Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology
Transformer-based architectures have become the backbone of both uni-modal and multi-modal foundation models, largely due to their scalability via attention mechanisms, resulting in a rich ecosystem of publicly available pre-trained models such as LLaVA, CLIP, and DeiT, etc. In parallel, emerging sub-quadratic architectures like Mamba offer promising efficiency gains by enabling global context modeling with linear complexity. However, training these architectures from scratch remains resource-intensive (e.g., in terms of data and time). Motivated by this challenge, we explore a cross-architecture knowledge transfer paradigm, termed TransMamba, that facilitates the reuse of Transformer pre-trained knowledge. We propose a two-stage framework to accelerate the training of Mamba-based models, ensuring their effectiveness across both uni-modal and multi-modal tasks. The first stage leverages pre-trained Transformer models to initialize critical components of the Mamba architecture. To bridge architectural and dimensional gaps, we develop a selective weight subcloning strategy and a layered initialization scheme that prioritizes the early n layers. Building on this initialization, the second stage introduces an adaptive multi-directional knowledge distillation method. This mechanism employs layer-wise adaptive scaling factors to align Mamba representations with their Transformer counterparts, while accommodating the scanning order variations inherent to multi-modal Mamba architectures. Despite operating with a reduced training dataset and a more compact model architecture, TransMamba consistently outperforms baseline approaches across diverse mamba-based backbones (e.g., PlainMamba, Vmamba, ViM and VideoMamba) and downstream tasks (e.g., image classification, visual question answering, text-video retrieval and multimodal reasoning). All code and implementation details will be released.
The UKP Lab at Technical University of Darmstadt introduces LAZYREVIEW, the first dataset for identifying 'lazy thinking' in NLP peer reviews, addressing the decline in review quality due to reviewer workload. The research demonstrates that instruction-tuned Large Language Models can effectively detect these nuanced patterns, and explicit feedback on 'lazy thinking' measurably improves the constructiveness and adherence of human-written reviews.
05 Jun 2025
Traditional offline evaluation methods for recommender systems struggle to
capture the complexity of modern platforms due to sparse behavioural signals,
noisy data, and limited modelling of user personality traits. While simulation
frameworks can generate synthetic data to address these gaps, existing methods
fail to replicate behavioural diversity, limiting their effectiveness. To
overcome these challenges, we propose the Personality-driven User Behaviour
Simulator (PUB), an LLM-based simulation framework that integrates the Big Five
personality traits to model personalised user behaviour. PUB dynamically infers
user personality from behavioural logs (e.g., ratings, reviews) and item
metadata, then generates synthetic interactions that preserve statistical
fidelity to real-world data. Experiments on the Amazon review datasets show
that logs generated by PUB closely align with real user behaviour and reveal
meaningful associations between personality traits and recommendation outcomes.
These results highlight the potential of the personality-driven simulator to
advance recommender system evaluation, offering scalable, controllable,
high-fidelity alternatives to resource-intensive real-world experiments.
To detect unauthorized data usage in training large-scale generative models (e.g., ChatGPT or Midjourney), membership inference attacks (MIA) have proven effective in distinguishing a single training instance (a member) from a single non-training instance (a non-member). This success is mainly credited to a memorization effect: models tend to perform better on a member than a non-member. However, we find that standard MIAs fail against distilled generative models (i.e., student models) that are increasingly deployed in practice for efficiency (e.g., ChatGPT 4o-mini). Trained exclusively on data generated from a large-scale model (a teacher model), the student model lacks direct exposure to any members (teacher's training data), nullifying the memorization effect that standard MIAs rely on. This finding reveals a serious privacy loophole, where generation-service providers could deploy a student model whose teacher was potentially trained on unauthorized data, yet claim the deployed model is clean because it was not directly trained on such data. Hence, are distilled models inherently unauditable for upstream privacy violations, and should we discard them when we care about privacy? We contend no, as we uncover a memory chain connecting the student and teacher's member data: the distribution of student-generated data aligns more closely with the distribution of the teacher's members than with non-members, thus we can detect unauthorized data usage even when direct instance-level memorization is absent. This leads us to posit that MIAs on distilled generative models should shift from instance-level scores to distribution-level statistics. We further propose three principles of distribution-based MIAs for detecting unauthorized training data through distilled generative models, and validate our position through an exemplar framework. We lastly discuss the implications of our position.
Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in various natural language processing
tasks but remain vulnerable to generating harmful content or being exploited
for malicious purposes. Although safety alignment datasets have been introduced
to mitigate such risks through supervised fine-tuning (SFT), these datasets
often lack comprehensive risk coverage. Most existing datasets focus primarily
on lexical diversity while neglecting other critical dimensions. To address
this limitation, we propose a novel analysis framework to systematically
measure the risk coverage of alignment datasets across three essential
dimensions: Lexical Diversity, Malicious Intent, and Jailbreak Tactics. We
further introduce TRIDENT, an automated pipeline that leverages persona-based,
zero-shot LLM generation to produce diverse and comprehensive instructions
spanning these dimensions. Each harmful instruction is paired with an ethically
aligned response, resulting in two datasets: TRIDENT-Core, comprising 26,311
examples, and TRIDENT-Edge, with 18,773 examples. Fine-tuning Llama 3.1-8B on
TRIDENT-Edge demonstrates substantial improvements, achieving an average 14.29%
reduction in Harm Score, and a 20% decrease in Attack Success Rate compared to
the best-performing baseline model fine-tuned on the WildBreak dataset.
Large language models (LLMs) frequently refuse to respond to pseudo-malicious
instructions: semantically harmless input queries triggering unnecessary LLM
refusals due to conservative safety alignment, significantly impairing user
experience. Collecting such instructions is crucial for evaluating and
mitigating over-refusals, but existing instruction curation methods, like
manual creation or instruction rewriting, either lack scalability or fail to
produce sufficiently diverse and effective refusal-inducing prompts. To address
these limitations, we introduce EVOREFUSE, a prompt optimization approach that
generates diverse pseudo-malicious instructions consistently eliciting
confident refusals across LLMs. EVOREFUSE employs an evolutionary algorithm
exploring the instruction space in more diverse directions than existing
methods via mutation strategies and recombination, and iteratively evolves seed
instructions to maximize evidence lower bound on LLM refusal probability. Using
EVOREFUSE, we create two novel datasets: EVOREFUSE-TEST, a benchmark of 582
pseudo-malicious instructions that outperforms the next-best benchmark with
140.41% higher average refusal triggering rate across 9 LLMs, 34.86% greater
lexical diversity, and 40.03% improved LLM response confidence scores; and
EVOREFUSE-ALIGN, which provides 3,000 pseudo-malicious instructions with
responses for supervised and preference-based alignment training.
LLAMA3.1-8B-INSTRUCT supervisedly fine-tuned on EVOREFUSE-ALIGN achieves up to
14.31% fewer over-refusals than models trained on the second-best alignment
dataset, without compromising safety. Our analysis with EVOREFUSE-TEST reveals
models trigger over-refusals by overly focusing on sensitive keywords while
ignoring broader context.
The grain size distribution (GSD) plays an important role in the mechanical properties of amorphous disordered systems and complex granular materials. Varying GSD causes segregation issues and alters critical behaviors. This work used the discrete element method (DEM) to investigate the rheological and critical behaviors of sheared granular flows with various GSDs. The results show that, while a unified rheological relation can be obtained, a characteristic length scale, which is associated with the contact probability and can be obtained from any GSD, is embedded within such a polydisperse disordered system. We further acquire a correlation function between critical solid fractions and dimensionless grain volume distributions. This work elucidates the effect of particle volumes on the rheology and micromechanics of dry granular systems and provides further insights in better incorporating the influence of other particle properties into a unified framework, which is helpful and critical for the corresponding engineering and geophysical problems.
The prediction of learning curves for Natural Language Processing (NLP) models enables informed decision-making to meet specific performance objectives, while reducing computational overhead and lowering the costs associated with dataset acquisition and curation. In this work, we formulate the prediction task as a multitask learning problem, where each task's data is modelled as being organized within a two-layer hierarchy. To model the shared information and dependencies across tasks and hierarchical levels, we employ latent variable multi-output Gaussian Processes, enabling to account for task correlations and supporting zero-shot prediction of learning curves (LCs). We demonstrate that this approach facilitates the development of probabilistic scaling laws at lower costs. Applying an active learning strategy, LCs can be queried to reduce predictive uncertainty and provide predictions close to ground truth scaling laws. We validate our framework on three small-scale NLP datasets with up to 30 LCs. These are obtained from nanoGPT models, from bilingual translation using mBART and Transformer models, and from multilingual translation using M2M100 models of varying sizes.
Relative compression, where a set of similar strings are compressed with respect to a reference string, is a very effective method of compressing DNA datasets containing multiple similar sequences. Relative compression is fast to perform and also supports rapid random access to the underlying data. The main difficulty of relative compression is in selecting an appropriate reference sequence. In this paper, we explore using the dictionary of repeats generated by Comrad, Re-pair and Dna-x algorithms as reference sequences for relative compression. We show this technique allows better compression and supports random access just as well. The technique also allows more general repetitive datasets to be compressed using relative compression.
Machine unlearning aims to eliminate the influence of specific data from trained models to ensure privacy compliance. However, most existing methods assume full access to the original training dataset, which is often impractical. We address a more realistic yet challenging setting: few-shot zero-glance, where only a small subset of the retained data is available and the forget set is entirely inaccessible. We introduce GFOES, a novel framework comprising a Generative Feedback Network (GFN) and a two-phase fine-tuning procedure. GFN synthesises Optimal Erasure Samples (OES), which induce high loss on target classes, enabling the model to forget class-specific knowledge without access to the original forget data, while preserving performance on retained classes. The two-phase fine-tuning procedure enables aggressive forgetting in the first phase, followed by utility restoration in the second. Experiments on three image classification datasets demonstrate that GFOES achieves effective forgetting at both logit and representation levels, while maintaining strong performance using only 5% of the original data. Our framework offers a practical and scalable solution for privacy-preserving machine learning under data-constrained conditions.
Vision language models (VLMs) that enable natural language interaction with satellite imagery can democratize Earth observation by accelerating expert workflows, making data accessible to non-specialists, and enabling planet-scale automation. However, existing datasets focus mainly on short-term, high-resolution imagery from a limited number of satellites, overlooking low-resolution, multi-satellite, long-term archives, such as Landsat, that are essential for affordable and bias-robust global monitoring. We address this gap with Landsat30-AU, a large-scale vision-language dataset built from 30-meter resolution imagery collected by four Landsat satellites (5, 7, 8, and 9) over Australia, spanning more than 36 years. The dataset includes two components: Landsat30-AU-Cap, containing 196,262 image-caption pairs, and Landsat30-AU-VQA, comprising 17,725 human-verified visual question answering (VQA) samples across eight remote sensing domains. Both datasets are curated through a bootstrapped pipeline that leverages generic VLMs with iterative refinement and human verification to ensure quality. Our evaluation of eight VLMs on our benchmark reveals that off-the-shelf models struggle to understand satellite imagery. The open-source remote-sensing VLM EarthDial achieves only 0.07 SPIDEr in captioning and a VQA accuracy of 0.48, highlighting the limitations of current approaches. Encouragingly, lightweight fine-tuning of Qwen2.5-VL-7B on Landsat30-AU improves captioning performance from 0.11 to 0.31 SPIDEr and boosts VQA accuracy from 0.74 to 0.87. Code and data are available at this https URL.
This paper introduces a 'green list stealing attack' that exploits fundamental vulnerabilities in current large language model (LLM) watermarking schemes. The attack leverages mixed integer programming to reconstruct the secret token lists, demonstrating the ability to effectively remove watermarks from AI-generated text.
The evolution of 3D visualization techniques has fundamentally transformed how we interact with digital content. At the forefront of this change is point cloud technology, offering an immersive experience that surpasses traditional 2D representations. However, the massive data size of point clouds presents significant challenges in data compression. Current methods for lossy point cloud attribute compression (PCAC) generally focus on reconstructing the original point clouds with minimal error. However, for point cloud visualization scenarios, the reconstructed point clouds with distortion still need to undergo a complex rendering process, which affects the final user-perceived quality. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end deep learning framework that seamlessly integrates PCAC with differentiable rendering, denoted as rendering-oriented PCAC (RO-PCAC), directly targeting the quality of rendered multiview images for viewing. In a differentiable manner, the impact of the rendering process on the reconstructed point clouds is taken into account. Moreover, we characterize point clouds as sparse tensors and propose a sparse tensor-based transformer, called SP-Trans. By aligning with the local density of the point cloud and utilizing an enhanced local attention mechanism, SP-Trans captures the intricate relationships within the point cloud, further improving feature analysis and synthesis within the framework. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed RO-PCAC achieves state-of-the-art compression performance, compared to existing reconstruction-oriented methods, including traditional, learning-based, and hybrid methods.
04 Nov 2025
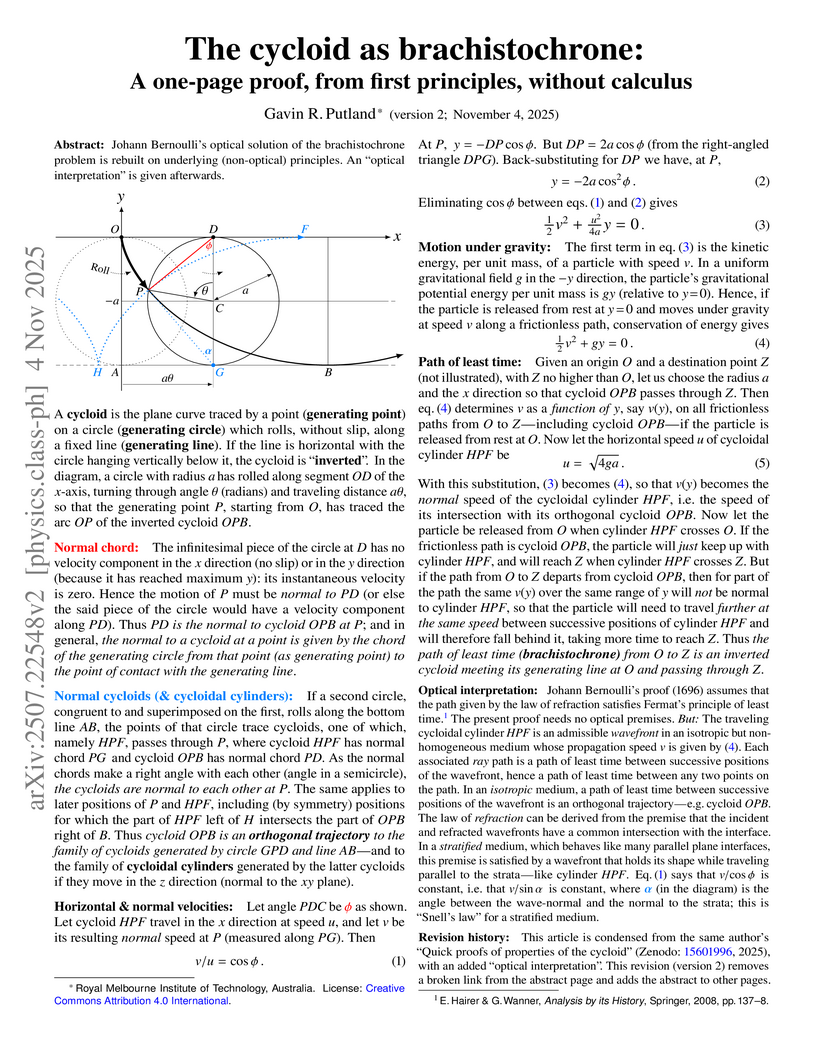
Johann Bernoulli's optical solution of the brachistochrone problem is rebuilt on underlying (non-optical) principles. An "optical interpretation" is given afterwards.
This paper shows how a multimodal large language model (MLLM) can expand urban measurement capacity and support tracking of place-based policy interventions. Using a structured, reason-then-estimate pipeline on street-view imagery, GPT-4o infers neighborhood poverty and tree canopy, which we embed in a quasi-experimental design evaluating the legacy of 1930s redlining. GPT-4o recovers the expected adverse socio-environmental legacy effects of redlining, with estimates statistically indistinguishable from authoritative sources, and it outperforms a conventional pixel-based segmentation baseline-consistent with the idea that holistic scene reasoning extracts higher-order information beyond object counts alone. These results position MLLMs as policy-grade instruments for neighborhood measurement and motivate broader validation across policy-evaluation settings.
Pedestrians are among the most endangered traffic participants in road traffic. While pedestrian detection in nominal conditions is well established, the sensor and, therefore, the pedestrian detection performance degrades under adverse weather conditions. Understanding the influences of rain and fog on a specific radar and lidar sensor requires extensive testing, and if the sensors' specifications are altered, a retesting effort is required. These challenges are addressed in this paper, firstly by conducting comprehensive measurements collecting empirical data of pedestrian detection performance under varying rain and fog intensities in a controlled environment, and secondly, by introducing a dedicated Weather Filter (WF) model that predicts the effects of rain and fog on a user-specified radar and lidar on pedestrian detection performance. We use a state-of-the-art baseline model representing the physical relation of sensor specifications, which, however, lacks the representation of secondary weather effects, e.g., changes in pedestrian reflectivity or droplets on a sensor, and adjust it with empirical data to account for such. We find that our measurement results are in agreement with existent literature related to weather degredation and our WF outperforms the baseline model in predicting weather effects on pedestrian detection while only requiring a minimal testing effort.
Column generation (CG) is a well-established method for solving large-scale linear programs. It involves iteratively optimizing a subproblem containing a subset of columns and using its dual solution to generate new columns with negative reduced costs. This process continues until the dual values converge to the optimal dual solution to the original problem. A natural phenomenon in CG is the heavy oscillation of the dual values during iterations, which can lead to a substantial slowdown in the convergence rate. Stabilization techniques are devised to accelerate the convergence of dual values by using information beyond the state of the current subproblem. However, there remains a significant gap in obtaining more accurate dual values at an earlier stage. To further narrow this gap, this paper introduces a novel approach consisting of 1) a machine learning approach for accurate prediction of optimal dual solutions and 2) an adaptive stabilization technique that effectively capitalizes on accurate predictions. On the graph coloring problem, we show that our method achieves a significantly improved convergence rate compared to traditional methods.
19 Feb 2020
With the rapidly-developing high-speed wireless communications, the 60 GHz
millimeter-wave frequency range and radio-over-fiber systems have been
investigated as a promising solution to deliver mm-wave signals. Neural
networks have been studied to improve the mm-wave RoF system performances at
the receiver side by suppressing linear and nonlinear impairments. However,
previous neural network studies in mm-wave RoF systems focus on the off-line
implementation with high-end GPUs , which is not practical for low
power-consumption, low-cost and limited computation platform applications. To
solve this issue, we investigate neural network hardware accelerator
implementations using the field programmable gate array (FPGA), taking
advantage of the low power consumption, parallel computation capability, and
reconfigurablity features of FPGA. Convolutional neural network (CNN) and
binary convolutional neural network (BCNN) hardware accelerators are
demonstrated. In addition, to satisfy the low-latency requirement in mm-wave
RoF systems and to enable the use of low-cost compact FPGA devices, a novel
inner parallel optimization method is proposed. Compared with the embedded
processor (ARM Cortex A9) execution latency, the CNN/BCNN FPGA-based hardware
accelerator reduces their latency by over 92%. Compared with non-optimized FPGA
implementations, the proposed optimization method reduces the processing
latency by over 44% for CNN and BCNN. Compared with the GPU implementation, the
latency of CNN implementation with the proposed optimization method is reduced
by 85.49%, while the power consumption is reduced by 86.91%. Although the
latency of BCNN implementation with the proposed optimization method is larger
compared with the GPU implementation, the power consumption is reduced by
86.14%. The FPGA-based neural network hardware accelerators provide a promising
solution for mm-wave RoF systems.
Geometry-based point cloud compression (G-PCC), an international standard designed by MPEG, provides a generic framework for compressing diverse types of point clouds while ensuring interoperability across applications and devices. However, G-PCC underperforms compared to recent deep learning-based PCC methods despite its lower computational power consumption. To enhance the efficiency of G-PCC without sacrificing its interoperability or computational flexibility, we propose a novel preprocessing framework that integrates a compression-oriented voxelization network with a differentiable G-PCC surrogate model, jointly optimized in the training phase. The surrogate model mimics the rate-distortion behaviour of the non-differentiable G-PCC codec, enabling end-to-end gradient propagation. The versatile voxelization network adaptively transforms input point clouds using learning-based voxelization and effectively manipulates point clouds via global scaling, fine-grained pruning, and point-level editing for rate-distortion trade-offs. During inference, only the lightweight voxelization network is appended to the G-PCC encoder, requiring no modifications to the decoder, thus introducing no computational overhead for end users. Extensive experiments demonstrate a 38.84% average BD-rate reduction over G-PCC. By bridging classical codecs with deep learning, this work offers a practical pathway to enhance legacy compression standards while preserving their backward compatibility, making it ideal for real-world deployment.
One of the major issues in signed networks is to use network structure to
predict the missing sign of an edge. In this paper, we introduce a novel
probabilistic approach for the sign prediction problem. The main characteristic
of the proposed models is their ability to adapt to the sparsity level of an
input network. The sparsity of networks is one of the major reasons for the
poor performance of many link prediction algorithms, in general, and sign
prediction algorithms, in particular. Building a model that has an ability to
adapt to the sparsity of the data has not yet been considered in the previous
related works. We suggest that there exists a dilemma between local and global
structures and attempt to build sparsity adaptive models by resolving this
dilemma. To this end, we propose probabilistic prediction models based on local
and global structures and integrate them based on the concept of smoothing. The
model relies more on the global structures when the sparsity increases, whereas
it gives more weights to the information obtained from local structures for low
levels of the sparsity. The proposed model is assessed on three real-world
signed networks, and the experiments reveal its consistent superiority over the
state of the art methods. As compared to the previous methods, the proposed
model not only better handles the sparsity problem, but also has lower
computational complexity and can be updated using real-time data streams.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.