École Polytechnique de Montréal
This paper presents FitNets, a method for training deep and thin neural networks by transferring intermediate representations from larger, shallower teacher networks. The approach enables smaller, more efficient student models to outperform their teachers, achieving better accuracy and significantly reduced parameter counts and inference times on datasets like CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100.
09 Feb 2024
Researchers developed a reinforcement learning approach that enables diverse robot platforms, including quadrupeds, bipeds, and wheeled-legged systems, to climb stairs using only proprioceptive feedback and a terrain mode signal. This method demonstrates successful sim-to-real transfer, allowing robots like the Ascento to climb 15cm steps without external perception.
The FIGR framework integrates Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) with the Reptile meta-learning algorithm, enabling the generation of new images from only a few examples for a given class. The approach is evaluated on MNIST and Omniglot datasets, and a newly introduced FIGR-8 dataset comprising over 1.5 million pictograms across 18,409 classes, showing the ability to generate conceptually coherent images from limited data.
01 Oct 2025
Classical and multiscale non-equilibrium thermodynamics have different histories and different objectives. In this Note we explain the differences and review some topics in which the multiscale viewpoint of mesoscopic time evolution of macroscopic systems helped to advance the classical non-equilibrium thermodynamics. Eventually, we illustrate the Braun-Le Chatelier principle in dissipative thermodynamics.
23 Dec 2024
We present design principles for ultrashort-pulse, type-0 phase-matched
optical parametric amplifiers to generate and measure spectrally pure
degenerate squeezed light. We achieve a Schmidt number of K≈1.02 with
squeezing levels greater than 15 dB spanning over >5 THz bandwidth with
cm-scale devices on thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) on insulator platform. Our
work opens up promising avenues for large-scale circuits for ultrafast quantum
information processing and quantum sensing applications on rapidly advancing
TFLN platform with already demonstrated linear components and photodetection
capabilities.
Hybrid beamforming is a promising technique to reduce the complexity and cost of massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems while providing high data rate. However, the hybrid precoder design is a challenging task requiring channel state information (CSI) feedback and solving a complex optimization problem. This paper proposes a novel RSSI-based unsupervised deep learning method to design the hybrid beamforming in massive MIMO systems. Furthermore, we propose i) a method to design the synchronization signal (SS) in initial access (IA); and ii) a method to design the codebook for the analog precoder. We also evaluate the system performance through a realistic channel model in various scenarios. We show that the proposed method not only greatly increases the spectral efficiency especially in frequency-division duplex (FDD) communication by using partial CSI feedback, but also has near-optimal sum-rate and outperforms other state-of-the-art full-CSI solutions.
Understanding the mechanisms behind decisions taken by large foundation models in sequential decision making tasks is critical to ensuring that such systems operate transparently and safely. In this work, we perform exploratory analysis on the Video PreTraining (VPT) Minecraft playing agent, one of the largest open-source vision-based agents. We aim to illuminate its reasoning mechanisms by applying various interpretability techniques. First, we analyze the attention mechanism while the agent solves its training task - crafting a diamond pickaxe. The agent pays attention to the last four frames and several key-frames further back in its six-second memory. This is a possible mechanism for maintaining coherence in a task that takes 3-10 minutes, despite the short memory span. Secondly, we perform various interventions, which help us uncover a worrying case of goal misgeneralization: VPT mistakenly identifies a villager wearing brown clothes as a tree trunk when the villager is positioned stationary under green tree leaves, and punches it to death.
Neural networks for NLP are becoming increasingly complex and widespread, and there is a growing concern if these models are responsible to use. Explaining models helps to address the safety and ethical concerns and is essential for accountability. Interpretability serves to provide these explanations in terms that are understandable to humans. Additionally, post-hoc methods provide explanations after a model is learned and are generally model-agnostic. This survey provides a categorization of how recent post-hoc interpretability methods communicate explanations to humans, it discusses each method in-depth, and how they are validated, as the latter is often a common concern.
13 Mar 2024
In this note we summarize four important matrix decompositions commonly used in quantum optics, namely the Takagi/Autonne, Bloch-Messiah/Euler, Iwasawa, and Williamson decompositions. The first two of these decompositions are specialized versions of the singular-value decomposition when applied to symmetric or symplectic matrices. The third factors any symplectic matrix in a unique way in terms of matrices that belong to different subgroups of the symplectic group. The last one instead gives the symplectic diagonalization of real, positive definite matrices of even size. While proofs of the existence of these decompositions exist in the literature, we focus on providing explicit constructions to implement these decompositions using standard linear algebra packages and functionalities such as singular-value, polar, Schur and QR decompositions, and matrix square roots and inverses.
28 Apr 2020
We present a method to produce abstractive summaries of long documents that exceed several thousand words via neural abstractive summarization. We perform a simple extractive step before generating a summary, which is then used to condition the transformer language model on relevant information before being tasked with generating a summary. We show that this extractive step significantly improves summarization results. We also show that this approach produces more abstractive summaries compared to prior work that employs a copy mechanism while still achieving higher rouge scores. Note: The abstract above was not written by the authors, it was generated by one of the models presented in this paper.
This paper deals with the reachability analysis of {P,A}-Time Petri nets ({P,A}-TPN in short) in the context of strong semantics. It investigates the convexity of the union of state classes reached by different interleavings of the same set of transitions. In BB08, the authors have considered the T-TPN model and its Contracted State Class Graph (CSCG) and shown that this union is not necessarily convex. They have however established some sufficient conditions which ensure convexity. This paper shows that for the CSCG of {P,A}-TPN, this union is convex and can be computed without computing intermediate state classes. These results allow to improve the forward reachability analysis by agglomerating, in the same state class, all state classes reached by different interleavings of the same set of transitions (abstraction by convex-union).
18 Nov 2025
If classical algorithms have been successful in reproducing the estimation of expectation values of observables of some quantum circuits using off-the-shelf computing resources, matching the performance of the most advanced quantum devices on sampling problems usually requires extreme cost in terms of memory and computing operations, making them accessible to only a handful of supercomputers around the world. In this work, we demonstrate for the first time a classical simulation outperforming Gaussian boson sampling experiments of one hundred modes on established benchmark tests using a single CPU or GPU. Being embarrassingly parallelizable, a small number of CPUs or GPUs allows us to match previous sampling rates that required more than one hundred GPUs. We believe algorithmic and implementation improvements will generalize our tools to photo-counting, single-photon inputs, and pseudo-photon-number-resolving scenarios beyond one thousand modes. Finally, most of the innovations in our tools remain valid for generic probability distributions over binary variables, rendering it potentially applicable to the simulation of qubit-based sampling problems and creating classical surrogates for classical-quantum algorithms.
In this paper, we present neural networks learning mechanical systems that are both symplectic (for instance particle mechanics) and non-symplectic (for instance rotating rigid body). Mechanical systems have Hamiltonian evolution, which consists of two building blocks: a Poisson bracket and an energy functional. We feed a set of snapshots of a Hamiltonian system to our neural network models which then find both the two building blocks. In particular, the models distinguish between symplectic systems (with non-degenerate Poisson brackets) and non-symplectic systems (degenerate brackets). In contrast with earlier works, our approach does not assume any further a priori information about the dynamics except its Hamiltonianity, and it returns Poisson brackets that satisfy Jacobi identity. Finally, the models indicate whether a system of equations is Hamiltonian or not.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) can generate near photo realistic images in narrow domains such as human faces. Yet, modeling complex distributions of datasets such as ImageNet and COCO-Stuff remains challenging in unconditional settings. In this paper, we take inspiration from kernel density estimation techniques and introduce a non-parametric approach to modeling distributions of complex datasets. We partition the data manifold into a mixture of overlapping neighborhoods described by a datapoint and its nearest neighbors, and introduce a model, called instance-conditioned GAN (IC-GAN), which learns the distribution around each datapoint. Experimental results on ImageNet and COCO-Stuff show that IC-GAN significantly improves over unconditional models and unsupervised data partitioning baselines. Moreover, we show that IC-GAN can effortlessly transfer to datasets not seen during training by simply changing the conditioning instances, and still generate realistic images. Finally, we extend IC-GAN to the class-conditional case and show semantically controllable generation and competitive quantitative results on ImageNet; while improving over BigGAN on ImageNet-LT. Code and trained models to reproduce the reported results are available at this https URL.
Quantization lowers memory usage, computational requirements, and latency by
utilizing fewer bits to represent model weights and activations. In this work,
we investigate the generalization properties of quantized neural networks, a
characteristic that has received little attention despite its implications on
model performance. In particular, first, we develop a theoretical model for
quantization in neural networks and demonstrate how quantization functions as a
form of regularization. Second, motivated by recent work connecting the
sharpness of the loss landscape and generalization, we derive an approximate
bound for the generalization of quantized models conditioned on the amount of
quantization noise. We then validate our hypothesis by experimenting with over
2000 models trained on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and ImageNet datasets on
convolutional and transformer-based models.
This study introduces a lightweight U-Net model optimized for real-time
semantic segmentation of aerial images, targeting the efficient utilization of
Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) embedded computing platforms. We maintain the
accuracy of the U-Net on a real-world dataset while significantly reducing the
model's parameters and Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) operations by a factor of 16.
Our comprehensive analysis covers three hardware platforms (CPU, GPU, and FPGA)
and five different toolchains (TVM, FINN, Vitis AI, TensorFlow GPU, and cuDNN),
assessing each on metrics such as latency, power consumption, memory footprint,
energy efficiency, and FPGA resource usage. The results highlight the
trade-offs between these platforms and toolchains, with a particular focus on
the practical deployment challenges in real-world applications. Our findings
demonstrate that while the FPGA with Vitis AI emerges as the superior choice
due to its performance, energy efficiency, and maturity, it requires
specialized hardware knowledge, emphasizing the need for a balanced approach in
selecting embedded computing solutions for semantic segmentation tasks
The primary purpose of this study is to investigate the system modeling of a nanoquadcopter as well as designing position and trajectory control algorithms, with the ultimate goal of testing the system both in simulation and on a real platform.
The open source nanoquadcopter platform named Crazyflie 2.0 was chosen for the project. The first phase consisted in the development of a mathematical model that describes the dynamics of the quadcopter. Secondly, a simulation environment was created to design two different control architectures: cascaded PID position tracker and LQT trajectory tracker. Finally, the implementation phase consisted in testing the controllers on the chosen platform and comparing their performance in trajectory tracking.
Our simulations agreed with the experimental results, and further refinement of the model is proposed as future work through closed-loop model identification techniques. The results show that the LQT controller performed better at tracking trajectories, with RMS errors in position up to four times smaller than those obtained with the PID. LQT control effort was greater, but eliminated the high control peaks that induced motor saturation in the PID controller. The LQT controller was also tested using an ultra-wide band two-way ranging system, and comparisons with the more precise VICON system indicate that the controller could track a trajectory in both cases despise the difference in noise levels between the two systems.
Seamless interaction between AI agents and humans using natural language
remains a key goal in AI research. This paper addresses the challenges of
developing interactive agents capable of understanding and executing grounded
natural language instructions through the IGLU competition at NeurIPS. Despite
advancements, challenges such as a scarcity of appropriate datasets and the
need for effective evaluation platforms persist. We introduce a scalable data
collection tool for gathering interactive grounded language instructions within
a Minecraft-like environment, resulting in a Multi-Modal dataset with around
9,000 utterances and over 1,000 clarification questions. Additionally, we
present a Human-in-the-Loop interactive evaluation platform for qualitative
analysis and comparison of agent performance through multi-turn communication
with human annotators. We offer to the community these assets referred to as
IDAT (IGLU Dataset And Toolkit) which aim to advance the development of
intelligent, interactive AI agents and provide essential resources for further
research.
For most deep learning algorithms training is notoriously time consuming.
Since most of the computation in training neural networks is typically spent on
floating point multiplications, we investigate an approach to training that
eliminates the need for most of these. Our method consists of two parts: First
we stochastically binarize weights to convert multiplications involved in
computing hidden states to sign changes. Second, while back-propagating error
derivatives, in addition to binarizing the weights, we quantize the
representations at each layer to convert the remaining multiplications into
binary shifts. Experimental results across 3 popular datasets (MNIST, CIFAR10,
SVHN) show that this approach not only does not hurt classification performance
but can result in even better performance than standard stochastic gradient
descent training, paving the way to fast, hardware-friendly training of neural
networks.
24 Jan 2019
Perceptual aliasing is one of the main causes of failure for Simultaneous
Localization and Mapping (SLAM) systems operating in the wild. Perceptual
aliasing is the phenomenon where different places generate a similar visual
(or, in general, perceptual) footprint. This causes spurious measurements to be
fed to the SLAM estimator, which typically results in incorrect localization
and mapping results. The problem is exacerbated by the fact that those outliers
are highly correlated, in the sense that perceptual aliasing creates a large
number of mutually-consistent outliers. Another issue stems from the fact that
most state-of-the-art techniques rely on a given trajectory guess (e.g., from
odometry) to discern between inliers and outliers and this makes the resulting
pipeline brittle, since the accumulation of error may result in incorrect
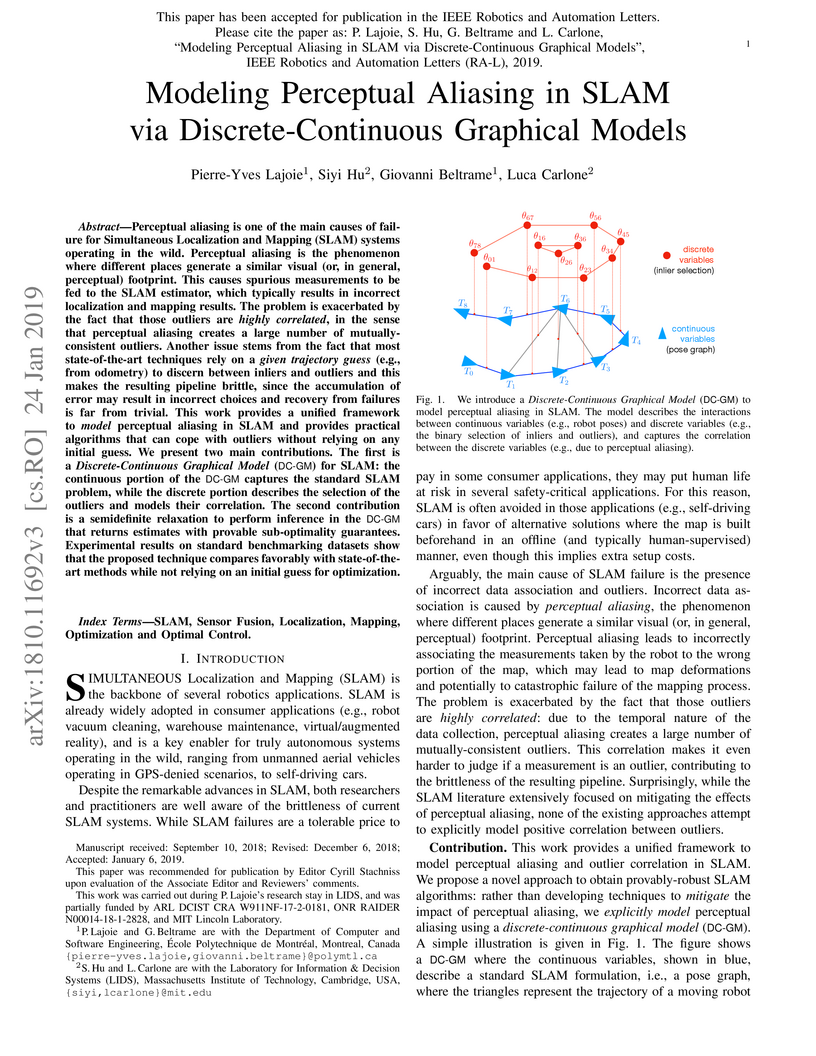
choices and recovery from failures is far from trivial. This work provides a
unified framework to model perceptual aliasing in SLAM and provides practical
algorithms that can cope with outliers without relying on any initial guess. We
present two main contributions. The first is a Discrete-Continuous Graphical
Model (DC-GM) for SLAM: the continuous portion of the DC-GM captures the
standard SLAM problem, while the discrete portion describes the selection of
the outliers and models their correlation. The second contribution is a
semidefinite relaxation to perform inference in the DC-GM that returns
estimates with provable sub-optimality guarantees. Experimental results on
standard benchmarking datasets show that the proposed technique compares
favorably with state-of-the-art methods while not relying on an initial guess
for optimization.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.