JD.COM
Developed by JD.com and academic partners, xLLM is an intelligent and efficient LLM inference framework optimized for high-performance, enterprise-grade serving on diverse AI accelerators, achieving up to 2.2 times throughput improvement over leading baselines like vLLM-Ascend.
FastVID, developed by researchers from Tsinghua University and JD.com, accelerates Video Large Language Models by introducing a dynamic density pruning framework. It achieves a 7.1x speedup in the prefilling stage and prunes over 90% of video tokens while retaining 98.0% of the original model's accuracy.
Researchers from Australian National University, University of Sydney, Tencent, and other institutions developed "Motion Anything," a framework for human motion generation that adaptively integrates multimodal conditions like text and music. It employs an attention-based masking strategy to dynamically prioritize motion segments, outperforming prior models in text-to-motion (e.g., 15% lower FID on HumanML3D) and music-to-dance tasks, and introduces a new Text-Music-Dance dataset.
Researchers at JD.COM developed LREF, an LLM-based framework to improve e-commerce search relevance by addressing data quality, reasoning optimization, and optimistic bias. The framework, incorporating a novel data selection strategy, Multi-Chain of Thought tuning, and Direct Preference Optimization, demonstrated increased user conversion and click-through rates on the JD.COM platform.
Traditional sparse and dense retrieval methods struggle to leverage general world knowledge and often fail to capture the nuanced features of queries and products. With the advent of large language models (LLMs), industrial search systems have started to employ LLMs to generate identifiers for product retrieval. Commonly used identifiers include (1) static/semantic IDs and (2) product term sets. The first approach requires creating a product ID system from scratch, missing out on the world knowledge embedded within LLMs. While the second approach leverages this general knowledge, the significant difference in word distribution between queries and products means that product-based identifiers often do not align well with user search queries, leading to missed product recalls. Furthermore, when queries contain numerous attributes, these algorithms generate a large number of identifiers, making it difficult to assess their quality, which results in low overall recall efficiency.
To address these challenges, this paper introduces a novel e-commerce retrieval paradigm: the Generative Retrieval and Alignment Model (GRAM). GRAM employs joint training on text information from both queries and products to generate shared text identifier codes, effectively bridging the gap between queries and products. This approach not only enhances the connection between queries and products but also improves inference efficiency. The model uses a co-alignment strategy to generate codes optimized for maximizing retrieval efficiency. Additionally, it introduces a query-product scoring mechanism to compare product values across different codes, further boosting retrieval efficiency. Extensive offline and online A/B testing demonstrates that GRAM significantly outperforms traditional models and the latest generative retrieval models, confirming its effectiveness and practicality.
13 Oct 2025
JD.com researchers developed SHERLOCK, an LLM-enhanced framework for e-commerce risk management that integrates dynamic knowledge adaptation and a reflection mechanism. The system reduces expert review time by 387% and achieves an expert acceptance rate of 82% in live operations.
Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) offers a parameter-efficient paradigm for tuning large models. While recent spectral initialization methods improve convergence and performance over the naive "Noise & Zeros" scheme, their extra computational and storage overhead undermines efficiency. In this paper, we establish update magnitude as the fundamental driver of LoRA performance and propose LoRAM, a magnitude-driven "Basis & Basis" initialization scheme that matches spectral methods without their inefficiencies. Our key contributions are threefold: (i) Magnitude of weight updates determines convergence. We prove low-rank structures intrinsically bound update magnitudes, unifying hyperparameter tuning in learning rate, scaling factor, and initialization as mechanisms to optimize magnitude regulation. (ii) Spectral initialization succeeds via magnitude amplification. We demystify that the presumed knowledge-driven benefit of the spectral component essentially arises from the boost in the weight update magnitude. (iii) A novel and compact initialization strategy, LoRAM, scales deterministic orthogonal bases using pretrained weight magnitudes to simulate spectral gains. Extensive experiments show that LoRAM serves as a strong baseline, retaining the full efficiency of LoRA while matching or outperforming spectral initialization across benchmarks.
RePainter introduces a reinforcement learning framework for e-commerce object removal, leveraging spatial-matting trajectory refinement and a local-global composite reward mechanism. The method generates visually seamless and semantically coherent images, outperforming existing state-of-the-art inpainting techniques across multiple quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
The Logic-of-Thought (LoT) framework enhances large language models' logical reasoning by augmenting their input context with expanded natural language logical descriptions derived from propositional logic laws. This zero-shot prompting method consistently boosts performance across various reasoning tasks and prompting techniques, notably improving accuracy by up to +9.82% on ReClor with GPT-3.5 and outperforming other neuro-symbolic methods.
16 Sep 2025
This paper presents data-driven approaches for integrated assortment planning and inventory allocation that significantly improve fulfillment efficiency at JD\,.com, a leading E-commerce company. JD\,.com uses a two-level distribution network that includes regional distribution centers (RDCs) and front distribution centers (FDCs). Selecting products to stock at FDCs and then optimizing daily inventory allocation from RDCs to FDCs is critical to improving fulfillment efficiency, which is crucial for enhancing customer experiences. For assortment planning, we propose efficient algorithms to maximize the number of orders that can be fulfilled by FDCs (local fulfillment). For inventory allocation, we develop a novel end-to-end algorithm that integrates forecasting, optimization, and simulation to minimize lost sales and inventory transfer costs. Numerical experiments demonstrate that our methods outperform existing approaches, increasing local order fulfillment rates by 0.54% and our inventory allocation algorithm increases FDC demand satisfaction rates by 1.05%. Considering the high-volume operations of JD\,.com, with millions of weekly orders per region, these improvements yield substantial benefits beyond the company's established supply chain system. Implementation across JD\,.com's network has reduced costs, improved stock availability, and increased local order fulfillment rates for millions of orders annually.
Time series neural networks perform exceptionally well in real-world applications but encounter challenges such as limited scalability, poor generalization, and suboptimal zero-shot performance. Inspired by large language models, there is interest in developing large time series models (LTM) to address these issues. However, current methods struggle with training complexity, adapting human feedback, and achieving high predictive accuracy. We introduce TimeHF, a novel pipeline for creating LTMs with 6 billion parameters, incorporating human feedback. We use patch convolutional embedding to capture long time series information and design a human feedback mechanism called time-series policy optimization. Deployed in this http URL's supply chain, TimeHF handles automated replenishment for over 20,000 products, improving prediction accuracy by 33.21% over existing methods. This work advances LTM technology and shows significant industrial benefits.
Robust Reinforcement Learning aims to find the optimal policy with some
extent of robustness to environmental dynamics. Existing learning algorithms
usually enable the robustness through disturbing the current state or
simulating environmental parameters in a heuristic way, which lack quantified
robustness to the system dynamics (i.e. transition probability). To overcome
this issue, we leverage Wasserstein distance to measure the disturbance to the
reference transition kernel. With Wasserstein distance, we are able to connect
transition kernel disturbance to the state disturbance, i.e. reduce an
infinite-dimensional optimization problem to a finite-dimensional risk-aware
problem. Through the derived risk-aware optimal Bellman equation, we show the
existence of optimal robust policies, provide a sensitivity analysis for the
perturbations, and then design a novel robust learning algorithm--Wasserstein
Robust Advantage Actor-Critic algorithm (WRAAC). The effectiveness of the
proposed algorithm is verified in the Cart-Pole environment.
15 Jul 2025
A two-stage generative framework, GenCTR, enhances Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction by pre-training a conditional generative model on user behavior sequences for next-item prediction. This method, deployed at JD.com, improved online CTR by up to 1.88% and Revenue Per Mille by up to 2.91% during A/B testing.
24 Jun 2025
JoyAgents-R1 introduces a joint evolutionary framework for heterogeneous multi-LLM agents, adapting Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with node-wise sampling and an innovative memory evolution mechanism. The framework achieves competitive performance, particularly in e-commerce function-call tasks (48% accuracy), often outperforming larger open-source models while utilizing smaller 3B parameter models.
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have been rapidly advancing, enabling cross-modal understanding and generation, and propelling artificial intelligence towards artificial general intelligence. However, existing MLLM inference systems are typically designed based on the architecture of language models, integrating image processing and language processing as a single scheduling unit. This design struggles to accommodate the heterogeneous demands of different stages in terms of computational resources, memory access patterns, and service-level objectives (SLOs), leading to low resource utilization and high request latency, ultimately failing to meet the service requirements of diverse inference scenarios.
To address these challenges, we propose HydraInfer, an efficient MLLM inference system that adopts a Hybrid Encode-Prefill-Decode (EPD) Disaggregation architecture. By scheduling the three stages - encode, prefill, and decode - onto separate heterogeneous inference instances, the system flexibly reallocates resources across stages, significantly reducing idle computation, alleviating resource bottlenecks, and improving overall system throughput and scalability. In addition, HydraInfer supports a stage-level batching strategy that enhances load balancing, enables parallel execution of visual and language models, and further optimizes inference performance. Experiments under real multimodal inference workloads demonstrate that HydraInfer can achieve up to 4x higher inference throughput compared to state-of-the-art systems (e.g., vLLM) on a single-node 8xH800 GPU cluster, while meeting the 90th percentile request SLO.
Large language models (LLMs) have recently demonstrated the ability to act as function call agents by invoking external tools, enabling them to solve tasks beyond their static knowledge. However, existing agents typically call tools step by step at a time without a global view of task structure. As tools depend on each other, this leads to error accumulation and limited scalability, particularly when scaling to thousands of tools. To address these limitations, we propose NaviAgent, a novel bilevel architecture that decouples task planning from tool execution through graph-based modeling of the tool ecosystem. At the task-planning level, the LLM-based agent decides whether to respond directly, clarify user intent, invoke a toolchain, or execute tool outputs, ensuring broad coverage of interaction scenarios independent of inter-tool complexity. At the execution level, a continuously evolving Tool World Navigation Model (TWNM) encodes structural and behavioral relations among tools, guiding the agent to generate scalable and robust invocation sequences. By incorporating feedback from real tool interactions, NaviAgent supports closed-loop optimization of planning and execution, moving beyond tool calling toward adaptive navigation of large-scale tool ecosystems. Experiments show that NaviAgent achieves the best task success rates across models and tasks, and integrating TWMN further boosts performance by up to 17 points on complex tasks, underscoring its key role in toolchain orchestration.
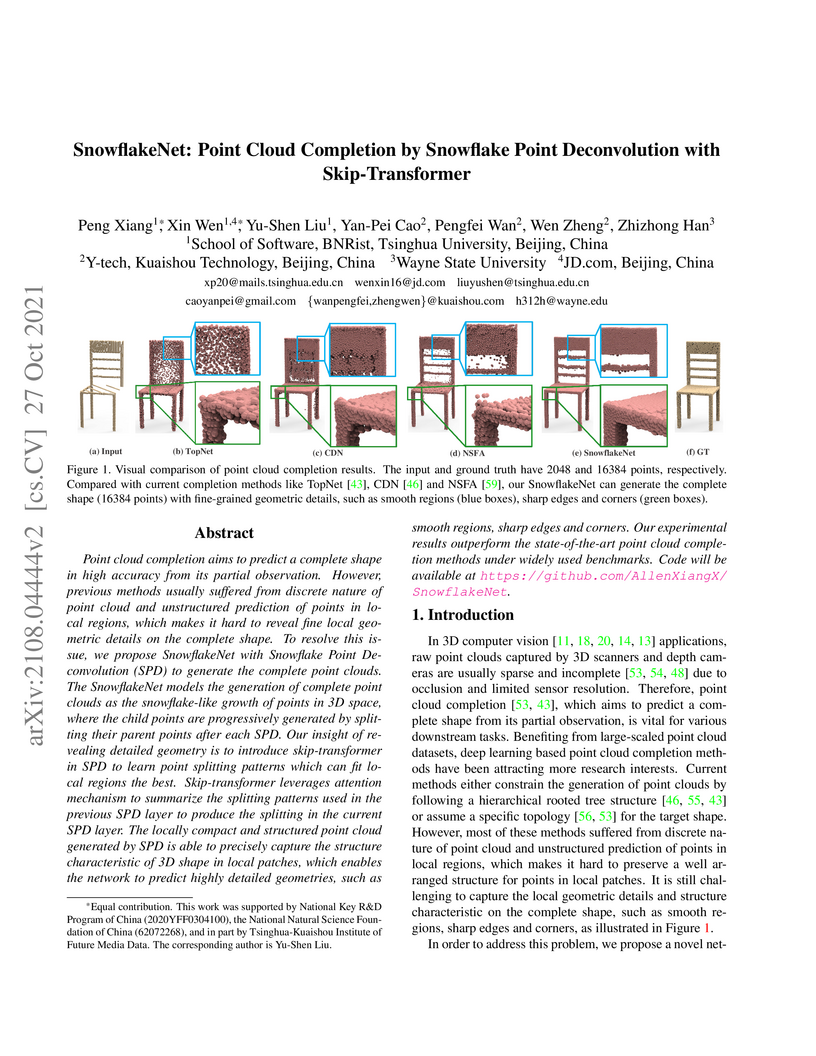
SnowflakeNet presents a novel method for 3D point cloud completion, employing snowflake point deconvolution with a skip-transformer to generate fine-grained geometric details from partial inputs. The approach achieves state-of-the-art results, reducing the L1 Chamfer distance on the PCN dataset by 10.5% and the L2 Chamfer distance on the Completion3D dataset by 17.3%.
Most text-video retrieval methods utilize the text-image pre-trained models
like CLIP as a backbone. These methods process each sampled frame independently
by the image encoder, resulting in high computational overhead and limiting
practical deployment. Addressing this, we focus on efficient text-video
retrieval by tackling two key challenges: 1. From the perspective of trainable
parameters, current parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods incur high
inference costs; 2. From the perspective of model complexity, current token
compression methods are mainly designed for images to reduce spatial redundancy
but overlook temporal redundancy in consecutive frames of a video. To tackle
these challenges, we propose Temporal Token Merging (TempMe), a
parameter-efficient and training-inference efficient text-video retrieval
architecture that minimizes trainable parameters and model complexity.
Specifically, we introduce a progressive multi-granularity framework. By
gradually combining neighboring clips, we reduce spatio-temporal redundancy and
enhance temporal modeling across different frames, leading to improved
efficiency and performance. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of
our TempMe. Compared to previous parameter-efficient text-video retrieval
methods, TempMe achieves superior performance with just 0.50M trainable
parameters. It significantly reduces output tokens by 95% and GFLOPs by 51%,
while achieving a 1.8X speedup and a 4.4% R-Sum improvement. With full
fine-tuning, TempMe achieves a significant 7.9% R-Sum improvement, trains 1.57X
faster, and utilizes 75.2% GPU memory usage. The code is available at
this https URL
In recent years, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), which can naturally integrate
node information and topological structure, have been demonstrated to be
powerful in learning on graph data. These advantages of GNNs provide great
potential to advance social recommendation since data in social recommender
systems can be represented as user-user social graph and user-item graph; and
learning latent factors of users and items is the key. However, building social
recommender systems based on GNNs faces challenges. For example, the user-item
graph encodes both interactions and their associated opinions; social relations
have heterogeneous strengths; users involve in two graphs (e.g., the user-user
social graph and the user-item graph). To address the three aforementioned
challenges simultaneously, in this paper, we present a novel graph neural
network framework (GraphRec) for social recommendations. In particular, we
provide a principled approach to jointly capture interactions and opinions in
the user-item graph and propose the framework GraphRec, which coherently models
two graphs and heterogeneous strengths. Extensive experiments on two real-world
datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework GraphRec. Our
code is available at \url{https://github.com/wenqifan03/GraphRec-WWW19}
Auto-bidding systems are widely used in advertising to automatically determine bid values under constraints such as total budget and Return-on-Spend (RoS) targets. Existing works often assume that the value of an ad impression, such as the conversion rate, is known. This paper considers the more realistic scenario where the true value is unknown. We propose a novel method that uses conformal prediction to quantify the uncertainty of these values based on machine learning methods trained on historical bidding data with contextual features, without assuming the data are i.i.d. This approach is compatible with current industry systems that use machine learning to predict values. Building on prediction intervals, we introduce an adjusted value estimator derived from machine learning predictions, and show that it provides performance guarantees without requiring knowledge of the true value. We apply this method to enhance existing auto-bidding algorithms with budget and RoS constraints, and establish theoretical guarantees for achieving high reward while keeping RoS violations low. Empirical results on both simulated and real-world industrial datasets demonstrate that our approach improves performance while maintaining computational efficiency.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.