Huawei Technologies
Swin-Unet, a pure Transformer-based U-shaped encoder-decoder network from Technische Universität München, Fudan University, and Huawei Technologies, improves medical image segmentation by effectively capturing long-range dependencies. It achieved an average Dice-Similarity Coefficient of 79.13% and a Hausdorff Distance of 21.55 on the Synapse multi-organ CT dataset, showing more precise boundary predictions compared to prior methods.
The Iterative step-level Process Refinement (IPR) framework enhances large language model agent performance by integrating detailed step-level process supervision. It achieves this by automatically acquiring step-level rewards via Monte Carlo estimation and iteratively refining agent policy through offline optimization on contrastive action pairs, resulting in an average 4.5% improvement over state-of-the-art methods across diverse interactive tasks.
A survey from Huawei Technologies comprehensively defines and categorizes hallucination in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), synthesizing current evaluation methods, root causes, and mitigation strategies to provide a structured overview of this critical issue. The work maps hallucination types, identifies its origins across the LVLM pipeline components, and reviews diverse solutions being developed.
This survey provides a comprehensive, industry-informed analysis of map evolution in autonomous driving, categorizing it into High-Definition (HD), Lightweight (Lite), and Implicit maps. It identifies key challenges and solutions across these stages, asserting that maps, in various forms, remain indispensable for autonomous systems.
A systematic review synthesizes the rapidly evolving field of memory-augmented Transformers by establishing comprehensive taxonomies that bridge neuroscience principles and architectural designs. It reveals a clear evolutionary trajectory towards hybrid memory systems with adaptive learning, specialized retrieval, and optimized capacity, addressing key limitations in context handling and continual learning.
As Model Context Protocol (MCP) introduces an easy-to-use ecosystem for users and developers, it also brings underexplored safety risks. Its decentralized architecture, which separates clients and servers, poses unique challenges for systematic safety analysis. This paper proposes a novel framework to enhance MCP safety. Guided by the MAESTRO framework, we first analyze the missing safety mechanisms in MCP, and based on this analysis, we propose the Model Contextual Integrity Protocol (MCIP), a refined version of MCP that addresses these gaps. Next, we develop a fine-grained taxonomy that captures a diverse range of unsafe behaviors observed in MCP scenarios. Building on this taxonomy, we develop benchmark and training data that support the evaluation and improvement of LLMs' capabilities in identifying safety risks within MCP interactions. Leveraging the proposed benchmark and training data, we conduct extensive experiments on state-of-the-art LLMs. The results highlight LLMs' vulnerabilities in MCP interactions and demonstrate that our approach substantially improves their safety performance.
This research introduces AGENTBANK, a large-scale, high-quality interaction trajectory dataset designed for training generalized LLM agents. Fine-tuning open-source models like Llama-2 on AGENTBANK produces the SAMOYED series, which exhibits improved agent capabilities, generalizes to unseen tasks, and surpasses GPT-3.5-Turbo on specific in-domain benchmarks.
Generative models have excelled in audio tasks using approaches such as
language models, diffusion, and flow matching. However, existing generative
approaches for speech enhancement (SE) face notable challenges: language
model-based methods suffer from quantization loss, leading to compromised
speaker similarity and intelligibility, while diffusion models require complex
training and high inference latency. To address these challenges, we propose
FlowSE, a flow-matching-based model for SE. Flow matching learns a continuous
transformation between noisy and clean speech distributions in a single pass,
significantly reducing inference latency while maintaining high-quality
reconstruction. Specifically, FlowSE trains on noisy mel spectrograms and
optional character sequences, optimizing a conditional flow matching loss with
ground-truth mel spectrograms as supervision. It implicitly learns speech's
temporal-spectral structure and text-speech alignment. During inference, FlowSE
can operate with or without textual information, achieving impressive results
in both scenarios, with further improvements when transcripts are available.
Extensive experiments demonstrate that FlowSE significantly outperforms
state-of-the-art generative methods, establishing a new paradigm for
generative-based SE and demonstrating the potential of flow matching to advance
the field. Our code, pre-trained checkpoints, and audio samples are available.
Drive-OccWorld integrates a vision-centric 4D occupancy forecasting world model with an end-to-end planning framework, addressing safety and robustness challenges in autonomous driving. The system achieved state-of-the-art results in 4D occupancy and flow forecasting, outperforming previous methods by 9.4% in weighted mIoU for future occupancy on nuScenes, and reduced L2 error for planning by 33% at 1s compared to UniAD.
24 May 2025
A novel Speculative Search (SpecSearch) framework accelerates tree-search-based large language model (LLM) reasoning by optimizing thought generation. This approach achieves up to 4.11x speedup over autoregressive decoding and 2.12x over token-level speculative decoding, while consistently maintaining or enhancing reasoning accuracy across various models and tasks.
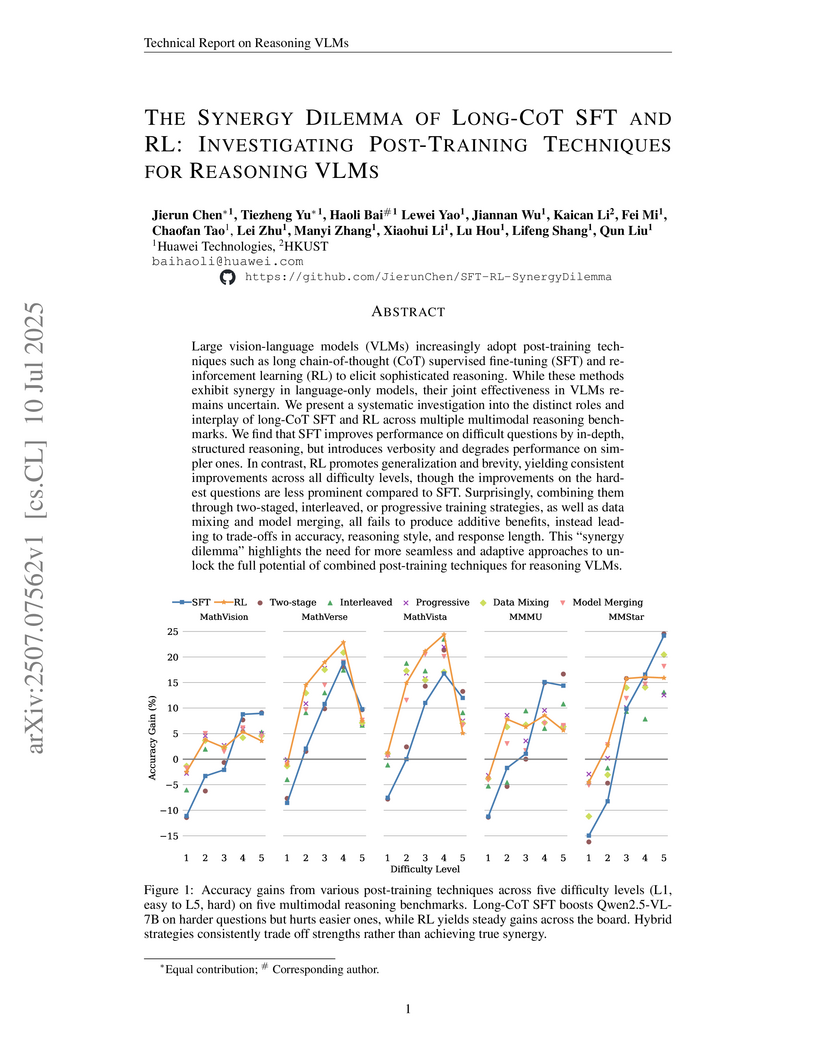
Large vision-language models (VLMs) increasingly adopt post-training techniques such as long chain-of-thought (CoT) supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL) to elicit sophisticated reasoning. While these methods exhibit synergy in language-only models, their joint effectiveness in VLMs remains uncertain. We present a systematic investigation into the distinct roles and interplay of long-CoT SFT and RL across multiple multimodal reasoning benchmarks. We find that SFT improves performance on difficult questions by in-depth, structured reasoning, but introduces verbosity and degrades performance on simpler ones. In contrast, RL promotes generalization and brevity, yielding consistent improvements across all difficulty levels, though the improvements on the hardest questions are less prominent compared to SFT. Surprisingly, combining them through two-staged, interleaved, or progressive training strategies, as well as data mixing and model merging, all fails to produce additive benefits, instead leading to trade-offs in accuracy, reasoning style, and response length. This ``synergy dilemma'' highlights the need for more seamless and adaptive approaches to unlock the full potential of combined post-training techniques for reasoning VLMs.
Diffusion Transformers (DiT) have become the de-facto model for generating high-quality visual content like videos and images. A huge bottleneck is the attention mechanism where complexity scales quadratically with resolution and video length. One logical way to lessen this burden is sparse attention, where only a subset of tokens or patches are included in the calculation. However, existing techniques fail to preserve visual quality at extremely high sparsity levels and might even incur non-negligible compute overheads. To address this concern, we propose Re-ttention, which implements very high sparse attention for visual generation models by leveraging the temporal redundancy of Diffusion Models to overcome the probabilistic normalization shift within the attention mechanism. Specifically, Re-ttention reshapes attention scores based on the prior softmax distribution history in order to preserve the visual quality of the full quadratic attention at very high sparsity levels. Experimental results on T2V/T2I models such as CogVideoX and the PixArt DiTs demonstrate that Re-ttention requires as few as 3.1% of the tokens during inference, outperforming contemporary methods like FastDiTAttn, Sparse VideoGen and MInference.
04 Dec 2025
STARE-VLA introduces a framework featuring Stage-Aware Reinforcement (StARe) and an Imitation → Preference → Interaction (IPI) pipeline to fine-tune Vision-Language-Action models. This approach, which decomposes tasks into semantically meaningful stages and provides granular feedback, achieves state-of-the-art success rates of 98.0% on SimplerEnv and 96.4% on ManiSkill3 robotic manipulation benchmarks.
29 May 2025
Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China and Huawei Technologies’ Noah’s Ark Lab developed HyperTree Planning (HTP), a novel reasoning paradigm that utilizes a hypertree structure to enhance large language model capabilities in complex planning tasks. HTP consistently achieves state-of-the-art success rates on various benchmarks by enabling hierarchical thinking, outperforming existing methods and powerful closed-source models while significantly reducing token costs.
The EMAGE framework unifies full-body co-speech gesture generation, encompassing facial expressions, local body movements, hand gestures, and global translations, by integrating audio and customizable masked gesture priors. It introduces BEAT2, a large-scale, mesh-level dataset, and achieves state-of-the-art quantitative performance and user preference for realism and expressiveness.
Researchers from Huawei Technologies introduced Top-Theta Attention, a training-free method for sparsifying transformer attention that employs calibrated static thresholds to overcome the efficiency issues of Top-k attention. This technique reduces active attention elements by up to 10x and V-cache memory usage by 3-10x during generative decoding, typically maintaining model accuracy within 1% degradation and sometimes yielding improvements.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success across various domains. However, a fundamental question remains: Can LLMs effectively utilize causal knowledge for prediction and generation? Through empirical studies, we find that LLMs trained directly on large-scale data often capture spurious correlations rather than true causal relationships, leading to suboptimal performance, especially in out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose Causal Attention Tuning (CAT), a novel approach that injects fine-grained causal knowledge into the attention mechanism. We propose an automated pipeline that leverages human priors to automatically generate token-level causal signals and introduce the Re-Attention mechanism to guide training, helping the model focus on causal structures while mitigating noise and biases in attention scores. Experimental results on our proposed Spurious Token Game (STG) benchmark and multiple downstream tasks demonstrate that our approach effectively leverages causal knowledge for prediction and remains robust in OOD scenarios. The CAT achieves an average improvement of 5.76% on the STG dataset and 1.56% on downstream tasks. Notably, the OOD performance of the Llama-3.1-8B model on STG_M increased from 64.5% to 90.5%, and Qwen's OOD performance on the STG_H dataset improved from 25.4% to 55.9%. Implementation details can be found at this https URL.
With the development of large language models (LLMs), efficient inference through Key-Value (KV) cache compression has attracted considerable attention, especially for long-context generation. To compress the KV cache, recent methods identify critical KV tokens through static modeling of attention scores. However, these methods often struggle to accurately determine critical tokens as they neglect the temporal patterns in attention scores, resulting in a noticeable degradation in LLM performance. To address this challenge, we propose AttentionPredictor, which is the first learning-based method to directly predict attention patterns for KV cache compression and critical token identification. Specifically, AttentionPredictor learns a lightweight, unified convolution model to dynamically capture spatiotemporal patterns and predict the next-token attention scores. An appealing feature of AttentionPredictor is that it accurately predicts the attention score and shares the unified prediction model, which consumes negligible memory, among all transformer layers. Moreover, we propose a cross-token critical cache prefetching framework that hides the token estimation time overhead to accelerate the decoding stage. By retaining most of the attention information, AttentionPredictor achieves 13× KV cache compression and 5.6× speedup in a cache offloading scenario with comparable LLM performance, significantly outperforming the state-of-the-arts. The code is available at this https URL.
19 Sep 2025
Large language models (LLMs) rely on key-value (KV) caches for efficient autoregressive decoding; however, cache size grows linearly with context length and model depth, becoming a major bottleneck in long-context inference. Prior KV cache compression methods either enforce rigid heuristics, disrupt tensor layouts with per-attention-head variability, or require specialized compute kernels.
We propose a simple, yet effective, KV cache compression framework based on attention-guided, layer-adaptive composite tokens. Our method aggregates attention scores to estimate token importance, selects head-specific tokens independently, and aligns them into composite tokens that respect the uniform cache structure required by existing inference engines. A global allocation mechanism further adapts retention budgets across layers, assigning more capacity to layers with informative tokens. This approach achieves significant memory reduction while preserving accuracy, consistently outperforming prior structured and semi-structured methods. Crucially, our approach remains fully compatible with standard inference pipelines, offering a practical and scalable solution for efficient long-context LLM deployment.
C²DLM introduces a paradigm that integrates concept-level causal knowledge into Diffusion Language Models (DLMs), enhancing their reasoning capabilities and training efficiency. By guiding attention mechanisms with extracted concept-level causal graphs, C²DLM achieved a 12% performance increase in normal Chain-of-Thought settings and a 3.2x training speedup compared to baseline DLMs.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.