Uber AI
This paper presents Plug and Play Language Models (PPLM), a method that enables controllable text generation from unconditional pre-trained language models like GPT-2 without retraining them. The approach steers generation by applying gradients from lightweight attribute models directly to the language model's latent representations, achieving substantial improvements in attribute relevance (e.g., 51.7% for topic, 73.7% for sentiment) while largely preserving fluency.
TuRBO (Trust Region Bayesian Optimization) introduces a local probabilistic optimization framework that uses multiple simultaneous trust regions with local Gaussian Process models, efficiently allocating sampling budget via an implicit multi-armed bandit strategy. This method consistently outperformed existing Bayesian optimization and evolutionary algorithms on high-dimensional, expensive black-box problems, scaling effectively to 200 dimensions and thousands of evaluations.
This research introduces Go-Explore, a new reinforcement learning paradigm designed to solve hard exploration problems in sparse-reward environments by explicitly remembering promising states and reliably returning to them before exploring further. The method achieved superhuman performance on all previously unsolved Atari games, including setting a new world record on Montezuma's Revenge, and successfully solved a complex robotics manipulation task.
The global optimization of a high-dimensional black-box function under black-box constraints is a pervasive task in machine learning, control, and engineering. These problems are challenging since the feasible set is typically non-convex and hard to find, in addition to the curses of dimensionality and the heterogeneity of the underlying functions. In particular, these characteristics dramatically impact the performance of Bayesian optimization methods, that otherwise have become the de facto standard for sample-efficient optimization in unconstrained settings, leaving practitioners with evolutionary strategies or heuristics. We propose the scalable constrained Bayesian optimization (SCBO) algorithm that overcomes the above challenges and pushes the applicability of Bayesian optimization far beyond the state-of-the-art. A comprehensive experimental evaluation demonstrates that SCBO achieves excellent results on a variety of benchmarks. To this end, we propose two new control problems that we expect to be of independent value for the scientific community.
MixturePFN is a transformer-based approach for tabular data learning that addresses the scalability limitations of Prior-Fitted Networks (PFNs). It achieves state-of-the-art performance on various tabular datasets while scaling logarithmically with dataset size, outperforming traditional methods and existing PFNs.
Neural architectures inspired by our own human cognitive system, such as the
recently introduced world models, have been shown to outperform traditional
deep reinforcement learning (RL) methods in a variety of different domains.
Instead of the relatively simple architectures employed in most RL experiments,
world models rely on multiple different neural components that are responsible
for visual information processing, memory, and decision-making. However, so far
the components of these models have to be trained separately and through a
variety of specialized training methods. This paper demonstrates the surprising
finding that models with the same precise parts can be instead efficiently
trained end-to-end through a genetic algorithm (GA), reaching a comparable
performance to the original world model by solving a challenging car racing
task. An analysis of the evolved visual and memory system indicates that they
include a similar effective representation to the system trained through
gradient descent. Additionally, in contrast to gradient descent methods that
struggle with discrete variables, GAs also work directly with such
representations, opening up opportunities for classical planning in latent
space. This paper adds additional evidence on the effectiveness of deep
neuroevolution for tasks that require the intricate orchestration of multiple
components in complex heterogeneous architectures.
In this work we present Ludwig, a flexible, extensible and easy to use
toolbox which allows users to train deep learning models and use them for
obtaining predictions without writing code. Ludwig implements a novel approach
to deep learning model building based on two main abstractions: data types and
declarative configuration files. The data type abstraction allows for easier
code and sub-model reuse, and the standardized interfaces imposed by this
abstraction allow for encapsulation and make the code easy to extend.
Declarative model definition configuration files enable inexperienced users to
obtain effective models and increase the productivity of expert users.
Alongside these two innovations, Ludwig introduces a general modularized deep
learning architecture called Encoder-Combiner-Decoder that can be instantiated
to perform a vast amount of machine learning tasks. These innovations make it
possible for engineers, scientists from other fields and, in general, a much
broader audience to adopt deep learning models for their tasks, concretely
helping in its democratization.
24 Jul 2019
We present the first complete attempt at concurrently training conversational
agents that communicate only via self-generated language. Using DSTC2 as seed
data, we trained natural language understanding (NLU) and generation (NLG)
networks for each agent and let the agents interact online. We model the
interaction as a stochastic collaborative game where each agent (player) has a
role ("assistant", "tourist", "eater", etc.) and their own objectives, and can
only interact via natural language they generate. Each agent, therefore, needs
to learn to operate optimally in an environment with multiple sources of
uncertainty (its own NLU and NLG, the other agent's NLU, Policy, and NLG). In
our evaluation, we show that the stochastic-game agents outperform deep
learning based supervised baselines.
19 Jul 2021
An ambitious goal for machine learning is to create agents that behave
ethically: The capacity to abide by human moral norms would greatly expand the
context in which autonomous agents could be practically and safely deployed,
e.g. fully autonomous vehicles will encounter charged moral decisions that
complicate their deployment. While ethical agents could be trained by rewarding
correct behavior under a specific moral theory (e.g. utilitarianism), there
remains widespread disagreement about the nature of morality. Acknowledging
such disagreement, recent work in moral philosophy proposes that ethical
behavior requires acting under moral uncertainty, i.e. to take into account
when acting that one's credence is split across several plausible ethical
theories. This paper translates such insights to the field of reinforcement
learning, proposes two training methods that realize different points among
competing desiderata, and trains agents in simple environments to act under
moral uncertainty. The results illustrate (1) how such uncertainty can help
curb extreme behavior from commitment to single theories and (2) several
technical complications arising from attempting to ground moral philosophy in
RL (e.g. how can a principled trade-off between two competing but incomparable
reward functions be reached). The aim is to catalyze progress towards
morally-competent agents and highlight the potential of RL to contribute
towards the computational grounding of moral philosophy.
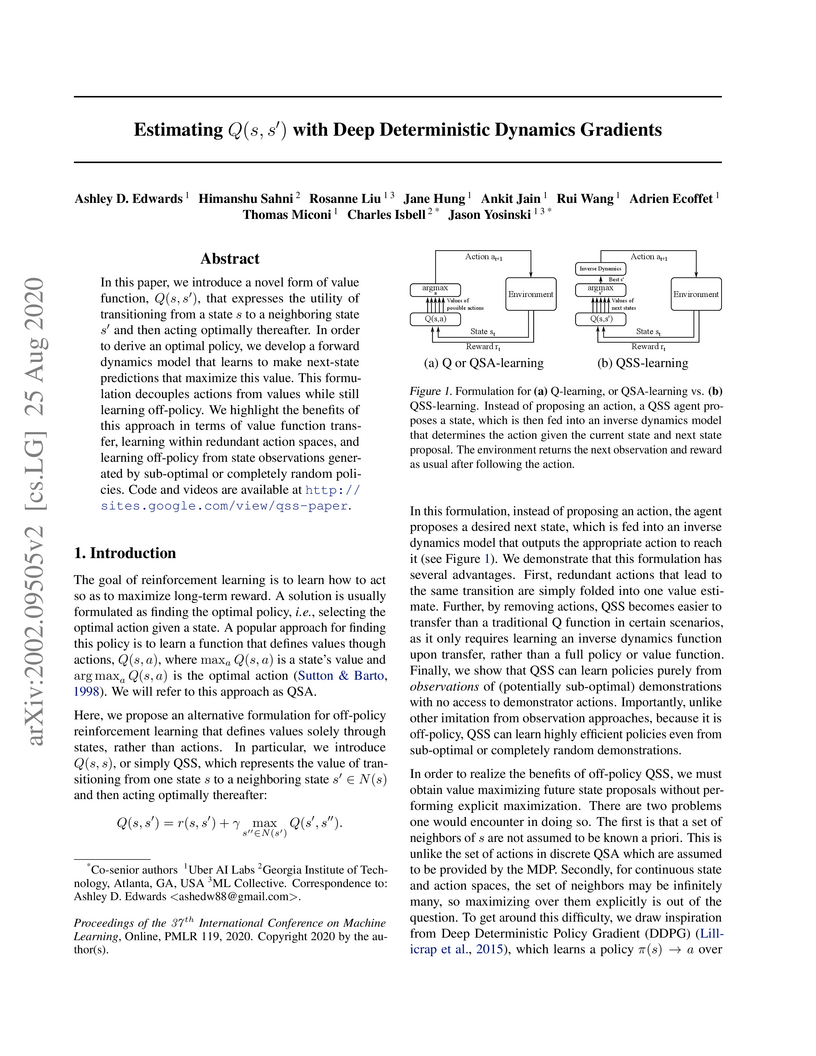
In this paper, we introduce a novel form of value function, Q(s,s′), that expresses the utility of transitioning from a state s to a neighboring state s′ and then acting optimally thereafter. In order to derive an optimal policy, we develop a forward dynamics model that learns to make next-state predictions that maximize this value. This formulation decouples actions from values while still learning off-policy. We highlight the benefits of this approach in terms of value function transfer, learning within redundant action spaces, and learning off-policy from state observations generated by sub-optimal or completely random policies. Code and videos are available at this http URL.
Probabilistic neural networks are typically modeled with independent weight priors, which do not capture weight correlations in the prior and do not provide a parsimonious interface to express properties in function space. A desirable class of priors would represent weights compactly, capture correlations between weights, facilitate calibrated reasoning about uncertainty, and allow inclusion of prior knowledge about the function space such as periodicity or dependence on contexts such as inputs. To this end, this paper introduces two innovations: (i) a Gaussian process-based hierarchical model for network weights based on unit embeddings that can flexibly encode correlated weight structures, and (ii) input-dependent versions of these weight priors that can provide convenient ways to regularize the function space through the use of kernels defined on contextual inputs. We show these models provide desirable test-time uncertainty estimates on out-of-distribution data, demonstrate cases of modeling inductive biases for neural networks with kernels which help both interpolation and extrapolation from training data, and demonstrate competitive predictive performance on an active learning benchmark.
Recent developments in artificial intelligence and machine learning have
spurred interest in the growing field of AI safety, which studies how to
prevent human-harming accidents when deploying AI systems. This paper thus
explores the intersection of AI safety with evolutionary computation, to show
how safety issues arise in evolutionary computation and how understanding from
evolutionary computational and biological evolution can inform the broader
study of AI safety.
This paper proposes a novel end-to-end architecture for task-oriented
dialogue systems. It is based on a simple and practical yet very effective
sequence-to-sequence approach, where language understanding and state tracking
tasks are modeled jointly with a structured copy-augmented sequential decoder
and a multi-label decoder for each slot. The policy engine and language
generation tasks are modeled jointly following that. The copy-augmented
sequential decoder deals with new or unknown values in the conversation, while
the multi-label decoder combined with the sequential decoder ensures the
explicit assignment of values to slots. On the generation part, slot binary
classifiers are used to improve performance. This architecture is scalable to
real-world scenarios and is shown through an empirical evaluation to achieve
state-of-the-art performance on both the Cambridge Restaurant dataset and the
Stanford in-car assistant dataset\footnote{The code is available at
\url{this https URL}}
17 Jan 2020
As the field of Spoken Dialogue Systems and Conversational AI grows, so does the need for tools and environments that abstract away implementation details in order to expedite the development process, lower the barrier of entry to the field, and offer a common test-bed for new ideas. In this paper, we present Plato, a flexible Conversational AI platform written in Python that supports any kind of conversational agent architecture, from standard architectures to architectures with jointly-trained components, single- or multi-party interactions, and offline or online training of any conversational agent component. Plato has been designed to be easy to understand and debug and is agnostic to the underlying learning frameworks that train each component.
This work presents an exploration and imitation-learning-based agent capable
of state-of-the-art performance in playing text-based computer games.
Text-based computer games describe their world to the player through natural
language and expect the player to interact with the game using text. These
games are of interest as they can be seen as a testbed for language
understanding, problem-solving, and language generation by artificial agents.
Moreover, they provide a learning environment in which these skills can be
acquired through interactions with an environment rather than using fixed
corpora. One aspect that makes these games particularly challenging for
learning agents is the combinatorially large action space. Existing methods for
solving text-based games are limited to games that are either very simple or
have an action space restricted to a predetermined set of admissible actions.
In this work, we propose to use the exploration approach of Go-Explore for
solving text-based games. More specifically, in an initial exploration phase,
we first extract trajectories with high rewards, after which we train a policy
to solve the game by imitating these trajectories. Our experiments show that
this approach outperforms existing solutions in solving text-based games, and
it is more sample efficient in terms of the number of interactions with the
environment. Moreover, we show that the learned policy can generalize better
than existing solutions to unseen games without using any restriction on the
action space.
Automatic speaker verification systems are vulnerable to audio replay attacks
which bypass security by replaying recordings of authorized speakers. Replay
attack detection (RA) detection systems built upon Residual Neural Networks
(ResNet)s have yielded astonishing results on the public benchmark ASVspoof
2019 Physical Access challenge. With most teams using fine-tuned feature
extraction pipelines and model architectures, the generalizability of such
systems remains questionable though. In this work, we analyse the effect of
discriminative feature learning in a multi-task learning (MTL) setting can have
on the generalizability and discriminability of RA detection systems. We use a
popular ResNet architecture optimized by the cross-entropy criterion as our
baseline and compare it to the same architecture optimized by MTL using Siamese
Neural Networks (SNN). It can be shown that SNN outperform the baseline by
relative 26.8 % Equal Error Rate (EER). We further enhance the model's
architecture and demonstrate that SNN with additional reconstruction loss yield
another significant improvement of relative 13.8 % EER.
Bayesian optimization (BO) is a class of sample-efficient global optimization methods, where a probabilistic model conditioned on previous observations is used to determine future evaluations via the optimization of an acquisition function. Most acquisition functions are myopic, meaning that they only consider the impact of the next function evaluation. Non-myopic acquisition functions consider the impact of the next h function evaluations and are typically computed through rollout, in which h steps of BO are simulated. These rollout acquisition functions are defined as h-dimensional integrals, and are expensive to compute and optimize. We show that a combination of quasi-Monte Carlo, common random numbers, and control variates significantly reduce the computational burden of rollout. We then formulate a policy-search based approach that removes the need to optimize the rollout acquisition function. Finally, we discuss the qualitative behavior of rollout policies in the setting of multi-modal objectives and model error.
It is a significant challenge to design probabilistic programming systems that can accommodate a wide variety of inference strategies within a unified framework. Noting that the versatility of modern automatic differentiation frameworks is based in large part on the unifying concept of tensors, we describe a software abstraction for integration --functional tensors-- that captures many of the benefits of tensors, while also being able to describe continuous probability distributions. Moreover, functional tensors are a natural candidate for generalized variable elimination and parallel-scan filtering algorithms that enable parallel exact inference for a large family of tractable modeling motifs. We demonstrate the versatility of functional tensors by integrating them into the modeling frontend and inference backend of the Pyro programming language. In experiments we show that the resulting framework enables a large variety of inference strategies, including those that mix exact and approximate inference.
11 Aug 2021
This report explores the limitations of existing feature stores in managing high-dimensional, semantically complex embeddings and proposes a data-centric approach to address the unique challenges of embedding ecosystems. It outlines how data management principles can enhance the reliability and effectiveness of embedding-based ML pipelines across their lifecycle, from training data to model monitoring.
Current approaches to Natural Language Generation (NLG) for dialog mainly
focus on domain-specific, task-oriented applications (e.g. restaurant booking)
using limited ontologies (up to 20 slot types), usually without considering the
previous conversation context. Furthermore, these approaches require large
amounts of data for each domain, and do not benefit from examples that may be
available for other domains. This work explores the feasibility of applying
statistical NLG to scenarios requiring larger ontologies, such as multi-domain
dialog applications or open-domain question answering (QA) based on knowledge
graphs. We model NLG through an Encoder-Decoder framework using a large dataset
of interactions between real-world users and a conversational agent for
open-domain QA. First, we investigate the impact of increasing the number of
slot types on the generation quality and experiment with different partitions
of the QA data with progressively larger ontologies (up to 369 slot types).
Second, we perform multi-task learning experiments between open-domain QA and
task-oriented dialog, and benchmark our model on a popular NLG dataset.
Moreover, we experiment with using the conversational context as an additional
input to improve response generation quality. Our experiments show the
feasibility of learning statistical NLG models for open-domain QA with larger
ontologies.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.