Soongsil University
We propose EnCLAP, a novel framework for automated audio captioning. EnCLAP
employs two acoustic representation models, EnCodec and CLAP, along with a
pretrained language model, BART. We also introduce a new training objective
called masked codec modeling that improves acoustic awareness of the pretrained
language model. Experimental results on AudioCaps and Clotho demonstrate that
our model surpasses the performance of baseline models. Source code will be
available at this https URL . An online demo is
available at this https URL .
Researchers from Seoul National University and collaborators at Amazon and Samsung Research developed NegationCLIP, a data-driven approach that enhances the limited negation understanding in Vision-Language Models like CLIP. By generating high-quality, visually aligned negation data and fine-tuning CLIP's text encoder, the model achieved substantial improvements on negation-specific benchmarks, for instance, raising ViT-L/14 performance on VALSE Existence from 66.85% to 79.59%, while preserving general vision-language capabilities.
05 Aug 2025
AGENTiGraph introduces a multi-agent framework that enables interactive, natural language-driven creation, manipulation, and visualization of knowledge graphs for domain-specific chatbots. It achieves 95.12% accuracy in user intent classification and a 90.45% success rate in graph operations, significantly outperforming zero-shot LLM baselines, and received an average user satisfaction rating of 6.0 out of 7.0.
Large Audio Language Models (LALMs) have emerged as powerful tools for speech-related tasks but remain underexplored for fine-tuning, especially with limited speech data. To bridge this gap, we systematically examine how different fine-tuning schemes including text-only, direct mixing, and curriculum learning affect spoken language understanding (SLU), focusing on scenarios where text-label pairs are abundant while paired speech-label data are limited. Results show that LALMs already achieve competitive performance with text-only fine-tuning, highlighting their strong generalization ability. Adding even small amounts of speech data (2-5%) yields substantial further gains, with curriculum learning particularly effective under scarce data. In cross-lingual SLU, combining source-language speech data with target-language text and minimal target-language speech data enables effective adaptation. Overall, this study provides practical insights into the LALM fine-tuning under realistic data constraints.
Erasing harmful or proprietary concepts from powerful text to image generators is an emerging safety requirement, yet current "concept erasure" techniques either collapse image quality, rely on brittle adversarial losses, or demand prohibitive retraining cycles. We trace these limitations to a myopic view of the denoising trajectories that govern diffusion based generation. We introduce EraseFlow, the first framework that casts concept unlearning as exploration in the space of denoising paths and optimizes it with GFlowNets equipped with the trajectory balance objective. By sampling entire trajectories rather than single end states, EraseFlow learns a stochastic policy that steers generation away from target concepts while preserving the model's prior. EraseFlow eliminates the need for carefully crafted reward models and by doing this, it generalizes effectively to unseen concepts and avoids hackable rewards while improving the performance. Extensive empirical results demonstrate that EraseFlow outperforms existing baselines and achieves an optimal trade off between performance and prior preservation.
17 Mar 2025
Computer-mediated concerts can be enjoyed on various devices, from desktop
and mobile to VR devices, often supporting multiple devices simultaneously.
However, due to the limited accessibility of VR devices, relatively small
audience members tend to congregate in VR venues, resulting in diminished
unique social experiences. To address this gap and enrich VR concert
experiences, we present a novel approach that leverages non-VR user interaction
data, specifically chat from audiences watching the same content on a
live-streaming platform. Based on an analysis of audience reactions in offline
concerts, we designed and prototyped a concert interaction translation system
that extracts the level of engagement and emotions from chats and translates
them to collective movements, cheers, and singalongs of virtual audience
avatars in a VR venue. Our user study (n=48) demonstrates that our system,
which combines both movement and audio reactions, significantly enhances the
sense of immersion and co-presence than the previous method.
 University of CopenhagenShanghaiTech UniversityRadboud University
University of CopenhagenShanghaiTech UniversityRadboud University Seoul National UniversityUniversity of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Seoul National UniversityUniversity of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Inria
Inria Shandong UniversitySoongsil UniversityUniversity of Michigan at Ann ArborCentre de Recherche en Num ́erique de SfaxUdiniOsstem Implant Co., Ltd.Radboud University Nijmegen Medical CentreBerlin Institute of Health at Charit ́e
Shandong UniversitySoongsil UniversityUniversity of Michigan at Ann ArborCentre de Recherche en Num ́erique de SfaxUdiniOsstem Implant Co., Ltd.Radboud University Nijmegen Medical CentreBerlin Institute of Health at Charit ́eTeeth localization, segmentation, and labeling from intra-oral 3D scans are essential tasks in modern dentistry to enhance dental diagnostics, treatment planning, and population-based studies on oral health. However, developing automated algorithms for teeth analysis presents significant challenges due to variations in dental anatomy, imaging protocols, and limited availability of publicly accessible data. To address these challenges, the 3DTeethSeg'22 challenge was organized in conjunction with the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) in 2022, with a call for algorithms tackling teeth localization, segmentation, and labeling from intraoral 3D scans. A dataset comprising a total of 1800 scans from 900 patients was prepared, and each tooth was individually annotated by a human-machine hybrid algorithm. A total of 6 algorithms were evaluated on this dataset. In this study, we present the evaluation results of the 3DTeethSeg'22 challenge. The 3DTeethSeg'22 challenge code can be accessed at: this https URL
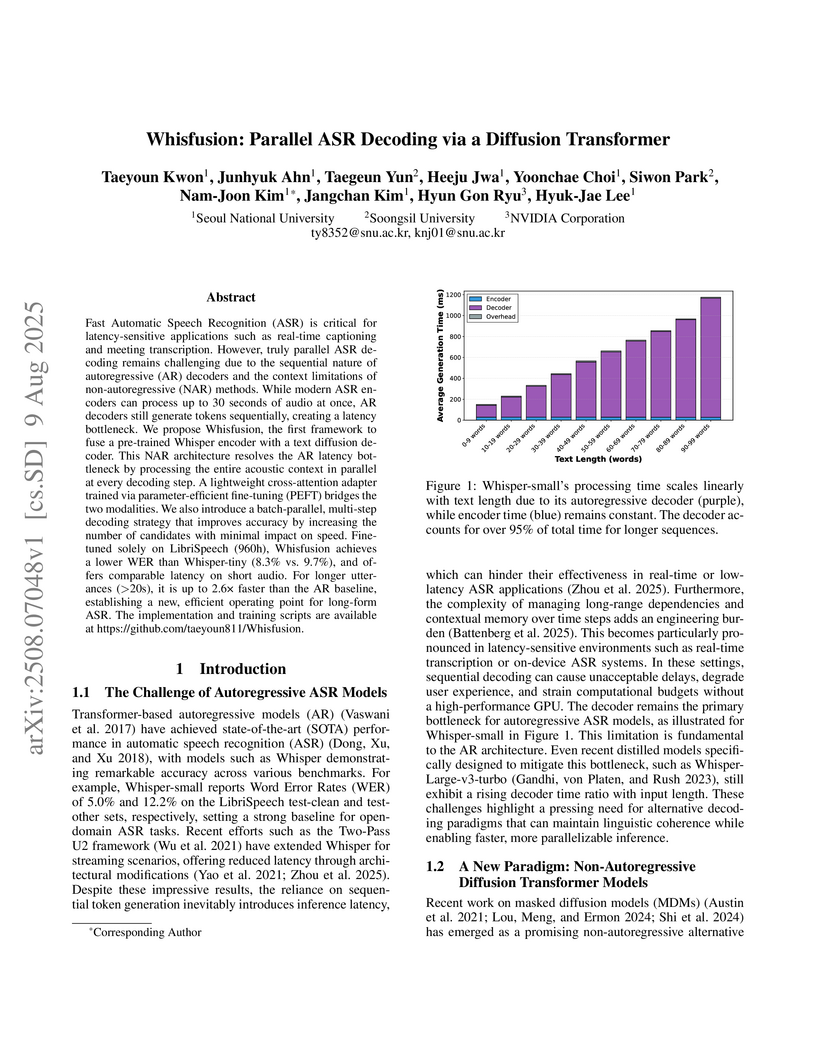
Fast Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is critical for latency-sensitive applications such as real-time captioning and meeting transcription. However, truly parallel ASR decoding remains challenging due to the sequential nature of autoregressive (AR) decoders and the context limitations of non-autoregressive (NAR) methods. While modern ASR encoders can process up to 30 seconds of audio at once, AR decoders still generate tokens sequentially, creating a latency bottleneck. We propose Whisfusion, the first framework to fuse a pre-trained Whisper encoder with a text diffusion decoder. This NAR architecture resolves the AR latency bottleneck by processing the entire acoustic context in parallel at every decoding step. A lightweight cross-attention adapter trained via parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) bridges the two modalities. We also introduce a batch-parallel, multi-step decoding strategy that improves accuracy by increasing the number of candidates with minimal impact on speed. Fine-tuned solely on LibriSpeech (960h), Whisfusion achieves a lower WER than Whisper-tiny (8.3% vs. 9.7%), and offers comparable latency on short audio. For longer utterances (>20s), it is up to 2.6x faster than the AR baseline, establishing a new, efficient operating point for long-form ASR. The implementation and training scripts are available at this https URL.
Unsupervised real world super resolution (USR) aims to restore high-resolution (HR) images given low-resolution (LR) inputs, and its difficulty stems from the absence of paired dataset. One of the most common approaches is synthesizing noisy LR images using GANs (i.e., degradation generators) and utilizing a synthetic dataset to train the model in a supervised manner. Although the goal of training the degradation generator is to approximate the distribution of LR images given a HR image, previous works have heavily relied on the unrealistic assumption that the conditional distribution is a delta function and learned the deterministic mapping from the HR image to a LR image. In this paper, we show that we can improve the performance of USR models by relaxing the assumption and propose to train the probabilistic degradation generator. Our probabilistic degradation generator can be viewed as a deep hierarchical latent variable model and is more suitable for modeling the complex conditional distribution. We also reveal the notable connection with the noise injection of StyleGAN. Furthermore, we train multiple degradation generators to improve the mode coverage and apply collaborative learning for ease of training. We outperform several baselines on benchmark datasets in terms of PSNR and SSIM and demonstrate the robustness of our method on unseen data distribution. Code is available at this https URL.
This work critically re-evaluates the foundational assumption of entropy as a reliable confidence metric in test-time adaptation, demonstrating its unreliability in scenarios with spurious correlations. The authors propose DeYO, a new adaptation method that leverages a novel Pseudo-Label Probability Difference (PLPD) metric to identify and prioritize trustworthy samples, leading to improved performance across diverse distribution shifts including biased and wild scenarios.
A sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture has emerged as a highly scalable solution by conditionally activating sub-modules without a proportional increase in computational costs. However, improving expert specialization to enhance performance and generalization remains a challenge for MoE, especially in instruction tuning scenarios characterized by significant input heterogeneity. In this work, we propose the Mixture-of-Clustered-Experts (MoCE) to address this limitation through a dual-stage routing mechanism. The first stage in the mechanism performs expert group routing based on sequence-level features, while the second stage activates the top-k experts within the group at the token level. This approach enables the effective partitioning of heterogeneous inputs based on their knowledge requirements, encouraging expert group specialization while maintaining the advantages of token-level routing. We evaluate MoCE across a comprehensive set of benchmarks, demonstrating its consistent superiority over strong baselines and its enhanced generalization capabilities. Detailed analysis further highlights the robustness and effectiveness of MoCE.
Transformer-based models have achieved remarkable performance in NLP tasks. However, their structural characteristics-multiple layers and attention heads-introduce efficiency challenges in inference and deployment. To address these challenges, various pruning methods have recently been proposed. Notably, gradient-based methods using Head Importance Scores (HIS) have gained traction for interpretability, efficiency, and ability to identify redundant heads. However, HIS alone has limitations as it captures only the gradient-driven contribution, overlooking the diversity of attention patterns. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a novel pruning criterion, HIES (Head Importance-Entropy Score), which integrates head importance scores with attention entropy, providing complementary evidence on per-head contribution. Empirically, HIES-based pruning yields up to 15.2% improvement in model quality and 2.04x improvement in stability over HIS-only methods, enabling substantial model compression without sacrificing either accuracy or stability. Code will be released upon publication.
Using a relativistic mean-field model calibrated to finite-nucleus observables and bulk properties of dense nuclear matter, we investigate hyperonic neutron-star matter within an SU(3) flavor-symmetry scheme. To retain SU(6)-based couplings within SU(3) flavor symmetry, we add a quartic ϕ self-interaction and ϕ-ρ mixing. We demonstrate the roles of αv (F/(F+D) ratio), θv (mixing angle), and zv (singlet-to-octet coupling ratio) in SU(3)-invariant vector-meson couplings. It is found that zv predominantly controls the maximum mass of a neutron star, and 2M⊙ neutron stars can be supported for zv≤0.15. The αv also helps sustain large masses, whereas θv has a smaller effect on neutron-star properties. This SU(3) framework reconciles nuclear and astrophysical constraints, and offers a plausible resolution to the hyperon puzzle.
This paper introduces PG-Rainbow, a novel algorithm that incorporates a distributional reinforcement learning framework with a policy gradient algorithm. Existing policy gradient methods are sample inefficient and rely on the mean of returns when calculating the state-action value function, neglecting the distributional nature of returns in reinforcement learning tasks. To address this issue, we use an Implicit Quantile Network that provides the quantile information of the distribution of rewards to the critic network of the Proximal Policy Optimization algorithm. We show empirical results that through the integration of reward distribution information into the policy network, the policy agent acquires enhanced capabilities to comprehensively evaluate the consequences of potential actions in a given state, facilitating more sophisticated and informed decision-making processes. We evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm in the Atari-2600 game suite, simulated via the Arcade Learning Environment (ALE).
This research re-evaluates LLM-based query expansion for zero-shot retrieval, demonstrating that observed performance gains on fact verification benchmarks are largely attributed to "knowledge leakage" where LLMs reproduce information from their pretraining data. When this leakage is absent, query expansion methods show limited or even negative impact compared to baselines.
Recent ODE/SDE-based generative models, such as diffusion models, rectified
flows, and flow matching, define a generative process as a time reversal of a
fixed forward process. Even though these models show impressive performance on
large-scale datasets, numerical simulation requires multiple evaluations of a
neural network, leading to a slow sampling speed. We attribute the reason to
the high curvature of the learned generative trajectories, as it is directly
related to the truncation error of a numerical solver. Based on the
relationship between the forward process and the curvature, here we present an
efficient method of training the forward process to minimize the curvature of
generative trajectories without any ODE/SDE simulation. Experiments show that
our method achieves a lower curvature than previous models and, therefore,
decreased sampling costs while maintaining competitive performance. Code is
available at https://github.com/sangyun884/fast-ode.
The goal of offline reinforcement learning (RL) is to extract a
high-performance policy from the fixed datasets, minimizing performance
degradation due to out-of-distribution (OOD) samples. Offline model-based RL
(MBRL) is a promising approach that ameliorates OOD issues by enriching
state-action transitions with augmentations synthesized via a learned dynamics
model. Unfortunately, seminal offline MBRL methods often struggle in
sparse-reward, long-horizon tasks. In this work, we introduce a novel MBRL
framework, dubbed Temporal Distance-Aware Transition Augmentation (TempDATA),
that generates augmented transitions in a temporally structured latent space
rather than in raw state space. To model long-horizon behavior, TempDATA learns
a latent abstraction that captures a temporal distance from both trajectory and
transition levels of state space. Our experiments confirm that TempDATA
outperforms previous offline MBRL methods and achieves matching or surpassing
the performance of diffusion-based trajectory augmentation and goal-conditioned
RL on the D4RL AntMaze, FrankaKitchen, CALVIN, and pixel-based FrankaKitchen.
Video Frame Interpolation (VFI) aims to synthesize intermediate frames
between existing frames to enhance visual smoothness and quality. Beyond the
conventional methods based on the reconstruction loss, recent works have
employed generative models for improved perceptual quality. However, they
require complex training and large computational costs for pixel space
modeling. In this paper, we introduce disentangled Motion Modeling (MoMo), a
diffusion-based approach for VFI that enhances visual quality by focusing on
intermediate motion modeling. We propose a disentangled two-stage training
process. In the initial stage, frame synthesis and flow models are trained to
generate accurate frames and flows optimal for synthesis. In the subsequent
stage, we introduce a motion diffusion model, which incorporates our novel
U-Net architecture specifically designed for optical flow, to generate
bi-directional flows between frames. By learning the simpler low-frequency
representation of motions, MoMo achieves superior perceptual quality with
reduced computational demands compared to the generative modeling methods on
the pixel space. MoMo surpasses state-of-the-art methods in perceptual metrics
across various benchmarks, demonstrating its efficacy and efficiency in VFI.
Image-based virtual try-on aims to synthesize an image of a person wearing a given clothing item. To solve the task, the existing methods warp the clothing item to fit the person's body and generate the segmentation map of the person wearing the item before fusing the item with the person. However, when the warping and the segmentation generation stages operate individually without information exchange, the misalignment between the warped clothes and the segmentation map occurs, which leads to the artifacts in the final image. The information disconnection also causes excessive warping near the clothing regions occluded by the body parts, so-called pixel-squeezing artifacts. To settle the issues, we propose a novel try-on condition generator as a unified module of the two stages (i.e., warping and segmentation generation stages). A newly proposed feature fusion block in the condition generator implements the information exchange, and the condition generator does not create any misalignment or pixel-squeezing artifacts. We also introduce discriminator rejection that filters out the incorrect segmentation map predictions and assures the performance of virtual try-on frameworks. Experiments on a high-resolution dataset demonstrate that our model successfully handles the misalignment and occlusion, and significantly outperforms the baselines. Code is available at this https URL.
Automatic font generation (AFG) is the process of creating a new font using
only a few examples of the style images. Generating fonts for complex languages
like Korean and Chinese, particularly in handwritten styles, presents
significant challenges. Traditional AFGs, like Generative adversarial networks
(GANs) and Variational Auto-Encoders (VAEs), are usually unstable during
training and often face mode collapse problems. They also struggle to capture
fine details within font images. To address these problems, we present a
diffusion-based AFG method which generates high-quality, diverse Korean font
images using only a single reference image, focusing on handwritten and printed
styles. Our approach refines noisy images incrementally, ensuring stable
training and visually appealing results. A key innovation is our text encoder,
which processes phonetic representations to generate accurate and contextually
correct characters, even for unseen characters. We used a pre-trained style
encoder from DG FONT to effectively and accurately encode the style images. To
further enhance the generation quality, we used perceptual loss that guides the
model to focus on the global style of generated images. Experimental results on
over 2000 Korean characters demonstrate that our model consistently generates
accurate and detailed font images and outperforms benchmark methods, making it
a reliable tool for generating authentic Korean fonts across different styles.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.