Hanyang University
Researchers at Hanyang University developed the Feature Dequantization Module (FDM) to counteract detail degradation caused by feature quantization in VQGAN-based generative models. This module improves the fidelity and consistency of images generated by pluralistic image inpainting models and other VQGAN-based image synthesis tasks through an efficient training approach.
Researchers investigated the use of fundamental Natural Language Processing (NLP) text classification methods on drug SMILES strings for drug classification, treating SMILES as conventional sentences. They demonstrated that a simple bag-of-n-grams model combined with an MLP can achieve competitive performance, with the 3-gram+MLP achieving an accuracy of 0.737 and ROC-AUC of 0.848, compared to specialized molecular fingerprint methods.
Modern large language models (LLMs) extend context lengths to millions of tokens, enabling coherent, personalized responses grounded in long conversational histories. This ability, however, hinges on Key-Value (KV) caching, whose memory grows linearly with dialogue length and quickly becomes the bottleneck in resource-constrained environments. An active line of research for reducing memory bottleneck is KV cache compression, which seeks to limit cache size while preserving accuracy. Yet existing methods face two major limitations: (i) evicting the KV cache after full-context prefill causes unbounded peak memory, and (ii) query-dependent eviction narrows the cache to a single query, leading to failure cases in multi-turn conversations. We introduce EpiCache, a training-free KV cache management framework for long conversational question answering (LongConvQA) under fixed memory budgets. EpiCache bounds cache growth through block-wise prefill and preserves topic-relevant context via episodic KV compression, which clusters conversation history into coherent episodes and applies episode-specific KV cache eviction. We further design an adaptive layer-wise budget allocation strategy that measures each layer's sensitivity to eviction and distributes the memory budget across layers accordingly. Across three LongConvQA benchmarks, EpiCache improves accuracy by up to 40%, maintains near-full KV accuracy under 4-6x compression, and reduces latency/memory by up to 2.4x/3.5x, enabling efficient multi-turn interaction under strict resource limits. Our code is available at this https URL.
Researchers from Qualcomm AI Research and Hanyang University developed InfiniPot-V, a training-free, query-agnostic framework that enables Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to process streaming video on memory-constrained edge devices by enforcing a fixed memory cap on the Key-Value (KV) cache. This method reduces peak GPU memory usage by up to 94% and improves generation throughput by up to 7.3x on edge hardware, all while maintaining or exceeding full-cache accuracy.
This work introduces Diffusion by Maximum Entropy Inverse Reinforcement Learning (DxMI), a framework that recasts diffusion model training as an inverse reinforcement learning problem to enable high-quality image generation with significantly fewer steps. The approach integrates a novel dynamic programming-based reinforcement learning algorithm and allows for stable, MCMC-free training of energy-based models, which are also shown to be effective for anomaly detection.
Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate strong reasoning capabilities but struggle with hallucinations and limited transparency. Recently, KG-enhanced LLMs that integrate knowledge graphs (KGs) have been shown to improve reasoning performance, particularly for complex, knowledge-intensive tasks. However, these methods still face significant challenges, including inaccurate retrieval and reasoning failures, often exacerbated by long input contexts that obscure relevant information or by context constructions that struggle to capture the richer logical directions required by different question types. Furthermore, many of these approaches rely on LLMs to directly retrieve evidence from KGs, and to self-assess the sufficiency of this evidence, which often results in premature or incorrect reasoning. To address the retrieval and reasoning failures, we propose ProgRAG, a multi-hop knowledge graph question answering (KGQA) framework that decomposes complex questions into sub-questions, and progressively extends partial reasoning paths by answering each sub-question. At each step, external retrievers gather candidate evidence, which is then refined through uncertainty-aware pruning by the LLM. Finally, the context for LLM reasoning is optimized by organizing and rearranging the partial reasoning paths obtained from the sub-question answers. Experiments on three well-known datasets demonstrate that ProgRAG outperforms existing baselines in multi-hop KGQA, offering improved reliability and reasoning quality.
Fine-tuning pre-trained language models (PLMs) has recently shown a potential
to improve knowledge graph completion (KGC). However, most PLM-based methods
focus solely on encoding textual information, neglecting the long-tailed nature
of knowledge graphs and their various topological structures, e.g., subgraphs,
shortest paths, and degrees. We claim that this is a major obstacle to
achieving higher accuracy of PLMs for KGC. To this end, we propose a
Subgraph-Aware Training framework for KGC (SATKGC) with two ideas: (i)
subgraph-aware mini-batching to encourage hard negative sampling and to
mitigate an imbalance in the frequency of entity occurrences during training,
and (ii) new contrastive learning to focus more on harder in-batch negative
triples and harder positive triples in terms of the structural properties of
the knowledge graph. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to
comprehensively incorporate the structural inductive bias of the knowledge
graph into fine-tuning PLMs. Extensive experiments on three KGC benchmarks
demonstrate the superiority of SATKGC. Our code is available.
Large language models (LLMs) have advanced code generation from single-function tasks to competitive-programming problems, but existing multi-agent solutions either rely on costly large-scale (> 30B) models or collapse when downsized to small open-source models. We present MapCoder-Lite, which upgrades a single 7B model into four role-specialised agents-retriever, planner, coder, and debugger-using only rank-32, role-specific LoRA adapters (<3\% extra parameters). Three lightweight techniques make this possible: (i) trajectory distillation from strong LLMs fixes format fragility in retrieval and debugging, (ii) supervisor-guided correction strengthens planning and coding agents, and (iii) agent-wise LoRA fine-tuning delivers memory-efficient specialisation. Comprehensive evaluation on xCodeEval, APPS, and CodeContests shows that MapCoder-Lite more than doubles xCodeEval accuracy (from 13.2% to 28.3%), eliminates all format failures, and closes to within six points of a 32B baseline while cutting GPU memory and token-generation time by 4×. These results demonstrate that careful agent-wise fine-tuning unleashes high-quality multi-agent coding on a small language model.
Large-scale deep learning models with a pretraining-finetuning paradigm have
led to a surge of numerous task-specific models fine-tuned from a common
pre-trained model. Recently, several research efforts have been made on merging
these large models into a single multi-task model, particularly with simple
arithmetic on parameters. Such merging methodology faces a central challenge:
interference between model parameters fine-tuned on different tasks. Few recent
works have focused on designing a new fine-tuning scheme that can lead to small
parameter interference, however at the cost of the performance of each
task-specific fine-tuned model and thereby limiting that of a merged model. To
improve the performance of a merged model, we note that a fine-tuning scheme
should aim for (1) smaller parameter interference and (2) better performance of
each fine-tuned model on the corresponding task. In this work, we aim to design
a new fine-tuning objective function to work towards these two goals. In the
course of this process, we find such objective function to be strikingly
similar to sharpness-aware minimization (SAM) objective function, which aims to
achieve generalization by finding flat minima. Drawing upon our observation, we
propose to fine-tune pre-trained models via sharpness-aware minimization. The
experimental and theoretical results showcase the effectiveness and
orthogonality of our proposed approach, improving performance upon various
merging and fine-tuning methods. Our code is available at
this https URL
Researchers from Hanyang University and Qualcomm AI Research developed InfiniPot, a framework enabling pre-trained Large Language Models to process arbitrarily long input contexts within strict, fixed memory constraints, without additional training. The method achieved state-of-the-art performance on long-context benchmarks like LongBench and Needle In A Haystack, extending effective context windows by over 30 times while maintaining memory and computational efficiency.
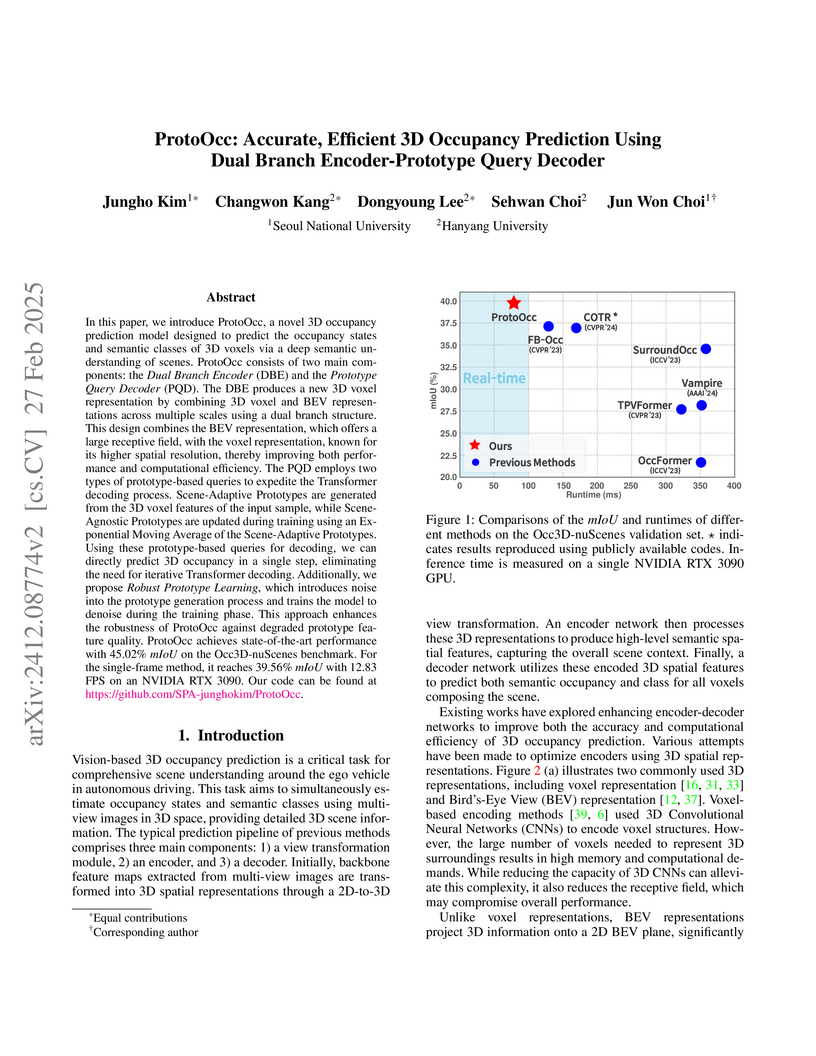
In this paper, we introduce ProtoOcc, a novel 3D occupancy prediction model
designed to predict the occupancy states and semantic classes of 3D voxels
through a deep semantic understanding of scenes. ProtoOcc consists of two main
components: the Dual Branch Encoder (DBE) and the Prototype Query Decoder
(PQD). The DBE produces a new 3D voxel representation by combining 3D voxel and
BEV representations across multiple scales through a dual branch structure.
This design enhances both performance and computational efficiency by providing
a large receptive field for the BEV representation while maintaining a smaller
receptive field for the voxel representation. The PQD introduces Prototype
Queries to accelerate the decoding process. Scene-Adaptive Prototypes are
derived from the 3D voxel features of input sample, while Scene-Agnostic
Prototypes are computed by applying Scene-Adaptive Prototypes to an Exponential
Moving Average during the training phase. By using these prototype-based
queries for decoding, we can directly predict 3D occupancy in a single step,
eliminating the need for iterative Transformer decoding. Additionally, we
propose the Robust Prototype Learning, which injects noise into prototype
generation process and trains the model to denoise during the training phase.
ProtoOcc achieves state-of-the-art performance with 45.02% mIoU on the
Occ3D-nuScenes benchmark. For single-frame method, it reaches 39.56% mIoU with
an inference speed of 12.83 FPS on an NVIDIA RTX 3090. Our code can be found at
this https URL
Few-shot anomaly generation is emerging as a practical solution for augmenting the scarce anomaly data in industrial quality control settings. An ideal generator would meet three demands at once, namely (i) keep the normal background intact, (ii) inpaint anomalous regions to tightly overlap with the corresponding anomaly masks, and (iii) generate anomalous regions in a semantically valid location, while still producing realistic, diverse appearances from only a handful of real examples. Existing diffusion-based methods usually satisfy at most two of these requirements: global anomaly generators corrupt the background, whereas mask-guided ones often falter when the mask is imprecise or misplaced. We propose MAGIC--Mask-guided inpainting with multi-level perturbations and Context-aware alignment--to resolve all three issues. At its core, MAGIC fine-tunes a Stable Diffusion inpainting backbone that preserves normal regions and ensures strict adherence of the synthesized anomaly to the supplied mask, directly addressing background corruption and misalignment. To offset the diversity loss that fine-tuning can cause, MAGIC adds two complementary perturbation strategies: (i) Gaussian prompt-level perturbation applied during fine-tuning and inference that broadens the global appearance of anomalies while avoiding low-fidelity textual appearances, and (ii) mask-guided spatial noise injection that enriches local texture variations. Additionally, the context-aware mask alignment module forms semantic correspondences and relocates masks so that every anomaly remains plausibly contained within the host object, eliminating out-of-boundary artifacts. Under a consistent identical evaluation protocol on the MVTec-AD dataset, MAGIC outperforms previous state-of-the-arts in downstream anomaly tasks.
While the mainstream research in anomaly detection has mainly followed the one-class classification, practical industrial environments often incur noisy training data due to annotation errors or lack of labels for new or refurbished products. To address these issues, we propose a novel learning-based approach for fully unsupervised anomaly detection with unlabeled and potentially contaminated training data. Our method is motivated by two observations, that i) the pairwise feature distances between the normal samples are on average likely to be smaller than those between the anomaly samples or heterogeneous samples and ii) pairs of features mutually closest to each other are likely to be homogeneous pairs, which hold if the normal data has smaller variance than the anomaly data. Building on the first observation that nearest-neighbor distances can distinguish between confident normal samples and anomalies, we propose a pseudo-labeling strategy using an iteratively reconstructed memory bank (IRMB). The second observation is utilized as a new loss function to promote class-homogeneity between mutually closest pairs thereby reducing the ill-posedness of the task. Experimental results on two public industrial anomaly benchmarks and semantic anomaly examples validate the effectiveness of FUN-AD across different scenarios and anomaly-to-normal ratios. Our code is available at this https URL.
19 Mar 2025
Materials synthesis is vital for innovations such as energy storage,
catalysis, electronics, and biomedical devices. Yet, the process relies heavily
on empirical, trial-and-error methods guided by expert intuition. Our work aims
to support the materials science community by providing a practical,
data-driven resource. We have curated a comprehensive dataset of 17K
expert-verified synthesis recipes from open-access literature, which forms the
basis of our newly developed benchmark, AlchemyBench. AlchemyBench offers an
end-to-end framework that supports research in large language models applied to
synthesis prediction. It encompasses key tasks, including raw materials and
equipment prediction, synthesis procedure generation, and characterization
outcome forecasting. We propose an LLM-as-a-Judge framework that leverages
large language models for automated evaluation, demonstrating strong
statistical agreement with expert assessments. Overall, our contributions offer
a supportive foundation for exploring the capabilities of LLMs in predicting
and guiding materials synthesis, ultimately paving the way for more efficient
experimental design and accelerated innovation in materials science.
10 Oct 2025
Researchers from Samsung Electronics, Hanyang University, Miami University, and The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, collaborating at the Artificial Consciousness Lab, MODULABS, developed a multi-agent LLM framework that models layered consciousness inspired by psychodynamic theories. The system achieved a 71.4% preference over a GPT-4o baseline and reduced response variability by 37.8% through targeted fine-tuning and personalized internal states.
The expansion of large language models (LLMs) with hundreds of billions of
parameters presents significant challenges to computational resources,
particularly data movement and memory bandwidth. Long-context LLMs, which
process sequences of tens of thousands of tokens, further increase the demand
on the memory system as the complexity in attention layers and key-value cache
sizes is proportional to the context length. Processing-in-Memory (PIM)
maximizes memory bandwidth by moving compute to the data and can address the
memory bandwidth challenges; however, PIM is not necessarily scalable to
accelerate long-context LLM because of limited per-module memory capacity and
the inflexibility of fixed-functional unit PIM architecture and static memory
management. In this work, we propose LoL-PIM which is a multi-node PIM
architecture that accelerates long context LLM through hardware-software
co-design. In particular, we propose how pipeline parallelism can be exploited
across a multi-PIM module while a direct PIM access (DPA) controller (or DMA
for PIM) is proposed that enables dynamic PIM memory management and results in
efficient PIM utilization across a diverse range of context length. We
developed an MLIR-based compiler for LoL-PIM extending a commercial PIM-based
compiler where the software modifications were implemented and evaluated, while
the hardware changes were modeled in the simulator. Our evaluations demonstrate
that LoL-PIM significantly improves throughput and reduces latency for
long-context LLM inference, outperforming both multi-GPU and GPU-PIM systems
(up to 8.54x and 16.0x speedup, respectively), thereby enabling more efficient
deployment of LLMs in real-world applications.
RILQ introduces a Rank-Insensitive LoRA-based method to compensate for 2-bit quantization errors in Large Language Models, which it identifies as high-rank, by optimizing a model-wise discrepancy loss combined with a language modeling objective. This approach consistently improves zero-shot accuracy and perplexity across LLaMA-2 and LLaMA-3 models, boosting 2-bit accuracy by up to 8.1% for LLaMA-3 with QuIP#, making highly compressed LLMs practical for deployment.
In this paper, we introduce Mask2Map, a novel end-to-end online HD map
construction method designed for autonomous driving applications. Our approach
focuses on predicting the class and ordered point set of map instances within a
scene, represented in the bird's eye view (BEV). Mask2Map consists of two
primary components: the Instance-Level Mask Prediction Network (IMPNet) and the
Mask-Driven Map Prediction Network (MMPNet). IMPNet generates Mask-Aware
Queries and BEV Segmentation Masks to capture comprehensive semantic
information globally. Subsequently, MMPNet enhances these query features using
local contextual information through two submodules: the Positional Query
Generator (PQG) and the Geometric Feature Extractor (GFE). PQG extracts
instance-level positional queries by embedding BEV positional information into
Mask-Aware Queries, while GFE utilizes BEV Segmentation Masks to generate
point-level geometric features. However, we observed limited performance in
Mask2Map due to inter-network inconsistency stemming from different predictions
to Ground Truth (GT) matching between IMPNet and MMPNet. To tackle this
challenge, we propose the Inter-network Denoising Training method, which guides
the model to denoise the output affected by both noisy GT queries and perturbed
GT Segmentation Masks. Our evaluation conducted on nuScenes and Argoverse2
benchmarks demonstrates that Mask2Map achieves remarkable performance
improvements over previous state-of-the-art methods, with gains of 10.1% mAP
and 4.1 mAP, respectively. Our code can be found at
this https URL
This paper presents a comprehensive tutorial and systematic consolidation of best practices for training Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) by adapting techniques from deep learning, including backpropagation and gradient descent. It also provides practical, open-source tools with its `snnTorch` Python package and interactive tutorials.
Deep neural network (DNN)-based policy models like vision-language-action (VLA) models are transformative in automating complex decision-making across applications by interpreting multi-modal data. However, scaling these models greatly increases computational costs, which presents challenges in fields like robot manipulation and autonomous driving that require quick, accurate responses. To address the need for deployment on resource-limited hardware, we propose a new quantization framework for IL-based policy models that fine-tunes parameters to enhance robustness against low-bit precision errors during training, thereby maintaining efficiency and reliability under constrained conditions. Our evaluations with representative robot manipulation for 4-bit weight-quantization on a real edge GPU demonstrate that our framework achieves up to 2.5x speedup and 2.5x energy savings while preserving accuracy. For 4-bit weight and activation quantized self-driving models, the framework achieves up to 3.7x speedup and 3.1x energy saving on a low-end GPU. These results highlight the practical potential of deploying IL-based policy models on resource-constrained devices.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.