Large Language Models (LLMs) have made remarkable progress in mathematical reasoning, but still continue to struggle with high-precision tasks like numerical computation and formal symbolic manipulation. Integrating external tools has emerged as a promising approach to bridge this gap. Despite recent advances, existing methods struggle with three key challenges: constructing tool-integrated reasoning data, performing fine-grained optimization, and enhancing inference. To overcome these limitations, we propose THOR (Tool-Integrated Hierarchical Optimization via RL). First, we introduce TIRGen, a multi-agent actor-critic-based pipeline for constructing high-quality datasets of tool-integrated reasoning paths, aligning with the policy and generalizing well across diverse models. Second, to perform fine-grained hierarchical optimization, we introduce an RL strategy that jointly optimizes for both episode-level problem solving and step-level code generation. This is motivated by our key insight that the success of an intermediate tool call is a strong predictor of the final answer's correctness. Finally, THOR incorporates a self-correction mechanism that leverages immediate tool feedback to dynamically revise erroneous reasoning paths during inference. Our approach demonstrates strong generalization across diverse models, performing effectively in both reasoning and non-reasoning models. It further achieves state-of-the-art performance for models of a similar scale on multiple mathematical benchmarks, while also delivering consistent improvements on code benchmarks. Our code will be publicly available at this https URL.
DocR1 introduces an MLLM and an Evidence Page-Guided GRPO (EviGRPO) framework that extends document understanding capabilities from single to multi-page contexts. It achieves an average score of 59.36 on multi-page datasets, representing an absolute improvement of 6.93 points over the baseline, and maintains strong performance on single-page tasks using a 7B parameter model.
This research introduces Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with a novel off-the-shelf ASR-derived composite reward to fine-tune large language model (LLM)-based Text-to-Speech (TTS) models. The approach enhances speech intelligibility and naturalness, achieving consistent improvements in character/word error rates and Mean Opinion Scores across multiple languages and diverse LLM-TTS architectures.
Researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology and iFLYTEK Research developed and open-sourced a suite of pre-trained language models for Chinese, introducing MacBERT which addresses the pre-training/fine-tuning discrepancy by using 'MLM as correction' with similar word replacements. MacBERT demonstrated state-of-the-art performance across ten Chinese NLP tasks, notably achieving an F1 score of 60% on CMRC 2018.
Scientific question answering (SQA) is an important task aimed at answering questions based on papers. However, current SQA datasets have limited reasoning types and neglect the relevance between tables and text, creating a significant gap with real scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose a QA benchmark for scientific tables and text with diverse reasoning types (SciTaT). To cover more reasoning types, we summarize various reasoning types from real-world questions. To involve both tables and text, we require the questions to incorporate tables and text as much as possible. Based on SciTaT, we propose a strong baseline (CaR), which combines various reasoning methods to address different reasoning types and process tables and text at the same time. CaR brings average improvements of 12.9% over other baselines on SciTaT, validating its effectiveness. Error analysis reveals the challenges of SciTaT, such as complex numerical calculations and domain knowledge.
Time series forecasting plays a vital role in supporting decision-making across a wide range of critical applications, including energy, healthcare, and finance. Despite recent advances, forecasting accuracy remains limited due to the challenge of integrating historical numerical sequences with contextual features, which often comprise unstructured textual data. To address this challenge, we propose TokenCast, an LLM-driven framework that leverages language-based symbolic representations as a unified intermediary for context-aware time series forecasting. Specifically, TokenCast employs a discrete tokenizer to transform continuous numerical sequences into temporal tokens, enabling structural alignment with language-based inputs. To bridge the semantic gap between modalities, both temporal and contextual tokens are embedded into a shared representation space via a pre-trained large language model (LLM), further optimized with autoregressive generative objectives. Building upon this unified semantic space, the aligned LLM is subsequently fine-tuned in a supervised manner to predict future temporal tokens, which are then decoded back into the original numerical space. Extensive experiments on diverse real-world datasets enriched with contextual features demonstrate the effectiveness and generalizability of TokenCast.
Researchers from Wuhan University, The University of Sydney, iFlytek, and Nanyang Technological University introduce MTP, a multi-task pretraining paradigm that enhances remote sensing foundation models by simultaneously learning from semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, and rotated object detection. MTP consistently improves performance across 14 diverse remote sensing datasets and four downstream tasks, demonstrating particular efficacy in low-data finetuning scenarios.
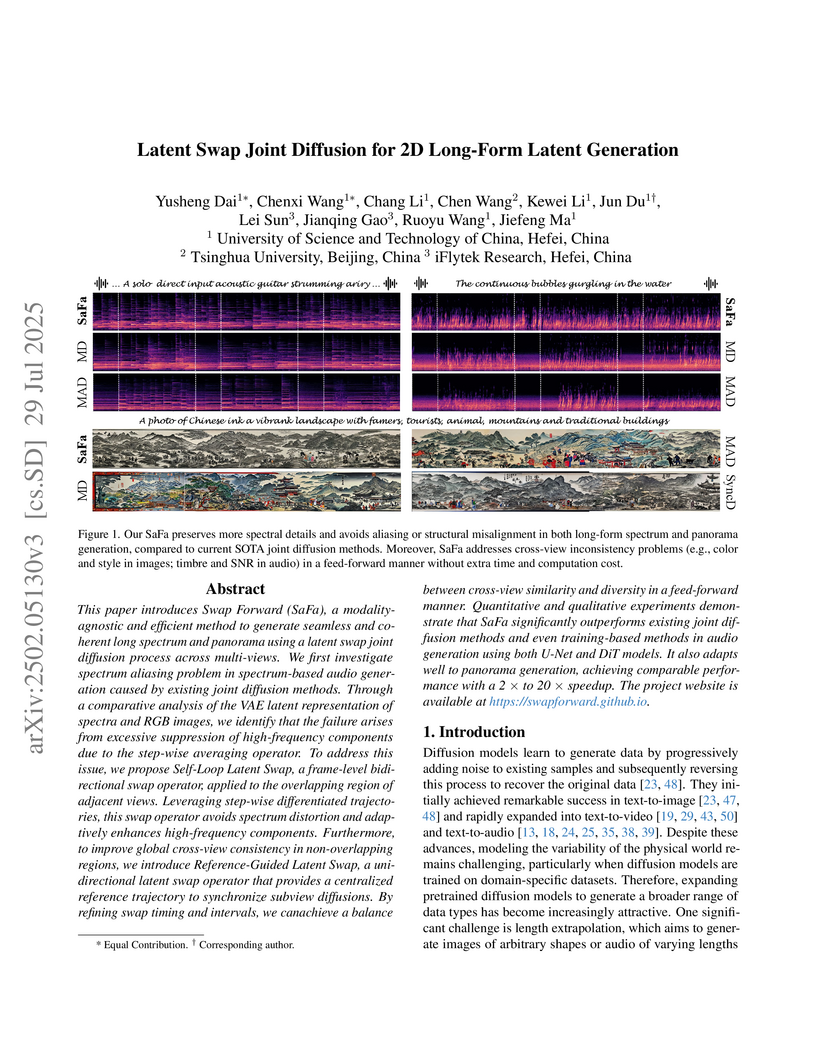
Latent Swap Joint Diffusion (SaFa) is an efficient, training-free method that enables pre-trained diffusion models to generate coherent long-form 2D latent content, like audio spectrograms and image panoramas. The method achieves a 2x to 20x speedup over existing approaches while producing outputs with superior quality and cross-view consistency, notably resolving spectrum aliasing in audio generation.
This work introduces MacBERT, a new Chinese pre-trained language model that refines the masked language modeling task by replacing masked tokens with similar words. The model achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple Chinese Natural Language Processing benchmarks, including a 60.2% F1-score on the CMRC 2018 challenging set.
Automatically generating high-quality mathematical problems that align with
educational objectives is a crucial task in NLP-based educational technology.
Traditional generation methods focus primarily on textual quality, but they
often overlook educational objectives. Moreover, these methods address only
single-dimensional, simple question generation, failing to meet complex,
multifaceted educational requirements. To address these challenges, we
constructed and annotated EduMath, a dataset of 16k mathematical questions with
multi-dimensional educational objectives. Based on this dataset, we developed
EQGEVAL, which incorporates three evaluation dimensions and is designed to
assess the ability of models to generate educational questions. Drawing
inspiration from teachers' problem design processes, we propose the Educational
Question Planning with self-Reflection (EQPR) method for educational
mathematical question generation, following a "plan-evaluate-optimize"
approach. Specifically, by combining planning algorithm based on Monte Carlo
Tree Search with the generative capabilities of Large Language Models, we
continuously optimize questions through iterative feedback. This
self-optimization mechanism ensures that the generated questions both fit the
educational context and strategically achieve specific basic educational
objectives. Through extensive experiments based on EQGEVAL, we have
demonstrated that EQPR achieves significant improvements in generating
questions that meet multi-dimensional educational objectives.
15 Apr 2025
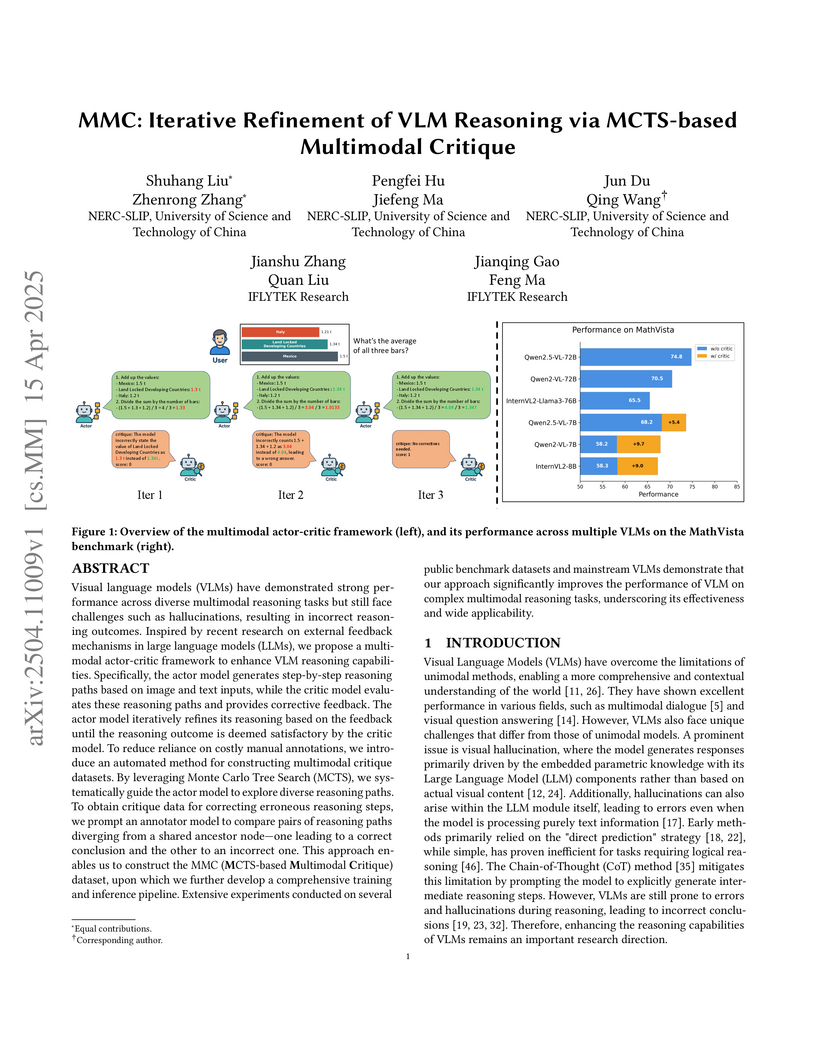
MMC (Multimodal Critique) introduces an iterative actor-critic framework that enhances Visual Language Model (VLM) reasoning by automatically generating step-level critiques using an MCTS-based approach, leading to consistent performance improvements of up to 15.9% on complex multimodal reasoning benchmarks. This method constructs a high-quality critique dataset by identifying deviations between correct and incorrect reasoning paths.
Research is a fundamental process driving the advancement of human civilization, yet it demands substantial time and effort from researchers. In recent years, the rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies has inspired researchers to explore how AI can accelerate and enhance research. To monitor relevant advancements, this paper presents a systematic review of the progress in this domain. Specifically, we organize the relevant studies into three main categories: hypothesis formulation, hypothesis validation, and manuscript publication. Hypothesis formulation involves knowledge synthesis and hypothesis generation. Hypothesis validation includes the verification of scientific claims, theorem proving, and experiment validation. Manuscript publication encompasses manuscript writing and the peer review process. Furthermore, we identify and discuss the current challenges faced in these areas, as well as potential future directions for research. Finally, we also offer a comprehensive overview of existing benchmarks and tools across various domains that support the integration of AI into the research process. We hope this paper serves as an introduction for beginners and fosters future research. Resources have been made publicly available at this https URL.
JiuZhang3.0 introduces an efficient data synthesis approach for improving large language models' mathematical reasoning by training a small 7B parameter model to generate high-quality math problems and solutions. This method drastically reduces the development cost to approximately $8,480, achieving state-of-the-art performance among open-source models on various mathematical reasoning and tool manipulation tasks.
 CNRSAcademia Sinica
CNRSAcademia Sinica University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Nagoya UniversityUniversity of Edinburgh
Nagoya UniversityUniversity of Edinburgh Aalto University
Aalto University InriaTrinity College DublinNational Institute of InformaticsGoogle Inc.University of Eastern FinlandiFlytek ResearchADAPT CentreNTT Communication Science LaboratoriesAvignon universityaudEERING GmbHNEC CorpEurécomUniversit
e de LorraineHOYA
InriaTrinity College DublinNational Institute of InformaticsGoogle Inc.University of Eastern FinlandiFlytek ResearchADAPT CentreNTT Communication Science LaboratoriesAvignon universityaudEERING GmbHNEC CorpEurécomUniversit
e de LorraineHOYAAutomatic speaker verification (ASV) is one of the most natural and convenient means of biometric person recognition. Unfortunately, just like all other biometric systems, ASV is vulnerable to spoofing, also referred to as "presentation attacks." These vulnerabilities are generally unacceptable and call for spoofing countermeasures or "presentation attack detection" systems. In addition to impersonation, ASV systems are vulnerable to replay, speech synthesis, and voice conversion attacks. The ASVspoof 2019 edition is the first to consider all three spoofing attack types within a single challenge. While they originate from the same source database and same underlying protocol, they are explored in two specific use case scenarios. Spoofing attacks within a logical access (LA) scenario are generated with the latest speech synthesis and voice conversion technologies, including state-of-the-art neural acoustic and waveform model techniques. Replay spoofing attacks within a physical access (PA) scenario are generated through carefully controlled simulations that support much more revealing analysis than possible previously. Also new to the 2019 edition is the use of the tandem detection cost function metric, which reflects the impact of spoofing and countermeasures on the reliability of a fixed ASV system. This paper describes the database design, protocol, spoofing attack implementations, and baseline ASV and countermeasure results. It also describes a human assessment on spoofed data in logical access. It was demonstrated that the spoofing data in the ASVspoof 2019 database have varied degrees of perceived quality and similarity to the target speakers, including spoofed data that cannot be differentiated from bona-fide utterances even by human subjects.
A framework for Large Language Models, Retrieval Heads-Induced Optimization (RHIO), enhances contextual faithfulness in Long-Form Question Answering by training models to explicitly differentiate faithful from unfaithful generations through retrieval heads-induced data augmentation. RHIO enables a Llama-2-13B model to reach an average faithfulness of 83.77% on the GroundBench benchmark, outperforming GPT-4o's 82.33%.
Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China and iFLYTEK Research enhanced Multimodal Large Language Models' (MLLMs) ability to solve geometry problems by integrating neural networks with symbolic reasoning systems. Their GeoGen pipeline generates high-quality, step-by-step solution data, and GeoLogic translates MLLM outputs into formal logic for symbolic verification, leading to consistent performance improvements and reduced hallucinations in geometric reasoning.
Talking head generation intends to produce vivid and realistic talking head
videos from a single portrait and speech audio clip. Although significant
progress has been made in diffusion-based talking head generation, almost all
methods rely on autoregressive strategies, which suffer from limited context
utilization beyond the current generation step, error accumulation, and slower
generation speed. To address these challenges, we present DAWN (Dynamic frame
Avatar With Non-autoregressive diffusion), a framework that enables all-at-once
generation of dynamic-length video sequences. Specifically, it consists of two
main components: (1) audio-driven holistic facial dynamics generation in the
latent motion space, and (2) audio-driven head pose and blink generation.
Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method generates authentic and vivid
videos with precise lip motions, and natural pose/blink movements.
Additionally, with a high generation speed, DAWN possesses strong extrapolation
capabilities, ensuring the stable production of high-quality long videos. These
results highlight the considerable promise and potential impact of DAWN in the
field of talking head video generation. Furthermore, we hope that DAWN sparks
further exploration of non-autoregressive approaches in diffusion models. Our
code will be publicly available at this https URL
PaMMA-Net, a data-driven deep learning framework, predicts the multi-horizon evolution of tokamak magnetic measurements. This approach achieved an MAE of 2.661 × 10⁻³ and a similarity of 95.86% on EAST tokamak data, demonstrating superior accuracy, strong generalization, and effective integration with equilibrium reconstruction.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown significant promise in automated theorem proving, yet progress is often constrained by the scarcity of diverse and high-quality formal language data. To address this issue, we introduce Spark-Prover-X1, a 7B parameter model trained via an three-stage framework designed to unlock the reasoning potential of more accessible and moderately-sized LLMs. The first stage infuses deep knowledge through continuous pre-training on a broad mathematical corpus, enhanced by a suite of novel data tasks. Key innovation is a "CoT-augmented state prediction" task to achieve fine-grained reasoning. The second stage employs Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT) within an expert iteration loop to specialize both the Spark-Prover-X1-7B and Spark-Formalizer-X1-7B models. Finally, a targeted round of Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) is applied to sharpen the prover's capabilities on the most challenging problems. To facilitate robust evaluation, particularly on problems from real-world examinations, we also introduce ExamFormal-Bench, a new benchmark dataset of 402 formal problems. Experimental results demonstrate that Spark-Prover achieves state-of-the-art performance among similarly-sized open-source models within the "Whole-Proof Generation" paradigm. It shows exceptional performance on difficult competition benchmarks, notably solving 27 problems on PutnamBench (pass@32) and achieving 24.0\% on CombiBench (pass@32). Our work validates that this diverse training data and progressively refined training pipeline provides an effective path for enhancing the formal reasoning capabilities of lightweight LLMs. We will release both Spark-Prover-X1-7B and Spark-Formalizer-X1-7B, along with the ExamFormal-Bench dataset, in the near future.
Recently, research on open domain dialogue systems have attracted extensive interests of academic and industrial researchers. The goal of an open domain dialogue system is to imitate humans in conversations. Previous works on single turn conversation generation have greatly promoted the research of open domain dialogue systems. However, understanding multiple single turn conversations is not equal to the understanding of multi turn dialogue due to the coherent and context dependent properties of human dialogue. Therefore, in open domain multi turn dialogue generation, it is essential to modeling the contextual semantics of the dialogue history, rather than only according to the last utterance. Previous research had verified the effectiveness of the hierarchical recurrent encoder-decoder framework on open domain multi turn dialogue generation. However, using RNN-based model to hierarchically encoding the utterances to obtain the representation of dialogue history still face the problem of a vanishing gradient. To address this issue, in this paper, we proposed a static and dynamic attention-based approach to model the dialogue history and then generate open domain multi turn dialogue responses. Experimental results on Ubuntu and Opensubtitles datasets verify the effectiveness of the proposed static and dynamic attention-based approach on automatic and human evaluation metrics in various experimental settings. Meanwhile, we also empirically verify the performance of combining the static and dynamic attentions on open domain multi turn dialogue generation.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.