Jimei University
Open-Vocabulary semantic segmentation (OVSS) and domain generalization in semantic segmentation (DGSS) highlight a subtle complementarity that motivates Open-Vocabulary Domain-Generalized Semantic Segmentation (OV-DGSS). OV-DGSS aims to generate pixel-level masks for unseen categories while maintaining robustness across unseen domains, a critical capability for real-world scenarios such as autonomous driving in adverse conditions. We introduce Vireo, a novel single-stage framework for OV-DGSS that unifies the strengths of OVSS and DGSS for the first time. Vireo builds upon the frozen Visual Foundation Models (VFMs) and incorporates scene geometry via Depth VFMs to extract domain-invariant structural features. To bridge the gap between visual and textual modalities under domain shift, we propose three key components: (1) GeoText Prompts, which align geometric features with language cues and progressively refine VFM encoder representations; (2) Coarse Mask Prior Embedding (CMPE) for enhancing gradient flow for faster convergence and stronger textual influence; and (3) the Domain-Open-Vocabulary Vector Embedding Head (DOV-VEH), which fuses refined structural and semantic features for robust prediction. Comprehensive evaluation on these components demonstrates the effectiveness of our designs. Our proposed Vireo achieves the state-of-the-art performance and surpasses existing methods by a large margin in both domain generalization and open-vocabulary recognition, offering a unified and scalable solution for robust visual understanding in diverse and dynamic environments. Code is available at this https URL.
4KDehazeFlow introduces a method for ultra-high-definition image dehazing using a Flow Matching framework that balances perceptual quality and computational efficiency. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on UHD datasets like 4KID, I-HAZE, and O-HAZE, demonstrating notably lower computational overhead compared to existing approaches.
Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) have delivered remarkable performance in Domain Generalized Semantic Segmentation (DGSS). However, recent methods often overlook the fact that visual cues are susceptible, whereas the underlying geometry remains stable, rendering depth information more robust. In this paper, we investigate the potential of integrating depth information with features from VFMs, to improve the geometric consistency within an image and boost the generalization performance of VFMs. We propose a novel fine-tuning DGSS framework, named DepthForge, which integrates the visual cues from frozen DINOv2 or EVA02 and depth cues from frozen Depth Anything V2. In each layer of the VFMs, we incorporate depth-aware learnable tokens to continuously decouple domain-invariant visual and spatial information, thereby enhancing depth awareness and attention of the VFMs. Finally, we develop a depth refinement decoder and integrate it into the model architecture to adaptively refine multi-layer VFM features and depth-aware learnable tokens. Extensive experiments are conducted based on various DGSS settings and five different datsets as unseen target domains. The qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms alternative approaches with stronger performance, steadier visual-spatial attention, and superior generalization ability. In particular, DepthForge exhibits outstanding performance under extreme conditions (e.g., night and snow). Code is available at this https URL.
Copy-move forgery detection aims at detecting duplicated regions in a
suspected forged image, and deep learning based copy-move forgery detection
methods are in the ascendant. These deep learning based methods heavily rely on
synthetic training data, and the performance will degrade when facing new
tasks. In this paper, we propose a Transformer-style copy-move forgery
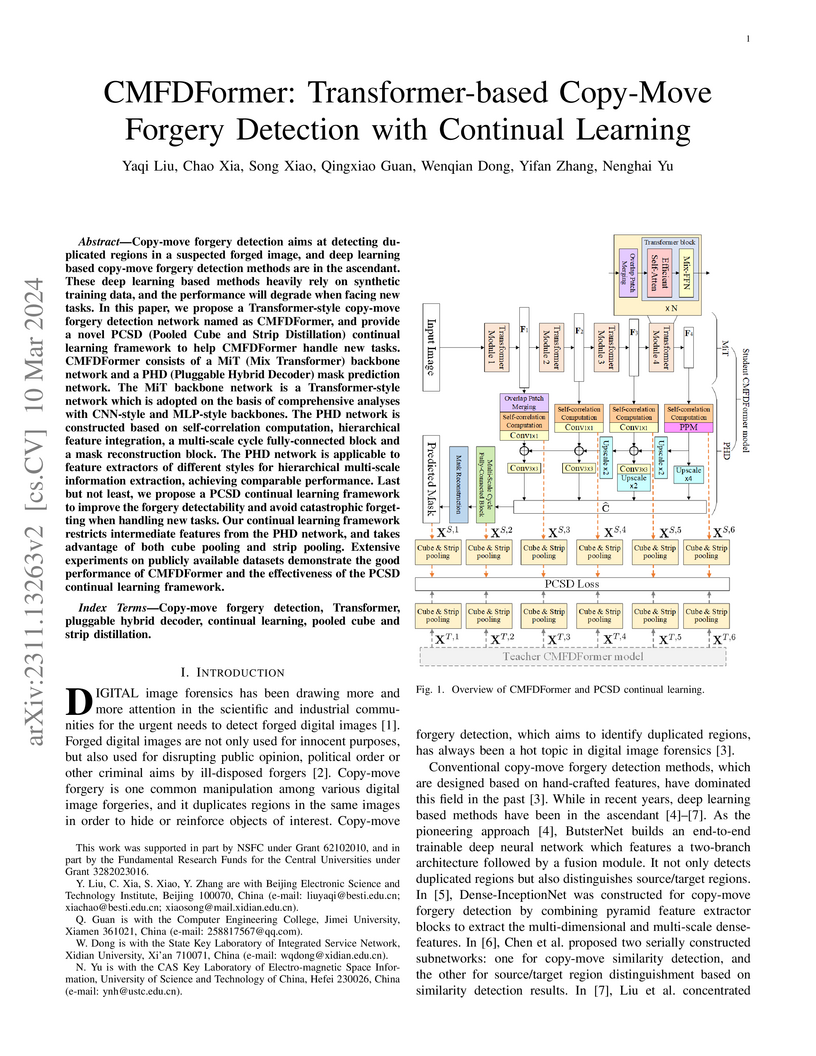
detection network named as CMFDFormer, and provide a novel PCSD (Pooled Cube
and Strip Distillation) continual learning framework to help CMFDFormer handle
new tasks. CMFDFormer consists of a MiT (Mix Transformer) backbone network and
a PHD (Pluggable Hybrid Decoder) mask prediction network. The MiT backbone
network is a Transformer-style network which is adopted on the basis of
comprehensive analyses with CNN-style and MLP-style backbones. The PHD network
is constructed based on self-correlation computation, hierarchical feature
integration, a multi-scale cycle fully-connected block and a mask
reconstruction block. The PHD network is applicable to feature extractors of
different styles for hierarchical multi-scale information extraction, achieving
comparable performance. Last but not least, we propose a PCSD continual
learning framework to improve the forgery detectability and avoid catastrophic
forgetting when handling new tasks. Our continual learning framework restricts
intermediate features from the PHD network, and takes advantage of both cube
pooling and strip pooling. Extensive experiments on publicly available datasets
demonstrate the good performance of CMFDFormer and the effectiveness of the
PCSD continual learning framework.
Event cameras have gained increasing popularity in computer vision due to their ultra-high dynamic range and temporal resolution. However, event networks heavily rely on task-specific designs due to the unstructured data distribution and spatial-temporal (S-T) inhomogeneity, making it hard to reuse existing architectures for new tasks. We propose OmniEvent, the first unified event representation learning framework that achieves SOTA performance across diverse tasks, fully removing the need of task-specific designs. Unlike previous methods that treat event data as 3D point clouds with manually tuned S-T scaling weights, OmniEvent proposes a decouple-enhance-fuse paradigm, where the local feature aggregation and enhancement is done independently on the spatial and temporal domains to avoid inhomogeneity issues. Space-filling curves are applied to enable large receptive fields while improving memory and compute efficiency. The features from individual domains are then fused by attention to learn S-T interactions. The output of OmniEvent is a grid-shaped tensor, which enables standard vision models to process event data without architecture change. With a unified framework and similar hyper-parameters, OmniEvent out-performs (tasks-specific) SOTA by up to 68.2% across 3 representative tasks and 10 datasets (Fig.1). Code will be ready in this https URL .
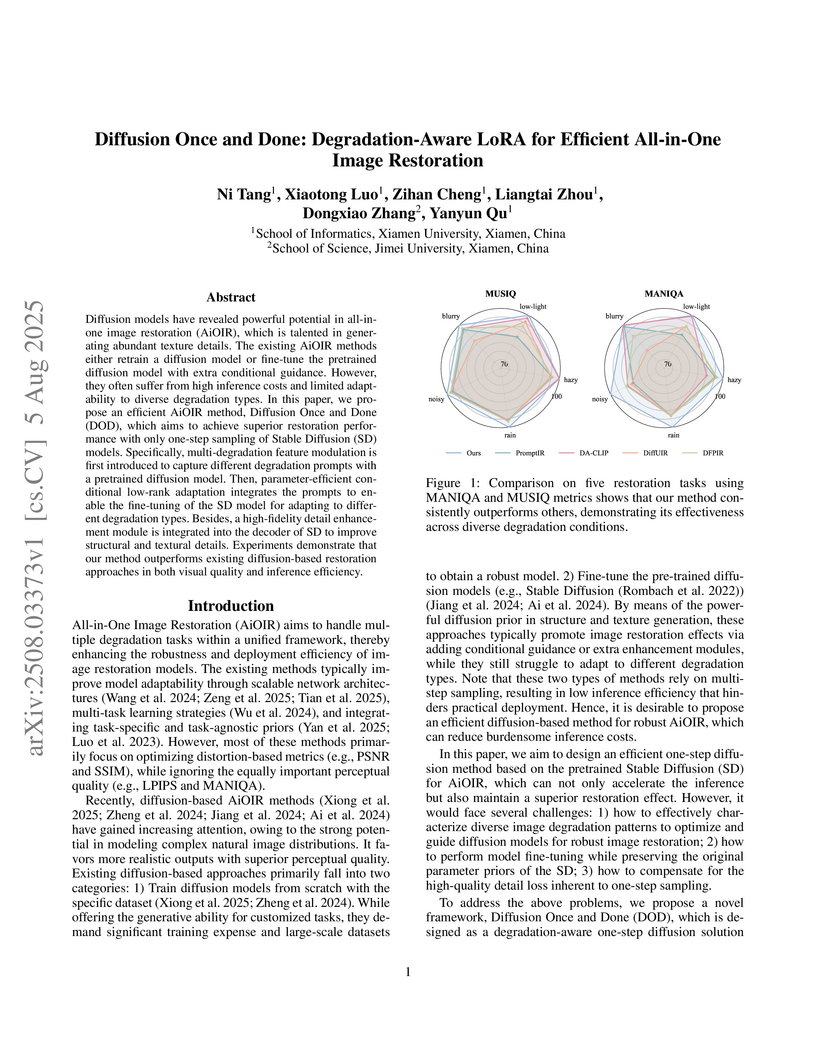
Diffusion models have revealed powerful potential in all-in-one image restoration (AiOIR), which is talented in generating abundant texture details. The existing AiOIR methods either retrain a diffusion model or fine-tune the pretrained diffusion model with extra conditional guidance. However, they often suffer from high inference costs and limited adaptability to diverse degradation types. In this paper, we propose an efficient AiOIR method, Diffusion Once and Done (DOD), which aims to achieve superior restoration performance with only one-step sampling of Stable Diffusion (SD) models. Specifically, multi-degradation feature modulation is first introduced to capture different degradation prompts with a pretrained diffusion model. Then, parameter-efficient conditional low-rank adaptation integrates the prompts to enable the fine-tuning of the SD model for adapting to different degradation types. Besides, a high-fidelity detail enhancement module is integrated into the decoder of SD to improve structural and textural details. Experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms existing diffusion-based restoration approaches in both visual quality and inference efficiency.
Attention mechanisms have revolutionized natural language processing.
Combining them with quantum computing aims to further advance this technology.
This paper introduces a novel Quantum Mixed-State Self-Attention Network
(QMSAN) for natural language processing tasks. Our model leverages quantum
computing principles to enhance the effectiveness of self-attention mechanisms.
QMSAN uses a quantum attention mechanism based on mixed state, allowing for
direct similarity estimation between queries and keys in the quantum domain.
This approach leads to more effective attention coefficient calculations. We
also propose an innovative quantum positional encoding scheme, implemented
through fixed quantum gates within the circuit, improving the model's ability
to capture sequence information without additional qubit resources. In
numerical experiments of text classification tasks on public datasets, QMSAN
outperforms Quantum Self-Attention Neural Network (QSANN). Furthermore, we
demonstrate QMSAN's robustness in different quantum noise environments,
highlighting its potential for near-term quantum devices.
04 May 2025
This survey provides a comprehensive classification and analysis of privacy risks in Large Language Models (LLMs), outlining various leakage mechanisms and attack vectors. It also surveys existing and emerging protection techniques, offering a framework for understanding and addressing the multifaceted privacy challenges in LLM development and deployment.
Large Language Models (LLMs), now a foundation in advancing natural language processing, power applications such as text generation, machine translation, and conversational systems. Despite their transformative potential, these models inherently rely on massive amounts of training data, often collected from diverse and uncurated sources, which exposes them to serious data security risks. Harmful or malicious data can compromise model behavior, leading to issues such as toxic output, hallucinations, and vulnerabilities to threats such as prompt injection or data poisoning. As LLMs continue to be integrated into critical real-world systems, understanding and addressing these data-centric security risks is imperative to safeguard user trust and system reliability. This survey offers a comprehensive overview of the main data security risks facing LLMs and reviews current defense strategies, including adversarial training, RLHF, and data augmentation. Additionally, we categorize and analyze relevant datasets used for assessing robustness and security across different domains, providing guidance for future research. Finally, we highlight key research directions that focus on secure model updates, explainability-driven defenses, and effective governance frameworks, aiming to promote the safe and responsible development of LLM technology. This work aims to inform researchers, practitioners, and policymakers, driving progress toward data security in LLMs.
A comprehensive survey synthesizes research on Large Language Model (LLM) security by systematically categorizing attack vectors and defense strategies, analyzing vulnerabilities in both model architectures and applications while mapping current challenges and future research directions through examination of prevention and detection approaches across multiple Chinese institutions.
pyFAST is a modular PyTorch framework that addresses challenges in time series modeling by providing native support for multi-source, sparse, and irregular data, and integrating LLM-inspired architectures for alignment-free data fusion. The framework decouples data processing from model computation, enabling researchers to rapidly prototype and evaluate advanced time series models efficiently.
With the continuous improvement of device imaging resolution, the popularity of Ultra-High-Definition (UHD) images is increasing. Unfortunately, existing methods for fusing multi-exposure images in dynamic scenes are designed for low-resolution images, which makes them inefficient for generating high-quality UHD images on a resource-constrained device. To alleviate the limitations of extremely long-sequence inputs, inspired by the Large Language Model (LLM) for processing infinitely long texts, we propose a novel learning paradigm to achieve UHD multi-exposure dynamic scene image fusion on a single consumer-grade GPU, named Infinite Pixel Learning (IPL). The design of our approach comes from three key components: The first step is to slice the input sequences to relieve the pressure generated by the model processing the data stream; Second, we develop an attention cache technique, which is similar to KV cache for infinite data stream processing; Finally, we design a method for attention cache compression to alleviate the storage burden of the cache on the device. In addition, we provide a new UHD benchmark to evaluate the effectiveness of our method. Extensive experimental results show that our method maintains high-quality visual performance while fusing UHD dynamic multi-exposure images in real-time (>40fps) on a single consumer-grade GPU.
The rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has introduced Deep
Neural Network (DNN)-based tasks to the ecosystem of vehicular networks. These
tasks are often computation-intensive, requiring substantial computation
resources, which are beyond the capability of a single vehicle. To address this
challenge, Vehicular Edge Computing (VEC) has emerged as a solution, offering
computing services for DNN-based tasks through resource pooling via
Vehicle-to-Vehicle/Infrastructure (V2V/V2I) communications. In this paper, we
formulate the problem of joint DNN partitioning, task offloading, and resource
allocation in VEC as a dynamic long-term optimization. Our objective is to
minimize the DNN-based task completion time while guaranteeing the system
stability over time. To this end, we first leverage a Lyapunov optimization
technique to decouple the original long-term optimization with stability
constraints into a per-slot deterministic problem. Afterwards, we propose a
Multi-Agent Diffusion-based Deep Reinforcement Learning (MAD2RL) algorithm,
incorporating the innovative use of diffusion models to determine the optimal
DNN partitioning and task offloading decisions. Furthermore, we integrate
convex optimization techniques into MAD2RL as a subroutine to allocate
computation resources, enhancing the learning efficiency. Through simulations
under real-world movement traces of vehicles, we demonstrate the superior
performance of our proposed algorithm compared to existing benchmark solutions.
20 Sep 2025
Learning large-scale pre-trained models on broad-ranging data and then transfer to a wide range of target tasks has become the de facto paradigm in many machine learning (ML) communities. Such big models are not only strong performers in practice but also offer a promising way to break out of the task-specific modeling restrictions, thereby enabling task-agnostic and unified ML systems. However, such a popular paradigm is mainly unexplored by the recommender systems (RS) community. A critical issue is that standard recommendation models are primarily built on categorical identity features. That is, the users and the interacted items are represented by their unique IDs, which are generally not shareable across different systems or platforms. To pursue the transferable recommendations, we propose studying pre-trained RS models in a novel scenario where a user's interaction feedback involves a mixture-of-modality (MoM) items, e.g., text and images. We then present TransRec, a very simple modification made on the popular ID-based RS framework. TransRec learns directly from the raw features of the MoM items in an end-to-end training manner and thus enables effective transfer learning under various scenarios without relying on overlapped users or items. We empirically study the transferring ability of TransRec across four different real-world recommendation settings. Besides, we look at its effects by scaling source and target data size. Our results suggest that learning neural recommendation models from MoM feedback provides a promising way to realize universal RS.
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) rely on LiDAR sensors for environmental perception and decision-making in driving scenarios. However, ensuring the safety and reliability of AVs in complex environments remains a pressing challenge. To address this issue, we introduce a real-world dataset (ROLiD) comprising LiDAR-scanned point clouds of two random objects: water mist and smoke. In this paper, we introduce a novel adversarial perspective by proposing an attack framework that utilizes water mist and smoke to simulate environmental interference. Specifically, we propose a point cloud sequence generation method using a motion and content decomposition generative adversarial network named PCS-GAN to simulate the distribution of random objects. Furthermore, leveraging the simulated LiDAR scanning characteristics implemented with Range Image, we examine the effects of introducing random object perturbations at various positions on the target vehicle. Extensive experiments demonstrate that adversarial perturbations based on random objects effectively deceive vehicle detection and reduce the recognition rate of 3D object detection models.
Low altitude uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs) are expected to facilitate the development of aerial-ground integrated intelligent transportation systems and unlocking the potential of the emerging low-altitude economy. However, several critical challenges persist, including the dynamic optimization of network resources and UAV trajectories, limited UAV endurance, and imperfect channel state information (CSI). In this paper, we offer new insights into low-altitude economy networking by exploring intelligent UAV-assisted vehicle-to-everything communication strategies aligned with UAV energy efficiency. Particularly, we formulate an optimization problem of joint channel allocation, power control, and flight altitude adjustment in UAV-assisted vehicular networks. Taking CSI feedback delay into account, our objective is to maximize the vehicle-to-UAV communication sum rate while satisfying the UAV's long-term energy constraint. To this end, we first leverage Lyapunov optimization to decompose the original long-term problem into a series of per-slot deterministic subproblems. We then propose a diffusion-based deep deterministic policy gradient (D3PG) algorithm, which innovatively integrates diffusion models to determine optimal channel allocation, power control, and flight altitude adjustment decisions. Through extensive simulations using real-world vehicle mobility traces, we demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed D3PG algorithm compared to existing benchmark solutions.
11 Aug 2025
Invoking external tools enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to perform complex, real-world tasks, yet selecting the correct tool from large, hierarchically-structured libraries remains a significant challenge. The limited context windows of LLMs and noise from irrelevant options often lead to low selection accuracy and high computational costs. To address this, we propose the Hierarchical Gaussian Mixture Framework (HGMF), a probabilistic pruning method for scalable tool invocation. HGMF first maps the user query and all tool descriptions into a unified semantic space. The framework then operates in two stages: it clusters servers using a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) and filters them based on the query's likelihood. Subsequently, it applies the same GMM-based clustering and filtering to the tools associated with the selected servers. This hierarchical process produces a compact, high-relevance candidate set, simplifying the final selection task for the LLM. Experiments on a public dataset show that HGMF significantly improves tool selection accuracy while reducing inference latency, confirming the framework's scalability and effectiveness for large-scale tool libraries.
Annotation-efficient segmentation of the numerous mitochondria instances from various electron microscopy (EM) images is highly valuable for biological and neuroscience research. Although unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) methods can help mitigate domain shifts and reduce the high costs of annotating each domain, they typically have relatively low performance in practical applications. Thus, we investigate weakly supervised domain adaptation (WDA) that utilizes additional sparse point labels on the target domain, which require minimal annotation effort and minimal expert knowledge. To take full use of the incomplete and imprecise point annotations, we introduce a multitask learning framework that jointly conducts segmentation and center detection with a novel cross-teaching mechanism and class-focused cross-domain contrastive learning. While leveraging unlabeled image regions is essential, we introduce segmentation self-training with a novel instance-aware pseudo-label (IPL) selection strategy. Unlike existing methods that typically rely on pixel-wise pseudo-label filtering, the IPL semantically selects reliable and diverse pseudo-labels with the help of the detection task. Comprehensive validations and comparisons on challenging datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing UDA and WDA methods, significantly narrowing the performance gap with the supervised upper bound. Furthermore, under the UDA setting, our method also achieves substantial improvements over other UDA techniques.
We introduce RMAvatar, a novel human avatar representation with Gaussian splatting embedded on mesh to learn clothed avatar from a monocular video. We utilize the explicit mesh geometry to represent motion and shape of a virtual human and implicit appearance rendering with Gaussian Splatting. Our method consists of two main modules: Gaussian initialization module and Gaussian rectification module. We embed Gaussians into triangular faces and control their motion through the mesh, which ensures low-frequency motion and surface deformation of the avatar. Due to the limitations of LBS formula, the human skeleton is hard to control complex non-rigid transformations. We then design a pose-related Gaussian rectification module to learn fine-detailed non-rigid deformations, further improving the realism and expressiveness of the avatar. We conduct extensive experiments on public datasets, RMAvatar shows state-of-the-art performance on both rendering quality and quantitative evaluations. Please see our project page at this https URL.
A lightweight underwater image enhancement network is of great significance for resource-constrained platforms, but balancing model size, computational efficiency, and enhancement performance has proven difficult for previous approaches. In this work, we propose the Five A+ Network (FA+Net), a highly efficient and lightweight real-time underwater image enhancement network with only ∼ 9k parameters and ∼ 0.01s processing time. The FA+Net employs a two-stage enhancement structure. The strong prior stage aims to decompose challenging underwater degradations into sub-problems, while the fine-grained stage incorporates multi-branch color enhancement module and pixel attention module to amplify the network's perception of details. To the best of our knowledge, FA+Net is the only network with the capability of real-time enhancement of 1080P images. Thorough extensive experiments and comprehensive visual comparison, we show that FA+Net outperforms previous approaches by obtaining state-of-the-art performance on multiple datasets while significantly reducing both parameter count and computational complexity. The code is open source at this https URL.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.