University of Manchester
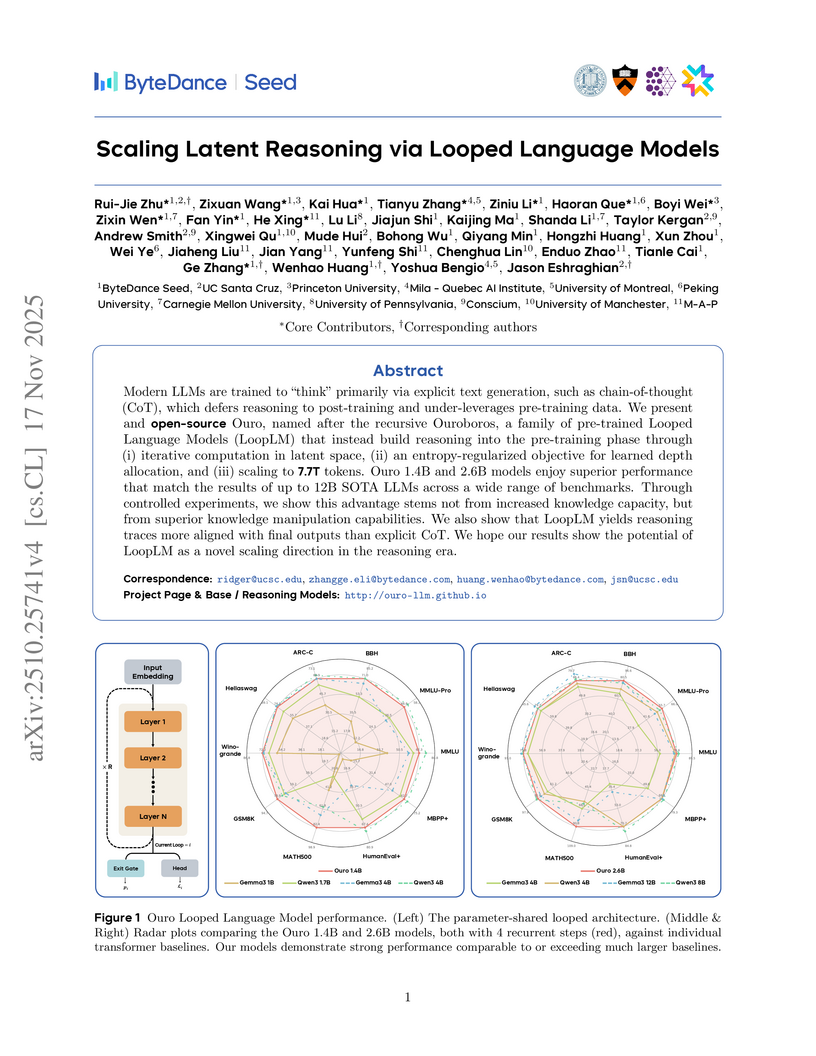
University of ManchesterOuro, a family of Looped Language Models (LoopLMs), embeds iterative computation directly into the pre-training process through parameter reuse, leading to enhanced parameter efficiency and reasoning abilities. These models achieve the performance of much larger non-looped Transformers while demonstrating improved safety and a more causally faithful internal reasoning process.
06 Dec 2025
 Monash UniversityCSIRO
Monash UniversityCSIRO Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University University of Manchester
University of Manchester Beihang University
Beihang University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology
ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology Beijing Jiaotong University
Beijing Jiaotong University Huawei
Huawei Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield
Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOM
TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOMA comprehensive synthesis of Large Language Models for automated software development covers the entire model lifecycle, from data curation to autonomous agents, and offers practical guidance derived from empirical experiments on pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, alongside a detailed analysis of challenges and future directions.
This comprehensive survey from a large multi-institutional collaboration examines "Latent Reasoning" in Large Language Models, an emerging paradigm that performs multi-step inference entirely within the model's high-bandwidth continuous hidden states to overcome the limitations of natural language-based explicit reasoning. It highlights the significant bandwidth advantage of latent representations (approximately 2700x higher) and provides a unified taxonomy of current methodologies.
 University of TorontoMax Planck Institute for Intelligent SystemsUniversity of Utah
University of TorontoMax Planck Institute for Intelligent SystemsUniversity of Utah UCLA
UCLA University of Manchester
University of Manchester National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore University of Oxford
University of Oxford Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University The Chinese University of Hong Kong
The Chinese University of Hong Kong Westlake UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of China
Westlake UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of China University of California, San Diego
University of California, San Diego Peking University
Peking University Columbia University
Columbia University University of SydneyUniversit`a degli Studi di GenovaIstituto Italiano di TecnologiaUniversity of Birmingham
University of SydneyUniversit`a degli Studi di GenovaIstituto Italiano di TecnologiaUniversity of BirminghamResearchers at the University of Toronto, Westlake University, and the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, along with a global consortium, developed aiXiv, an open-access ecosystem designed for AI-generated scientific content and human-AI collaboration. This platform, featuring a multi-agent review system and iterative refinement, raised the acceptance rate of AI-generated proposals from 0% to 45.2% and papers from 10% to 70% in multi-AI voting, demonstrating enhanced quality and trustworthiness.
23 Sep 2025
Tianjin UniversityHuawei Noah’s Ark Lab Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Imperial College London
Imperial College London Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University University of Manchester
University of Manchester University College LondonTongji University
University College LondonTongji University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Peking University
Peking University King’s College LondonTU DarmstadtPengcheng LaboratoryHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)
King’s College LondonTU DarmstadtPengcheng LaboratoryHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Imperial College London
Imperial College London Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University University of Manchester
University of Manchester University College LondonTongji University
University College LondonTongji University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Peking University
Peking University King’s College LondonTU DarmstadtPengcheng LaboratoryHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)
King’s College LondonTU DarmstadtPengcheng LaboratoryHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)Researchers from a global consortium, including Tianjin University and Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab, developed Embodied Arena, a comprehensive platform for evaluating Embodied AI agents, featuring a systematic capability taxonomy and an automated, LLM-driven data generation pipeline. This platform integrates over 22 benchmarks and 30 models, revealing that specialized embodied models often outperform general models on targeted tasks and identifying object and spatial perception as key performance bottlenecks.
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Imperial College London
Imperial College London University of Manchester
University of Manchester National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore Georgia Institute of TechnologyIndiana University
Georgia Institute of TechnologyIndiana University Kyoto University
Kyoto University Zhejiang UniversityUniversity of EdinburghAarhus UniversityThe University of Texas at DallasNational Taiwan Normal UniversityAppCubic
Zhejiang UniversityUniversity of EdinburghAarhus UniversityThe University of Texas at DallasNational Taiwan Normal UniversityAppCubic University of Wisconsin-Madison
University of Wisconsin-Madison Rutgers University
Rutgers University Purdue University
Purdue University HKUSTNational Tsing-Hua UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iXi'an Jiaotong Liverpool UniversitySchool of Visual ArtsPingtan Research Institute of Xiamen UniversityJTB Technology Corp.
HKUSTNational Tsing-Hua UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iXi'an Jiaotong Liverpool UniversitySchool of Visual ArtsPingtan Research Institute of Xiamen UniversityJTB Technology Corp.A comprehensive guide created by a large inter-institutional collaboration synthesizes the field of Explainable AI (XAI), from classical models to Large Language Models (LLMs). It details diverse XAI techniques and their practical implementation, providing clear definitions, evaluations, and future directions for transparent and trustworthy AI.
Researchers at Alibaba Group and collaborating universities developed the D-CPT Law, a predictive framework that optimizes the data mixture ratio for domain-specific continual pre-training of Large Language Models. This law accurately predicts performance based on model size, dataset size, and data composition, leading to reduced computational costs and improved domain adaptation without exhaustive grid-searching.
This review paper from Huawei RAMS Lab, the University of Pisa, and other institutions systematically analyzes the safety challenges of World Models for embodied AI agents in autonomous driving and robotics. It identifies and quantifies recurring safety-critical failures, termed "pathologies," across state-of-the-art models, revealing consistent shortcomings in areas like physical conformity, temporal consistency, and traffic adherence.
Recent advancements in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have focused on integrating multiple modalities, yet their ability to simultaneously process and reason across different inputs remains underexplored. We introduce OmniBench, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate models' ability to recognize, interpret, and reason across visual, acoustic, and textual inputs simultaneously. We define language models capable of such tri-modal processing as omni-language models (OLMs). OmniBench features high-quality human annotations that require integrated understanding across all modalities. Our evaluation reveals that: i) open-source OLMs show significant limitations in instruction-following and reasoning in tri-modal contexts; and ii) most baseline models perform poorly (around 50% accuracy) even with textual alternatives to image/audio inputs. To address these limitations, we develop OmniInstruct, an 96K-sample instruction tuning dataset for training OLMs. We advocate for developing more robust tri-modal integration techniques and training strategies to enhance OLM performance. Codes and data could be found at our repo (this https URL).
MIRA, a medical time series foundation model developed by researchers at Microsoft Research and collaborating universities, is designed to forecast patient health trajectories from real-world data characterized by irregular intervals, heterogeneous sampling rates, and frequent missing values. It achieved state-of-the-art performance on seven unseen benchmarks, reducing RMSE by an average of 8% compared to leading baselines, and demonstrated strong robustness to missing data up to 90%.
Researchers developed Deliberate Practice Policy Optimization (DPPO), a metacognitive training framework that integrates Reinforcement Learning and Supervised Fine-tuning to build embodied intelligence. The resulting Pelican-VL 1.0 model (72B parameters) achieved a 20.3% performance improvement over its base model and outperformed several 200B-level closed-source models on various embodied tasks.
FeynCraft presents an interactive, browser-based game designed for students to learn and practice drawing valid Standard Model Feynman diagrams. The platform integrates real-time rule-based validation and pedagogical visualization overlays, improving comprehension and correct application of particle physics interaction rules.
03 Aug 2025
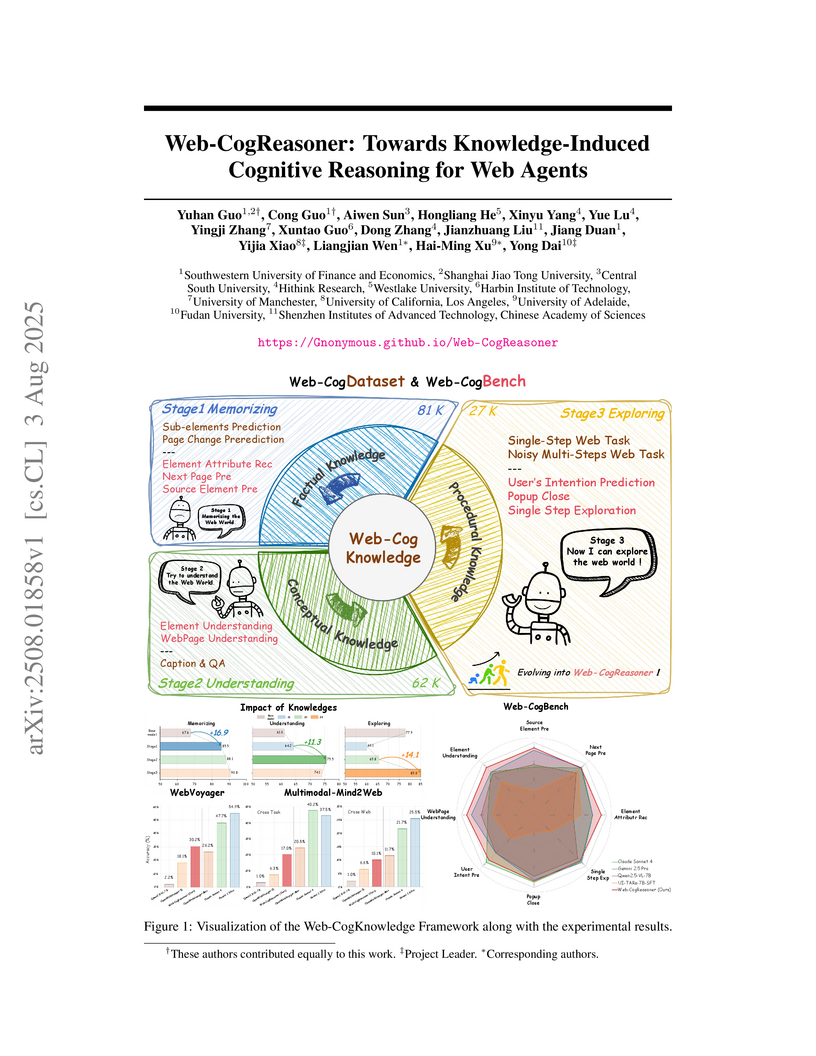
A framework called Web-CogReasoner enables web agents to learn and apply factual, conceptual, and procedural knowledge through a human-inspired curriculum. This structured approach, using the Qwen2.5-VL-7B LMM, leads to an 84.4% accuracy on cognitive reasoning tasks and establishes a new state-of-the-art for open-source agents on the WebVoyager benchmark with a 30.2% success rate.
 University of ManchesterUniversity of Technology NurembergUniversity of SheffieldUniversity of TübingenUniversity of AberdeenUniversity of HamburgUniversity of ManitobaTIB – Leibniz Information Centre for Science and TechnologyIT:U Interdisciplinary Transformation University AustriaAustrian Research Institute for Artificial Intelligence
University of ManchesterUniversity of Technology NurembergUniversity of SheffieldUniversity of TübingenUniversity of AberdeenUniversity of HamburgUniversity of ManitobaTIB – Leibniz Information Centre for Science and TechnologyIT:U Interdisciplinary Transformation University AustriaAustrian Research Institute for Artificial IntelligenceThis survey provides a comprehensive overview of how large multimodal language models are transforming scientific discovery, experimentation, content generation, and evaluation. It maps current advancements, limitations, and ethical considerations across five stages of the research cycle, identifying specific AI applications and their impact on scientific workflows.
Deep neural networks, when trained for next-token prediction, spontaneously learn to represent beliefs over minimal generative models of stochastic processes, including those optimally described by quantum or post-quantum theories. This universal capability, observed across Transformers, LSTMs, GRUs, and RNNs, allows classical networks to achieve memory compression advantages typically associated with non-classical computational systems.
Researchers at the University of Manchester and Technion – Israel Institute of Technology developed "Logit Flow" to analyze information flow in LLMs, revealing a four-stage single-hop reasoning process and identifying conflicting logit interference as a failure point in multi-hop reasoning. Informed by these insights, they propose "Back Attention," a lightweight architectural modification that improved LLM accuracy on various reasoning datasets and enabled smaller models to achieve performance comparable to larger counterparts.
Researchers from the IAA SETI Committee updated the "Declaration of Principles Concerning Activities Following the Detection of Extraterrestrial Intelligence" through a multi-year, interdisciplinary, and consultative process. The revised protocols broaden the scope to all technosignatures, address modern communication challenges, and establish rigorous guidelines for verification, public communication, and international consultation on a potential reply to extraterrestrial intelligence.
19 Feb 2025
FLAG-TRADER introduces a framework integrating Large Language Models with gradient-based Reinforcement Learning for financial trading, where the LLM acts as the policy network. The framework enables small-scale, open-source LLMs to achieve superior performance in single-asset trading tasks compared to larger, proprietary models by effectively leveraging RL-based fine-tuning for sequential decision-making.
Recent studies have explored the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) with Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) for Knowledge Graph Question Answering (KGQA). They typically require rewriting retrieved subgraphs into natural language formats comprehensible to LLMs. However, when tackling complex questions, the knowledge rewritten by existing methods may include irrelevant information, omit crucial details, or fail to align with the question's semantics. To address them, we propose a novel rewriting method CoTKR, Chain-of-Thought Enhanced Knowledge Rewriting, for generating reasoning traces and corresponding knowledge in an interleaved manner, thereby mitigating the limitations of single-step knowledge rewriting. Additionally, to bridge the preference gap between the knowledge rewriter and the question answering (QA) model, we propose a training strategy PAQAF, Preference Alignment from Question Answering Feedback, for leveraging feedback from the QA model to further optimize the knowledge rewriter. We conduct experiments using various LLMs across several KGQA benchmarks. Experimental results demonstrate that, compared with previous knowledge rewriting methods, CoTKR generates the most beneficial knowledge representation for QA models, which significantly improves the performance of LLMs in KGQA.
19 Sep 2025
The design of the humanoid ankle is critical for safe and efficient ground interaction. Key factors such as mechanical compliance and motor mass distribution have driven the adoption of parallel mechanism architectures. However, selecting the optimal configuration depends on both actuator availability and task requirements. We propose a unified methodology for the design and evaluation of parallel ankle mechanisms. A multi-objective optimization synthesizes the mechanism geometry, the resulting solutions are evaluated using a scalar cost function that aggregates key performance metrics for cross-architecture comparison. We focus on two representative architectures: the Spherical-Prismatic-Universal (SPU) and the Revolute-Spherical-Universal (RSU). For both, we resolve the kinematics, and for the RSU, introduce a parameterization that ensures workspace feasibility and accelerates optimization. We validate our approach by redesigning the ankle of an existing humanoid robot. The optimized RSU consistently outperforms both the original serial design and a conventionally engineered RSU, reducing the cost function by up to 41% and 14%, respectively.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.