Zhongguancun Academy
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Beihang University
Beihang University The Hong Kong Polytechnic UniversityBeijing Academy of Artificial IntelligenceZhongguancun AcademyLuxiTechKey Laboratory of Brain Cognition and Brain-inspired Intelligence TechnologyBeijing Key Laboratory of Brain-Inspired General Intelligence Large ModelMetaX Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd.
The Hong Kong Polytechnic UniversityBeijing Academy of Artificial IntelligenceZhongguancun AcademyLuxiTechKey Laboratory of Brain Cognition and Brain-inspired Intelligence TechnologyBeijing Key Laboratory of Brain-Inspired General Intelligence Large ModelMetaX Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd.Mainstream Transformer-based large language models face major efficiency bottlenecks: training computation scales quadratically with sequence length, and inference memory grows linearly, limiting long-context processing. Building large models on non-NVIDIA platforms also poses challenges for stable and efficient training. To address this, we introduce SpikingBrain, a family of brain-inspired models designed for efficient long-context training and inference. SpikingBrain leverages the MetaX GPU cluster and focuses on three aspects: (1) Model Architecture: linear and hybrid-linear attention architectures with adaptive spiking neurons; (2) Algorithmic Optimizations: an efficient, conversion-based training pipeline and a dedicated spike coding framework; (3) System Engineering: customized training frameworks, operator libraries, and parallelism strategies tailored to MetaX hardware.
Using these techniques, we develop two models: SpikingBrain-7B, a linear LLM, and SpikingBrain-76B, a hybrid-linear MoE LLM. These models demonstrate the feasibility of large-scale LLM development on non-NVIDIA platforms, and training remains stable for weeks on hundreds of MetaX GPUs with Model FLOPs Utilization at expected levels. SpikingBrain achieves performance comparable to open-source Transformer baselines while using only about 150B tokens for continual pre-training. Our models also significantly improve long-context efficiency and deliver inference with (partially) constant memory and event-driven spiking behavior. For example, SpikingBrain-7B attains over 100x speedup in Time to First Token for 4M-token sequences. Furthermore, the proposed spiking scheme achieves 69.15 percent sparsity, enabling low-power operation. Overall, this work demonstrates the potential of brain-inspired mechanisms to drive the next generation of efficient and scalable large model design.
08 Oct 2025
RLinf-VLA presents a unified and efficient framework for training Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models with reinforcement learning (RL), achieving up to 2.27x speedup and establishing new performance benchmarks, including a 98.11% success rate on LIBERO-130 and improved real-world zero-shot generalization over supervised methods.
19 Sep 2025
RLinf introduces a high-performance system for large-scale reinforcement learning, employing a Macro-to-Micro Flow Transformation (M2Flow) paradigm to dynamically optimize execution. The system achieves 1.10x to 1.58x speedup over existing RLHF systems and up to 2.13x speedup in embodied RL training, leading to state-of-the-art model quality in reasoning and embodied tasks.
21 Nov 2025
The OmniScientist framework integrates AI agents within a simulated human scientific ecosystem by encoding collaborative and infrastructural norms, allowing AI to participate as "genuine scientists." The approach achieved superior literature review, a dramatic reduction in solution error for experiment automation, and enhanced human-AI collaboration in complex problem-solving.
MM-UPT establishes an Unsupervised Post-Training (UPT) paradigm for multi-modal large language models, allowing them to continually refine reasoning capabilities without relying on human-annotated data. The framework employs an online reinforcement learning approach with a majority-voting self-reward mechanism and enables the models to generate their own synthetic training data, leading to enhanced performance across diverse multi-modal benchmarks.
DEFACTO presents a counterfactual reasoning framework that enables multimodal language models to achieve state-of-the-art performance across diverse visual question answering benchmarks by enforcing evidence-grounded and faithful reasoning. The approach trains models to identify question-relevant visual evidence and abstain when that evidence is absent, leading to improved accuracy and robustness.
This study reveals a "no free lunch" principle for Reinforcement Learning from Internal Feedback (RLIF) in LLM reasoning, showing it initially benefits base models by reducing underconfidence but degrades performance with prolonged training by inducing overconfidence. RLIF effectively improves instruction following in models with high initial policy entropy but offers little benefit and can be detrimental to already instruction-tuned models.
26 Oct 2025
Training expressive flow-based policies with off-policy reinforcement learning is notoriously unstable due to gradient pathologies in the multi-step action sampling process. We trace this instability to a fundamental connection: the flow rollout is algebraically equivalent to a residual recurrent computation, making it susceptible to the same vanishing and exploding gradients as RNNs. To address this, we reparameterize the velocity network using principles from modern sequential models, introducing two stable architectures: Flow-G, which incorporates a gated velocity, and Flow-T, which utilizes a decoded velocity. We then develop a practical SAC-based algorithm, enabled by a noise-augmented rollout, that facilitates direct end-to-end training of these policies. Our approach supports both from-scratch and offline-to-online learning and achieves state-of-the-art performance on continuous control and robotic manipulation benchmarks, eliminating the need for common workarounds like policy distillation or surrogate objectives.
Ultra-high-resolution (UHR) remote sensing (RS) imagery offers valuable data for Earth observation but pose challenges for existing multimodal foundation models due to two key bottlenecks: (1) limited availability of UHR training data, and (2) token explosion caused by the large image size. To address data scarcity, we introduce SuperRS-VQA (avg. 8,376×8,376) and HighRS-VQA (avg. 2,000×1,912), the highest-resolution vision-language datasets in RS to date, covering 22 real-world dialogue tasks. To mitigate token explosion, our pilot studies reveal significant redundancy in RS images: crucial information is concentrated in a small subset of object-centric tokens, while pruning background tokens (e.g., ocean or forest) can even improve performance. Motivated by these findings, we propose two strategies: Background Token Pruning and Anchored Token Selection, to reduce the memory footprint while preserving key this http URL these techniques, we introduce GeoLLaVA-8K, the first RS-focused multimodal large language model capable of handling inputs up to 8K×8K resolution, built on the LLaVA framework. Trained on SuperRS-VQA and HighRS-VQA, GeoLLaVA-8K sets a new state-of-the-art on the XLRS-Bench.
11 Jun 2025
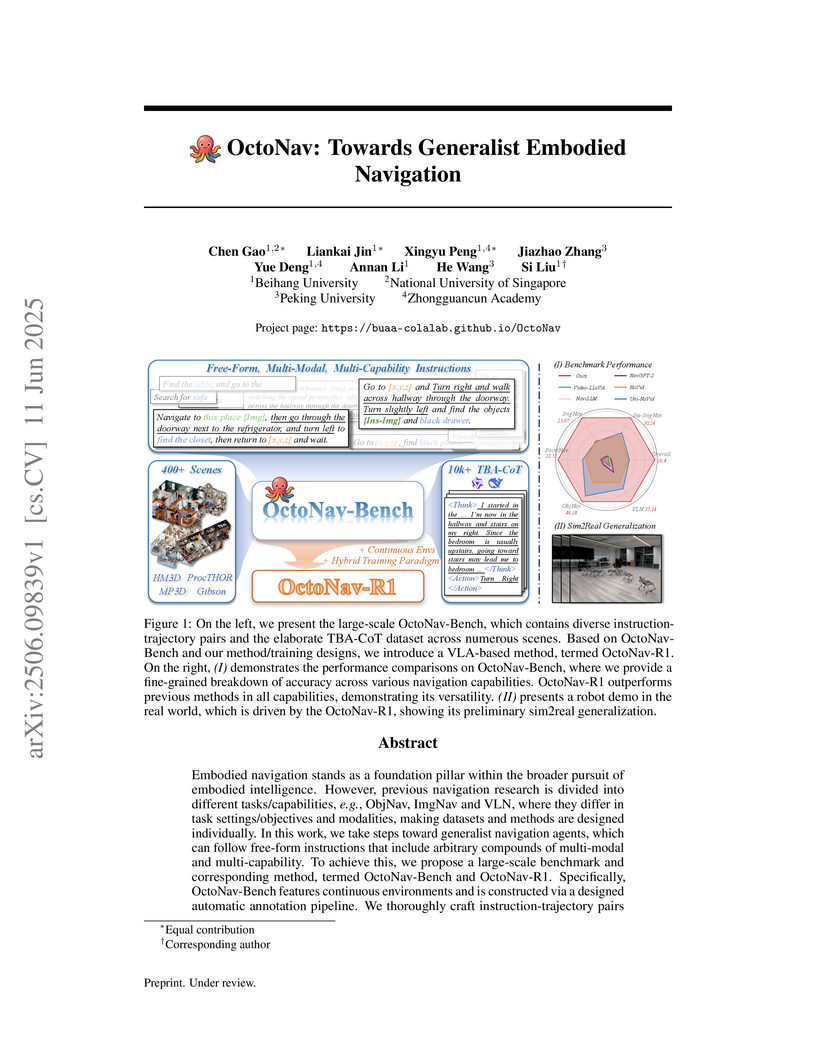
"OctoNav" presents a unified benchmark and a "Think-Before-Action" (TBA) Vision-Language Agent (VLA) for generalist embodied navigation, enabling agents to interpret and execute free-form, multi-modal instructions. The OctoNav-R1 model achieves an overall Success Rate (SR) of 19.40% on the new OctoNav-Bench, more than double the prior best baseline, and demonstrates preliminary sim2real transfer on a physical robot.
Researchers from multiple Chinese institutions introduce XLRS-Bench, a benchmark dataset of 1,400 ultra-high-resolution (8,500x8,500 pixel) remote sensing images with expert annotations across 16 perception and reasoning tasks, revealing significant limitations in current multimodal language models' ability to process large-scale satellite imagery.
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is essential for enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs), yet the widely adopted Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) suffers from entropy collapse, causing exploration to vanish and policies to converge prematurely. As a result, RL is widely believed to be incapable of expanding the reasoning frontier of LLMs. Existing entropy-regularized methods introduce an inevitable trade-off between reward and entropy, leading to exploration accompanied by non-negligible optimization bias. In this work, we prove that temperature-guided REINFORCE can modulate policy entropy, and propose Arbitrary Entropy Policy Optimization (AEPO), which reformulates entropy regularization as a policy-gradient optimization problem. Rather than manipulating entropy directly, AEPO implicitly regulates it by applying a REINFORCE regularization term on temperature-adjusted samples, ensuring that entropy is controlled but never dominates optimization, thereby enabling arbitrary and principled entropy regulation. Experiments show that AEPO outperforms RL baselines on both pass@1 and pass@k, and even surpasses the base model on pass@1024. By modulating entropy precisely, AEPO achieves more effective optimization dynamics and provides direct empirical evidence that entropy, exploration, and performance are intrinsically linked.
Researchers enhanced the spatial perception and reasoning capabilities of vision-language models by fine-tuning them on Euclidean geometry problems. This approach, leveraging the newly created Euclid30K dataset, consistently improved zero-shot performance across diverse spatial reasoning benchmarks, outperforming prior specialized methods.
Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive chain-of-thought reasoning capabilities, with reinforcement learning (RL) playing a crucial role in this progress. While "aha moment" patterns--where models exhibit self-correction through reflection--are often attributed to emergent properties from RL, we first demonstrate that these patterns exist in multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) prior to RL training but may not necessarily correlate with improved reasoning performance. Building on these insights, we present a comprehensive study on enhancing multimodal reasoning through a two-stage approach: (1) supervised fine-tuning (SFT) as a cold start with structured chain-of-thought reasoning patterns, followed by (2) reinforcement learning via GRPO to further refine these capabilities. Our extensive experiments show that this combined approach consistently outperforms both SFT-only and RL-only methods across challenging multimodal reasoning benchmarks. The resulting models achieve state-of-the-art performance among open-source MLLMs at both 3B and 7B scales, with our 7B model showing substantial improvements over base models (e.g., 66.3 %→73.4 % on MathVista, 62.9 %→70.4 % on We-Math) and our 3B model achieving performance competitive with several 7B models. Overall, this work provides practical guidance for building advanced multimodal reasoning models. Our code is available at this https URL.
Researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology, East China Normal University, and Zhongguancun Academy & Institute of Artificial Intelligence introduce Long-Short Chain-of-Thought Mixture Supervised Fine-Tuning (LS-Mixture SFT), a method that enables non-reasoning LLMs to perform efficient reasoning by learning from both detailed and concise reasoning paths. The approach reduces inference response length by an average of 47.61% and training data length by 41.33% while improving reasoning accuracy by an average of 2.3% across challenging benchmarks like MATH500, AIME24, and GPQA.
PoliCon introduces a benchmark to assess large language models' capabilities in facilitating and achieving political consensus under diverse real-world objectives. Experiments revealed that while models like Gemini-2.5-Flash perform well on straightforward consensus tasks, all tested LLMs struggle with complex goals such as Rawlsianism and exhibit inherent partisan biases, highlighting limitations in sophisticated coalition-building.
TrajSelector, developed by a collaboration including Harbin Institute of Technology and Zhongguancun Academy, introduces a method for efficient Best-of-N selection in LLM reasoning by utilizing the sampler LLM's latent representations with a 0.6B-parameter verifier and a data-driven training approach, improving mathematical reasoning accuracy by an average of 4.61% over majority voting baselines.
07 Jun 2025
Light Society presents a framework for modeling human-like societies with over one billion LLM-powered agents, achieving unprecedented scale in social simulations while maintaining high behavioral fidelity. The framework leverages a modular design and a multi-tiered optimization pipeline to overcome computational barriers, demonstrating its capabilities in simulating trust games and opinion propagation among diverse agent populations.
MIHBench: Benchmarking and Mitigating Multi-Image Hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models
MIHBench: Benchmarking and Mitigating Multi-Image Hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models
Introduces MIHBench, the first benchmark for systematically evaluating object-related hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) across multiple images, and proposes Dynamic Attention Balancing (DAB), a training-free mitigation mechanism. The research reveals that hallucinations increase with more input images and that DAB consistently improves MLLM performance on multi-image tasks.
Accurately grounding regions of interest (ROIs) is critical for diagnosis and treatment planning in medical imaging. While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) combine visual perception with natural language, current medical-grounding pipelines still rely on supervised fine-tuning with explicit spatial hints, making them ill-equipped to handle the implicit queries common in clinical practice. This work makes three core contributions. We first define Unified Medical Reasoning Grounding (UMRG), a novel vision-language task that demands clinical reasoning and pixel-level grounding. Second, we release U-MRG-14K, a dataset of 14K samples featuring pixel-level masks alongside implicit clinical queries and reasoning traces, spanning 10 modalities, 15 super-categories, and 108 specific categories. Finally, we introduce MedReasoner, a modular framework that distinctly separates reasoning from segmentation: an MLLM reasoner is optimized with reinforcement learning, while a frozen segmentation expert converts spatial prompts into masks, with alignment achieved through format and accuracy rewards. MedReasoner achieves state-of-the-art performance on U-MRG-14K and demonstrates strong generalization to unseen clinical queries, underscoring the significant promise of reinforcement learning for interpretable medical grounding.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.