Human Technopole
Fluorescence microscopy, while being a key driver for progress in the life
sciences, is also subject to technical limitations. To overcome them,
computational multiplexing techniques have recently been proposed, which allow
multiple cellular structures to be captured in a single image and later be
unmixed. Existing image decomposition methods are trained on a set of
superimposed input images and the respective unmixed target images. It is
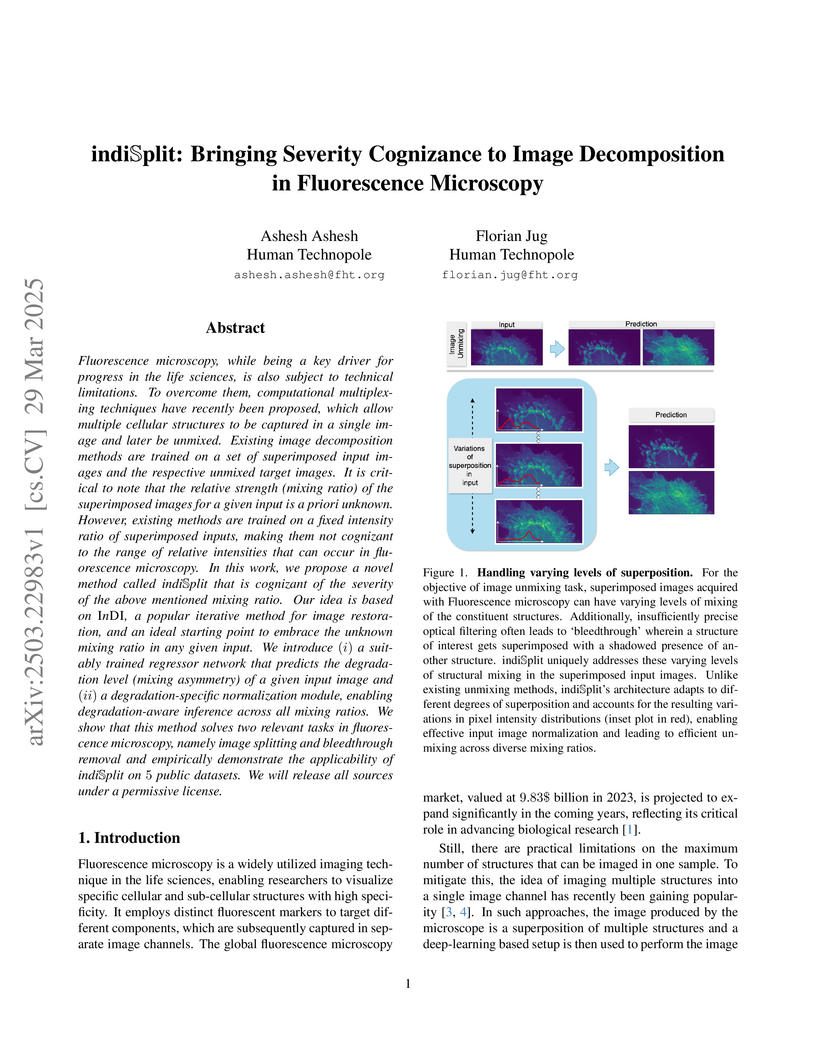
critical to note that the relative strength (mixing ratio) of the superimposed
images for a given input is a priori unknown. However, existing methods are
trained on a fixed intensity ratio of superimposed inputs, making them not
cognizant to the range of relative intensities that can occur in fluorescence
microscopy. In this work, we propose a novel method called indiSplit that is
cognizant of the severity of the above mentioned mixing ratio. Our idea is
based on InDI, a popular iterative method for image restoration, and an ideal
starting point to embrace the unknown mixing ratio in any given input. We
introduce (i) a suitably trained regressor network that predicts the
degradation level (mixing asymmetry) of a given input image and (ii) a
degradation-specific normalization module, enabling degradation-aware inference
across all mixing ratios. We show that this method solves two relevant tasks in
fluorescence microscopy, namely image splitting and bleedthrough removal, and
empirically demonstrate the applicability of indiSplit on 5 public datasets.
We will release all sources under a permissive license.
Fluorescence microscopy is a major driver of scientific progress in the life sciences. Although high-end confocal microscopes are capable of filtering out-of-focus light, cheaper and more accessible microscopy modalities, such as widefield microscopy, can not, which consequently leads to hazy image data. Computational dehazing is trying to combine the best of both worlds, leading to cheap microscopy but crisp-looking images. The perception-distortion trade-off tells us that we can optimize either for data fidelity, e.g. low MSE or high PSNR, or for data realism, measured by perceptual metrics such as LPIPS or FID. Existing methods either prioritize fidelity at the expense of realism, or produce perceptually convincing results that lack quantitative accuracy. In this work, we propose HazeMatching, a novel iterative method for dehazing light microscopy images, which effectively balances these objectives. Our goal was to find a balanced trade-off between the fidelity of the dehazing results and the realism of individual predictions (samples). We achieve this by adapting the conditional flow matching framework by guiding the generative process with a hazy observation in the conditional velocity field. We evaluate HazeMatching on 5 datasets, covering both synthetic and real data, assessing both distortion and perceptual quality. Our method is compared against 7 baselines, achieving a consistent balance between fidelity and realism on average. Additionally, with calibration analysis, we show that HazeMatching produces well-calibrated predictions. Note that our method does not need an explicit degradation operator to exist, making it easily applicable on real microscopy data. All data used for training and evaluation and our code will be publicly available under a permissive license.
University of New South WalesCSIRO Imperial College LondonUniversity of Zurich
Imperial College LondonUniversity of Zurich University College LondonDalian University of TechnologyOtto von Guericke University MagdeburgHuman TechnopoleXiamen UniversityThe Alan Turing Institute
University College LondonDalian University of TechnologyOtto von Guericke University MagdeburgHuman TechnopoleXiamen UniversityThe Alan Turing Institute Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial IntelligenceUniversity of QueenslandUniversity of LeedsGoogle Inc.Universidad de Los AndesManteia Technologies Co., LtdNational Yang Ming-Chiao Tung UniversitySorbonne Universit
eEurécom
Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial IntelligenceUniversity of QueenslandUniversity of LeedsGoogle Inc.Universidad de Los AndesManteia Technologies Co., LtdNational Yang Ming-Chiao Tung UniversitySorbonne Universit
eEurécom
 Imperial College LondonUniversity of Zurich
Imperial College LondonUniversity of Zurich University College LondonDalian University of TechnologyOtto von Guericke University MagdeburgHuman TechnopoleXiamen UniversityThe Alan Turing Institute
University College LondonDalian University of TechnologyOtto von Guericke University MagdeburgHuman TechnopoleXiamen UniversityThe Alan Turing Institute Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial IntelligenceUniversity of QueenslandUniversity of LeedsGoogle Inc.Universidad de Los AndesManteia Technologies Co., LtdNational Yang Ming-Chiao Tung UniversitySorbonne Universit
eEurécom
Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial IntelligenceUniversity of QueenslandUniversity of LeedsGoogle Inc.Universidad de Los AndesManteia Technologies Co., LtdNational Yang Ming-Chiao Tung UniversitySorbonne Universit
eEurécomThe human brain receives nutrients and oxygen through an intricate network of blood vessels. Pathology affecting small vessels, at the mesoscopic scale, represents a critical vulnerability within the cerebral blood supply and can lead to severe conditions, such as Cerebral Small Vessel Diseases. The advent of 7 Tesla MRI systems has enabled the acquisition of higher spatial resolution images, making it possible to visualise such vessels in the brain. However, the lack of publicly available annotated datasets has impeded the development of robust, machine learning-driven segmentation algorithms. To address this, the SMILE-UHURA challenge was organised. This challenge, held in conjunction with the ISBI 2023, in Cartagena de Indias, Colombia, aimed to provide a platform for researchers working on related topics. The SMILE-UHURA challenge addresses the gap in publicly available annotated datasets by providing an annotated dataset of Time-of-Flight angiography acquired with 7T MRI. This dataset was created through a combination of automated pre-segmentation and extensive manual refinement. In this manuscript, sixteen submitted methods and two baseline methods are compared both quantitatively and qualitatively on two different datasets: held-out test MRAs from the same dataset as the training data (with labels kept secret) and a separate 7T ToF MRA dataset where both input volumes and labels are kept secret. The results demonstrate that most of the submitted deep learning methods, trained on the provided training dataset, achieved reliable segmentation performance. Dice scores reached up to 0.838 ± 0.066 and 0.716 ± 0.125 on the respective datasets, with an average performance of up to 0.804 ± 0.15.
In this work, we study the problem of clustering survival data − a challenging and so far under-explored task. We introduce a novel semi-supervised probabilistic approach to cluster survival data by leveraging recent advances in stochastic gradient variational inference. In contrast to previous work, our proposed method employs a deep generative model to uncover the underlying distribution of both the explanatory variables and censored survival times. We compare our model to the related work on clustering and mixture models for survival data in comprehensive experiments on a wide range of synthetic, semi-synthetic, and real-world datasets, including medical imaging data. Our method performs better at identifying clusters and is competitive at predicting survival times. Relying on novel generative assumptions, the proposed model offers a holistic perspective on clustering survival data and holds a promise of discovering subpopulations whose survival is regulated by different generative mechanisms.
By exploiting a bipartite network representation of the relationships between
mutual funds and portfolio holdings, we propose an indicator that we derive
from the analysis of the network, labelled the Average Commonality Coefficient
(ACC), which measures how frequently the assets in the fund portfolio are
present in the portfolios of the other funds of the market. This indicator
reflects the investment behavior of funds' managers as a function of the
popularity of the assets they held. We show that ACC provides useful
information to discriminate between funds investing in niche markets and those
investing in more popular assets. More importantly, we find that ACC is able
to provide indication on the performance of the funds. In particular, we find
that funds investing in less popular assets generally outperform those
investing in more popular financial instruments, even when correcting for
standard factors. Moreover, funds with a low ACC have been less affected by
the 2007-08 global financial crisis, likely because less exposed to fire sales
spillovers.
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, National governments have applied
lockdown restrictions to reduce the infection rate. We perform a massive
analysis on near real-time Italian data provided by Facebook to investigate how
lockdown strategies affect economic conditions of individuals and local
governments. We model the change in mobility as an exogenous shock similar to a
natural disaster. We identify two ways through which mobility restrictions
affect Italian citizens. First, we find that the impact of lockdown is stronger
in municipalities with higher fiscal capacity. Second, we find a segregation
effect, since mobility restrictions are stronger in municipalities for which
inequality is higher and where individuals have lower income per capita.
10 Oct 2024
We study the defect CFT associated with the half-BPS Wilson line in N=4 Super Yang-Mills theory in four dimensions. Using a perturbative bootstrap approach, we derive new analytical results for multipoint correlators of protected defect operators at large N and weak coupling. At next-to-next-to-leading order, we demonstrate that the simplest five- and six-point functions are fully determined by non-perturbative constraints -- which include superconformal symmetry, crossing symmetry, and the pinching of operators to lower-point functions -- as well as by a single integral, known as the train track integral. Additionally, we present new analytical results for the four-point functions ⟨1122⟩ and ⟨1212⟩.
Medical domain automated text generation is an active area of research and development; however, evaluating the clinical quality of generated reports remains a challenge, especially in instances where domain-specific metrics are lacking, e.g. histopathology. We propose HARE (Histopathology Automated Report Evaluation), a novel entity and relation centric framework, composed of a benchmark dataset, a named entity recognition (NER) model, a relation extraction (RE) model, and a novel metric, which prioritizes clinically relevant content by aligning critical histopathology entities and relations between reference and generated reports. To develop the HARE benchmark, we annotated 813 de-identified clinical diagnostic histopathology reports and 652 histopathology reports from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) with domain-specific entities and relations. We fine-tuned GatorTronS, a domain-adapted language model to develop HARE-NER and HARE-RE which achieved the highest overall F1-score (0.915) among the tested models. The proposed HARE metric outperformed traditional metrics including ROUGE and Meteor, as well as radiology metrics such as RadGraph-XL, with the highest correlation and the best regression to expert evaluations (higher than the second best method, GREEN, a large language model based radiology report evaluator, by Pearson r=0.168, Spearman ρ=0.161, Kendall τ=0.123, R2=0.176, RMSE=0.018). We release HARE, datasets, and the models at this https URL to foster advancements in histopathology report generation, providing a robust framework for improving the quality of reports.
23 Nov 2023
This study aims to analyse the effects of reducing Received Dose Intensity
(RDI) in chemotherapy treatment for osteosarcoma patients on their survival by
using a novel approach. In this scenario, toxic side effects are risk factors
for mortality and predictors of future exposure levels, introducing
post-assignment confounding.
Chemotherapy administration data from BO03 and BO06 Randomized Clinical
Trials (RCTs) in ostosarcoma are employed to emulate a target trial with three
RDI-based exposure strategies: 1) standard, 2) reduced, and 3) highly-reduced
RDI. Investigations are conducted between subgroups of patients characterised
by poor or good Histological Responses (HRe). Inverse Probability of Treatment
Weighting (IPTW) is first used to transform the original population into a
pseudo-population which mimics the target randomized cohort. Then, a Marginal
Structural Cox Model with effect modification is employed. Conditional Average
Treatment Effects (CATEs) are ultimately measured as the difference between the
Restricted Mean Survival Time of reduced/highly-reduced RDI strategy and the
standard one. Confidence Intervals for CATEs are obtained using a novel
IPTW-based bootstrap procedure.
Significant effect modifications based on HRe were found. Increasing
RDI-reductions led to contrasting trends for poor and good responders: the
higher the reduction, the better (worsen) was the survival in poor (good)
reponders. This study introduces a novel approach to (i) comprehensively
address the challenges related to the analysis of chemotherapy data, (ii)
mitigate the toxicity-treatment-adjustment bias, and (iii) repurpose existing
RCT data for retrospective analyses extending beyond the original trials'
intended scopes.
26 Oct 2023
In recent years, research interest in personalised treatments has been growing. However, treatment effect heterogeneity and possibly time-varying treatment effects are still often overlooked in clinical studies. Statistical tools are needed for the identification of treatment response patterns, taking into account that treatment response is not constant over time. We aim to provide an innovative method to obtain dynamic treatment effect phenotypes on a time-to-event outcome, conditioned on a set of relevant effect modifiers. The proposed method does not require the assumption of proportional hazards for the treatment effect, which is rarely realistic. We propose a spline-based survival neural network, inspired by the Royston-Parmar survival model, to estimate time-varying conditional treatment effects. We then exploit the functional nature of the resulting estimates to apply a functional clustering of the treatment effect curves in order to identify different patterns of treatment effects. The application that motivated this work is the discontinuation of treatment with Mineralocorticoid receptor Antagonists (MRAs) in patients with heart failure, where there is no clear evidence as to which patients it is the safest choice to discontinue treatment and, conversely, when it leads to a higher risk of adverse events. The data come from an electronic health record database. A simulation study was performed to assess the performance of the spline-based neural network and the stability of the treatment response phenotyping procedure. In light of the results, the suggested approach has the potential to support personalized medical choices by assessing unique treatment responses in various medical contexts over a period of time.
In the domain of medical imaging, many supervised learning based methods for
segmentation face several challenges such as high variability in annotations
from multiple experts, paucity of labelled data and class imbalanced datasets.
These issues may result in segmentations that lack the requisite precision for
clinical analysis and can be misleadingly overconfident without associated
uncertainty quantification. This work proposes the PULASki method as a
computationally efficient generative tool for biomedical image segmentation
that accurately captures variability in expert annotations, even in small
datasets. This approach makes use of an improved loss function based on
statistical distances in a conditional variational autoencoder structure
(Probabilistic UNet), which improves learning of the conditional decoder
compared to the standard cross-entropy particularly in class imbalanced
problems. The proposed method was analysed for two structurally different
segmentation tasks (intracranial vessel and multiple sclerosis (MS) lesion) and
compare our results to four well-established baselines in terms of quantitative
metrics and qualitative output. These experiments involve class-imbalanced
datasets characterised by challenging features, including suboptimal
signal-to-noise ratios and high ambiguity. Empirical results demonstrate the
PULASKi method outperforms all baselines at the 5\% significance level. Our
experiments are also of the first to present a comparative study of the
computationally feasible segmentation of complex geometries using 3D patches
and the traditional use of 2D slices. The generated segmentations are shown to
be much more anatomically plausible than in the 2D case, particularly for the
vessel task.
18 May 2024
Evaluating hospitals' performance and its relation to patients' characteristics is of utmost importance to ensure timely, effective, and optimal treatment. Such a matter is particularly relevant in areas and situations where the healthcare system must contend with an unexpected surge in hospitalizations, such as for heart failure patients in the Lombardy region of Italy during the COVID-19 pandemic. Motivated by this issue, the paper introduces a novel Multilevel Logistic Cluster-Weighted Model (ML-CWMd) for predicting 45-day mortality following hospitalization due to COVID-19. The methodology flexibly accommodates dependence patterns among continuous, categorical, and dichotomous variables; effectively accounting for hospital-specific effects in distinct patient subgroups showing different attributes. A tailored Expectation-Maximization algorithm is developed for parameter estimation, and extensive simulation studies are conducted to evaluate its performance against competing models. The novel approach is applied to administrative data from the Lombardy Region, aiming to profile heart failure patients hospitalized for COVID-19 and investigate the hospital-level impact on their overall mortality. A scenario analysis demonstrates the model's efficacy in managing multiple sources of heterogeneity, thereby yielding promising results in aiding healthcare providers and policy-makers in the identification of patient-specific treatment pathways.
Identification of vessel structures of different sizes in biomedical images is crucial in the diagnosis of many neurodegenerative diseases. However, the sparsity of good-quality annotations of such images makes the task of vessel segmentation challenging. Deep learning offers an efficient way to segment vessels of different sizes by learning their high-level feature representations and the spatial continuity of such features across dimensions. Semi-supervised patch-based approaches have been effective in identifying small vessels of one to two voxels in diameter. This study focuses on improving the segmentation quality by considering the spatial correlation of the features using the Maximum Intensity Projection~(MIP) as an additional loss criterion. Two methods are proposed with the incorporation of MIPs of label segmentation on the single~(z-axis) and multiple perceivable axes of the 3D volume. The proposed MIP-based methods produce segmentations with improved vessel continuity, which is evident in visual examinations of ROIs. Patch-based training is improved by introducing an additional loss term, MIP loss, to penalise the predicted discontinuity of vessels. A training set of 14 volumes is selected from the StudyForrest dataset comprising of 18 7-Tesla 3D Time-of-Flight~(ToF) Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) images. The generalisation performance of the method is evaluated using the other unseen volumes in the dataset. It is observed that the proposed method with multi-axes MIP loss produces better quality segmentations with a median Dice of 80.245±0.129. Also, the method with single-axis MIP loss produces segmentations with a median Dice of 79.749±0.109. Furthermore, a visual comparison of the ROIs in the predicted segmentation reveals a significant improvement in the continuity of the vessels when MIP loss is incorporated into training.
Hyperthermia (HT) in combination with radio- and/or chemotherapy has become an accepted cancer treatment for distinct solid tumour entities. In HT, tumour tissue is exogenously heated to temperatures between 39 and 43 ∘C for 60 minutes. Temperature monitoring can be performed non-invasively using dynamic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, the slow nature of MRI leads to motion artefacts in the images due to the movements of patients during image acquisition. By discarding parts of the data, the speed of the acquisition can be increased - known as undersampling. However, due to the invalidation of the Nyquist criterion, the acquired images might be blurry and can also produce aliasing artefacts. The aim of this work was, therefore, to reconstruct highly undersampled MR thermometry acquisitions with better resolution and with fewer artefacts compared to conventional methods. The use of deep learning in the medical field has emerged in recent times, and various studies have shown that deep learning has the potential to solve inverse problems such as MR image reconstruction. However, most of the published work only focuses on the magnitude images, while the phase images are ignored, which are fundamental requirements for MR thermometry. This work, for the first time, presents deep learning-based solutions for reconstructing undersampled MR thermometry data. Two different deep learning models have been employed here, the Fourier Primal-Dual network and the Fourier Primal-Dual UNet, to reconstruct highly undersampled complex images of MR thermometry. The method reduced the temperature difference between the undersampled MRIs and the fully sampled MRIs from 1.3 ∘C to 0.6 ∘C in full volume and 0.49 ∘C to 0.06 ∘C in the tumour region for an acceleration factor of 10.
 CNRS
CNRS University of Toronto
University of Toronto California Institute of Technology
California Institute of Technology Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University Stanford University
Stanford University University of California, San Diego
University of California, San Diego Yale UniversityHuman TechnopoleHarvard Medical School
Yale UniversityHuman TechnopoleHarvard Medical School University of PennsylvaniaKarolinska InstitutetIstituto Italiano di TecnologiaINSERM
University of PennsylvaniaKarolinska InstitutetIstituto Italiano di TecnologiaINSERM University of BaselEcole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)Univ MontpellierUniversity of DundeeUMass Chan Medical SchoolSciLifeLab
University of BaselEcole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)Univ MontpellierUniversity of DundeeUMass Chan Medical SchoolSciLifeLabA key output of the NIH Common Fund 4D Nucleome (4DN) project is the open publication of datasets on the structure of the human cell nucleus and genome. In recent years, multiplexed Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) and FISH-omics methods have rapidly expanded, enabling quantification of chromatin organization in single cells, sometimes alongside RNA and protein measurements. These approaches have deepened our understanding of how 3D chromosome architecture relates to transcriptional activity and cell development in health and disease. However, results from Chromatin Tracing FISH-omics experiments remain difficult to share, reuse, and analyze due to the absence of standardized data-exchange specifications. Building on the recent release of microscopy metadata standards, we introduce the 4DN FISH Omics Format-Chromatin Tracing (FOF-CT), a community-developed standard for processed results from diverse imaging techniques. Current studies generally use one of two representations: ball-and-stick, where genomic segments appear as individual fluorescence spots, or volumetric, representing them as clouds of single-molecule localizations. This manuscript focuses on ball-and-stick methods, including those from the pioneering study of Wang et al. (2016) and related techniques. We describe the FOF-CT structure and present newly deposited datasets in the 4DN Data Portal and the OME Image Data Resource (IDR), highlighting their potential for reuse, integration, and modeling. We also outline example analysis pipelines and illustrate biological insights enabled by standardized, FAIR-compliant Chromatin Tracing datasets.
Objective: Recognizing diseases from discharge letters is crucial for cohort selection and epidemiological analyses, as this is the only type of data consistently produced across hospitals. This is a classic document classification problem, typically requiring supervised learning. However, manual annotation of large datasets of discharge letters is uncommon since it is extremely time-consuming. We propose a novel weakly-supervised pipeline to recognize diseases from Italian discharge letters. Methods: Our Natural Language Processing pipeline is based on a fine-tuned version of the Italian Umberto model. The pipeline extracts diagnosis-related sentences from a subset of letters and applies a two-level clustering using the embeddings generated by the fine-tuned Umberto model. These clusters are summarized and those mapped to the diseases of interest are selected as weak labels. Finally, the same BERT-based model is trained using these weak labels to detect the targeted diseases. Results: A case study related to the identification of bronchiolitis with 33'176 Italian discharge letters from 44 hospitals in the Veneto Region shows the potential of our method, with an AUC of 77.7 % and an F1-Score of 75.1 % on manually annotated labels, improving compared to other non-supervised methods and with a limited loss compared to fully supervised methods. Results are robust to the cluster selection and the identified clusters highlight the potential to recognize a variety of diseases. Conclusions: This study demonstrates the feasibility of diagnosis identification from Italian discharge letters in the absence of labelled data. Our pipeline showed strong performance and robustness, and its flexibility allows for easy adaptation to various diseases. This approach offers a scalable solution for clinical text classification, reducing the need for manual annotation while maintaining good accuracy.
Personalized medicine is the future of medical practice. In oncology, tumor
heterogeneity assessment represents a pivotal step for effective treatment
planning and prognosis prediction. Despite new procedures for DNA sequencing
and analysis, non-invasive methods for tumor characterization are needed to
impact on daily routine. On purpose, imaging texture analysis is rapidly
scaling, holding the promise to surrogate histopathological assessment of tumor
lesions. In this work, we propose a tree-based representation strategy for
describing intra-tumor heterogeneity of patients affected by metastatic cancer.
We leverage radiomics information extracted from PET/CT imaging and we provide
an exhaustive and easily readable summary of the disease spreading. We exploit
this novel patient representation to perform cancer subtyping according to
hierarchical clustering technique. To this purpose, a new heterogeneity-based
distance between trees is defined and applied to a case study of prostate
cancer. Clusters interpretation is explored in terms of concordance with
severity status, tumor burden and biological characteristics. Results are
promising, as the proposed method outperforms current literature approaches.
Ultimately, the proposed method draws a general analysis framework that would
allow to extract knowledge from daily acquired imaging data of patients and
provide insights for effective treatment planning.
Objective: Assessing the appropriateness of diagnostic referrals is critical for improving healthcare efficiency and reducing unnecessary procedures. However, this task becomes challenging when referral reasons are recorded only as free text rather than structured codes, like in the Italian NHS. To address this gap, we propose a fully unsupervised Natural Language Processing (NLP) pipeline capable of extracting and evaluating referral reasons without relying on labelled datasets.
Methods: Our pipeline leverages Transformer-based embeddings pre-trained on Italian medical texts to cluster referral reasons and assess their alignment with appropriateness guidelines. It operates in an unsupervised setting and is designed to generalize across different examination types. We analyzed two complete regional datasets from the Lombardy Region (Italy), covering all referrals between 2019 and 2021 for venous echocolordoppler of the lower limbs (ECD;n=496,971; development) and flexible endoscope colonoscopy (FEC; n=407,949; testing only). For both, a random sample of 1,000 referrals was manually annotated to measure performance.
Results: The pipeline achieved high performance in identifying referral reasons (Prec=92.43% (ECD), 93.59% (FEC); Rec=83.28% (ECD), 92.70% (FEC)) and appropriateness (Prec=93.58% (ECD), 94.66% (FEC); Rec=91.52% (ECD), 93.96% (FEC)). At the regional level, the analysis identified relevant inappropriate referral groups and variation across contexts, findings that informed a new Lombardy Region resolution to reinforce guideline adherence.
Conclusions: This study presents a robust, scalable, unsupervised NLP pipeline for assessing referral appropriateness in large, real-world datasets. It demonstrates how such data can be effectively leveraged, providing public health authorities with a deployable AI tool to monitor practices and support evidence-based policy.
EEG technology finds applications in several domains. Currently, most EEG systems require subjects to wear several electrodes on the scalp to be effective. However, several channels might include noisy information, redundant signals, induce longer preparation times and increase computational times of any automated system for EEG decoding. One way to reduce the signal-to-noise ratio and improve classification accuracy is to combine channel selection with feature extraction, but EEG signals are known to present high inter-subject variability. In this work we introduce a novel algorithm for subject-independent channel selection of EEG recordings. Considering multi-channel trial recordings as statistical units and the EEG decoding task as the class of reference, the algorithm (i) exploits channel-specific 1D-Convolutional Neural Networks (1D-CNNs) as feature extractors in a supervised fashion to maximize class separability; (ii) it reduces a high dimensional multi-channel trial representation into a unique trial vector by concatenating the channels' embeddings and (iii) recovers the complex inter-channel relationships during channel selection, by exploiting an ensemble of AutoEncoders (AE) to identify from these vectors the most relevant channels to perform classification. After training, the algorithm can be exploited by transferring only the parametrized subgroup of selected channel-specific 1D-CNNs to new signals from new subjects and obtain low-dimensional and highly informative trial vectors to be fed to any classifier.
 University of WashingtonCharles University
University of WashingtonCharles University University College LondonUniversity of Edinburgh
University College LondonUniversity of Edinburgh ETH ZürichHuman TechnopoleAustrian Academy of Sciences
ETH ZürichHuman TechnopoleAustrian Academy of Sciences Johns Hopkins UniversityUtrecht UniversityTechnische Universität BerlinUniversity of LondonUniversity of L’AquilaUniversity of CalgaryUniversity of KonstanzCharité – Universitätsmedizin BerlinMartin Luther University Halle-WittenbergThe Czech Academy of SciencesNational Institutes of HealthNational Cancer InstituteResearch Institute of Molecular Pathology (IMP)Birkbeck CollegeGregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology (GMI)Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA)
Johns Hopkins UniversityUtrecht UniversityTechnische Universität BerlinUniversity of LondonUniversity of L’AquilaUniversity of CalgaryUniversity of KonstanzCharité – Universitätsmedizin BerlinMartin Luther University Halle-WittenbergThe Czech Academy of SciencesNational Institutes of HealthNational Cancer InstituteResearch Institute of Molecular Pathology (IMP)Birkbeck CollegeGregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology (GMI)Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA)Crosslinking Mass Spectrometry (MS) can uncover protein-protein interactions and provide structural information on proteins in their native cellular environments. Despite its promise, the field remains hampered by inconsistent data formats, variable approaches to error control, and insufficient interoperability with global data repositories. Recent advances, especially in false discovery rate (FDR) models and pipeline benchmarking, show that Crosslinking MS data can reach a reliability that matches the demand of integrative structural biology. To drive meaningful progress, however, the community must agree on error estimation, open data formats, and streamlined repository submissions. This perspective highlights these challenges, clarifies remaining barriers, and frames practical next steps. Successful field harmonisation will enhance the acceptance of Crosslinking MS in the broader biological community and is critical for the dependability of the data, no matter where it is produced.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.