Universitat Politécnica de Valéncia
 ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich University of Washington
University of Washington University of Toronto
University of Toronto University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge Harvard University
Harvard University Université de Montréal
Université de Montréal New York University
New York University University of OxfordLMU Munich
University of OxfordLMU Munich Stanford University
Stanford University Mila - Quebec AI InstituteUniversity of Edinburgh
Mila - Quebec AI InstituteUniversity of Edinburgh Peking University
Peking University Allen Institute for AI
Allen Institute for AI Princeton University
Princeton University University of VirginiaUniversity of SussexUNC-Chapel HillNewcastle UniversityUniversitat Politécnica de ValénciaModulo ResearchUniversity of MichigianCenter for the Governance of AI
University of VirginiaUniversity of SussexUNC-Chapel HillNewcastle UniversityUniversitat Politécnica de ValénciaModulo ResearchUniversity of MichigianCenter for the Governance of AIThis work identifies 18 foundational challenges in assuring the alignment and safety of large language models (LLMs). These challenges are organized into three different categories: scientific understanding of LLMs, development and deployment methods, and sociotechnical challenges. Based on the identified challenges, we pose 200+ concrete research questions.
A comprehensive analysis identifies fundamental limitations of machine unlearning (MU) for AI safety, particularly for controlling complex, emergent AI capabilities and managing dual-use knowledge, concluding that MU is not a standalone solution despite its promise for privacy tasks. The work, involving researchers from leading institutions and AI safety organizations, maps out key challenges and open problems in this domain.
A new framework introduces 18 interpretable 'general scales' to evaluate AI capabilities and task demands, using automated LLM annotation to provide robust, non-saturating ability profiles for models. This methodology improves out-of-distribution performance prediction while offering transparency into what current benchmarks truly measure.
Stellar collisions in dense galactic nuclei might play an important role in fueling supermassive black holes (SMBHs) and shaping their environments. The gas released during these collisions can contribute to SMBH accretion, influencing phenomena such as active galactic nuclei and tidal disruption events of the remnants. We address the challenge of rapidly and accurately predicting the outcomes of stellar collisionsincluding remnant masses and unbound gasacross a broad parameter space of initial conditions. Existing smoothed-particle-hydrodynamic (SPH) simulation techniques, while detailed, are too resource-intensive for exploratory studies or real-time applications. We develop a machine learning framework trained on a dataset of ∼16,000 SPH simulations of main-sequence star collisions. By extracting physically meaningful parameters (e.g., masses, radii, impact parameters, and virial ratios) and employing gradient-boosted regression trees with Huber loss, we create a model that balances accuracy and computational efficiency. The method includes logarithmic transforms to handle dynamic ranges and regularization to ensure physical plausibility. The model achieves predictions of collision outcomes (remnant masses, and unbound mass) with very low mean absolute errors respect to the typical mass scale. It operates in fractions of a second, enabling large-scale parameter studies and real-time applications. Parameter importance analysis reveals that the impact parameter and the relative velocity dominate outcomes, aligning with theoretical expectations. Our approach provides a scalable tool for studying stellar collisions in galactic nuclei. The rapid predictions facilitate investigations into gas supply for SMBH accretion and the cumulative effects of collisions over cosmic time, particularly relevant to address the growth of SMBHs.
This paper introduces a framework to predict the success of Large Language Models (LLMs) on unseen data by evaluating them on a small set of reference instances. The approach demonstrates that as few as 100 reference instances are sufficient to achieve good predictive performance in in-distribution scenarios, providing a cost-effective method for LLM assessment.
Researchers demonstrated that supermassive black hole binaries (SMBHBs) are born highly eccentric but are rapidly circularized by interactions with geometrically thick nuclear discs, creating a "circularization trap." This mechanism forces binaries into nearly circular orbits, leading to a substantial cosmological delay of 0.3 to 2.5 Gyr before gravitational wave coalescence.
The increasing prevalence of mental health disorders globally highlights the
urgent need for effective digital screening methods that can be used in
multilingual contexts. Most existing studies, however, focus on English data,
overlooking critical mental health signals that may be present in non-English
texts. To address this important gap, we present the first survey on the
detection of mental health disorders using multilingual social media data. We
investigate the cultural nuances that influence online language patterns and
self-disclosure behaviors, and how these factors can impact the performance of
NLP tools. Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of multilingual data
collections that can be used for developing NLP models for mental health
screening. Our findings can inform the design of effective multilingual mental
health screening tools that can meet the needs of diverse populations,
ultimately improving mental health outcomes on a global scale.
22 Oct 2025
Data science aims to extract insights from data to support decision-making processes. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have been increasingly used as assistants for data science, by suggesting ideas, techniques and small code snippets, or for the interpretation of results and reporting. Proper automation of some data-science activities is now promised by the rise of LLM agents, i.e., AI systems powered by an LLM equipped with additional affordances--such as code execution and knowledge bases--that can perform self-directed actions and interact with digital environments. In this paper, we survey the evaluation of LLM assistants and agents for data science. We find (1) a dominant focus on a small subset of goal-oriented activities, largely ignoring data management and exploratory activities; (2) a concentration on pure assistance or fully autonomous agents, without considering intermediate levels of human-AI collaboration; and (3) an emphasis on human substitution, therefore neglecting the possibility of higher levels of automation thanks to task transformation.
23 Sep 2025
In a seminal paper [8] it was shown that Heisenberg-limited measurements could be achieved without using entangled states by coupling the quantum resources to a common environment that could be measured, at least, in part. The authors also claimed that their method would be robust under decoherence, and, in particular, applied it to derive an analytical expression to measure the change in length of an optical cavity within the Tavis-Cummings model using the superradiance approximation, which would still have a 1/N scaling. Here, we show that the analytical derivations in [8] are incompatible with the cavity superradiance, leading to the standard quantum-limited scaling 1/\sqrt{N}.
Aligning large language models (LLMs) with human values is essential for
their safe deployment and widespread adoption. Current LLM safety benchmarks
often focus solely on the refusal of individual problematic queries, which
overlooks the importance of the context where the query occurs and may cause
undesired refusal of queries under safe contexts that diminish user experience.
Addressing this gap, we introduce CASE-Bench, a Context-Aware SafEty Benchmark
that integrates context into safety assessments of LLMs. CASE-Bench assigns
distinct, formally described contexts to categorized queries based on
Contextual Integrity theory. Additionally, in contrast to previous studies
which mainly rely on majority voting from just a few annotators, we recruited a
sufficient number of annotators necessary to ensure the detection of
statistically significant differences among the experimental conditions based
on power analysis. Our extensive analysis using CASE-Bench on various
open-source and commercial LLMs reveals a substantial and significant influence
of context on human judgments (p<0.0001 from a z-test), underscoring the
necessity of context in safety evaluations. We also identify notable mismatches
between human judgments and LLM responses, particularly in commercial models
within safe contexts.
PredictaBoard introduces a collaborative benchmarking framework to jointly evaluate Large Language Model performance and the predictability of its outcomes on individual task instances. The framework uses specific metrics like Predictably Valid Region (PVR) and Area Under the Accuracy-Rejection Curve (AUARC) to assess how well an external assessor can anticipate an LLM's success or failure, revealing that reliable error prediction, particularly out-of-distribution or under strict error tolerances, remains a significant challenge.
Today, Wi-Fi is over 25 years old. Yet, despite sharing the same branding name, today's Wi-Fi boasts entirely new capabilities that were not even on the roadmap 25 years ago. This article aims to provide a holistic and comprehensive technical and historical tutorial on Wi-Fi, beginning with IEEE 802.11b (Wi-Fi 1) and looking forward to IEEE 802.11bn (Wi-Fi 8). This is the first tutorial article to span these eight generations. Rather than a generation-by-generation exposition, we describe the key mechanisms that have advanced Wi-Fi. We begin by discussing spectrum allocation and coexistence, and detailing the IEEE 802.11 standardization cycle. Second, we provide an overview of the physical layer and describe key elements that have enabled data rates to increase by over 1,000x. Third, we describe how Wi-Fi Medium Access Control has been enhanced from the original Distributed Coordination Function to now include capabilities spanning from frame aggregation to wideband spectrum access. Fourth, we describe how Wi-Fi 5 first broke the one-user-at-a-time paradigm and introduced multi-user access. Fifth, given the increasing use of mobile, battery-powered devices, we describe Wi-Fi's energy-saving mechanisms over the generations. Sixth, we discuss how Wi-Fi was enhanced to seamlessly aggregate spectrum across 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands to improve throughput, reliability, and latency. Finally, we describe how Wi-Fi enables nearby Access Points to coordinate in order to improve performance and efficiency. In the Appendix, we further discuss Wi-Fi developments beyond 802.11bn, including integrated mmWave operations, sensing, security and privacy extensions, and the adoption of AI/ML.
Initialization plays a critical role in Deep Neural Network training, directly influencing convergence, stability, and generalization. Common approaches such as Glorot and He initializations rely on randomness, which can produce uneven weight distributions across layer connections. In this paper, we introduce the Sinusoidal initialization, a novel deterministic method that employs sinusoidal functions to construct structured weight matrices expressly to improve the spread and balance of weights throughout the network while simultaneously fostering a more uniform, well-conditioned distribution of neuron activation states from the very first forward pass. Because Sinusoidal initialization begins with weights and activations that are already evenly and efficiently utilized, it delivers consistently faster convergence, greater training stability, and higher final accuracy across a wide range of models, including convolutional neural networks, vision transformers, and large language models. On average, our experiments show an increase of 4.9% in final validation accuracy and 20.9% in convergence speed. By replacing randomness with structure, this initialization provides a stronger and more reliable foundation for Deep Learning systems.
10 Sep 2025
Adaptation of foundation models using low-rank methods is a widespread approach. Another way to adapt these models is to employ orthogonal fine-tuning methods, which are less time and memory efficient despite their good generalization properties. In this work, we propose Householder Orthogonal Fine-tuning (HOFT), a novel orthogonal fine-tuning method that aims to alleviate time and space complexity. Moreover, some theoretical properties of the orthogonal fine-tuning paradigm are explored. From this exploration, Scaled Householder Orthogonal Fine-tuning (SHOFT) is proposed. Both HOFT and SHOFT are evaluated in downstream tasks, namely commonsense reasoning, machine translation, subject-driven generation and mathematical reasoning. Compared with state-of-the-art adaptation methods, HOFT and SHOFT show comparable or better results.
02 Oct 2023
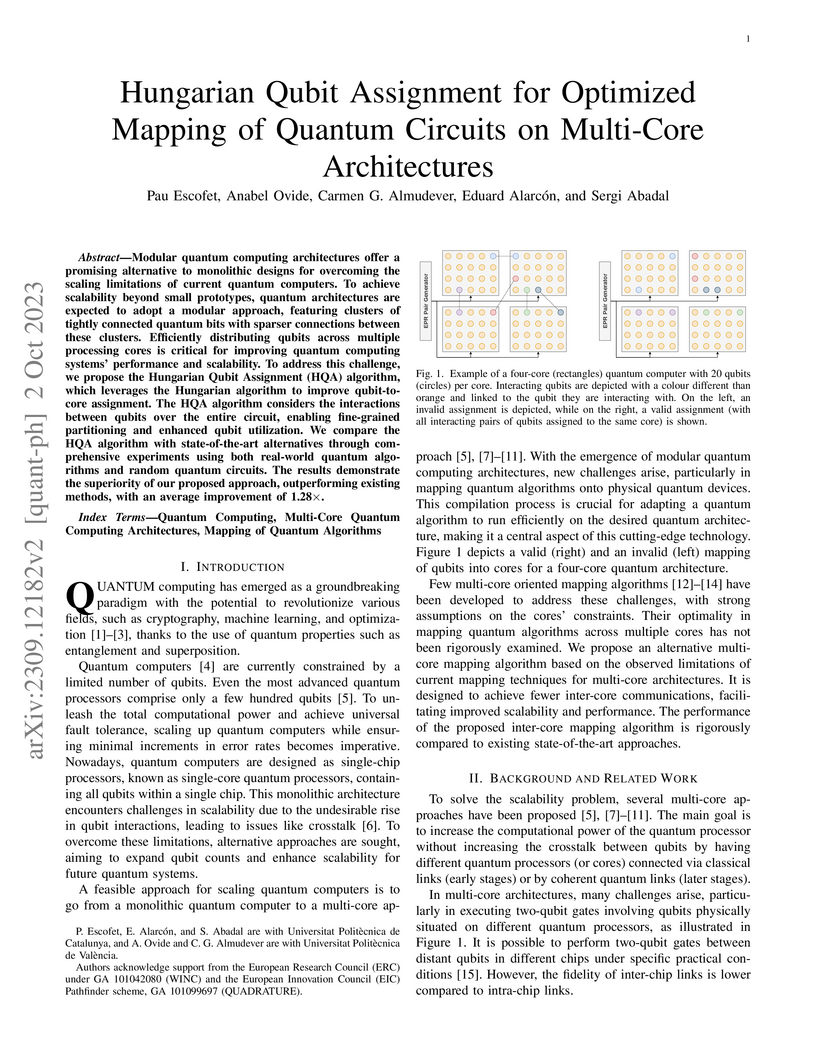
Modular quantum computing architectures offer a promising alternative to monolithic designs for overcoming the scaling limitations of current quantum computers. To achieve scalability beyond small prototypes, quantum architectures are expected to adopt a modular approach, featuring clusters of tightly connected quantum bits with sparser connections between these clusters. Efficiently distributing qubits across multiple processing cores is critical for improving quantum computing systems' performance and scalability. To address this challenge, we propose the Hungarian Qubit Assignment (HQA) algorithm, which leverages the Hungarian algorithm to improve qubit-to-core assignment. The HQA algorithm considers the interactions between qubits over the entire circuit, enabling fine-grained partitioning and enhanced qubit utilization. We compare the HQA algorithm with state-of-the-art alternatives through comprehensive experiments using both real-world quantum algorithms and random quantum circuits. The results demonstrate the superiority of our proposed approach, outperforming existing methods, with an average improvement of 1.28×.
18 Sep 2025
 CNRS
CNRS University of AmsterdamNational Central University
University of AmsterdamNational Central University New York UniversityNikhefUniversity of Melbourne
New York UniversityNikhefUniversity of Melbourne INFNUniversity of WarsawJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchUniversity of GranadaUniversity of Genoa
INFNUniversity of WarsawJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchUniversity of GranadaUniversity of Genoa Sorbonne Université
Sorbonne Université Technical University of Munich
Technical University of Munich Leiden UniversityUniversity of SheffieldUtrecht UniversityCadi Ayyad UniversityUniversity of JohannesburgINAFUnited Arab Emirates UniversityUniversity of South DakotaNCSR DemokritosLebedev Physical InstituteUniversity of ValenciaEberhard-Karls-Universität TübingenComenius UniversityGeorgian Technical UniversityUniversità di BariNational Centre for Nuclear ResearchWestern Sydney UniversityUniversitat Politécnica de ValénciaMohammed V UniversityInstitut de Physique des 2 Infinis de LyonUniversità di FirenzeUniversity of SalentoIFICUniversity of AthensUniversità degli Studi di Bari Aldo MoroPushchino Radio Astronomy ObservatoryLUPMLPC-CaenIFIN-HHChouaïb Doukkali UniversityInstitute of Experimental PhysicsTechnical University of KošiceUniversit di CataniaUniversité Sidi Mohamed Ben AbdellahRoyal Netherlands Institute for Sea ResearchUniversité Mohammed IerInstitut universitaire de technologie de Nantes* North–West UniversityUniversit degli Studi di FerraraUniversit
de ParisUniversit
Grenoble AlpesUniversit
degli Studi di GenovaAix-Marseille Universit",Universit
di SalernoUniversit
Roma TreUniversit
Paris CitUniversit
La SapienzaUniversit
de StrasbourgNantes UniversitUniversit
di PadovaUniversit
degli Studi di FirenzeUniversit
degli Studi di Napoli
Federico IIUniversit
Di Bologna
Leiden UniversityUniversity of SheffieldUtrecht UniversityCadi Ayyad UniversityUniversity of JohannesburgINAFUnited Arab Emirates UniversityUniversity of South DakotaNCSR DemokritosLebedev Physical InstituteUniversity of ValenciaEberhard-Karls-Universität TübingenComenius UniversityGeorgian Technical UniversityUniversità di BariNational Centre for Nuclear ResearchWestern Sydney UniversityUniversitat Politécnica de ValénciaMohammed V UniversityInstitut de Physique des 2 Infinis de LyonUniversità di FirenzeUniversity of SalentoIFICUniversity of AthensUniversità degli Studi di Bari Aldo MoroPushchino Radio Astronomy ObservatoryLUPMLPC-CaenIFIN-HHChouaïb Doukkali UniversityInstitute of Experimental PhysicsTechnical University of KošiceUniversit di CataniaUniversité Sidi Mohamed Ben AbdellahRoyal Netherlands Institute for Sea ResearchUniversité Mohammed IerInstitut universitaire de technologie de Nantes* North–West UniversityUniversit degli Studi di FerraraUniversit
de ParisUniversit
Grenoble AlpesUniversit
degli Studi di GenovaAix-Marseille Universit",Universit
di SalernoUniversit
Roma TreUniversit
Paris CitUniversit
La SapienzaUniversit
de StrasbourgNantes UniversitUniversit
di PadovaUniversit
degli Studi di FirenzeUniversit
degli Studi di Napoli
Federico IIUniversit
Di BolognaContext: The detection of the highest energy neutrino observed to date by KM3NeT, with an estimated energy of 220 PeV, opens up new possibilities for the study and identification of the astrophysical sources responsible for a diffuse flux of such ultra-high-energy neutrinos, among which gamma-ray bursts are longstanding candidates.
Aims: Based on the event KM3-230213A, we derive constraints on the baryon loading and density of the surrounding environment in models of blastwaves in long-duration gamma-ray bursts.
Methods: We compute the diffuse flux from gamma-ray burst blastwaves, either expanding in a constant density interstellar medium or developing in a radially decreasing density of a wind-like environment surrounding the gamma-ray burst progenitor star, by taking into account the expected neutrino spectra and luminosity function. We use a Poisson likelihood method to constrain the blastwave model parameters by calculating the expected number of neutrino events within the 90% confidence level energy range of KM3-230213A and by using the joint exposure of KM3NeT/ARCA, IceCube and Pierre Auger.
Results: We constrain the baryon loading to be ≤{392,131,39,13} at 90% confidence level, which is inversely proportional to a varying interstellar medium particle density of {1,3,10,30} cm−3. In the wind-like environment case, the baryon loading is ≤{20,50,100} at 90% confidence level, which is proportional to the sixth power of a varying density parameter of {0.05,0.06,0.07}.
The gravitational capture of a stellar-mass compact object (CO) by a supermassive black hole is a unique probe of gravity in the strong field regime. Because of the large mass ratio, we call these sources extreme-mass ratio inspirals (EMRIs). In a similar manner, COs can be captured by intermediate-mass black holes in globular clusters or dwarf galaxies. The mass ratio in this case is lower, and hence we refer to the system as an intermediate-mass ratio inspiral (IMRI). Also, sub-stellar objects such as a brown dwarf, with masses much lighter than our Sun, can inspiral into supermassive black holes such as Sgr A* at our Galactic centre. In this case, the mass ratio is extremely large and, hence, we call this system ab extremely-large mass ratio inspirals (XMRIs). All of these sources of gravitational waves will provide us with a collection of snapshots of spacetime around a supermassive black hole that will allow us to do a direct mapping of warped spacetime around the supermassive black hole, a live cartography of gravity in this extreme gravity regime. E/I/XMRIs will be detected by the future space-borne observatories like LISA. There has not been any other probe conceived, planned or even thought of ever that can do the science that we can do with these inspirals. We will discuss them from a viewpoint of relativistic astrophysics.
 Northeastern University
Northeastern University Imperial College LondonUniversity of Melbourne
Imperial College LondonUniversity of Melbourne McGill UniversityLancaster UniversityMBZUAI
McGill UniversityLancaster UniversityMBZUAI University of AlbertaUppsala UniversityUniversity of LiverpoolNational Research Council Canada
University of AlbertaUppsala UniversityUniversity of LiverpoolNational Research Council Canada Technical University of MunichCardiff UniversityUniversity of Santiago de CompostelaSkoltechSanta Clara UniversityIIIT Hyderabad
Technical University of MunichCardiff UniversityUniversity of Santiago de CompostelaSkoltechSanta Clara UniversityIIIT Hyderabad University of GöttingenHamburg UniversityUniversity of PretoriaUniversity of YorkUniversitas IndonesiaNational University of Science and Technology POLITEHNICA BucharestUniversity of PortoUniversitat Politécnica de ValénciaInstitut Teknologi BandungSailplane AIUniversity of BucharestAl Akhawayn UniversityMaseno UniversityBayero University KanoCentro Universitário FEIKaduna State UniversityUniversidad Politécnica Salesiana
University of GöttingenHamburg UniversityUniversity of PretoriaUniversity of YorkUniversitas IndonesiaNational University of Science and Technology POLITEHNICA BucharestUniversity of PortoUniversitat Politécnica de ValénciaInstitut Teknologi BandungSailplane AIUniversity of BucharestAl Akhawayn UniversityMaseno UniversityBayero University KanoCentro Universitário FEIKaduna State UniversityUniversidad Politécnica SalesianaThe BRIGHTER project introduces a human-annotated, multi-labeled dataset for textual emotion recognition across 28 languages, emphasizing under-resourced ones from Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, and Latin America, which includes emotion intensity for a subset. This resource provides benchmarks for multilingual and large language models, revealing their capabilities and limitations in diverse linguistic and cultural contexts.
Multi-agent systems (MAS) have gained relevance in the field of artificial intelligence by offering tools for modelling complex environments where autonomous agents interact to achieve common or individual goals. In these systems, norms emerge as a fundamental component to regulate the behaviour of agents, promoting cooperation, coordination and conflict resolution. This article presents a systematic review, following the PRISMA method, on the emergence of norms in MAS, exploring the main mechanisms and factors that influence this process. Sociological, structural, emotional and cognitive aspects that facilitate the creation, propagation and reinforcement of norms are addressed. The findings highlight the crucial role of social network topology, as well as the importance of emotions and shared values in the adoption and maintenance of norms. Furthermore, opportunities are identified for future research that more explicitly integrates emotional and ethical dynamics in the design of adaptive normative systems. This work provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of research on norm emergence in MAS, serving as a basis for advancing the development of more efficient and flexible systems in artificial and real-world contexts.
02 Oct 2025
Many computationally hard problems can be encoded in quantum Hamiltonians. The solution to these problems is given by the ground states of these Hamiltonians. A state-of-the-art algorithm for finding the ground state of a Hamiltonian is the so-called Quantum Imaginary Time Evolution (QITE) which approximates imaginary time evolution by a unitary evolution that can be implemented in quantum hardware. In this paper, we review the original algorithm together with a comprehensive computer program, as well as, the variational version of it.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.