Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya
10 Oct 2025
This paper offers a comprehensive review of the fundamental architectural components—Perception, Reasoning, Memory, and Execution—necessary for building autonomous Large Language Model (LLM) agents. It synthesizes state-of-the-art techniques to enhance the execution of complex automation tasks, providing a structured framework for future development.
09 Oct 2025
Academia SinicaNational Astronomical Observatory of Japan UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University College LondonNational Taiwan University
University College LondonNational Taiwan University University of Michigan
University of Michigan Boston UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the UniverseThe University of Texas at Dallas
Boston UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the UniverseThe University of Texas at Dallas Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Sorbonne UniversitéFermi National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversitat Politècnica de CatalunyaUniversity of Portsmouth
Sorbonne UniversitéFermi National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversitat Politècnica de CatalunyaUniversity of Portsmouth The Ohio State UniversitySejong UniversityUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoUniversitat Autònoma de Barcelona
The Ohio State UniversitySejong UniversityUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoUniversitat Autònoma de Barcelona University of California, Santa CruzNSF NOIRLabUniversidad de Los AndesUniversity of WyomingCIEMATInstitut de Física d’Altes Energies (IFAE)Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis AvançatsSiena CollegeInstituto Astrofisica de CanariasInstitute of Space Sciences (ICE–CSIC)Universit
degli Studi di MilanoINAF
Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera
University of California, Santa CruzNSF NOIRLabUniversidad de Los AndesUniversity of WyomingCIEMATInstitut de Física d’Altes Energies (IFAE)Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis AvançatsSiena CollegeInstituto Astrofisica de CanariasInstitute of Space Sciences (ICE–CSIC)Universit
degli Studi di MilanoINAF
Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera
 UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University College LondonNational Taiwan University
University College LondonNational Taiwan University University of Michigan
University of Michigan Boston UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the UniverseThe University of Texas at Dallas
Boston UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the UniverseThe University of Texas at Dallas Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Sorbonne UniversitéFermi National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversitat Politècnica de CatalunyaUniversity of Portsmouth
Sorbonne UniversitéFermi National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversitat Politècnica de CatalunyaUniversity of Portsmouth The Ohio State UniversitySejong UniversityUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoUniversitat Autònoma de Barcelona
The Ohio State UniversitySejong UniversityUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoUniversitat Autònoma de Barcelona University of California, Santa CruzNSF NOIRLabUniversidad de Los AndesUniversity of WyomingCIEMATInstitut de Física d’Altes Energies (IFAE)Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis AvançatsSiena CollegeInstituto Astrofisica de CanariasInstitute of Space Sciences (ICE–CSIC)Universit
degli Studi di MilanoINAF
Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera
University of California, Santa CruzNSF NOIRLabUniversidad de Los AndesUniversity of WyomingCIEMATInstitut de Física d’Altes Energies (IFAE)Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis AvançatsSiena CollegeInstituto Astrofisica de CanariasInstitute of Space Sciences (ICE–CSIC)Universit
degli Studi di MilanoINAF
Osservatorio Astronomico di BreraThis study comprehensively characterized the cool circumgalactic medium (CGM) around galaxies at redshifts below 0.4 using data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) Year 1 survey. It reveals persistent correlations between cool gas absorption and galaxy properties like stellar mass and star formation rate, along with an unexpected absence of azimuthal anisotropy, indicating a possible evolution in CGM dynamics at lower redshifts.
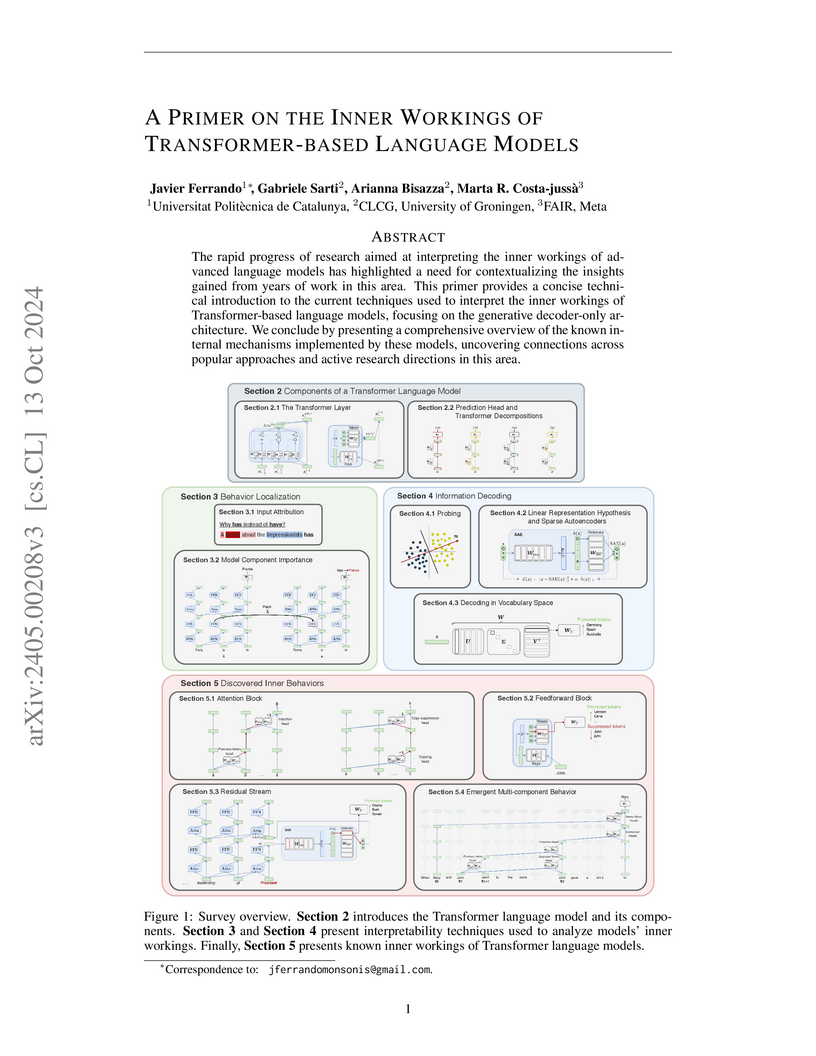
This primer provides a comprehensive technical introduction to interpreting transformer-based language models, particularly generative decoder-only architectures, by consolidating current techniques and systematically mapping discovered internal mechanisms and behaviors across model components.
This paper accelerates and simplifies deep Temporal Difference (TD) learning by theoretically demonstrating that LayerNormalization and L2 regularization enable provably convergent off-policy Q-learning without target networks or large replay buffers. The resulting Parallelized Q-Network (PQN) achieves competitive performance with state-of-the-art algorithms on single and multi-agent benchmarks, while being up to 50x faster due to its design for end-to-end GPU training.
26 Mar 2025
A detailed reverse engineering analysis of modern NVIDIA GPU cores uncovers key microarchitectural details and provides an updated simulation model in Accel-sim, reducing mean absolute percentage error in execution cycle predictions while revealing compiler-guided scheduling policies and software-based dependency management approaches used in current GPU designs.
The Expressive Neural Network (ENN) introduces a neural network architecture where activation functions are dynamically adapted during training using the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT). This approach enables the network to achieve significantly higher accuracy in complex classification tasks (up to 40% improvement in some scenarios) and orders of magnitude lower Mean Squared Error in regression compared to models with fixed activation functions.
Since the rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) a couple of years ago,
researchers in metaheuristics (MHs) have wondered how to use their power in a
beneficial way within their algorithms. This paper introduces a novel approach
that leverages LLMs as pattern recognition tools to improve MHs. The resulting
hybrid method, tested in the context of a social network-based combinatorial
optimization problem, outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches that
combine machine learning with MHs regarding the obtained solution quality. By
carefully designing prompts, we demonstrate that the output obtained from LLMs
can be used as problem knowledge, leading to improved results. Lastly, we
acknowledge LLMs' potential drawbacks and limitations and consider it essential
to examine them to advance this type of research further. Our method can be
reproduced using a tool available at: this https URL
18 Aug 2025
Researchers from Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya conducted a detailed empirical analysis of the SWE-Bench leaderboards, profiling 80 unique LLM- and agent-based repair systems submitted by diverse entities. The study reveals a dominance of industrial contributions and proprietary LLMs for top performance, along with insights into prevalent architectural patterns and pipeline strategies for automated program repair.
08 Jul 2025
Researchers at Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya introduce Multi-Agent Debate (MAD) strategies to improve Large Language Model performance in Requirements Engineering tasks. Their empirical evaluation demonstrated that MAD statistically outperforms single-agent LLM approaches in requirements classification, achieving F1-score improvements of over 10 points, despite incurring significantly higher computational costs.
Large-batch LLM inference for smaller models on GPUs remains memory-bound due to DRAM bandwidth saturation in the attention mechanism, not compute-bound as commonly assumed, leading to significant GPU underutilization. The research introduces a Batching Configuration Advisor (BCA) and model replication, achieving up to 33.7% throughput increase for OPT-1.3B by efficiently utilizing freed memory.
Coordination is one of the most difficult aspects of multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). One reason is that agents normally choose their actions independently of one another. In order to see coordination strategies emerging from the combination of independent policies, the recent research has focused on the use of a centralized function (CF) that learns each agent's contribution to the team reward. However, the structure in which the environment is presented to the agents and to the CF is typically overlooked. We have observed that the features used to describe the coordination problem can be represented as vertex features of a latent graph structure. Here, we present TransfQMix, a new approach that uses transformers to leverage this latent structure and learn better coordination policies. Our transformer agents perform a graph reasoning over the state of the observable entities. Our transformer Q-mixer learns a monotonic mixing-function from a larger graph that includes the internal and external states of the agents. TransfQMix is designed to be entirely transferable, meaning that same parameters can be used to control and train larger or smaller teams of agents. This enables to deploy promising approaches to save training time and derive general policies in MARL, such as transfer learning, zero-shot transfer, and curriculum learning. We report TransfQMix's performances in the Spread and StarCraft II environments. In both settings, it outperforms state-of-the-art Q-Learning models, and it demonstrates effectiveness in solving problems that other methods can not solve.
This research introduces an attribution-based method for interpreting Large Language Models by tracing "information flow routes," enabling automated, scalable analysis of internal computations. The approach provides a 100x speedup over existing patching methods and uncovers general and domain-specific component specialization in Llama 2-7B, offering a more comprehensive understanding of its internal mechanisms.
Advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP), have led to the emergence
of Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT, Llama, Claude, and Gemini, which
excel across a range of tasks but require extensive fine-tuning to align their
outputs with human expectations. A widely used method for achieving this
alignment is Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), which, despite
its success, faces challenges in accurately modelling human preferences. In
this paper, we introduce GazeReward, a novel framework that integrates implicit
feedback -- and specifically eye-tracking (ET) data -- into the Reward Model
(RM). In addition, we explore how ET-based features can provide insights into
user preferences. Through ablation studies we test our framework with different
integration methods, LLMs, and ET generator models, demonstrating that our
approach significantly improves the accuracy of the RM on established human
preference datasets. This work advances the ongoing discussion on optimizing AI
alignment with human values, exploring the potential of cognitive data for
shaping future NLP research.
Analyzing feed-forward network (FFN) neurons in large language models using a lightweight, single-GPU approach, this research categorizes neuron types and demonstrates that FFN neurons explicitly suppress information about their triggering tokens, a mechanism distinct from previous understandings of information addition. The study found many "dead" neurons in early layers and identified neurons dedicated to positional information, with behaviors evolving as models scale.
15 Sep 2025
Researchers developed an enhanced Morgan-Pitman test to compare the equality of prediction error variances for machine learning models, offering a statistically sound criterion for model evaluation and selection. This robust method, which handles non-normal errors and dependent residuals, helps identify simpler, more generalizable models that exhibit equivalent predictive stability.
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has shown a dramatic improvement in decision-making and automated control problems. Consequently, DRL represents a promising technique to efficiently solve many relevant optimization problems (e.g., routing) in self-driving networks. However, existing DRL-based solutions applied to networking fail to generalize, which means that they are not able to operate properly when applied to network topologies not observed during training. This lack of generalization capability significantly hinders the deployment of DRL technologies in production networks. This is because state-of-the-art DRL-based networking solutions use standard neural networks (e.g., fully connected, convolutional), which are not suited to learn from information structured as graphs.
In this paper, we integrate Graph Neural Networks (GNN) into DRL agents and we design a problem specific action space to enable generalization. GNNs are Deep Learning models inherently designed to generalize over graphs of different sizes and structures. This allows the proposed GNN-based DRL agent to learn and generalize over arbitrary network topologies. We test our DRL+GNN agent in a routing optimization use case in optical networks and evaluate it on 180 and 232 unseen synthetic and real-world network topologies respectively. The results show that the DRL+GNN agent is able to outperform state-of-the-art solutions in topologies never seen during training.
3D scene reconstruction and understanding have gained increasing popularity, yet existing methods still struggle to capture fine-grained, language-aware 3D representations from 2D images. In this paper, we present GALA, a novel framework for open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding with 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). GALA distills a scene-specific 3D instance feature field via self-supervised contrastive learning. To extend to generalized language feature fields, we introduce the core contribution of GALA, a cross-attention module with two learnable codebooks that encode view-independent semantic embeddings. This design not only ensures intra-instance feature similarity but also supports seamless 2D and 3D open-vocabulary queries. It reduces memory consumption by avoiding per-Gaussian high-dimensional feature learning. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate GALA's remarkable open-vocabulary performance on both 2D and 3D.
27 Sep 2025
In this exploratory numerical study, we assess the suitability of Quantum Linear Solvers (QLSs) toward providing a quantum advantage for Networks-based Linear System Problems (NLSPs). NLSPs are of importance as they are naturally connected to real-world applications. In an NLSP, one starts with a graph and arrives at a system of linear equations. The advantage that one may obtain with a QLS for an NLSP is determined by the interplay between three variables: the scaling of condition number and sparsity functions of matrices associated with the graphs considered, as well as the function describing the system size growth. We recommend graph families that can offer potential for an exponential advantage (best graph families) and those that offer sub-exponential but at least polynomial advantage (better graph families), with the HHL algorithm considered relative to an efficient classical linear solver. Within the scope of our analyses, we observe that only 4% of the 50 considered graph families offer prospects for an exponential advantage, whereas about 20% of the considered graph families show a polynomial advantage. Furthermore, we observe and report some interesting cases where some graph families not only fare better with improved algorithms such as the Childs-Kothari-Somma algorithm but also graduate from offering no advantage to promising a polynomial advantage, graph families that exhibit futile exponential advantage, etc. Given the limited number of graph families that one can survey through numerical studies, we discuss an interesting case where we unify several graph families into one superfamily, and show the existence of infinite best and better graphs in it. Lastly, we very briefly touch upon some practical issues that one may face even if the aforementioned graph theoretic requirements are satisfied, including quantum hardware challenges.
This research comprehensively benchmarks Small Language Models (SLMs) to reveal that they achieve Pareto-optimal throughput on a single high-end GPU, unlike larger models that require distributed systems. The study demonstrates that replicating SLMs on a single accelerator significantly boosts overall throughput and GPU utilization, offering a new approach to efficient serving.
Neuroscience research has made immense progress over the last decade, but our
understanding of the brain remains fragmented and piecemeal: the dream of
probing an arbitrary brain region and automatically reading out the information
encoded in its neural activity remains out of reach. In this work, we build
towards a first foundation model for neural spiking data that can solve a
diverse set of tasks across multiple brain areas. We introduce a novel
self-supervised modeling approach for population activity in which the model
alternates between masking out and reconstructing neural activity across
different time steps, neurons, and brain regions. To evaluate our approach, we
design unsupervised and supervised prediction tasks using the International
Brain Laboratory repeated site dataset, which is comprised of Neuropixels
recordings targeting the same brain locations across 48 animals and
experimental sessions. The prediction tasks include single-neuron and
region-level activity prediction, forward prediction, and behavior decoding. We
demonstrate that our multi-task-masking (MtM) approach significantly improves
the performance of current state-of-the-art population models and enables
multi-task learning. We also show that by training on multiple animals, we can
improve the generalization ability of the model to unseen animals, paving the
way for a foundation model of the brain at single-cell, single-spike
resolution.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.