Fordham University
This research introduces a Smart Agent-Based Modeling (SABM) framework leveraging GPT-4 to simulate firm competition and collusion, demonstrating that GPT-4 agents can achieve sophisticated tacit collusion and higher-level collusion with communication, mirroring human economic behavior. The study shows prices stabilizing around 7 in tacit collusion without communication and close to the cartel price of 8 with explicit communication, which also accelerates collusion formation.
The TokUR framework introduces a training-free method for estimating token-level uncertainty in large language model reasoning, decomposing it into aleatoric and epistemic components. This principled approach, developed by Rutgers University and UIUC researchers, consistently improves detection of incorrect reasoning paths and enhances solution selection quality on mathematical benchmarks.
A comprehensive review surveys machine learning methods for generating synthetic data, exploring diverse applications, the capabilities of deep generative models, and critical ethical considerations. The paper outlines current challenges and future opportunities in creating high-quality, privacy-preserving synthetic datasets across various fields.
As Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) become increasingly popular for learning from large-scale graph data across various domains, their susceptibility to adversarial attacks when using graph reduction techniques for scalability remains underexplored. In this paper, we present an extensive empirical study to investigate the impact of graph reduction techniques, specifically graph coarsening and sparsification, on the robustness of GNNs against adversarial attacks. Through extensive experiments involving multiple datasets and GNN architectures, we examine the effects of four sparsification and six coarsening methods on the poisoning attacks. Our results indicate that, while graph sparsification can mitigate the effectiveness of certain poisoning attacks, such as Mettack, it has limited impact on others, like PGD. Conversely, graph coarsening tends to amplify the adversarial impact, significantly reducing classification accuracy as the reduction ratio decreases. Additionally, we provide a novel analysis of the causes driving these effects and examine how defensive GNN models perform under graph reduction, offering practical insights for designing robust GNNs within graph acceleration systems.
06 Jun 2024
Jailbreak attacks in large language models (LLMs) entail inducing the models
to generate content that breaches ethical and legal norm through the use of
malicious prompts, posing a substantial threat to LLM security. Current
strategies for jailbreak attack and defense often focus on optimizing locally
within specific algorithmic frameworks, resulting in ineffective optimization
and limited scalability. In this paper, we present a systematic analysis of the
dependency relationships in jailbreak attack and defense techniques,
generalizing them to all possible attack surfaces. We employ directed acyclic
graphs (DAGs) to position and analyze existing jailbreak attacks, defenses, and
evaluation methodologies, and propose three comprehensive, automated, and
logical frameworks. \texttt{AutoAttack} investigates dependencies in two lines
of jailbreak optimization strategies: genetic algorithm (GA)-based attacks and
adversarial-generation-based attacks, respectively. We then introduce an
ensemble jailbreak attack to exploit these dependencies. \texttt{AutoDefense}
offers a mixture-of-defenders approach by leveraging the dependency
relationships in pre-generative and post-generative defense strategies.
\texttt{AutoEvaluation} introduces a novel evaluation method that distinguishes
hallucinations, which are often overlooked, from jailbreak attack and defense
responses. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that the proposed
ensemble jailbreak attack and defense framework significantly outperforms
existing research.
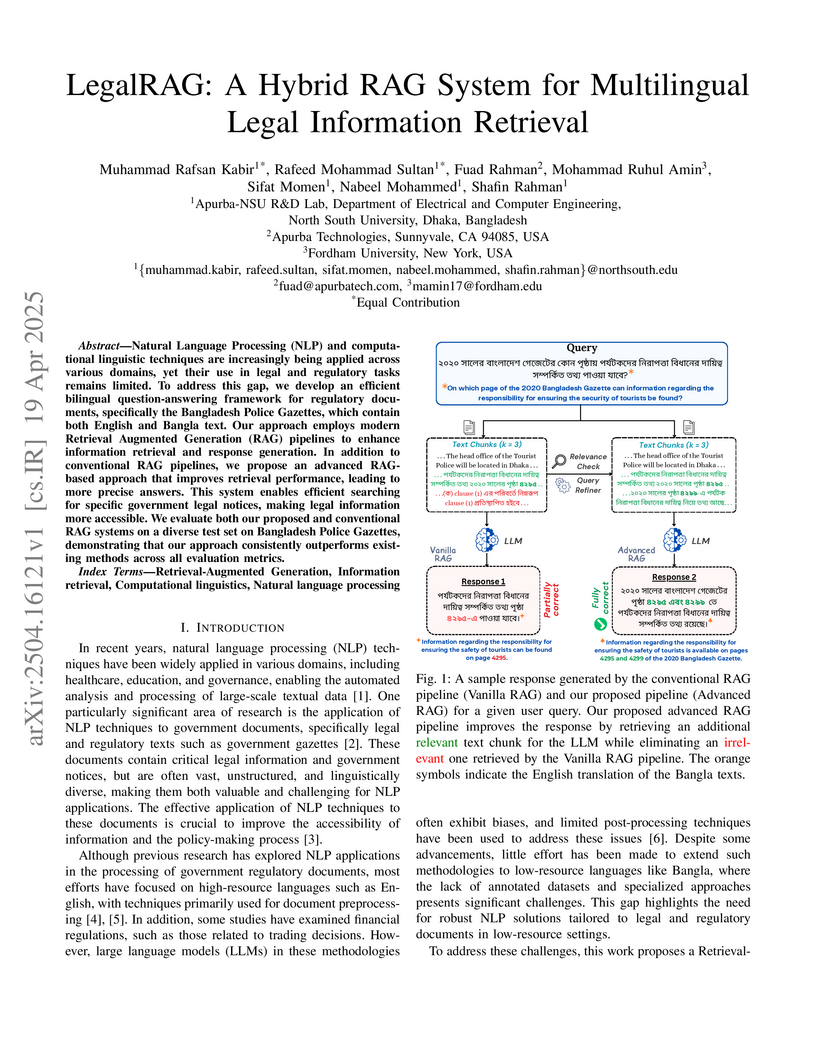
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and computational linguistic techniques are
increasingly being applied across various domains, yet their use in legal and
regulatory tasks remains limited. To address this gap, we develop an efficient
bilingual question-answering framework for regulatory documents, specifically
the Bangladesh Police Gazettes, which contain both English and Bangla text. Our
approach employs modern Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines to
enhance information retrieval and response generation. In addition to
conventional RAG pipelines, we propose an advanced RAG-based approach that
improves retrieval performance, leading to more precise answers. This system
enables efficient searching for specific government legal notices, making legal
information more accessible. We evaluate both our proposed and conventional RAG
systems on a diverse test set on Bangladesh Police Gazettes, demonstrating that
our approach consistently outperforms existing methods across all evaluation
metrics.
22 Mar 2025
Where are we in audio deepfake detection? A systematic analysis over generative and detection models
Where are we in audio deepfake detection? A systematic analysis over generative and detection models
Recent advances in Text-to-Speech (TTS) and Voice-Conversion (VC) using
generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology have made it possible to
generate high-quality and realistic human-like audio. This poses growing
challenges in distinguishing AI-synthesized speech from the genuine human voice
and could raise concerns about misuse for impersonation, fraud, spreading
misinformation, and scams. However, existing detection methods for
AI-synthesized audio have not kept pace and often fail to generalize across
diverse datasets. In this paper, we introduce SONAR, a synthetic AI-Audio
Detection Framework and Benchmark, aiming to provide a comprehensive evaluation
for distinguishing cutting-edge AI-synthesized auditory content. SONAR includes
a novel evaluation dataset sourced from 9 diverse audio synthesis platforms,
including leading TTS providers and state-of-the-art TTS models. It is the
first framework to uniformly benchmark AI-audio detection across both
traditional and foundation model-based detection systems. Through extensive
experiments, (1) we reveal the limitations of existing detection methods and
demonstrate that foundation models exhibit stronger generalization
capabilities, likely due to their model size and the scale and quality of
pretraining data. (2) Speech foundation models demonstrate robust cross-lingual
generalization capabilities, maintaining strong performance across diverse
languages despite being fine-tuned solely on English speech data. This finding
also suggests that the primary challenges in audio deepfake detection are more
closely tied to the realism and quality of synthetic audio rather than
language-specific characteristics. (3) We explore the effectiveness and
efficiency of few-shot fine-tuning in improving generalization, highlighting
its potential for tailored applications, such as personalized detection systems
for specific entities or individuals.
This paper presents LP-DETR (Layer-wise Progressive DETR), a novel approach
that enhances DETR-based object detection through multi-scale relation
modeling. Our method introduces learnable spatial relationships between object
queries through a relation-aware self-attention mechanism, which adaptively
learns to balance different scales of relations (local, medium and global)
across decoder layers. This progressive design enables the model to effectively
capture evolving spatial dependencies throughout the detection pipeline.
Extensive experiments on COCO 2017 dataset demonstrate that our method improves
both convergence speed and detection accuracy compared to standard
self-attention module. The proposed method achieves competitive results,
reaching 52.3\% AP with 12 epochs and 52.5\% AP with 24 epochs using ResNet-50
backbone, and further improving to 58.0\% AP with Swin-L backbone. Furthermore,
our analysis reveals an interesting pattern: the model naturally learns to
prioritize local spatial relations in early decoder layers while gradually
shifting attention to broader contexts in deeper layers, providing valuable
insights for future research in object detection.
Large Language Models (LLMs) represent the recent success of deep learning in achieving remarkable human-like predictive performance. It has become a mainstream strategy to leverage fine-tuning to adapt LLMs for various real-world applications due to the prohibitive expenses associated with LLM training. The learning rate is one of the most important hyperparameters in LLM fine-tuning with direct impacts on both fine-tuning efficiency and fine-tuned LLM quality. Existing learning rate policies are primarily designed for training traditional deep neural networks (DNNs), which may not work well for LLM fine-tuning. We reassess the research challenges and opportunities of learning rate tuning in the coming era of Large Language Models. This paper makes three original contributions. First, we revisit existing learning rate policies to analyze the critical challenges of learning rate tuning in the era of LLMs. Second, we present LRBench++ to benchmark learning rate policies and facilitate learning rate tuning for both traditional DNNs and LLMs. Third, our experimental analysis with LRBench++ demonstrates the key differences between LLM fine-tuning and traditional DNN training and validates our analysis.
Recent advances in uncertainty estimation for Large Language Models (LLMs)
during downstream adaptation have addressed key challenges of reliability and
simplicity. However, existing Bayesian methods typically require multiple
sampling iterations during inference, creating significant efficiency issues
that limit practical deployment. In this paper, we investigate the possibility
of eliminating the need for test-time sampling for LLM uncertainty estimation.
Specifically, when given an off-the-shelf Bayesian LLM, we distill its aligned
confidence into a non-Bayesian student LLM by minimizing the divergence between
their predictive distributions. Unlike typical calibration methods, our
distillation is carried out solely on the training dataset without the need of
an additional validation dataset. This simple yet effective approach achieves
N-times more efficient uncertainty estimation during testing, where N is the
number of samples traditionally required by Bayesian LLMs. Our extensive
experiments demonstrate that uncertainty estimation capabilities on training
data can successfully generalize to unseen test data through our distillation
technique, consistently producing results comparable to (or even better than)
state-of-the-art Bayesian LLMs.
With the remarkable success of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) on multimodal tasks, concerns regarding their deployment efficiency have become increasingly prominent. In particular, the number of tokens consumed during the generation process has emerged as a key evaluation this http URL studies have shown that specific inputs can induce VLMs to generate lengthy outputs with low information density, which significantly increases energy consumption, latency, and token costs. However, existing methods simply delay the occurrence of the EOS token to implicitly prolong output, and fail to directly maximize the output token length as an explicit optimization objective, lacking stability and this http URL address these limitations, this paper proposes a novel verbose-text induction attack (VTIA) to inject imperceptible adversarial perturbations into benign images via a two-stage framework, which identifies the most malicious prompt embeddings for optimizing and maximizing the output token of the perturbed this http URL, we first perform adversarial prompt search, employing reinforcement learning strategies to automatically identify adversarial prompts capable of inducing the LLM component within VLMs to produce verbose outputs. We then conduct vision-aligned perturbation optimization to craft adversarial examples on input images, maximizing the similarity between the perturbed image's visual embeddings and those of the adversarial prompt, thereby constructing malicious images that trigger verbose text generation. Comprehensive experiments on four popular VLMs demonstrate that our method achieves significant advantages in terms of effectiveness, efficiency, and generalization capability.
Researchers from Fordham University and collaborating institutions introduce Adaptive Threshold Pruning (ATP), a data encoding method for quantum neural networks that reduces qubit requirements while maintaining model performance, achieving 7% improved accuracy on IBM's quantum hardware compared to traditional encoding approaches.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have increasingly been utilized in social
simulations, where they are often guided by carefully crafted instructions to
stably exhibit human-like behaviors during simulations. Nevertheless, we doubt
the necessity of shaping agents' behaviors for accurate social simulations.
Instead, this paper emphasizes the importance of spontaneous phenomena, wherein
agents deeply engage in contexts and make adaptive decisions without explicit
directions. We explored spontaneous cooperation across three competitive
scenarios and successfully simulated the gradual emergence of cooperation,
findings that align closely with human behavioral data. This approach not only
aids the computational social science community in bridging the gap between
simulations and real-world dynamics but also offers the AI community a novel
method to assess LLMs' capability of deliberate reasoning.
This study focuses on recognizing Bangladeshi dialects and converting diverse Bengali accents into standardized formal Bengali speech. Dialects, often referred to as regional languages, are distinctive variations of a language spoken in a particular location and are identified by their phonetics, pronunciations, and lexicon. Subtle changes in pronunciation and intonation are also influenced by geographic location, educational attainment, and socioeconomic status. Dialect standardization is needed to ensure effective communication, educational consistency, access to technology, economic opportunities, and the preservation of linguistic resources while respecting cultural diversity. Being the fifth most spoken language with around 55 distinct dialects spoken by 160 million people, addressing Bangla dialects is crucial for developing inclusive communication tools. However, limited research exists due to a lack of comprehensive datasets and the challenges of handling diverse dialects. With the advancement in multilingual Large Language Models (mLLMs), emerging possibilities have been created to address the challenges of dialectal Automated Speech Recognition (ASR) and Machine Translation (MT). This study presents an end-to-end pipeline for converting dialectal Noakhali speech to standard Bangla speech. This investigation includes constructing a large-scale diverse dataset with dialectal speech signals that tailored the fine-tuning process in ASR and LLM for transcribing the dialect speech to dialect text and translating the dialect text to standard Bangla text. Our experiments demonstrated that fine-tuning the Whisper ASR model achieved a CER of 0.8% and WER of 1.5%, while the BanglaT5 model attained a BLEU score of 41.6% for dialect-to-standard text translation.
Estimating the causal effects of an intervention on outcomes is crucial to policy and decision-making. But often, information about outcomes can be missing or subject to non-standard measurement error. It may be possible to reveal ground-truth outcome information at a cost, for example via data annotation or follow-up; but budget constraints entail that only a fraction of the dataset can be labeled. In this setting, we optimize which data points should be sampled for outcome information and, therefore, efficient average treatment effect estimation with missing data. We do so by allocating data annotation in batches. We extend to settings where outcomes may be recorded in unstructured data that can be annotated at a cost, such as text or images, for example, in healthcare or social services. Our motivating application is a collaboration with a street outreach provider with millions of case notes, where it is possible to expertly label some, but not all, ground-truth outcomes. We demonstrate how expert labels and noisy imputed labels can be combined efficiently and responsibly into a doubly robust causal estimator. We run experiments on simulated data and two real-world datasets, including one on street outreach interventions in homelessness services, to show the versatility of our proposed method.
This study introduces SentiGOLD, a Bangla multi-domain sentiment analysis dataset. Comprising 70,000 samples, it was created from diverse sources and annotated by a gender-balanced team of linguists. SentiGOLD adheres to established linguistic conventions agreed upon by the Government of Bangladesh and a Bangla linguistics committee. Unlike English and other languages, Bangla lacks standard sentiment analysis datasets due to the absence of a national linguistics framework. The dataset incorporates data from online video comments, social media posts, blogs, news, and other sources while maintaining domain and class distribution rigorously. It spans 30 domains (e.g., politics, entertainment, sports) and includes 5 sentiment classes (strongly negative, weakly negative, neutral, and strongly positive). The annotation scheme, approved by the national linguistics committee, ensures a robust Inter Annotator Agreement (IAA) with a Fleiss' kappa score of 0.88. Intra- and cross-dataset evaluation protocols are applied to establish a standard classification system. Cross-dataset evaluation on the noisy SentNoB dataset presents a challenging test scenario. Additionally, zero-shot experiments demonstrate the generalizability of SentiGOLD. The top model achieves a macro f1 score of 0.62 (intra-dataset) across 5 classes, setting a benchmark, and 0.61 (cross-dataset from SentNoB) across 3 classes, comparable to the state-of-the-art. Fine-tuned sentiment analysis model can be accessed at this https URL.
Researchers from Fordham University and the University of Michigan-Dearborn analyzed how Large Language Models can create sophisticated phishing emails with higher evasion rates while also exploring their potential for strengthening detection systems. The study found that LLM-rephrased emails achieved a 16.4% evasion rate, but training detection models on LLM-augmented datasets significantly improved their ability to detect these advanced threats.
Thanks to the high potential for profit, trading has become increasingly attractive to investors as the cryptocurrency and stock markets rapidly expand. However, because financial markets are intricate and dynamic, accurately predicting prices remains a significant challenge. The volatile nature of the cryptocurrency market makes it even harder for traders and investors to make decisions. This study presents a classification-based machine learning model to forecast the direction of the cryptocurrency market, i.e., whether prices will increase or decrease. The model is trained using historical data and important technical indicators such as the Moving Average Convergence Divergence, the Relative Strength Index, and the Bollinger Bands. We illustrate our approach with an empirical study of the closing price of Bitcoin. Several simulations, including a confusion matrix and Receiver Operating Characteristic curve, are used to assess the model's performance, and the results show a buy/sell signal accuracy of over 92\%. These findings demonstrate how machine learning models can assist investors and traders of cryptocurrencies in making wise/informed decisions in a very volatile market.
Deep neural network ensembles hold the potential of improving generalization
performance for complex learning tasks. This paper presents formal analysis and
empirical evaluation to show that heterogeneous deep ensembles with high
ensemble diversity can effectively leverage model learning heterogeneity to
boost ensemble robustness. We first show that heterogeneous DNN models trained
for solving the same learning problem, e.g., object detection, can
significantly strengthen the mean average precision (mAP) through our weighted
bounding box ensemble consensus method. Second, we further compose ensembles of
heterogeneous models for solving different learning problems, e.g., object
detection and semantic segmentation, by introducing the connected component
labeling (CCL) based alignment. We show that this two-tier heterogeneity driven
ensemble construction method can compose an ensemble team that promotes high
ensemble diversity and low negative correlation among member models of the
ensemble, strengthening ensemble robustness against both negative examples and
adversarial attacks. Third, we provide a formal analysis of the ensemble
robustness in terms of negative correlation. Extensive experiments validate the
enhanced robustness of heterogeneous ensembles in both benign and adversarial
settings. The source codes are available on GitHub at
this https URL
 University of Toronto
University of Toronto Imperial College LondonFreie Universität Berlin
Imperial College LondonFreie Universität Berlin Stanford University
Stanford University University of California, San DiegoMax Planck Institute for the Science of LightUniversity of RochesterVector Institute for Artificial IntelligenceUniversity of ViennaFriedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena
University of California, San DiegoMax Planck Institute for the Science of LightUniversity of RochesterVector Institute for Artificial IntelligenceUniversity of ViennaFriedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyEcole Polytechnique Fédérale de LausanneFordham UniversityJulius-Maximilians-Universität WürzburgCanadian Institute for Advanced ResearchUniversity of São PauloIBM Research EuropeVrije Universiteit AmsterdamUniversidad Autónoma de ChihuahuaSyngenta Jealott’s Hill International Research Centre
Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyEcole Polytechnique Fédérale de LausanneFordham UniversityJulius-Maximilians-Universität WürzburgCanadian Institute for Advanced ResearchUniversity of São PauloIBM Research EuropeVrije Universiteit AmsterdamUniversidad Autónoma de ChihuahuaSyngenta Jealott’s Hill International Research CentreArtificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are expanding in popularity for broad applications to challenging tasks in chemistry and materials science. Examples include the prediction of properties, the discovery of new reaction pathways, or the design of new molecules. The machine needs to read and write fluently in a chemical language for each of these tasks. Strings are a common tool to represent molecular graphs, and the most popular molecular string representation, SMILES, has powered cheminformatics since the late 1980s. However, in the context of AI and ML in chemistry, SMILES has several shortcomings -- most pertinently, most combinations of symbols lead to invalid results with no valid chemical interpretation. To overcome this issue, a new language for molecules was introduced in 2020 that guarantees 100\% robustness: SELFIES (SELF-referencIng Embedded Strings). SELFIES has since simplified and enabled numerous new applications in chemistry. In this manuscript, we look to the future and discuss molecular string representations, along with their respective opportunities and challenges. We propose 16 concrete Future Projects for robust molecular representations. These involve the extension toward new chemical domains, exciting questions at the interface of AI and robust languages and interpretability for both humans and machines. We hope that these proposals will inspire several follow-up works exploiting the full potential of molecular string representations for the future of AI in chemistry and materials science.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.