Ask or search anything...
 University of GroningenUniversity Medical Center Groningen
University of GroningenUniversity Medical Center GroningenThis primer provides a comprehensive technical introduction to interpreting transformer-based language models, particularly generative decoder-only architectures, by consolidating current techniques and systematically mapping discovered internal mechanisms and behaviors across model components.
View blogThis work systematically analyzes hybrid linear attention architectures to balance computational efficiency with long-range recall in large language models. The research demonstrates that a linear attention model's standalone performance does not predict its effectiveness in hybrid setups and identifies selective gating, hierarchical recurrence, and controlled forgetting as crucial architectural properties enabling near-Transformer recall with substantial KV-cache memory reductions.
View blogResearchers from the Vector Institute, Cornell University, and the University of Groningen present a comprehensive Trust, Risk, and Security Management (TRiSM) framework tailored for LLM-based Agentic Multi-Agent Systems (AMAS). This framework delineates unique threats, a risk taxonomy, and novel evaluation metrics, while aligning AMAS development with international AI governance and regulatory standards.
View blogEAGER introduces an entropy-aware generation method for adaptively scaling large language model inference, which dynamically adjusts computational budget based on token-wise uncertainty. This approach achieved up to 37% higher Pass@k performance while using 65% fewer tokens on various reasoning benchmarks, effectively improving the efficiency-performance trade-off for LLM reasoning tasks.
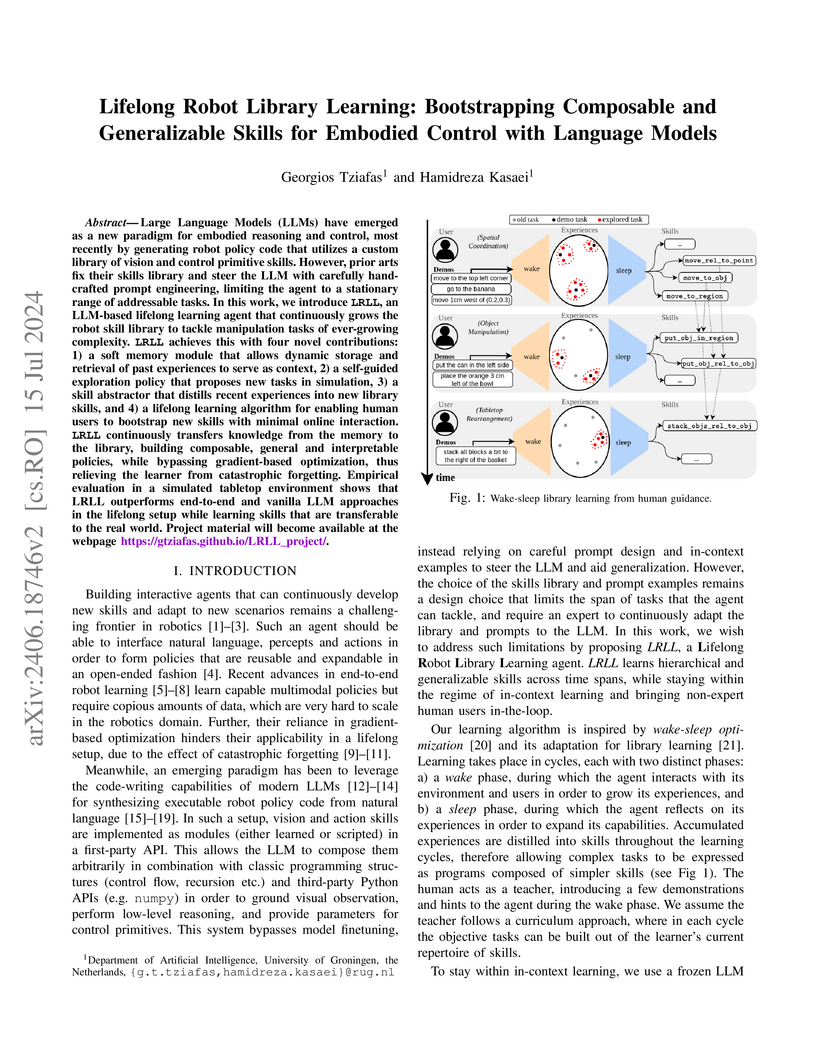
View blogLifelong Robot Library Learning (LRLL), developed by researchers at the University of Groningen, enables robots to continually expand their skill set by autonomously abstracting new, generalizable skills using large language models. The framework demonstrates superior generalization in simulated manipulation tasks, achieving 86.6% success on unseen instructions, and successfully performs zero-shot transfer of learned skills from simulation to a real robot without catastrophic forgetting.
View blogResearchers at Technion and Nvidia Research developed ACT-ViT, an architecture that re-conceptualizes large language model activation tensors as images to detect hallucinations with a Vision Transformer backbone. The method demonstrates superior performance and remarkable cross-LLM generalization, achieving inference times of approximately 10^-5 seconds per instance, vastly improving efficiency over existing techniques.
View blogGoogle researchers introduce PARSE-Ego4D, a dataset designed to enable proactive AI assistance for egocentric videos by providing personal action recommendation annotations. The dataset was created by leveraging large language models to generate initial suggestions, which were then rigorously validated and refined through extensive human annotation, demonstrating the viability of this hybrid approach and setting new benchmarks for intelligent AR/VR systems.
View blog CNRS
CNRS California Institute of Technology
California Institute of Technology
 University College London
University College London
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences University of St Andrews
University of St Andrews
 Nagoya University
Nagoya University
 Meta
Meta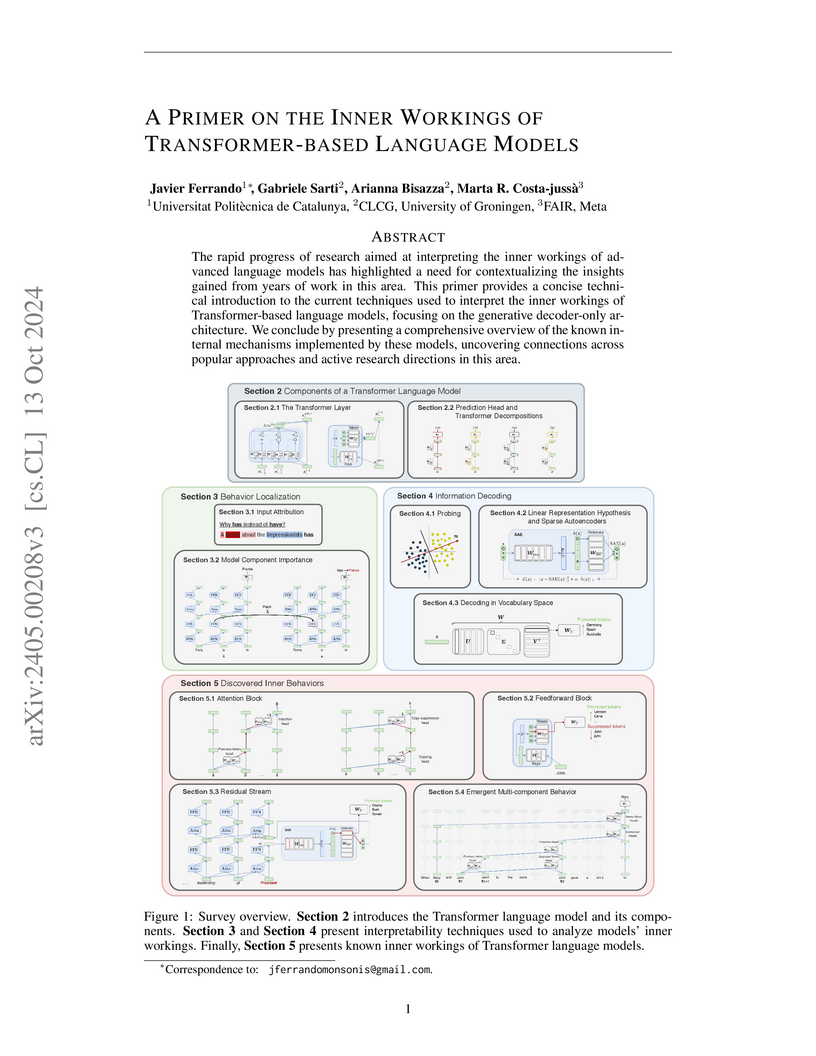
 ByteDance
ByteDance

 Cornell University
Cornell University
 Cohere
Cohere
 University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge

 NVIDIA
NVIDIA
 University of California, Davis
University of California, Davis

 Google
Google University of Central Florida
University of Central Florida

 University of Copenhagen
University of Copenhagen

