Ask or search anything...
A comprehensive survey by Chen et al. (2025) introduces the first unified taxonomy for latent Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning, organizing a rapidly growing field into token-wise horizontal and layer-wise vertical approaches. It synthesizes current research, practical applications, and outlines critical challenges for future advancements in LLM efficiency and cognitive capabilities.
View blogLS-Imagine allows visual reinforcement learning agents to plan and explore over long horizons in complex open-world environments by integrating a long short-term world model and affordance-driven guidance. It demonstrates improved success rates and reduced steps to completion across various MineDojo tasks, including "Harvest log in plains" and "Mine iron ore."
View blogBridgeAD, developed by researchers at Fudan University and Eastern Institute of Technology, introduces a framework for end-to-end autonomous driving that reformulates how historical temporal information is leveraged. It achieves state-of-the-art planning results on the nuScenes dataset by enabling fine-grained, step-level interactions with past data.
View blogAn autonomous driving framework, ImagiDrive, integrates Vision-Language Models with Driving World Models in a unified imagination-and-planning loop. This iterative process allows the system to generate future driving scenarios and refine its trajectory predictions, leading to improved collision avoidance and more robust navigation across multiple datasets.
View blogThe paper "Keeping Yourself is Important in Downstream Tuning Multimodal Large Language Model" provides a systematic review and unified benchmark for tuning MLLMs, classifying methods into Selective, Additive, and Reparameterization paradigms. It empirically analyzes the trade-offs between task-expert specialization and open-world stabilization, offering practical guidelines for MLLM deployment.
View blogThe VaCo framework enhances Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by intrinsically activating and coordinating vision-centric information. It utilizes query-based discriminative alignment to harness visual priors from multiple Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) and employs a Token Gateway Mask to resolve representational conflicts, leading to superior visual comprehension and efficiency. VaCo outperforms state-of-the-art MLLMs on benchmarks such as MMBench-English (78.6, +2.3 points over LLaVA-1.5) and MMMU (46.7, +4.9 points over LLaVA-1.5) with a 7B model, while using only a single visual encoder during inference.
View blogResearchers from Eastern Institute of Technology, Tencent, and collaborators develop SkipGPT, a dynamic layer pruning framework that introduces token-aware global routing and decoupled pruning policies for MLP versus self-attention modules, achieving over 40% parameter reduction while maintaining or exceeding original model performance through a two-stage training paradigm that first tunes lightweight routers (0.01% parameters) then applies LoRA fine-tuning, with SkipGPT-RT retaining over 90% performance on LLaMA2-7B/13B at 25% pruning and over 95% on LLaMA3.1-8B while outperforming static methods like ShortGPT and dynamic approaches like MoD-D across commonsense reasoning benchmarks, revealing through routing behavior analysis that attention modules exhibit higher redundancy than MLPs and that computational needs shift contextually with later tokens requiring more attention but less MLP processing, challenging the fixed 1:1 attention-MLP architecture design while demonstrating that joint training of routers with pre-trained parameters causes instability compared to their stable disentangled optimization approach.
View blogResearchers systematically investigated factors influencing the distillation of Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning into Small Language Models (SLMs), identifying that optimal CoT granularity is non-monotonic and student-dependent, format impact is minimal, and teacher choice effectiveness varies by task. The study revealed a 'Matthew Effect,' where stronger SLMs gained more from CoT distillation, challenging assumptions about knowledge transfer.
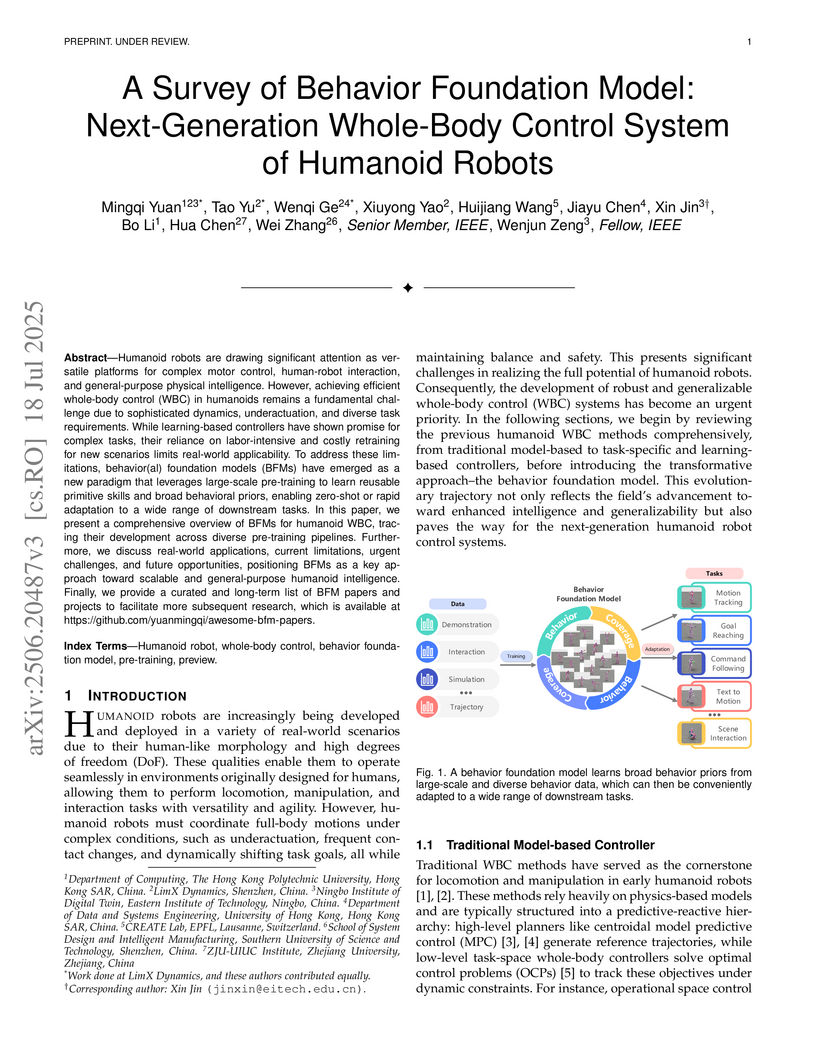
View blogA survey by researchers from LimX Dynamics and various universities outlines Behavior Foundation Models (BFMs) as the next-generation paradigm for humanoid whole-body control. It synthesizes current approaches, categorizing pre-training and adaptation strategies, and discusses BFMs' potential to enable general-purpose physical intelligence through broad behavioral priors and rapid adaptation while also identifying key challenges.
View blogResearchers from National University of Singapore and collaborators introduced the concept of LLM-empowered personalized Web agents, aiming to automate online tasks by incorporating user-specific data. They developed the PersonalWAB benchmark and proposed the PUMA framework, which notably improved task accuracy and efficiency by leveraging personalized user memory and preference optimization, outperforming larger general-purpose LLMs.
View blogResearchers from the Ningbo Institute of Digital Twin, Eastern Institute of Technology, developed a hybrid OCR-LLM framework to efficiently extract information from enterprise-scale copy-heavy documents. This framework achieved sub-second latency and near-perfect F1 scores across various document types, demonstrating up to a 54x speedup over multimodal approaches by leveraging document structure.
View blog The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
 Fudan University
Fudan University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign



 Imperial College London
Imperial College London
 Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University

 Nanjing University
Nanjing University

 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences
 National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore
 Westlake University
Westlake University
 University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China



