Macau University of Science and Technology
Discrete diffusion models represent a significant advance in generative modeling, demonstrating remarkable success in synthesizing complex, high-quality discrete data. However, to avoid exponential computational costs, they typically rely on calculating per-dimension transition probabilities when learning high-dimensional distributions. In this study, we rigorously prove that this approach leads to a worst-case linear scaling of Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence with data dimension. To address this, we propose a Quantum Discrete Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (QD3PM), which enables joint probability learning through diffusion and denoising in exponentially large Hilbert spaces, offering a theoretical pathway to faithfully capture the true joint distribution. By deriving posterior states through quantum Bayes' theorem, similar to the crucial role of posterior probabilities in classical diffusion models, and by learning the joint probability, we establish a solid theoretical foundation for quantum-enhanced diffusion models. For denoising, we design a quantum circuit that utilizes temporal information for parameter sharing and incorporates learnable classical-data-controlled rotations for encoding. Exploiting joint distribution learning, our approach enables single-step sampling from pure noise, eliminating iterative requirements of existing models. Simulations demonstrate the proposed model's superior accuracy in modeling complex distributions compared to factorization methods. Hence, this paper establishes a new theoretical paradigm in generative models by leveraging the quantum advantage in joint distribution learning.
10 Sep 2025
This survey provides a comprehensive review of dexterous manipulation using imitation learning, categorizing algorithmic advancements, analyzing end-effector designs and data acquisition methods, and outlining key challenges and future research directions. It consolidates a rapidly evolving interdisciplinary field to guide researchers and practitioners toward more capable robotic systems.
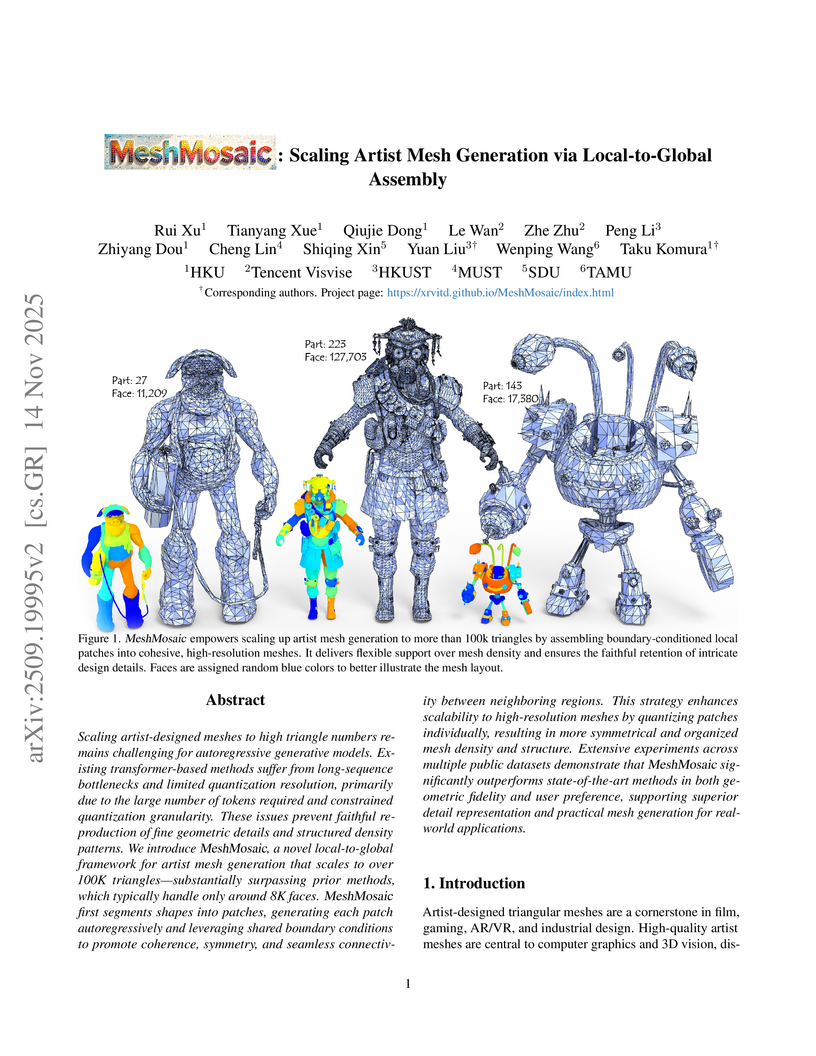
Scaling artist-designed meshes to high triangle numbers remains challenging for autoregressive generative models. Existing transformer-based methods suffer from long-sequence bottlenecks and limited quantization resolution, primarily due to the large number of tokens required and constrained quantization granularity. These issues prevent faithful reproduction of fine geometric details and structured density patterns. We introduce MeshMosaic, a novel local-to-global framework for artist mesh generation that scales to over 100K triangles--substantially surpassing prior methods, which typically handle only around 8K faces. MeshMosaic first segments shapes into patches, generating each patch autoregressively and leveraging shared boundary conditions to promote coherence, symmetry, and seamless connectivity between neighboring regions. This strategy enhances scalability to high-resolution meshes by quantizing patches individually, resulting in more symmetrical and organized mesh density and structure. Extensive experiments across multiple public datasets demonstrate that MeshMosaic significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both geometric fidelity and user preference, supporting superior detail representation and practical mesh generation for real-world applications.
Self-attention has revolutionized classical machine learning, yet existing
quantum self-attention models underutilize quantum states' potential due to
oversimplified or incomplete mechanisms. To address this limitation, we
introduce the Quantum Complex-Valued Self-Attention Model (QCSAM), the first
framework to leverage complex-valued similarities, which captures amplitude and
phase relationships between quantum states more comprehensively. To achieve
this, QCSAM extends the Linear Combination of Unitaries (LCUs) into the Complex
LCUs (CLCUs) framework, enabling precise complex-valued weighting of quantum
states and supporting quantum multi-head attention. Experiments on MNIST and
Fashion-MNIST show that QCSAM outperforms recent quantum self-attention models,
including QKSAN, QSAN, and GQHAN. With only 4 qubits, QCSAM achieves 100% and
99.2% test accuracies on MNIST and Fashion-MNIST, respectively. Furthermore, we
evaluate scalability across 3-8 qubits and 2-4 class tasks, while ablation
studies validate the advantages of complex-valued attention weights over
real-valued alternatives. This work advances quantum machine learning by
enhancing the expressiveness and precision of quantum self-attention in a way
that aligns with the inherent complexity of quantum mechanics.
The paper provides a systematic review of the integration between Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and large foundation models (LLMs, VLMs, VFMs), proposing an "Agentic UAV" framework for developing highly autonomous, intelligent low-altitude mobility systems. It synthesizes current advancements across perception, navigation, and planning, identifying key capabilities and challenges.
Multi-hop question answering (QA) presents significant challenges for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), particularly in decomposing complex queries into reliable reasoning paths and managing error propagation. Existing RAG methods often suffer from deviations in reasoning paths and cumulative errors in intermediate steps, reducing the fidelity of the final answer. To address these limitations, we propose PAR-RAG (Plan-then-Act-and-Review RAG), a novel framework inspired by the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle, to enhance both the accuracy and factual consistency in multi-hop question answering. Specifically, PAR-RAG selects exemplars matched by the semantic complexity of the current question to guide complexity-aware top-down planning, resulting in more precise and coherent multi-step reasoning trajectories. This design mitigates reasoning drift and reduces the risk of suboptimal path convergence, a common issue in existing RAG approaches. Furthermore, a dual-verification mechanism evaluates and corrects intermediate errors, ensuring that the reasoning process remains factually grounded. Experimental results on various QA benchmarks demonstrate that PAR-RAG outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, validating its effectiveness in both performance and reasoning robustness.
LiteVGGT introduces a geometry-aware cached token merging strategy to enhance the Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer (VGGT) for multi-view 3D reconstruction. This approach provides up to a 10x speedup in inference time and enables processing of 1000-image scenes without out-of-memory errors, while largely preserving geometric and pose estimation accuracy.
Segmenting 3D objects into parts is a long-standing challenge in computer vision. To overcome taxonomy constraints and generalize to unseen 3D objects, recent works turn to open-world part segmentation. These approaches typically transfer supervision from 2D foundation models, such as SAM, by lifting multi-view masks into 3D. However, this indirect paradigm fails to capture intrinsic geometry, leading to surface-only understanding, uncontrolled decomposition, and limited generalization. We present PartSAM, the first promptable part segmentation model trained natively on large-scale 3D data. Following the design philosophy of SAM, PartSAM employs an encoder-decoder architecture in which a triplane-based dual-branch encoder produces spatially structured tokens for scalable part-aware representation learning. To enable large-scale supervision, we further introduce a model-in-the-loop annotation pipeline that curates over five million 3D shape-part pairs from online assets, providing diverse and fine-grained labels. This combination of scalable architecture and diverse 3D data yields emergent open-world capabilities: with a single prompt, PartSAM achieves highly accurate part identification, and in a Segment-Every-Part mode, it automatically decomposes shapes into both surface and internal structures. Extensive experiments show that PartSAM outperforms state-of-the-art methods by large margins across multiple benchmarks, marking a decisive step toward foundation models for 3D part understanding.
Researchers at HKUST developed TrackingWorld, a framework for dense, world-centric 3D tracking of nearly all pixels in monocular videos, effectively disentangling camera and object motion. This method integrates foundation models with a novel optimization pipeline to track objects, including newly emerging ones, demonstrating superior camera pose estimation and 3D depth consistency, achieving, for example, an Abs Rel depth error of 0.218 on Sintel compared to 0.636 from baselines.
Reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a pivotal technique for
fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) on specific tasks. However, prevailing
RL fine-tuning methods predominantly rely on PPO and its variants. Though these
algorithms are effective in general RL settings, they often exhibit suboptimal
performance and vulnerability to distribution collapse when applied to the
fine-tuning of LLMs. In this paper, we propose CORY, extending the RL
fine-tuning of LLMs to a sequential cooperative multi-agent reinforcement
learning framework, to leverage the inherent coevolution and emergent
capabilities of multi-agent systems. In CORY, the LLM to be fine-tuned is
initially duplicated into two autonomous agents: a pioneer and an observer. The
pioneer generates responses based on queries, while the observer generates
responses using both the queries and the pioneer's responses. The two agents
are trained together. During training, the agents exchange roles periodically,
fostering cooperation and coevolution between them. Experiments evaluate CORY's
performance by fine-tuning GPT-2 and Llama-2 under subjective and objective
reward functions on the IMDB Review and GSM8K datasets, respectively. Results
show that CORY outperforms PPO in terms of policy optimality, resistance to
distribution collapse, and training robustness, thereby underscoring its
potential as a superior methodology for refining LLMs in real-world
applications.
Current image fusion methods struggle to address the composite degradations encountered in real-world imaging scenarios and lack the flexibility to accommodate user-specific requirements. In response to these challenges, we propose a controllable image fusion framework with language-vision prompts, termed ControlFusion, which adaptively neutralizes composite degradations. On the one hand, we develop a degraded imaging model that integrates physical imaging mechanisms, including the Retinex theory and atmospheric scattering principle, to simulate composite degradations, thereby providing potential for addressing real-world complex degradations from the data level. On the other hand, we devise a prompt-modulated restoration and fusion network that dynamically enhances features with degradation prompts, enabling our method to accommodate composite degradation of varying levels. Specifically, considering individual variations in quality perception of users, we incorporate a text encoder to embed user-specified degradation types and severity levels as degradation prompts. We also design a spatial-frequency collaborative visual adapter that autonomously perceives degradations in source images, thus eliminating the complete dependence on user instructions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ControlFusion outperforms SOTA fusion methods in fusion quality and degradation handling, particularly in countering real-world and compound degradations with various levels. The source code is publicly available at this https URL.
 University of WashingtonRensselaer Polytechnic Institute
University of WashingtonRensselaer Polytechnic Institute California Institute of Technology
California Institute of Technology University of Illinois at Urbana-ChampaignSLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
University of Illinois at Urbana-ChampaignSLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University Imperial College London
Imperial College London University of ChicagoNational Taiwan University
University of ChicagoNational Taiwan University Stanford UniversityUniversity of Hong Kong
Stanford UniversityUniversity of Hong Kong ETH Zürich
ETH Zürich University of California, San Diego
University of California, San Diego Northwestern University
Northwestern University University of Pennsylvania
University of Pennsylvania University of Minnesota
University of Minnesota University of Wisconsin-MadisonUniversity of Colorado
University of Wisconsin-MadisonUniversity of Colorado Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Purdue University
Purdue University Duke University
Duke University Virginia Tech
Virginia Tech MIT
MIT Princeton University
Princeton University The Ohio State UniversityUniversity of Delaware
The Ohio State UniversityUniversity of Delaware Dartmouth CollegeChungnam National UniversityUniversity of PerugiaMacau University of Science and TechnologyUniversity of Maryland Baltimore CountyUniversity of ZNational Tsinghua UniversityRicoh Software Research Center (Beijing) Co.National Yang Ming-Chiao Tung University
Dartmouth CollegeChungnam National UniversityUniversity of PerugiaMacau University of Science and TechnologyUniversity of Maryland Baltimore CountyUniversity of ZNational Tsinghua UniversityRicoh Software Research Center (Beijing) Co.National Yang Ming-Chiao Tung UniversityScientific discoveries are often made by finding a pattern or object that was
not predicted by the known rules of science. Oftentimes, these anomalous events
or objects that do not conform to the norms are an indication that the rules of
science governing the data are incomplete, and something new needs to be
present to explain these unexpected outliers. The challenge of finding
anomalies can be confounding since it requires codifying a complete knowledge
of the known scientific behaviors and then projecting these known behaviors on
the data to look for deviations. When utilizing machine learning, this presents
a particular challenge since we require that the model not only understands
scientific data perfectly but also recognizes when the data is inconsistent and
out of the scope of its trained behavior. In this paper, we present three
datasets aimed at developing machine learning-based anomaly detection for
disparate scientific domains covering astrophysics, genomics, and polar
science. We present the different datasets along with a scheme to make machine
learning challenges around the three datasets findable, accessible,
interoperable, and reusable (FAIR). Furthermore, we present an approach that
generalizes to future machine learning challenges, enabling the possibility of
large, more compute-intensive challenges that can ultimately lead to scientific
discovery.
03 Aug 2024
Classical diffusion models have shown superior generative results. Exploring them in the quantum domain can advance the field of quantum generative learning. This work introduces Quantum Generative Diffusion Model (QGDM) as their simple and elegant quantum counterpart. Through a non-unitary forward process, any target quantum state can be transformed into a completely mixed state that has the highest entropy and maximum uncertainty about the system. A trainable backward process is used to recover the former from the latter. The design requirements for its backward process includes non-unitarity and small parameter count. We introduce partial trace operations to enforce non-unitary and reduce the number of trainable parameters by using a parameter-sharing strategy and incorporating temporal information as an input in the backward process. We present QGDM's resource-efficient version to reduce auxiliary qubits while preserving generative capabilities. QGDM exhibits faster convergence than Quantum Generative Adversarial Network (QGAN) because its adopted convex-based optimization can result in better convergence. The results of comparing it with QGAN demonstrate its effectiveness in generating both pure and mixed quantum states. It can achieve 53.02% higher fidelity in mixed-state generation than QGAN. The results highlight its great potential to tackle challenging quantum generation tasks.
30 Jun 2025
Quantum Transformers integrate the representational power of classical Transformers with the computational advantages of quantum computing. Since 2022, research in this area has rapidly expanded, giving rise to diverse technical paradigms and early applications. To address the growing need for consolidation, this paper presents the first comprehensive, systematic, and in-depth survey of quantum Transformer models. First, we delineate the research scope, focusing on improving Transformer parts with quantum methods, and introduce foundational concepts in classical Transformers and quantum machine learning. Then we organize existing studies into two main paradigms: PQC-based and QLA-based, with PQC-based paradigm further divided into QKV-only Quantum Mapping, Quantum Pairwise Attention, Quantum Holistic Attention. and Quantum-Assisted Optimization, analyzing their core mechanisms and architectural traits. We also summarize empirical results that demonstrate preliminary quantum advantages, especially on small-scale tasks or resource-constrained settings. Following this, we examine key technical challenges, such as complexity-resource trade-offs, scalability and generalization limitations, and trainability issues including barren plateaus, and provide potential solutions, including quantumizing classical transformer variants with lower complexity, hybrid designs, and improved optimization strategies. Finally, we propose several promising future directions, e.g., scaling quantum modules into large architectures, applying quantum Transformers to domains with inherently quantum data (e.g., physics, chemistry), and developing theory-driven designs grounded in quantum information science. This survey will help researchers and practitioners quickly grasp the overall landscape of current quantum Transformer research and promote future developments in this emerging field.
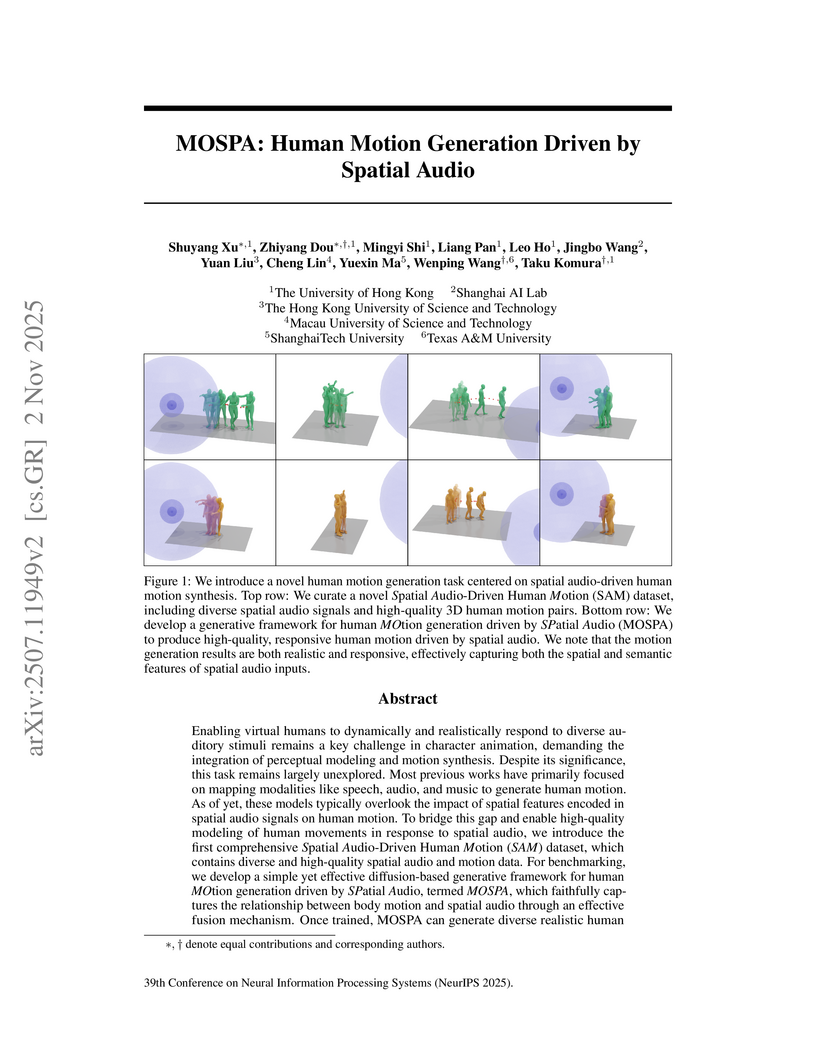
Enabling virtual humans to dynamically and realistically respond to diverse auditory stimuli remains a key challenge in character animation, demanding the integration of perceptual modeling and motion synthesis. Despite its significance, this task remains largely unexplored. Most previous works have primarily focused on mapping modalities like speech, audio, and music to generate human motion. As of yet, these models typically overlook the impact of spatial features encoded in spatial audio signals on human motion. To bridge this gap and enable high-quality modeling of human movements in response to spatial audio, we introduce the first comprehensive Spatial Audio-Driven Human Motion (SAM) dataset, which contains diverse and high-quality spatial audio and motion data. For benchmarking, we develop a simple yet effective diffusion-based generative framework for human MOtion generation driven by SPatial Audio, termed MOSPA, which faithfully captures the relationship between body motion and spatial audio through an effective fusion mechanism. Once trained, MOSPA can generate diverse, realistic human motions conditioned on varying spatial audio inputs. We perform a thorough investigation of the proposed dataset and conduct extensive experiments for benchmarking, where our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on this task. Our code and model are publicly available at this https URL
Although deep learning has advanced remote sensing change detection (RSCD), most methods rely solely on image modality, limiting feature representation, change pattern modeling, and generalization especially under illumination and noise disturbances. To address this, we propose MMChange, a multimodal RSCD method that combines image and text modalities to enhance accuracy and robustness. An Image Feature Refinement (IFR) module is introduced to highlight key regions and suppress environmental noise. To overcome the semantic limitations of image features, we employ a vision language model (VLM) to generate semantic descriptions of bitemporal images. A Textual Difference Enhancement (TDE) module then captures fine grained semantic shifts, guiding the model toward meaningful changes. To bridge the heterogeneity between modalities, we design an Image Text Feature Fusion (ITFF) module that enables deep cross modal integration. Extensive experiments on LEVIRCD, WHUCD, and SYSUCD demonstrate that MMChange consistently surpasses state of the art methods across multiple metrics, validating its effectiveness for multimodal RSCD. Code is available at: this https URL.
Jailbreak attacks can circumvent model safety guardrails and reveal critical blind spots. Prior attacks on text-to-video (T2V) models typically add adversarial perturbations to obviously unsafe prompts, which are often easy to detect and defend. In contrast, we show that benign-looking prompts containing rich, implicit cues can induce T2V models to generate semantically unsafe videos that both violate policy and preserve the original (blocked) intent. To realize this, we propose VEIL, a jailbreak framework that leverages T2V models' cross-modal associative patterns via a modular prompt design. Specifically, our prompts combine three components: neutral scene anchors, which provide the surface-level scene description extracted from the blocked intent to maintain plausibility; latent auditory triggers, textual descriptions of innocuous-sounding audio events (e.g., creaking, muffled noises) that exploit learned audio-visual co-occurrence priors to bias the model toward particular unsafe visual concepts; and stylistic modulators, cinematic directives (e.g., camera framing, atmosphere) that amplify and stabilize the latent trigger's effect. We formalize attack generation as a constrained optimization over the above modular prompt space and solve it with a guided search procedure that balances stealth and effectiveness. Extensive experiments over 7 T2V models demonstrate the efficacy of our attack, achieving a 23 percent improvement in average attack success rate in commercial models. Our demos and codes can be found at this https URL.
In this work, we introduce \textbf{Wonder3D++}, a novel method for efficiently generating high-fidelity textured meshes from single-view images. Recent methods based on Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) have shown the potential to recover 3D geometry from 2D diffusion priors, but they typically suffer from time-consuming per-shape optimization and inconsistent geometry. In contrast, certain works directly produce 3D information via fast network inferences, but their results are often of low quality and lack geometric details. To holistically improve the quality, consistency, and efficiency of single-view reconstruction tasks, we propose a cross-domain diffusion model that generates multi-view normal maps and the corresponding color images. To ensure the consistency of generation, we employ a multi-view cross-domain attention mechanism that facilitates information exchange across views and modalities. Lastly, we introduce a cascaded 3D mesh extraction algorithm that drives high-quality surfaces from the multi-view 2D representations in only about 3 minute in a coarse-to-fine manner. Our extensive evaluations demonstrate that our method achieves high-quality reconstruction results, robust generalization, and good efficiency compared to prior works. Code available at this https URL.
20 Jun 2025
AdverIntent-Agent, a multi-agent system developed by researchers from UCL, CMU, and other institutions, advances automated program repair by explicitly inferring and validating multiple adversarial program intents. This novel approach generated 77 correct patches on Defects4J 2.0 and 105 on HumanEval-Java under realistic fault localization, outperforming existing methods by utilizing adversarial tests to effectively mitigate patch overfitting.
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)Chongqing University HKUSTMacau University of Science and TechnologySun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen UniversityShenzhen People’s HospitalYunnan Cancer HospitalThe Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical UniversityShenshan Medical Center, Memorial Hospital of Sun Yat-sen UniversityPeking University Cancer Hospital YunnanGuangzhou First People’s Hospital, South China University of TechnologyThe Third Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University
HKUSTMacau University of Science and TechnologySun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen UniversityShenzhen People’s HospitalYunnan Cancer HospitalThe Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical UniversityShenshan Medical Center, Memorial Hospital of Sun Yat-sen UniversityPeking University Cancer Hospital YunnanGuangzhou First People’s Hospital, South China University of TechnologyThe Third Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University
 HKUSTMacau University of Science and TechnologySun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen UniversityShenzhen People’s HospitalYunnan Cancer HospitalThe Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical UniversityShenshan Medical Center, Memorial Hospital of Sun Yat-sen UniversityPeking University Cancer Hospital YunnanGuangzhou First People’s Hospital, South China University of TechnologyThe Third Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University
HKUSTMacau University of Science and TechnologySun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen UniversityShenzhen People’s HospitalYunnan Cancer HospitalThe Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical UniversityShenshan Medical Center, Memorial Hospital of Sun Yat-sen UniversityPeking University Cancer Hospital YunnanGuangzhou First People’s Hospital, South China University of TechnologyThe Third Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen UniversityVersaMammo is a versatile foundation model for AI-enabled mammogram interpretation, pre-trained on the largest multi-institutional dataset of 706,239 images using a novel two-stage hybrid strategy. The model achieved state-of-the-art performance across 92 diverse clinical tasks, including lesion detection (mean IoU 57.92%), segmentation (mean DICE 63.21%), and classification, matching the performance of senior radiologists in Bi-Rads assessment (AUC 82.95%).
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.