IMT School for Advanced Studies
04 Nov 2025
The rapid adoption of Large Language Model (LLM) agents and multi-agent systems enables remarkable capabilities in natural language processing and generation. However, these systems introduce security vulnerabilities that extend beyond traditional content generation to system-level compromises. This paper presents a comprehensive evaluation of the LLMs security used as reasoning engines within autonomous agents, highlighting how they can be exploited as attack vectors capable of achieving computer takeovers. We focus on how different attack surfaces and trust boundaries can be leveraged to orchestrate such takeovers. We demonstrate that adversaries can effectively coerce popular LLMs into autonomously installing and executing malware on victim machines. Our evaluation of 18 state-of-the-art LLMs reveals an alarming scenario: 94.4% of models succumb to Direct Prompt Injection, and 83.3% are vulnerable to the more stealthy and evasive RAG Backdoor Attack. Notably, we tested trust boundaries within multi-agent systems, where LLM agents interact and influence each other, and we revealed that LLMs which successfully resist direct injection or RAG backdoor attacks will execute identical payloads when requested by peer agents. We found that 100.0% of tested LLMs can be compromised through Inter-Agent Trust Exploitation attacks, and that every model exhibits context-dependent security behaviors that create exploitable blind spots.
15 Sep 2025
Random graphs defined by an occurrence probability that is invariant under node aggregation have been identified recently in the context of network renormalization. The invariance property requires that edges are drawn with a specific probability that, in the annealed case, depends on a necessarily infinite-mean node fitness. The diverging mean determines many properties that are uncommon in models with independent edges, but at the same time widespread in real-world networks. Here we focus on the leading eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the adjacency matrix of the model, where the n nodes are assigned a Pareto(α)-distributed fitness with 0 < α < 1. We find that the leading eigenvalues are all of order square root of n, alternate in sign and are located at the intersection between the real axis and a logarithmic spiral in the complex plane, which we characterize analytically in terms of the Gamma function. We also calculate the associated eigenvectors, finding that they display complexvalued scaling exponents and log-periodicity, which are signatures of discrete scale invariance. In contrast with the typical finite-rank behaviour of random graphs with finite-mean variables, we find that a growing number of the leading eigenvalues emerges from the bulk, whose edge extends up to order square root of n and therefore reaches the same scale as that of the structural eigenvalues.
10 Sep 2025
CyberRAG introduces an agent-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework to classify cyber attacks and generate structured reports, enhancing real-time threat analysis for Security Operations Centers. The system achieved a 94.92% overall classification accuracy and produced high-quality, interpretable explanations validated by expert evaluation.
This review paper by Gabrielli, Garlaschelli, Patil, and Serrano systematically surveys efforts to adapt the Renormalization Group (RG) framework from physics to complex, heterogeneous networks. It details principled approaches like Geometric, Laplacian, and Multiscale Renormalization that offer methods for consistently understanding network properties across various scales.
Lying at the interface between Network Science and Machine Learning, node embedding algorithms take a graph as input and encode its structure onto output vectors that represent nodes in an abstract geometric space, enabling various vector-based downstream tasks such as network modelling, data compression, link prediction, and community detection. Two apparently unrelated limitations affect these algorithms. On one hand, it is not clear what the basic operation defining vector spaces, i.e. the vector sum, corresponds to in terms of the original nodes in the network. On the other hand, while the same input network can be represented at multiple levels of resolution by coarse-graining the constituent nodes into arbitrary block-nodes, the relationship between node embeddings obtained at different hierarchical levels is not understood. Here, building on recent results in network renormalization theory, we address these two limitations at once and define a multiscale node embedding method that, upon arbitrary coarse-grainings, ensures statistical consistency of the embedding vector of a block-node with the sum of the embedding vectors of its constituent nodes. We illustrate the power of this approach on two economic networks that can be naturally represented at multiple resolution levels: namely, the international trade between (sets of) countries and the input-output flows among (sets of) industries in the Netherlands. We confirm the statistical consistency between networks retrieved from coarse-grained node vectors and networks retrieved from sums of fine-grained node vectors, a result that cannot be achieved by alternative methods. Several key network properties, including a large number of triangles, are successfully replicated already from embeddings of very low dimensionality, allowing for the generation of faithful replicas of the original networks at arbitrary resolution levels.
In machine learning, graph embedding algorithms seek low-dimensional representations of the input network data, thereby allowing for downstream tasks on compressed encodings. Recently, within the framework of network renormalization, multi-scale embeddings that remain consistent under an arbitrary aggregation of nodes onto block-nodes, and consequently under an arbitrary change of resolution of the input network data, have been proposed. Here we investigate such multi-scale graph embeddings in the modified context where the input network is not entirely observable, due to data limitations or privacy constraints. This situation is typical for financial and economic networks, where connections between individual banks or firms are hidden due to confidentiality, and one has to probabilistically reconstruct the underlying network from aggregate information. We first consider state-of-the-art network reconstruction techniques based on the maximum-entropy principle, which is designed to operate optimally at a fixed resolution level. We then discuss the limitations of these methods when they are used as graph embeddings to yield predictions across different resolution levels. Finally, we propose their natural 'renormalizable' counterparts derived from the distinct principle of scale invariance, yielding consistent graph embeddings for multi-scale network reconstruction. We illustrate these methods on national economic input-output networks and on international trade networks, which can be naturally represented at multiple levels of industrial and geographic resolution, respectively.
Researchers from the University of Naples Federico II mapped the current landscape of Generative AI (GenAI) applications in Network Monitoring and Management (NMM), categorizing its use across five key network operations and detailing the adaptation of Transformer-based models. The survey highlights that while GenAI demonstrates potential for enhancing network efficiency and automation, challenges remain in model adaptation, data quality, and the limited reproducibility of existing research.
12 Sep 2025
Migration patterns are complex and context-dependent, with the distances migrants travel varying greatly depending on socio-economic and demographic factors. While global migration studies often focus on Western countries, there is a crucial gap in our understanding of migration dynamics within the African continent, particularly in West Africa. Using data from over 60,000 individuals from eight West African countries, this study examines the determinants of migration distance in the region. Our analysis reveals a bimodal distribution of migration distances: while most migrants travel locally within a hundred km, a smaller yet significant portion undertakes long-distance journeys, often exceeding 3,000 km. Socio-economic factors such as employment status, marital status and level of education play a decisive role in determining migration distances. Unemployed migrants, for instance, travel substantially farther (1,467 km on average) than their employed counterparts (295 km). Furthermore, we find that conflict-induced migration is particularly variable, with migrants fleeing violence often undertaking longer and riskier journeys. Our findings highlight the importance of considering both local and long-distance migration in policy decisions and support systems, as well as the need for a comprehensive understanding of migration in non-Western contexts. This study contributes to the broader discourse on human mobility by providing new insights into migration patterns in Western Africa, which in turn has implications for global migration research and policy development.
In this paper, we propose a very efficient numerical method based on the
L-BFGS-B algorithm for identifying linear and nonlinear discrete-time
state-space models, possibly under ℓ1 and group-Lasso regularization for
reducing model complexity. For the identification of linear models, we show
that, compared to classical linear subspace methods, the approach often
provides better results, is much more general in terms of the loss and
regularization terms used (such as penalties for enforcing system stability),
and is also more stable from a numerical point of view. The proposed method not
only enriches the existing set of linear system identification tools but can
also be applied to identifying a very broad class of parametric nonlinear
state-space models, including recurrent neural networks. We illustrate the
approach on synthetic and experimental datasets and apply it to solve a
challenging industrial robot benchmark for nonlinear multi-input/multi-output
system identification. A Python implementation of the proposed identification
method is available in the package jax-sysid, available at
this https URL
05 Sep 2024
Researchers introduce a method leveraging the spectral radius of financial networks as an early-warning signal for systemic risk, demonstrating its ability to detect structural changes in the Dutch Interbank Network during the 2008 crisis and providing a computationally efficient approximation for its expected value.
26 Nov 2025
Many complex systems - be they financial, natural, or social - are composed of units - such as stocks, neurons, or agents - whose joint activity can be represented as a multivariate time series. An issue of both practical and theoretical importance concerns the possibility of inferring the presence of a static relationship between any two units solely from their dynamic state. The present contribution aims at tackling such an issue within the frame of traditional hypothesis testing: briefly speaking, our suggestion is that of linking any two units if behaving in a sufficiently similar way. To achieve such a goal, we project a multivariate time series onto a signed graph by i) comparing the empirical properties of the former with those expected under a suitable benchmark and ii) linking any two units with a positive (negative) edge in case the corresponding series shares a significantly large number of concordant (discordant) values. To define our benchmarks, we adopt an information-theoretic approach that is rooted into the constrained maximisation of Shannon entropy, a procedure inducing an ensemble of multivariate time series that preserves some of the empirical properties on average, while randomising everything else. We showcase the possible applications of our method by addressing one of the most timely issues in the domain of neurosciences, i.e. that of determining if brain networks are frustrated or not, and, if so, to what extent. As our results suggest, this is indeed the case, with the major contribution to the underlying negative subgraph coming from the subcortical structures (and, to a lesser extent, from the limbic regions). At the mesoscopic level, the minimisation of the Bayesian Information Criterion, instantiated with the Signed Stochastic Block Model, reveals that brain areas gather into modules aligning with the statistical variant of the Relaxed Balance Theory.
11 Nov 2025
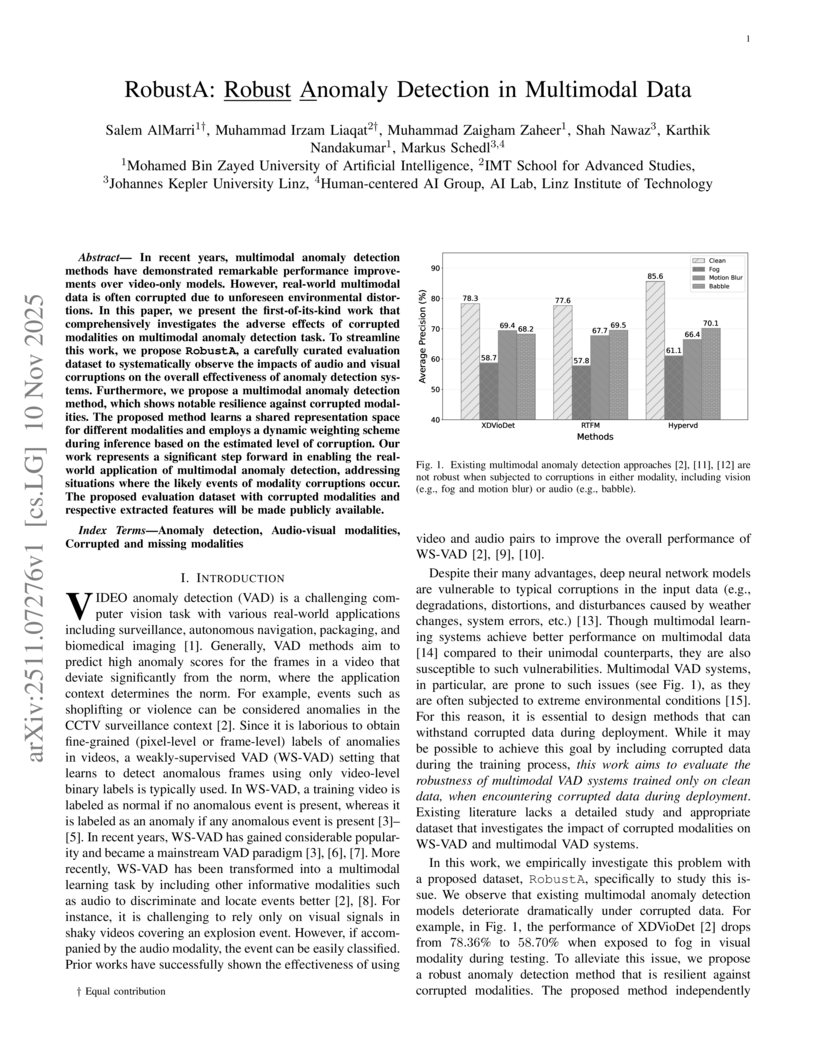
In recent years, multimodal anomaly detection methods have demonstrated remarkable performance improvements over video-only models. However, real-world multimodal data is often corrupted due to unforeseen environmental distortions. In this paper, we present the first-of-its-kind work that comprehensively investigates the adverse effects of corrupted modalities on multimodal anomaly detection task. To streamline this work, we propose RobustA, a carefully curated evaluation dataset to systematically observe the impacts of audio and visual corruptions on the overall effectiveness of anomaly detection systems. Furthermore, we propose a multimodal anomaly detection method, which shows notable resilience against corrupted modalities. The proposed method learns a shared representation space for different modalities and employs a dynamic weighting scheme during inference based on the estimated level of corruption. Our work represents a significant step forward in enabling the real-world application of multimodal anomaly detection, addressing situations where the likely events of modality corruptions occur. The proposed evaluation dataset with corrupted modalities and respective extracted features will be made publicly available.
Statistical physics of complex systems exploits network theory not only to
model, but also to effectively extract information from many dynamical
real-world systems. A pivotal case of study is given by financial systems:
market prediction represents an unsolved scientific challenge yet with crucial
implications for society, as financial crises have devastating effects on real
economies. Thus, nowadays the quest for a robust estimator of market efficiency
is both a scientific and institutional priority. In this work we study the
visibility graphs built from the time series of several trade market indices.
We propose a validation procedure for each link of these graphs against a null
hypothesis derived from ARCH-type modeling of such series. Building on this
framework, we devise a market indicator that turns out to be highly correlated
and even predictive of financial instability periods.
06 May 2016
The role of Network Theory in the study of the financial crisis has been
widely spotted in the latest years. It has been shown how the network topology
and the dynamics running on top of it can trigger the outbreak of large
systemic crisis. Following this methodological perspective we introduce here
the Accounting Network, i.e. the network we can extract through vector
similarities techniques from companies' financial statements. We build the
Accounting Network on a large database of worldwide banks in the period
2001-2013, covering the onset of the global financial crisis of mid-2007. After
a careful data cleaning, we apply a quality check in the construction of the
network, introducing a parameter (the Quality Ratio) capable of trading off the
size of the sample (coverage) and the representativeness of the financial
statements (accuracy). We compute several basic network statistics and check,
with the Louvain community detection algorithm, for emerging communities of
banks. Remarkably enough sensible regional aggregations show up with the
Japanese and the US clusters dominating the community structure, although the
presence of a geographically mixed community points to a gradual convergence of
banks into similar supranational practices. Finally, a Principal Component
Analysis procedure reveals the main economic components that influence
communities' heterogeneity. Even using the most basic vector similarity
hypotheses on the composition of the financial statements, the signature of the
financial crisis clearly arises across the years around 2008. We finally
discuss how the Accounting Networks can be improved to reflect the best
practices in the financial statement analysis.
This paper introduces Natural Language Processing for identifying ``true'' green patents from official supporting documents. We start our training on about 12.4 million patents that had been classified as green from previous literature. Thus, we train a simple neural network to enlarge a baseline dictionary through vector representations of expressions related to environmental technologies. After testing, we find that ``true'' green patents represent about 20\% of the total of patents classified as green from previous literature. We show heterogeneity by technological classes, and then check that `true' green patents are about 1\% less cited by following inventions. In the second part of the paper, we test the relationship between patenting and a dashboard of firm-level financial accounts in the European Union. After controlling for reverse causality, we show that holding at least one ``true'' green patent raises sales, market shares, and productivity. If we restrict the analysis to high-novelty ``true'' green patents, we find that they also yield higher profits. Our findings underscore the importance of using text analyses to gauge finer-grained patent classifications that are useful for policymaking in different domains.
In safety-critical applications that rely on the solution of an optimization problem, the certification of the optimization algorithm is of vital importance. Certification and suboptimality results are available for a wide range of optimization algorithms. However, a typical underlying assumption is that the operations performed by the algorithm are exact, i.e., that there is no numerical error during the mathematical operations, which is hardly a valid assumption in a real hardware implementation. This is particularly true in the case of fixed-point hardware, where computational inaccuracies are not uncommon. This article presents a certification procedure for the proximal gradient method for box-constrained QP problems implemented in fixed-point arithmetic. The procedure provides a method to select the minimal fractional precision required to obtain a certain suboptimality bound, indicating the maximum number of iterations of the optimization method required to obtain it. The procedure makes use of formal verification methods to provide arbitrarily tight bounds on the suboptimality guarantee. We apply the proposed certification procedure on the implementation of a non-trivial model predictive controller on 32-bit fixed-point hardware.
03 Apr 2025
We propose a novel approach for combining model predictive control (MPC) with
reinforcement learning (RL) to reduce online computation while achieving high
closed-loop tracking performance and constraint satisfaction. This method,
called Policy-Enhanced Partial Tightening (PEPT), approximates the optimal
value function through a Riccati recursion around a state-control trajectory
obtained by evaluating the RL policy. The result is a convex quadratic terminal
cost that can be seamlessly integrated into the MPC formulation. The proposed
controller is tested in simulations on a trajectory tracking problem for a
quadcopter with nonlinear dynamics and bounded state and control. The results
highlight PEPT's effectiveness, outperforming both pure RL policies and several
MPC variations. Compared to pure RL, PEPT achieves 1000 times lower constraint
violation cost with only twice the feedback time. Against the best MPC-based
policy, PEPT reduces constraint violations by 2 to 5 times and runs nearly 3
times faster while maintaining similar tracking performance. The code is
open-source at www.github.com/aghezz1/pept.
Our paper presents a methodology to study the heterogeneous effects of economy-wide shocks and applies it to the case of the impact of the COVID-19 crisis on exports. This methodology is applicable in scenarios where the pervasive nature of the shock hinders the identification of a control group unaffected by the shock, as well as the ex-ante definition of the intensity of the shock's exposure of each unit. In particular, our study investigates the effectiveness of various Machine Learning (ML) techniques in predicting firms' trade and, by building on recent developments in causal ML, uses these predictions to reconstruct the counterfactual distribution of firms' trade under different COVID-19 scenarios and to study treatment effect heterogeneity. Specifically, we focus on the probability of Colombian firms surviving in the export market under two different scenarios: a COVID-19 setting and a non-COVID-19 counterfactual situation. On average, we find that the COVID-19 shock decreased a firm's probability of surviving in the export market by about 20 percentage points in April 2020. We study the treatment effect heterogeneity by employing a classification analysis that compares the characteristics of the firms on the tails of the estimated distribution of the individual treatment effects.
The integration of bots in Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs) fosters
efficiency and automation. However, their use is also associated with predatory
trading and market manipulation, and can pose threats to system integrity. It
is therefore essential to understand the extent of bot deployment in DLTs;
despite this, current detection systems are predominantly rule-based and lack
flexibility. In this study, we present a novel approach that utilizes machine
learning for the detection of financial bots on the Ethereum platform. First,
we systematize existing scientific literature and collect anecdotal evidence to
establish a taxonomy for financial bots, comprising 7 categories and 24
subcategories. Next, we create a ground-truth dataset consisting of 133 human
and 137 bot addresses. Third, we employ both unsupervised and supervised
machine learning algorithms to detect bots deployed on Ethereum. The
highest-performing clustering algorithm is a Gaussian Mixture Model with an
average cluster purity of 82.6%, while the highest-performing model for binary
classification is a Random Forest with an accuracy of 83%. Our machine
learning-based detection mechanism contributes to understanding the Ethereum
ecosystem dynamics by providing additional insights into the current bot
landscape.
Federated learning (FL) goes beyond traditional, centralized machine learning by distributing model training among a large collection of edge clients. These clients cooperatively train a global, e.g., cloud-hosted, model without disclosing their local, private training data. The global model is then shared among all the participants which use it for local predictions. In this paper, we put forward a novel attacker model aiming at turning FL systems into covert channels to implement a stealth communication infrastructure. The main intuition is that, during federated training, a malicious sender can poison the global model by submitting purposely crafted examples. Although the effect of the model poisoning is negligible to other participants, and does not alter the overall model performance, it can be observed by a malicious receiver and used to transmit a single bit.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.