NOVA School of Science and TechnologyNOVA University Lisbon
The increasing number of satellites and orbital debris has made space congestion a critical issue, threatening satellite safety and sustainability. Challenges such as collision avoidance, station-keeping, and orbital maneuvering require advanced techniques to handle dynamic uncertainties and multi-agent interactions. Reinforcement learning (RL) has shown promise in this domain, enabling adaptive, autonomous policies for space operations; however, many existing RL frameworks rely on custom-built environments developed from scratch, which often use simplified models and require significant time to implement and validate the orbital dynamics, limiting their ability to fully capture real-world complexities. To address this, we introduce OrbitZoo, a versatile multi-agent RL environment built on a high-fidelity industry standard library, that enables realistic data generation, supports scenarios like collision avoidance and cooperative maneuvers, and ensures robust and accurate orbital dynamics. The environment is validated against a real satellite constellation, Starlink, achieving a Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) of 0.16% compared to real-world data. This validation ensures reliability for generating high-fidelity simulations and enabling autonomous and independent satellite operations.
25 May 2025
Researchers introduced a framework that leverages Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to align synthetically generated web queries with ranking objectives, resulting in neural retrieval models that achieve superior performance on standard Web benchmarks. This method moves beyond post-hoc filtering by directly guiding the query generator to produce higher-quality training data.
06 Mar 2025
First formulated by Sir Isaac Newton in his work "Philosophiae Naturalis
Principia Mathematica", the concept of the Three-Body Problem was put forth as
a study of the motion of the three celestial bodies within the Earth-Sun-Moon
system. In a generalized definition, it seeks to predict the motion for an
isolated system composed of three point masses freely interacting under
Newton's law of universal attraction. This proves to be analogous to a
multitude of interactions between celestial bodies, and thus, the problem finds
applicability within the studies of celestial mechanics. Despite numerous
attempts by renowned physicists to solve it throughout the last three
centuries, no general closed-form solutions have been reached due to its
inherently chaotic nature for most initial conditions. Current state-of-the-art
solutions are based on two approaches, either numerical high-precision
integration or machine learning-based. Notwithstanding the breakthroughs of
neural networks, these present a significant limitation, which is their
ignorance of any prior knowledge of the chaotic systems presented. Thus, in
this work, we propose a novel method that utilizes Physics-Informed Neural
Networks (PINNs). These deep neural networks are able to incorporate any prior
system knowledge expressible as an Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE) into
their learning processes as a regularizing agent. Our findings showcase that
PINNs surpass current state-of-the-art machine learning methods with comparable
prediction quality. Despite a better prediction quality, the usability of
numerical integrators suffers due to their prohibitively high computational
cost. These findings confirm that PINNs are both effective and time-efficient
open-form solvers of the Three-Body Problem that capitalize on the extensive
knowledge we hold of classical mechanics.
Research on supervised learning algorithms in 3D scene understanding has
risen in prominence and witness great increases in performance across several
datasets. The leading force of this research is the problem of autonomous
driving followed by indoor scene segmentation. However, openly available 3D
data on these tasks mainly focuses on urban scenarios. In this paper, we
propose TS40K, a 3D point cloud dataset that encompasses more than 40,000 Km on
electrical transmission systems situated in European rural terrain. This is not
only a novel problem for the research community that can aid in the high-risk
mission of power-grid inspection, but it also offers 3D point clouds with
distinct characteristics from those in self-driving and indoor 3D data, such as
high point-density and no occlusion. In our dataset, each 3D point is labeled
with 1 out of 22 annotated classes. We evaluate the performance of
state-of-the-art methods on our dataset concerning 3D semantic segmentation and
3D object detection. Finally, we provide a comprehensive analysis of the
results along with key challenges such as using labels that were not originally
intended for learning tasks.
22 Aug 2022
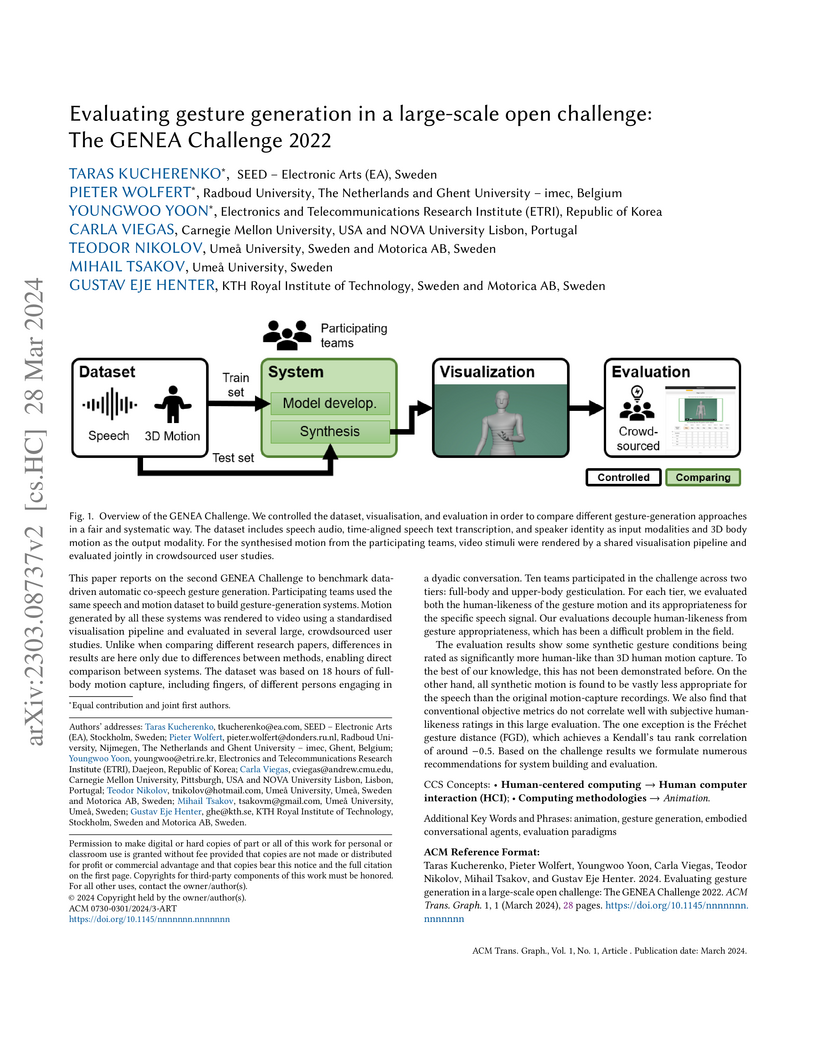
This paper reports on the second GENEA Challenge to benchmark data-driven
automatic co-speech gesture generation. Participating teams used the same
speech and motion dataset to build gesture-generation systems. Motion generated
by all these systems was rendered to video using a standardised visualisation
pipeline and evaluated in several large, crowdsourced user studies. Unlike when
comparing different research papers, differences in results are here only due
to differences between methods, enabling direct comparison between systems.
This year's dataset was based on 18 hours of full-body motion capture,
including fingers, of different persons engaging in dyadic conversation. Ten
teams participated in the challenge across two tiers: full-body and upper-body
gesticulation. For each tier we evaluated both the human-likeness of the
gesture motion and its appropriateness for the specific speech signal. Our
evaluations decouple human-likeness from gesture appropriateness, which
previously was a major challenge in the field.
The evaluation results are a revolution, and a revelation. Some synthetic
conditions are rated as significantly more human-like than human motion
capture. To the best of our knowledge, this has never been shown before on a
high-fidelity avatar. On the other hand, all synthetic motion is found to be
vastly less appropriate for the speech than the original motion-capture
recordings. Additional material is available via the project website at
this https URL
This paper reports on the second GENEA Challenge to benchmark data-driven
automatic co-speech gesture generation. Participating teams used the same
speech and motion dataset to build gesture-generation systems. Motion generated
by all these systems was rendered to video using a standardised visualisation
pipeline and evaluated in several large, crowdsourced user studies. Unlike when
comparing different research papers, differences in results are here only due
to differences between methods, enabling direct comparison between systems. The
dataset was based on 18 hours of full-body motion capture, including fingers,
of different persons engaging in a dyadic conversation. Ten teams participated
in the challenge across two tiers: full-body and upper-body gesticulation. For
each tier, we evaluated both the human-likeness of the gesture motion and its
appropriateness for the specific speech signal. Our evaluations decouple
human-likeness from gesture appropriateness, which has been a difficult problem
in the field.
The evaluation results show some synthetic gesture conditions being rated as
significantly more human-like than 3D human motion capture. To the best of our
knowledge, this has not been demonstrated before. On the other hand, all
synthetic motion is found to be vastly less appropriate for the speech than the
original motion-capture recordings. We also find that conventional objective
metrics do not correlate well with subjective human-likeness ratings in this
large evaluation. The one exception is the Fr\'echet gesture distance (FGD),
which achieves a Kendall's tau rank correlation of around −0.5. Based on the
challenge results we formulate numerous recommendations for system building and
evaluation.
We describe a design for generics in Go inspired by previous work on Featherweight Java by Igarashi, Pierce, and Wadler. Whereas subtyping in Java is nominal, in Go it is structural, and whereas generics in Java are defined via erasure, in Go we use monomorphisation. Although monomorphisation is widely used, we are one of the first to formalise it. Our design also supports a solution to The Expression Problem.
The BeEST experiment is a precision laboratory search for physics beyond the standard model that measures the electron capture decay of 7Be implanted into superconducting tunnel junction (STJ) detectors. For Phase-III of the experiment, we constructed a continuously sampling data acquisition system to extract pulse shape and timing information from 16 STJ pixels offline. Four additional pixels are read out with a fast list-mode digitizer, and one with a nuclear MCA already used in the earlier limit-setting phases of the experiment. We present the performance of the data acquisition system and discuss the relative advantages of the different digitizers.
This study presents the first large-scale quantitative analysis of the efficiency of X's Community Notes, a crowdsourced moderation system for identifying and contextualising potentially misleading content. Drawing on over 1.8 million notes, we examine three key dimensions of crowdsourced moderation: participation inequality, consensus formation, and timeliness. Despite the system's goal of collective moderation, we find substantial concentration effect, with the top 10% of contributors producing 58% of all notes (Gini Coefficient = 0.68). The observed consensus is rare-only 11.5% of notes reach agreement on publication, while 69% of posts receive conflicting classifications. A majority of noted posts (approximately 68%) are annotated as "Note Not Needed", reflecting the repurposing of the platform for debate rather than moderation. We found that such posts are paradoxically more likely to yield published notes (OR = 3.12). Temporal analyses show that the notes, on average, are published 65.7 hours after the original post, with longer delays significantly reducing the likelihood of consensus. These results portray Community Notes as a stratified, deliberative system dominated by a small contributor elite, marked by persistent dissensus, and constrained by timeliness. We conclude this study by outlining design strategies to promote equity, faster consensus, and epistemic reliability in community-based moderation.
13 Aug 2025
Wildfires pose a major threat to Portugal, with an average of over 115,000 hectares burned annually in the 45-year period of 1980-2024. Beyond a high number of ignitions, the country has experienced devastating mega-fires, such as those in 2017. Accurate forecasting of wildfire occurrence and burned areas is therefore essential for effective firefighting resource allocation and emergency preparedness. In this study, we present a novel two-stage ensemble approach that extends the widely used latent Gaussian modelling framework with the integrated nested Laplace approximation (INLA) for spatio-temporal wildfire forecasting. The first stage uses XGBoost, a gradient boosting model, to identify wildfire patterns from environmental covariates and historical fire records, producing one-month-ahead point forecasts for fire counts and burned area. These predictions are then incorporated as external covariates in a latent Gaussian model, which includes additional spatiotemporal random effects to produce the final probabilistic forecasts of monthly total fire counts and burned area at the council level. To effectively model both moderate and extreme wildfire events, we implement the extended generalised Pareto (eGP) likelihood (a sub-asymptotic distribution) within the INLA framework. We also develop and discuss penalised complexity priors (PC-priors) for the eGP parameters and provide a comprehensive comparison of the eGP likelihood against other commonly employed distributions in environmental modelling, such as the Gamma and Weibull distributions. The proposed framework addresses the challenge of accessing future environmental covariates, which are typically unavailable at prediction time, and demonstrates strong performance in one-month-ahead wildfire forecasting.
This study investigates the existence of positional biases in
Transformer-based models for text representation learning, particularly in the
context of web document retrieval. We build on previous research that
demonstrated loss of information in the middle of input sequences for causal
language models, extending it to the domain of representation learning. We
examine positional biases at various stages of training for an encoder-decoder
model, including language model pre-training, contrastive pre-training, and
contrastive fine-tuning. Experiments with the MS-MARCO document collection
reveal that after contrastive pre-training the model already generates
embeddings that better capture early contents of the input, with fine-tuning
further aggravating this effect.
An AI-powered algorithmic trading strategy for the energy sector integrates Hidden Markov Models with neural networks, complemented by Black-Litterman portfolio optimization and dual risk management. Backtested during the volatile COVID-19 period (2019-2022), the system achieved an 83% cumulative return with a 0.77 Sharpe Ratio.
Space debris is a major problem in space exploration. International bodies continuously monitor a large database of orbiting objects and emit warnings in the form of conjunction data messages. An important question for satellite operators is to estimate when fresh information will arrive so that they can react timely but sparingly with satellite maneuvers. We propose a statistical learning model of the message arrival process, allowing us to answer two important questions: (1) Will there be any new message in the next specified time interval? (2) When exactly and with what uncertainty will the next message arrive? The average prediction error for question (2) of our Bayesian Poisson process model is smaller than the baseline in more than 4 hours in a test set of 50k close encounter events.
 Cornell UniversityPacific Northwest National Laboratory
Cornell UniversityPacific Northwest National Laboratory Université Paris-SaclayTRIUMFLawrence Livermore National LaboratoryColorado School of MinesFacility for Rare Isotope BeamsNOVA School of Science and TechnologyXIA LLCSTAR CryoelectronicsLaboratoire de Physique CorpusculaireUniversit
de Strasbourg
Université Paris-SaclayTRIUMFLawrence Livermore National LaboratoryColorado School of MinesFacility for Rare Isotope BeamsNOVA School of Science and TechnologyXIA LLCSTAR CryoelectronicsLaboratoire de Physique CorpusculaireUniversit
de StrasbourgSuperconducting sensors doped with rare isotopes have recently demonstrated powerful sensing performance for sub-keV radiation from nuclear decay. Here, we report the first high-resolution recoil spectroscopy of a single, selected nuclear state using superconducting tunnel junction (STJ) sensors. The STJ sensors were used to measure the eV-scale nuclear recoils produced in 7Be electron capture decay in coincidence with a 478 keV γ-ray emitted in decays to the lowest-lying excited nuclear state in 7Li. Details of the Doppler broadened recoil spectrum depend on the slow-down dynamics of the recoil ion. The measured spectral broadening is compared to empirical stopping power models as well as modern molecular dynamics simulations at low energy. The results have implications in several areas from nuclear structure and stopping powers at eV-scale energies to direct searches for dark matter, neutrino mass measurements, and other physics beyond the standard model.
27 Mar 2023
We propose a new model-based algorithm solving the inverse rig problem in facial animation retargeting, exhibiting higher accuracy of the fit and sparser, more interpretable weight vector compared to SOTA. The proposed method targets a specific subdomain of human face animation - highly-realistic blendshape models used in the production of movies and video games. In this paper, we formulate an optimization problem that takes into account all the requirements of targeted models. Our objective goes beyond a linear blendshape model and employs the quadratic corrective terms necessary for correctly fitting fine details of the mesh. We show that the solution to the proposed problem yields highly accurate mesh reconstruction even when general-purpose solvers, like SQP, are used. The results obtained using SQP are highly accurate in the mesh space but do not exhibit favorable qualities in terms of weight sparsity and smoothness, and for this reason, we further propose a novel algorithm relying on a MM technique. The algorithm is specifically suited for solving the proposed objective, yielding a high-accuracy mesh fit while respecting the constraints and producing a sparse and smooth set of weights easy to manipulate and interpret by artists. Our algorithm is benchmarked with SOTA approaches, and shows an overall superiority of the results, yielding a smooth animation reconstruction with a relative improvement up to 45 percent in root mean squared mesh error while keeping the cardinality comparable with benchmark methods. This paper gives a comprehensive set of evaluation metrics that cover different aspects of the solution, including mesh accuracy, sparsity of the weights, and smoothness of the animation curves, as well as the appearance of the produced animation, which human experts evaluated.
Recommendation Systems (RS) are often used to address the issue of medical
doctor referrals. However, these systems require access to patient feedback and
medical records, which may not always be available in real-world scenarios. Our
research focuses on medical referrals and aims to predict recommendations in
different specialties of physicians for both new patients and those with a
consultation history. We use Extreme Multilabel Classification (XML), commonly
employed in text-based classification tasks, to encode available features and
explore different scenarios. While its potential for recommendation tasks has
often been suggested, this has not been thoroughly explored in the literature.
Motivated by the doctor referral case, we show how to recast a traditional
recommender setting into a multilabel classification problem that current XML
methods can solve. Further, we propose a unified model leveraging patient
history across different specialties. Compared to state-of-the-art RS using the
same features, our approach consistently improves standard recommendation
metrics up to approximately 10% for patients with a previous consultation
history. For new patients, XML proves better at exploiting available features,
outperforming the benchmark in favorable scenarios, with particular emphasis on
recall metrics. Thus, our approach brings us one step closer to creating more
effective and personalized doctor referral systems. Additionally, it highlights
XML as a promising alternative to current hybrid or content-based RS, while
identifying key aspects to take into account when using XML for recommendation
tasks.
Space debris is a major problem in space exploration. International bodies continuously monitor a large database of orbiting objects and emit warnings in the form of conjunction data messages. An important question for satellite operators is to estimate when fresh information will arrive so that they can react timely but sparingly with satellite maneuvers. We propose a statistical learning model of the message arrival process, allowing us to answer two important questions: (1) Will there be any new message in the next specified time interval? (2) When exactly and with what uncertainty will the next message arrive? The average prediction error for question (2) of our Bayesian Poisson process model is smaller than the baseline in more than 4 hours in a test set of 50k close encounter events.
Distributed systems adopt weak consistency to ensure high availability and
low latency, but state convergence is hard to guarantee due to conflicts.
Experts carefully design replicated data types (RDTs) that resemble sequential
data types and embed conflict resolution mechanisms that ensure convergence.
Designing RDTs is challenging as their correctness depends on subtleties such
as the ordering of concurrent operations. Currently, researchers manually
verify RDTs, either by paper proofs or using proof assistants. Unfortunately,
paper proofs are subject to reasoning flaws and mechanized proofs verify a
formalisation instead of a real-world implementation. Furthermore, writing
mechanized proofs is reserved to verification experts and is extremely time
consuming. To simplify the design, implementation, and verification of RDTs, we
propose VeriFx, a high-level programming language with automated proof
capabilities. VeriFx lets programmers implement RDTs atop functional
collections and express correctness properties that are verified automatically.
Verified RDTs can be transpiled to mainstream languages (currently Scala or
JavaScript). VeriFx also provides libraries for implementing and verifying
Conflict-free Replicated Data Types (CRDTs) and Operational Transformation (OT)
functions. These libraries implement the general execution model of those
approaches and define their correctness properties. We use the libraries to
implement and verify an extensive portfolio of 35 CRDTs and reproduce a study
on the correctness of OT functions.
Communication overhead is a known bottleneck in federated learning (FL). To
address this, lossy compression is commonly used on the information
communicated between the server and clients during training. In horizontal FL,
where each client holds a subset of the samples, such communication-compressed
training methods have recently seen significant progress. However, in their
vertical FL counterparts, where each client holds a subset of the features, our
understanding remains limited. To address this, we propose an error feedback
compressed vertical federated learning (EF-VFL) method to train split neural
networks. In contrast to previous communication-compressed methods for vertical
FL, EF-VFL does not require a vanishing compression error for the gradient norm
to converge to zero for smooth nonconvex problems. By leveraging error
feedback, our method can achieve a O(1/T) convergence rate for a
sufficiently large batch size, improving over the state-of-the-art
O(1/T) rate under O(1/T) compression
error, and matching the rate of uncompressed methods. Further, when the
objective function satisfies the Polyak-{\L}ojasiewicz inequality, our method
converges linearly. In addition to improving convergence, our method also
supports the use of private labels. Numerical experiments show that EF-VFL
significantly improves over the prior art, confirming our theoretical results.
The code for this work can be found at this https URL
26 Jul 2024
We present our work on the collaborative use of dynamic and static analysis
tools for the verification of software written in the OCaml language. We build
upon Gospel, a specification language for OCaml that can be used both in
dynamic and static analyses. We employ Ortac, for runtime assertion checking,
and Cameleer and CFML for the deductive verification of OCaml code. We report
on the use of such tools to build a case study of collaborative analysis of a
non-trivial OCaml program. This shows how these tools nicely complement each
others, while at the same highlights the differences when writing specification
targeting dynamic or static analysis methods.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.