University of Technology Sydney
This survey systematically reviews Knowledge Distillation (KD) techniques for Large Language Models (LLMs), outlining methods for transferring capabilities from large proprietary models to smaller, more accessible open-source ones. It categorizes KD approaches by algorithms, skill distillation, and verticalization, highlighting the central role of data augmentation and iterative self-improvement for democratizing advanced LLM capabilities.
Researchers from Zhejiang University's CCAI provide a comprehensive survey on world models for autonomous driving, establishing a three-tiered taxonomy to organize architectural innovations, training paradigms, and evaluation metrics. The survey synthesizes advancements in future physical world generation, intelligent agent behavior planning, and the interaction between prediction and planning, while identifying key trends and future research directions.
This paper presents MemVR, a novel decoding paradigm that effectively mitigates hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models by strategically re-injecting visual information into the model's memory space. It improves factual consistency and general capabilities across various benchmarks while incurring minimal computational overhead compared to existing methods.
22 Apr 2025
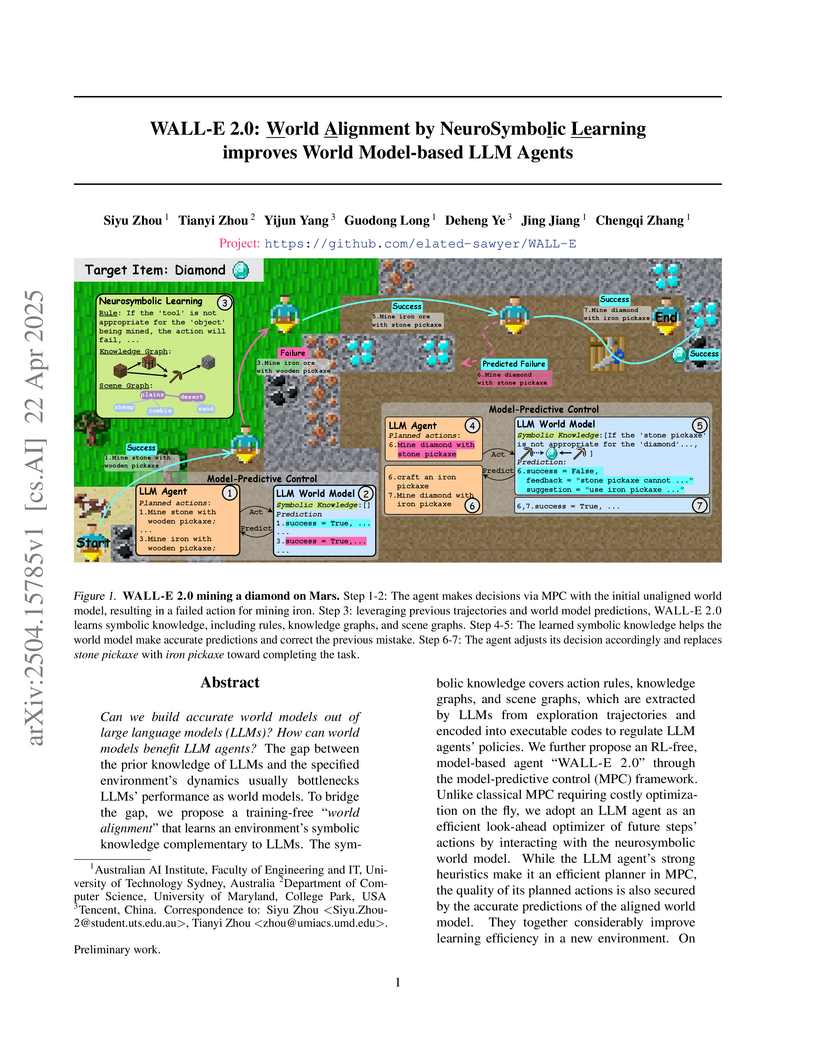
Researchers from Australian AI Institute and collaborating institutions introduce WALL-E 2.0, a neurosymbolic framework that enables LLM agents to build accurate world models through integration of symbolic knowledge (action rules, knowledge graphs, scene graphs), achieving 98% success rate in ALFWorld and outperforming baselines by 16.1-51.6% in Mars environments without requiring model fine-tuning.
26 Sep 2025
A memory management framework for multi-agent systems, SEDM, implements verifiable write admission, self-scheduling, and cross-domain knowledge diffusion to address noise accumulation and uncontrolled memory expansion. It enhances reasoning accuracy on benchmarks like LoCoMo, FEVER, and HotpotQA while reducing token consumption by up to 50% compared to previous memory systems.
 The Chinese University of Hong KongThe University of MelbourneUniversity of Technology SydneyThe University of Sydney
The Chinese University of Hong KongThe University of MelbourneUniversity of Technology SydneyThe University of Sydney Australian National UniversityKing Fahd University of Petroleum and MineralsUniversity of Engineering and TechnologyThe University of Western AustraliaCommonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research OrganisationSDAIA-KFUPM Joint Research Center for Artificial Intelligence
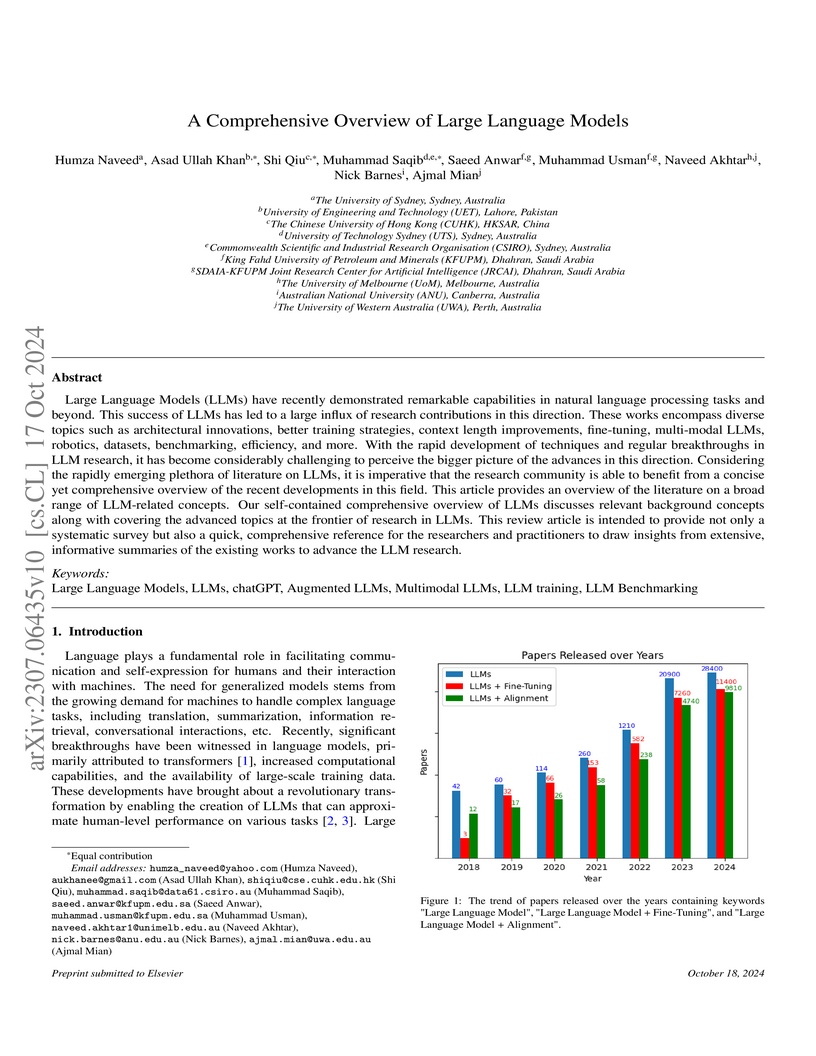
Australian National UniversityKing Fahd University of Petroleum and MineralsUniversity of Engineering and TechnologyThe University of Western AustraliaCommonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research OrganisationSDAIA-KFUPM Joint Research Center for Artificial IntelligenceThis paper synthesizes the extensive and rapidly evolving literature on Large Language Models (LLMs), offering a structured resource on their architectures, training strategies, and applications. It provides a comprehensive overview of existing works, highlighting key design aspects, model capabilities, augmentation strategies, and efficiency techniques, while also discussing challenges and future research directions.
R^2-Gaussian introduces a rectified 3D Gaussian Splatting framework for sparse-view X-ray tomographic reconstruction, correcting a previously unknown integration bias within 3DGS. This method achieves superior reconstruction quality, with up to 0.95 dB PSNR improvement, and significantly faster processing times, converging in approximately 15 minutes.
Object Goal Navigation-requiring an agent to locate a specific object in an unseen environment-remains a core challenge in embodied AI. Although recent progress in Vision-Language Model (VLM)-based agents has demonstrated promising perception and decision-making abilities through prompting, none has yet established a fully modular world model design that reduces risky and costly interactions with the environment by predicting the future state of the world. We introduce WMNav, a novel World Model-based Navigation framework powered by Vision-Language Models (VLMs). It predicts possible outcomes of decisions and builds memories to provide feedback to the policy module. To retain the predicted state of the environment, WMNav proposes the online maintained Curiosity Value Map as part of the world model memory to provide dynamic configuration for navigation policy. By decomposing according to a human-like thinking process, WMNav effectively alleviates the impact of model hallucination by making decisions based on the feedback difference between the world model plan and observation. To further boost efficiency, we implement a two-stage action proposer strategy: broad exploration followed by precise localization. Extensive evaluation on HM3D and MP3D validates WMNav surpasses existing zero-shot benchmarks in both success rate and exploration efficiency (absolute improvement: +3.2% SR and +3.2% SPL on HM3D, +13.5% SR and +1.1% SPL on MP3D). Project page: this https URL.
21 Apr 2010
Research establishes that genuinely entangled qubit states cannot be unique ground states of two-body frustration-free Hamiltonians, indicating such conditions preclude their use as natural, robust resource states for one-way quantum computing. The work also generally demonstrates that any two-body frustration-free Hamiltonian for a qubit system always has a ground state that is a product of single- or two-qubit states.
RICE (Region-based Cluster Discrimination) establishes a framework for learning fine-grained, region-level visual representations, unifying object and OCR understanding from billions of image regions. This approach enhances performance in dense prediction tasks, multimodal large language models, and video object tracking, achieving new benchmarks across various evaluations.
Researchers from the University of Technology Sydney, Monash University, and the University of Illinois at Chicago systematically organize the rapidly expanding field of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), proposing a novel four-category taxonomy. The survey comprehensively reviews diverse GNN models, details theoretical foundations, identifies practical challenges, and compiles extensive resources for the research community.
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing by achieving state-of-the-art performance across various tasks. Recently, their effectiveness as embedding models has gained attention, marking a paradigm shift from traditional encoder-only models like ELMo and BERT to decoder-only, large-scale LLMs such as GPT, LLaMA, and Mistral. This survey provides an in-depth overview of this transition, beginning with foundational techniques before the LLM era, followed by LLM-based embedding models through two main strategies to derive embeddings from LLMs. 1) Direct prompting: We mainly discuss the prompt designs and the underlying rationale for deriving competitive embeddings. 2) Data-centric tuning: We cover extensive aspects that affect tuning an embedding model, including model architecture, training objectives, data constructions, etc. Upon the above, we also cover advanced methods for producing embeddings from longer texts, multilingual, code, cross-modal data, as well as reasoning-aware and other domain-specific scenarios. Furthermore, we discuss factors affecting choices of embedding models, such as performance/efficiency comparisons, dense vs sparse embeddings, pooling strategies, and scaling law. Lastly, the survey highlights the limitations and challenges in adapting LLMs for embeddings, including cross-task embedding quality, trade-offs between efficiency and accuracy, low-resource, long-context, data bias, robustness, etc. This survey serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners by synthesizing current advancements, highlighting key challenges, and offering a comprehensive framework for future work aimed at enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of LLMs as embedding models.
Google DeepMind and University of Technology Sydney researchers establish scaling laws for deepfake detection using ScaleDF, the largest and most diverse dataset to date. The work reveals predictable power-law scaling for data diversity (real domains and deepfake methods), with no saturation, and a double-saturating power-law for training image quantity, providing a framework for data-centric development.
This survey paper presents a three-tier taxonomy for LLM-based recommender systems, categorizing developments from foundational understanding to industrial deployment. It outlines how Large Language Models improve user/item representation and recommendation understanding, details various integration strategies, and addresses the challenges and solutions for deploying these systems in real-world scenarios.
PersonaX is a user modeling framework that efficiently processes long user behavior sequences for recommendation agents by decoupling offline multi-persona generation from online inference. It consistently outperforms baselines, improving recommendation accuracy and reducing online inference latency by up to 95%.
The T2MIR framework, from researchers at Nanjing University and the University of Technology Sydney, enhances in-context reinforcement learning by incorporating Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) to explicitly address the multi-modal nature of RL data and the challenges of diverse task distributions. This approach yields consistent performance improvements and stronger generalization across multiple multi-task environments.
The WALL-E system enables Large Language Models to serve as more reliable world models for agents by learning environment-specific rules through a neurosymbolic approach. This method achieved 69% success in Minecraft TechTree tasks and 95% in ALFWorld while significantly reducing token costs and replanning rounds compared to prior baselines.
FreKoo, a framework from the Australian Artificial Intelligence Institute, addresses temporal domain generalization by decomposing model parameter trajectories into frequency components. It models low-frequency dynamics with a Koopman operator to capture long-term periodicity and regularizes high-frequency components to mitigate local uncertainties, achieving state-of-the-art performance across diverse benchmarks with a 1.7% error rate on a key benchmark, outperforming previous methods like Koodos at 2.1%.
Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN), as a crucial research problem of
Embodied AI, requires an embodied agent to navigate through complex 3D
environments following natural language instructions. Recent research has
highlighted the promising capacity of large language models (LLMs) in VLN by
improving navigational reasoning accuracy and interpretability. However, their
predominant use in an offline manner usually suffers from substantial domain
gap between the VLN task and the LLM training corpus. This paper introduces a
novel strategy called Navigational Chain-of-Thought (NavCoT), where we fulfill
parameter-efficient in-domain training to enable self-guided navigational
decision, leading to a significant mitigation of the domain gap in a
cost-effective manner. Specifically, at each timestep, the LLM is prompted to
forecast the navigational chain-of-thought by: 1) acting as a world model to
imagine the next observation according to the instruction, 2) selecting the
candidate observation that best aligns with the imagination, and 3) determining
the action based on the reasoning from the prior steps. Through constructing
formalized labels for training, the LLM can learn to generate desired and
reasonable chain-of-thought outputs for improving the action decision.
Experimental results across various training settings and popular VLN
benchmarks (e.g., Room-to-Room (R2R), Room-across-Room (RxR), Room-for-Room
(R4R)) show the significant superiority of NavCoT over the direct action
prediction variants. Through simple parameter-efficient finetuning, our NavCoT
outperforms a recent GPT4-based approach with ~7% relative improvement on the
R2R dataset. We believe that NavCoT will help unlock more task-adaptive and
scalable LLM-based embodied agents, which are helpful for developing real-world
robotics applications. Code is available at
this https URL
StructGS: Adaptive Spherical Harmonics and Rendering Enhancements for Superior 3D Gaussian Splatting
StructGS: Adaptive Spherical Harmonics and Rendering Enhancements for Superior 3D Gaussian Splatting
Recent advancements in 3D reconstruction coupled with neural rendering
techniques have greatly improved the creation of photo-realistic 3D scenes,
influencing both academic research and industry applications. The technique of
3D Gaussian Splatting and its variants incorporate the strengths of both
primitive-based and volumetric representations, achieving superior rendering
quality. While 3D Geometric Scattering (3DGS) and its variants have advanced
the field of 3D representation, they fall short in capturing the stochastic
properties of non-local structural information during the training process.
Additionally, the initialisation of spherical functions in 3DGS-based methods
often fails to engage higher-order terms in early training rounds, leading to
unnecessary computational overhead as training progresses. Furthermore, current
3DGS-based approaches require training on higher resolution images to render
higher resolution outputs, significantly increasing memory demands and
prolonging training durations. We introduce StructGS, a framework that enhances
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) for improved novel-view synthesis in 3D
reconstruction. StructGS innovatively incorporates a patch-based SSIM loss,
dynamic spherical harmonics initialisation and a Multi-scale Residual Network
(MSRN) to address the above-mentioned limitations, respectively. Our framework
significantly reduces computational redundancy, enhances detail capture and
supports high-resolution rendering from low-resolution inputs. Experimentally,
StructGS demonstrates superior performance over state-of-the-art (SOTA) models,
achieving higher quality and more detailed renderings with fewer artifacts.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.