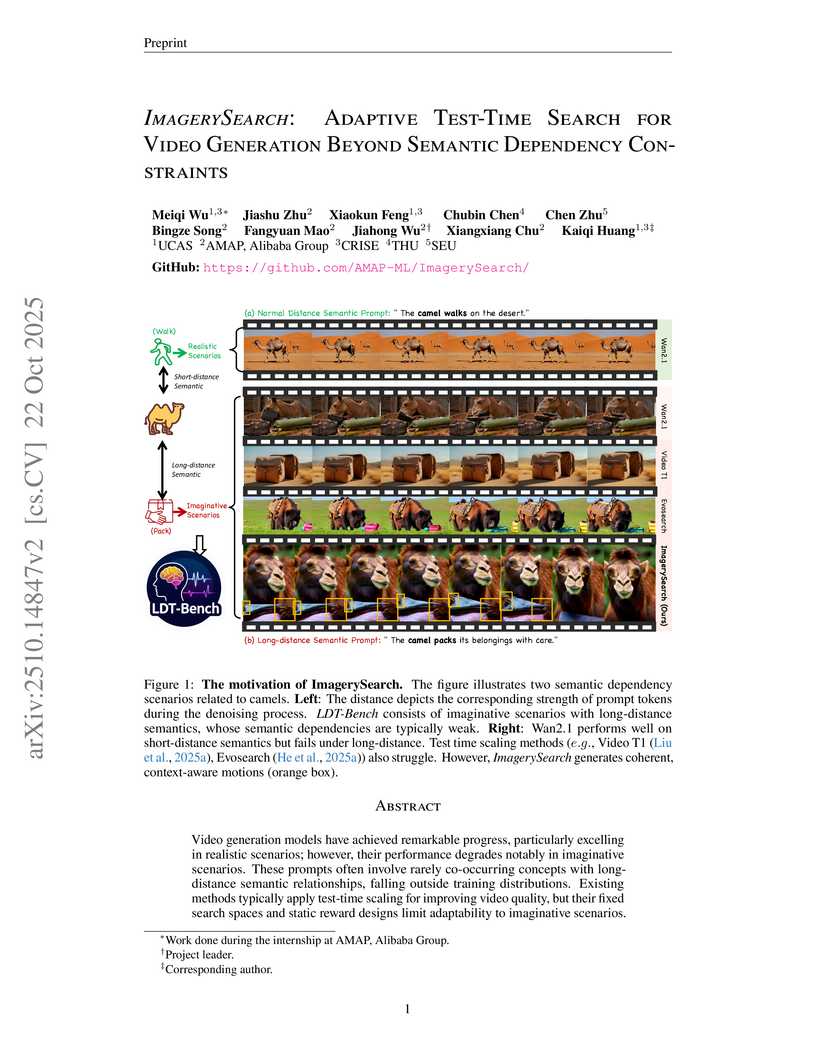
 Peking University
Peking University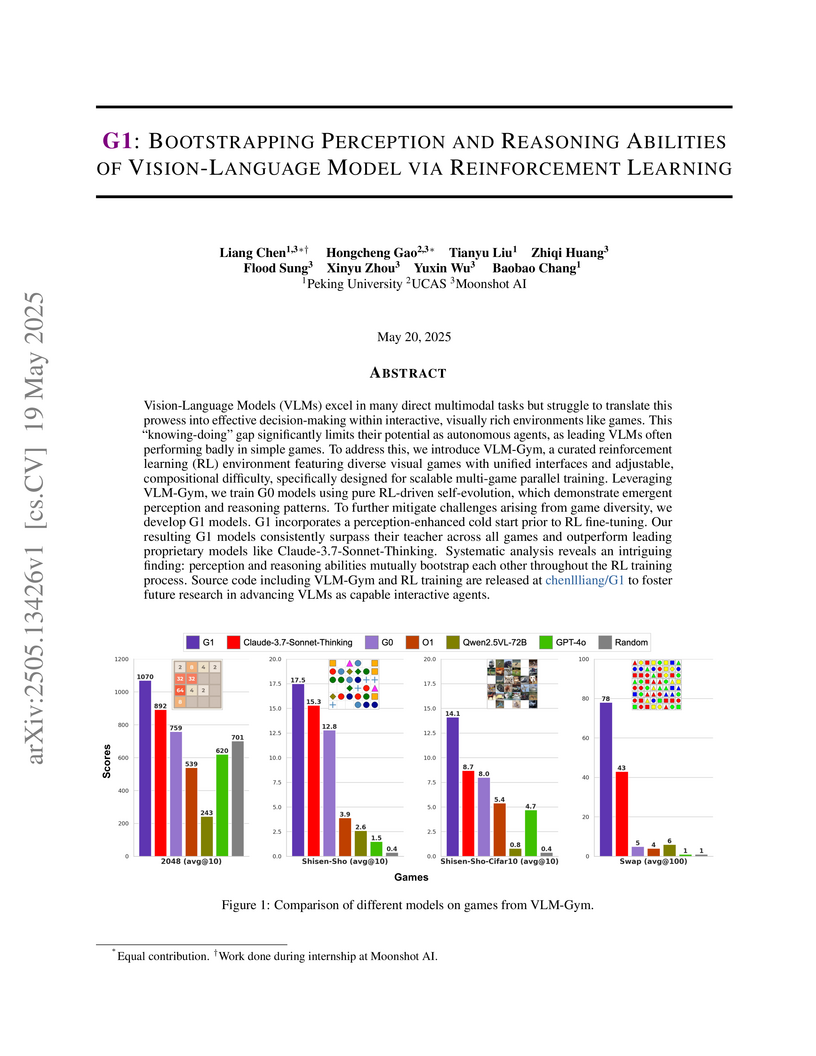

 Tencent
Tencent
 Renmin University of China
Renmin University of China