University of Eastern Finland
Researchers at the University of Eastern Finland developed zero-shot world models that predict environmental dynamics by leveraging similarity search on latent representations from a pre-trained Variational Autoencoder (VAE), circumventing explicit dynamics training. This approach frequently surpasses learning-based baselines in prediction quality and demonstrates higher data efficiency, particularly for long-horizon forecasting.
We propose an explainable probabilistic framework for characterizing spoofed
speech by decomposing it into probabilistic attribute embeddings. Unlike raw
high-dimensional countermeasure embeddings, which lack interpretability, the
proposed probabilistic attribute embeddings aim to detect specific speech
synthesizer components, represented through high-level attributes and their
corresponding values. We use these probabilistic embeddings with four
classifier back-ends to address two downstream tasks: spoofing detection and
spoofing attack attribution. The former is the well-known bonafide-spoof
detection task, whereas the latter seeks to identify the source method
(generator) of a spoofed utterance. We additionally use Shapley values, a
widely used technique in machine learning, to quantify the relative
contribution of each attribute value to the decision-making process in each
task. Results on the ASVspoof2019 dataset demonstrate the substantial role of
duration and conversion modeling in spoofing detection; and waveform generation
and speaker modeling in spoofing attack attribution. In the detection task, the
probabilistic attribute embeddings achieve 99.7% balanced accuracy and
0.22% equal error rate (EER), closely matching the performance of raw
embeddings (99.9% balanced accuracy and 0.22% EER). Similarly, in the
attribution task, our embeddings achieve 90.23% balanced accuracy and
2.07% EER, compared to 90.16% and 2.11% with raw embeddings. These
results demonstrate that the proposed framework is both inherently explainable
by design and capable of achieving performance comparable to raw CM embeddings.
Researchers at the University of Eastern Finland and KLASS Engineering and Solutions developed a Mixture-of-Low-Rank-Adapter-Experts (MoE-LoRA) framework to enhance the generalizability of audio deepfake detection. This approach reduced the average Equal Error Rate (EER) for out-of-domain deepfake attacks from 8.55% (with full fine-tuning) to 6.08%, particularly showing strong improvements on challenging "in-the-wild" datasets.
Despite improvements in automatic speaker verification (ASV), vulnerability against spoofing attacks remains a major concern. In this study, we investigate the integration of ASV and countermeasure (CM) subsystems into a modular spoof-aware speaker verification (SASV) framework. Unlike conventional single-stage score-level fusion methods, we explore the potential of a multi-stage approach that utilizes the ASV and CM systems in multiple stages. By leveraging ECAPA-TDNN (ASV) and AASIST (CM) subsystems, we consider support vector machine and logistic regression classifiers to achieve SASV. In the second stage, we integrate their outputs with the original score to revise fusion back-end classifiers. Additionally, we incorporate another auxiliary score from RawGAT (CM) to further enhance our SASV framework. Our approach yields an equal error rate (EER) of 1.30% on the evaluation dataset of the SASV2022 challenge, representing a 24% relative improvement over the baseline system.
Joint Optimization of Speaker and Spoof Detectors for Spoofing-Robust Automatic Speaker Verification
Joint Optimization of Speaker and Spoof Detectors for Spoofing-Robust Automatic Speaker Verification
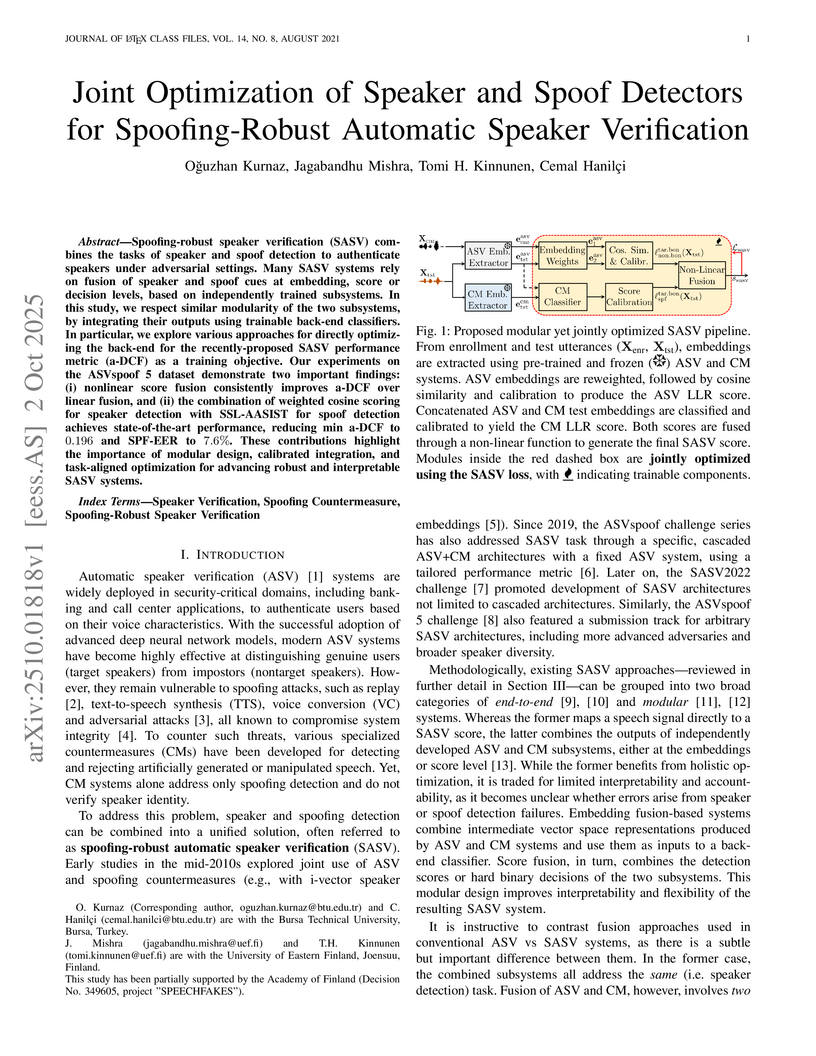
Spoofing-robust speaker verification (SASV) combines the tasks of speaker and spoof detection to authenticate speakers under adversarial settings. Many SASV systems rely on fusion of speaker and spoof cues at embedding, score or decision levels, based on independently trained subsystems. In this study, we respect similar modularity of the two subsystems, by integrating their outputs using trainable back-end classifiers. In particular, we explore various approaches for directly optimizing the back-end for the recently-proposed SASV performance metric (a-DCF) as a training objective. Our experiments on the ASVspoof 5 dataset demonstrate two important findings: (i) nonlinear score fusion consistently improves a-DCF over linear fusion, and (ii) the combination of weighted cosine scoring for speaker detection with SSL-AASIST for spoof detection achieves state-of-the-art performance, reducing min a-DCF to 0.196 and SPF-EER to 7.6%. These contributions highlight the importance of modular design, calibrated integration, and task-aligned optimization for advancing robust and interpretable SASV systems.
 CNRSAcademia Sinica
CNRSAcademia Sinica University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Nagoya UniversityUniversity of Edinburgh
Nagoya UniversityUniversity of Edinburgh Aalto University
Aalto University InriaTrinity College DublinNational Institute of InformaticsGoogle Inc.University of Eastern FinlandiFlytek ResearchADAPT CentreNTT Communication Science LaboratoriesAvignon universityaudEERING GmbHNEC CorpEurécomUniversit
e de LorraineHOYA
InriaTrinity College DublinNational Institute of InformaticsGoogle Inc.University of Eastern FinlandiFlytek ResearchADAPT CentreNTT Communication Science LaboratoriesAvignon universityaudEERING GmbHNEC CorpEurécomUniversit
e de LorraineHOYAAutomatic speaker verification (ASV) is one of the most natural and convenient means of biometric person recognition. Unfortunately, just like all other biometric systems, ASV is vulnerable to spoofing, also referred to as "presentation attacks." These vulnerabilities are generally unacceptable and call for spoofing countermeasures or "presentation attack detection" systems. In addition to impersonation, ASV systems are vulnerable to replay, speech synthesis, and voice conversion attacks. The ASVspoof 2019 edition is the first to consider all three spoofing attack types within a single challenge. While they originate from the same source database and same underlying protocol, they are explored in two specific use case scenarios. Spoofing attacks within a logical access (LA) scenario are generated with the latest speech synthesis and voice conversion technologies, including state-of-the-art neural acoustic and waveform model techniques. Replay spoofing attacks within a physical access (PA) scenario are generated through carefully controlled simulations that support much more revealing analysis than possible previously. Also new to the 2019 edition is the use of the tandem detection cost function metric, which reflects the impact of spoofing and countermeasures on the reliability of a fixed ASV system. This paper describes the database design, protocol, spoofing attack implementations, and baseline ASV and countermeasure results. It also describes a human assessment on spoofed data in logical access. It was demonstrated that the spoofing data in the ASVspoof 2019 database have varied degrees of perceived quality and similarity to the target speakers, including spoofed data that cannot be differentiated from bona-fide utterances even by human subjects.
Modern front-end design for speech deepfake detection relies on full fine-tuning of large pre-trained models like XLSR. However, this approach is not parameter-efficient and may lead to suboptimal generalization to realistic, in-the-wild data types. To address these limitations, we introduce a new family of parameter-efficient front-ends that fuse prompt-tuning with classical signal processing transforms. These include FourierPT-XLSR, which uses the Fourier Transform, and two variants based on the Wavelet Transform: WSPT-XLSR and Partial-WSPT-XLSR. We further propose WaveSP-Net, a novel architecture combining a Partial-WSPT-XLSR front-end and a bidirectional Mamba-based back-end. This design injects multi-resolution features into the prompt embeddings, which enhances the localization of subtle synthetic artifacts without altering the frozen XLSR parameters. Experimental results demonstrate that WaveSP-Net outperforms several state-of-the-art models on two new and challenging benchmarks, Deepfake-Eval-2024 and SpoofCeleb, with low trainable parameters and notable performance gains. The code and models are available at this https URL.
Tianjin University Carnegie Mellon UniversityUniversity of Stuttgart
Carnegie Mellon UniversityUniversity of Stuttgart University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Microsoft
Microsoft Seoul National UniversityUniversity of HelsinkiUniversity of RochesterUniversity at BuffaloNational Institute of InformaticsUniversity of Eastern FinlandFraunhofer AISECInstitute for Advancing IntelligencePindropKLASS Engineering and SolutionsEurécom
Seoul National UniversityUniversity of HelsinkiUniversity of RochesterUniversity at BuffaloNational Institute of InformaticsUniversity of Eastern FinlandFraunhofer AISECInstitute for Advancing IntelligencePindropKLASS Engineering and SolutionsEurécom
 Carnegie Mellon UniversityUniversity of Stuttgart
Carnegie Mellon UniversityUniversity of Stuttgart University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Microsoft
Microsoft Seoul National UniversityUniversity of HelsinkiUniversity of RochesterUniversity at BuffaloNational Institute of InformaticsUniversity of Eastern FinlandFraunhofer AISECInstitute for Advancing IntelligencePindropKLASS Engineering and SolutionsEurécom
Seoul National UniversityUniversity of HelsinkiUniversity of RochesterUniversity at BuffaloNational Institute of InformaticsUniversity of Eastern FinlandFraunhofer AISECInstitute for Advancing IntelligencePindropKLASS Engineering and SolutionsEurécomASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges which promote the
study of speech spoofing and deepfake attacks as well as the design of
detection solutions. We introduce the ASVspoof 5 database which is generated in
a crowdsourced fashion from data collected in diverse acoustic conditions (cf.
studio-quality data for earlier ASVspoof databases) and from ~2,000 speakers
(cf. ~100 earlier). The database contains attacks generated with 32 different
algorithms, also crowdsourced, and optimised to varying degrees using new
surrogate detection models. Among them are attacks generated with a mix of
legacy and contemporary text-to-speech synthesis and voice conversion models,
in addition to adversarial attacks which are incorporated for the first time.
ASVspoof 5 protocols comprise seven speaker-disjoint partitions. They include
two distinct partitions for the training of different sets of attack models,
two more for the development and evaluation of surrogate detection models, and
then three additional partitions which comprise the ASVspoof 5 training,
development and evaluation sets. An auxiliary set of data collected from an
additional 30k speakers can also be used to train speaker encoders for the
implementation of attack algorithms. Also described herein is an experimental
validation of the new ASVspoof 5 database using a set of automatic speaker
verification and spoof/deepfake baseline detectors. With the exception of
protocols and tools for the generation of spoofed/deepfake speech, the
resources described in this paper, already used by participants of the ASVspoof
5 challenge in 2024, are now all freely available to the community.
19 Mar 2016
This research from Eigenor Corporation, University of Warwick, Nokia Technologies, and University of Eastern Finland introduces Cauchy difference priors for edge-preserving Bayesian inversion, addressing the limitations of Gaussian and Total Variation priors. The method, applied to 1D deconvolution and 2D X-ray tomography, yields reconstructions with superior edge sharpness and demonstrates discretization-invariance, providing a robust approach to recovering piecewise smooth objects from noisy, indirect measurements.
The ASVspoof 2021 challenge evaluated countermeasures for spoofed and deepfake speech detection under increasingly realistic conditions, introducing tasks for telephony channel effects, real physical replay attacks, and compressed deepfake audio. The challenge found significant progress over baselines but identified key generalization weaknesses, particularly for unseen data sources and real-world physical access scenarios.
Researchers from the University of Turku and collaborators created a unique multicenter H&E stained slide dataset from 66 laboratories across 11 countries, utilizing identical tissue blocks to isolate staining variability. This dataset was used to benchmark various traditional and deep learning-based stain normalization methods, revealing that traditional methods like Histogram Matching often achieved comparable or superior color transfer accuracy to GAN-based approaches, while deep learning methods sometimes introduced visual artifacts.
Large language models (LLMs) offer the potential to simulate human-like
responses and behaviors, creating new opportunities for psychological science.
In the context of self-regulated learning (SRL), if LLMs can reliably simulate
survey responses at scale and speed, they could be used to test intervention
scenarios, refine theoretical models, augment sparse datasets, and represent
hard-to-reach populations. However, the validity of LLM-generated survey
responses remains uncertain, with limited research focused on SRL and existing
studies beyond SRL yielding mixed results. Therefore, in this study, we
examined LLM-generated responses to the 44-item Motivated Strategies for
Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ; Pintrich \& De Groot, 1990), a widely used
instrument assessing students' learning strategies and academic motivation.
Particularly, we used the LLMs GPT-4o, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, Gemini 2 Flash, LLaMA
3.1-8B, and Mistral Large. We analyzed item distributions, the psychological
network of the theoretical SRL dimensions, and psychometric validity based on
the latent factor structure. Our results suggest that Gemini 2 Flash was the
most promising LLM, showing considerable sampling variability and producing
underlying dimensions and theoretical relationships that align with prior
theory and empirical findings. At the same time, we observed discrepancies and
limitations, underscoring both the potential and current constraints of using
LLMs for simulating psychological survey data and applying it in educational
contexts.
We propose Region-wise (RW) loss for biomedical image segmentation. Region-wise loss is versatile, can simultaneously account for class imbalance and pixel importance, and it can be easily implemented as the pixel-wise multiplication between the softmax output and a RW map. We show that, under the proposed RW loss framework, certain loss functions, such as Active Contour and Boundary loss, can be reformulated similarly with appropriate RW maps, thus revealing their underlying similarities and a new perspective to understand these loss functions. We investigate the observed optimization instability caused by certain RW maps, such as Boundary loss distance maps, and we introduce a mathematically-grounded principle to avoid such instability. This principle provides excellent adaptability to any dataset and practically ensures convergence without extra regularization terms or optimization tricks. Following this principle, we propose a simple version of boundary distance maps called rectified Region-wise (RRW) maps that, as we demonstrate in our experiments, achieve state-of-the-art performance with similar or better Dice coefficients and Hausdorff distances than Dice, Focal, weighted Cross entropy, and Boundary losses in three distinct segmentation tasks. We quantify the optimization instability provided by Boundary loss distance maps, and we empirically show that our RRW maps are stable to optimize. The code to run all our experiments is publicly available at: this https URL.
Recent progress in generative AI has made it increasingly easy to create natural-sounding deepfake speech from just a few seconds of audio. While these tools support helpful applications, they also raise serious concerns by making it possible to generate convincing fake speech in many languages. Current research has largely focused on detecting fake speech, but little attention has been given to tracing the source models used to generate it. This paper introduces the first benchmark for multilingual speech deepfake source tracing, covering both mono- and cross-lingual scenarios. We comparatively investigate DSP- and SSL-based modeling; examine how SSL representations fine-tuned on different languages impact cross-lingual generalization performance; and evaluate generalization to unseen languages and speakers. Our findings offer the first comprehensive insights into the challenges of identifying speech generation models when training and inference languages differ. The dataset, protocol and code are available at this https URL.
Photonic time crystals (PhTCs) are spatially uniform media whose material parameters vary periodically in time, opening momentum bandgaps within which the fields of electromagnetic modes can grow exponentially in time. To date, PhTCs have utilized only passive, lossless materials with "positive" dispersion (Foster materials), and a theoretical framework addressing active materials with "negative" dispersion (non-Foster materials) in PhTCs and their associated physical properties remains undeveloped. Here, we explore the two classes of isotropic PhTCs with embedded non-Foster inclusions: a bulk medium with periodically modulated negative permittivity, and a metasurface whose surface capacitance alternates between positive and negative values. Employing an analytical transfer-matrix formulation, we demonstrate that non-Foster permittivity modulation not only broadens momentum bandgaps without bounds but also provides a gain rate that increases linearly with momentum. Remarkably, the proposed isotropic PhTCs support exponential amplification down to zero frequency-a regime inaccessible in conventional isotropic PhTCs. These results open new avenues for ultra-broadband wave control, high-gain signal processing, and energy-harvesting devices that leverage the unique dispersion of active, time-modulated circuitry.
 Tel Aviv University
Tel Aviv University University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Space Telescope Science Institute
Space Telescope Science Institute University of Southampton
University of Southampton Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University Stockholm UniversityUniversity of TurkuUniversity of SheffieldUniversity of GalwayMax-Planck-Institut für AstrophysikUniversity of Eastern Finland
Stockholm UniversityUniversity of TurkuUniversity of SheffieldUniversity of GalwayMax-Planck-Institut für AstrophysikUniversity of Eastern Finland European Southern ObservatoryPontificia Universidad Católica de ChileShanghai Astronomical ObservatoryUniversity of Hawai’iInstituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía-CSICQueen's University BelfastHeidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies (HITS)Warsaw University ObservatoryIstituto Nazionale di Astrofisica - Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte (INAF-OAC)INAF
Osservatorio Astrofisico di ArcetriINAF
Osservatorio Astronomico di PadovaAstronomisches Rechen–Institut
European Southern ObservatoryPontificia Universidad Católica de ChileShanghai Astronomical ObservatoryUniversity of Hawai’iInstituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía-CSICQueen's University BelfastHeidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies (HITS)Warsaw University ObservatoryIstituto Nazionale di Astrofisica - Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte (INAF-OAC)INAF
Osservatorio Astrofisico di ArcetriINAF
Osservatorio Astronomico di PadovaAstronomisches Rechen–InstitutWe present photometric and spectroscopic data sets for SN 2020pvb, a Type
IIn-P supernova (SN) similar to SNe 1994W, 2005cl, 2009kn and 2011ht, with a
precursor outburst detected (PS1 w-band ~ -13.8 mag) around four months before
the B-band maximum light. SN 2020pvb presents a relatively bright light curve
peaking at M_B = -17.95 +- 0.30 mag and a plateau lasting at least 40 days
before it went in solar conjunction. After this, the object is no longer
visible at phases > 150 days above -12.5 mag in the B-band, suggesting that the
SN 2020pvb ejecta interacts with a dense spatially confined circumstellar
envelope. SN 2020pvb shows in its spectra strong Balmer lines and a forest of
FeII lines with narrow P Cygni profiles. Using archival images from the Hubble
Space Telescope, we constrain the progenitor of SN 2020pvb to have a luminosity
of log(L/L_sun) <= 5.4, ruling out any single star progenitor over 50 M_sun.
All in all, SN 2020pvb is a Type IIn-P whose progenitor star had an outburst ~
0.5 yr before the final explosion, the material lost during this outburst is
probably playing a role in shaping the physical properties of the supernova.
We present the first use of influence functions for deep learning-based wireless receivers. Applied to DeepRx, a fully convolutional receiver, influence analysis reveals which training samples drive bit predictions, enabling targeted fine-tuning of poorly performing cases. We show that loss-relative influence with capacity-like binary cross-entropy loss and first-order updates on beneficial samples most consistently improves bit error rate toward genie-aided performance, outperforming random fine-tuning in single-target scenarios. Multi-target adaptation proved less effective, underscoring open challenges. Beyond experiments, we connect influence to self-influence corrections and propose a second-order, influence-aligned update strategy. Our results establish influence functions as both an interpretability tool and a basis for efficient receiver adaptation.
30 Sep 2025
 Stanford UniversityHarvard Medical SchoolRadboud UniversityMassachusetts General Hospital
Stanford UniversityHarvard Medical SchoolRadboud UniversityMassachusetts General Hospital Université Paris-Saclay
Université Paris-Saclay University of Alberta
University of Alberta King’s College LondonThe University of Sydney
King’s College LondonThe University of Sydney CEAEindhoven University of TechnologyUniversity of VeronaUniversity of ParmaTechnical University of DenmarkINSERMUniversity of LausanneUniversity of Eastern FinlandÉcole Polytechnique Fédérale de LausannePhilipps-Universität MarburgMax Planck Institute for Biological CyberneticsUniversity of California San FranciscoVanderbilt University Medical CenterNIHBrigham and Women’s HospitalIcahn School of Medicine at Mount SinaiMcLean HospitalMax Planck Institute for PsycholinguisticsUniversité du Québec à Montréal (UQAM)Lausanne University HospitalNational Institute of Biomedical Imaging and BioengineeringUniversity of GießenUniversity Medical Centre UtrechtUniversidad de ConcepciٞnCopenhagen University Hospital - Amager and HvidovreSorbonne UniversitiesUniversity of Rochester School of MedicineUniversity of DarmstadtNational Yang Ming-Chiao Tung UniversityUniversit
LavalUniversit
de SherbrookeUniversit
Paris Cit
CEAEindhoven University of TechnologyUniversity of VeronaUniversity of ParmaTechnical University of DenmarkINSERMUniversity of LausanneUniversity of Eastern FinlandÉcole Polytechnique Fédérale de LausannePhilipps-Universität MarburgMax Planck Institute for Biological CyberneticsUniversity of California San FranciscoVanderbilt University Medical CenterNIHBrigham and Women’s HospitalIcahn School of Medicine at Mount SinaiMcLean HospitalMax Planck Institute for PsycholinguisticsUniversité du Québec à Montréal (UQAM)Lausanne University HospitalNational Institute of Biomedical Imaging and BioengineeringUniversity of GießenUniversity Medical Centre UtrechtUniversidad de ConcepciٞnCopenhagen University Hospital - Amager and HvidovreSorbonne UniversitiesUniversity of Rochester School of MedicineUniversity of DarmstadtNational Yang Ming-Chiao Tung UniversityUniversit
LavalUniversit
de SherbrookeUniversit
Paris CitIn the spirit of the historic Millennium Prize Problems that heralded a new era for mathematics, the newly formed International Society for Tractography (IST) has launched the Millennium Pathways for Tractography, a community-driven roadmap designed to shape the future of the field. Conceived during the inaugural Tract-Anat Retreat, this initiative reflects a collective vision for advancing tractography over the coming decade and beyond. The roadmap consists of 40 grand challenges, developed by international experts and organized into seven categories spanning three overarching themes: neuroanatomy, tractography methods, and clinical applications. By defining shared short-, medium-, and long-term goals, these pathways provide a structured framework to confront fundamental limitations, promote rigorous validation, and accelerate the translation of tractography into a robust tool for neuroscience and medicine. Ultimately, the Millennium Pathways aim to guide and inspire future research and collaboration, ensuring the continued scientific and clinical relevance of tractography well into the future.
Spoofing detection is today a mainstream research topic. Standard metrics can
be applied to evaluate the performance of isolated spoofing detection solutions
and others have been proposed to support their evaluation when they are
combined with speaker detection. These either have well-known deficiencies or
restrict the architectural approach to combine speaker and spoof detectors. In
this paper, we propose an architecture-agnostic detection cost function
(a-DCF). A generalisation of the original DCF used widely for the assessment of
automatic speaker verification (ASV), the a-DCF is designed for the evaluation
of spoofing-robust ASV. Like the DCF, the a-DCF reflects the cost of decisions
in a Bayes risk sense, with explicitly defined class priors and detection cost
model. We demonstrate the merit of the a-DCF through the benchmarking
evaluation of architecturally-heterogeneous spoofing-robust ASV solutions.
Motion planning is the soul of robot decision making. Classical planning algorithms like graph search and reaction-based algorithms face challenges in cases of dense and dynamic obstacles. Deep learning algorithms generate suboptimal one-step predictions that cause many collisions. Reinforcement learning algorithms generate optimal or near-optimal time-sequential predictions. However, they suffer from slow convergence, suboptimal converged results, and overfittings. This paper introduces a hybrid algorithm for robotic motion planning: long short-term memory (LSTM) pooling and skip connection for attention-based discrete soft actor critic (LSA-DSAC). First, graph network (relational graph) and attention network (attention weight) interpret the environmental state for the learning of the discrete soft actor critic algorithm. The expressive power of attention network outperforms that of graph in our task by difference analysis of these two representation methods. However, attention based DSAC faces the overfitting problem in training. Second, the skip connection method is integrated to attention based DSAC to mitigate overfitting and improve convergence speed. Third, LSTM pooling is taken to replace the sum operator of attention weigh and eliminate overfitting by slightly sacrificing convergence speed at early-stage training. Experiments show that LSA-DSAC outperforms the state-of-the-art in training and most evaluations. The physical robot is also implemented and tested in the real world.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.